Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Energy Skate Park - Used
Caricato da
api-259781257Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Energy Skate Park - Used
Caricato da
api-259781257Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Simulations at http://phet.colorado.
edu/
PART A: The Skate Basic Park – Intro to Energy Potential and Kinetic PhET Lab
Procedure: google "skate park basics phet" and click on the first link.
Turn on the Bar Graph, Pie Chart, and Speed options.
1. Take some time and play with the skater. Write down five observations you notice in
relation to the skater and energy.
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
2. How does increasing skater's mass change the skater’s…
Kinetic Energy? ___________________Potential Energy? __________________Total Energy? _________________
3. How does the skater’s kinetic energy change as he moves down the ramp? _______________________________________
4. How does the skater’s kinetic energy change as he moves up the ramp? _________________________________________
5. How does the skater’s potential energy change as he moves down the ramp? _____________________________________
6. How does the skater’s potential energy change as he moves up the ramp? ________________________________________
7. How does the skater’s total energy change as he moves down the ramp? _________________________________________
8. How does the skater’s total energy change as he moves up the ramp? __________________________________________
9. Describe the skater’s kinetic energy at the bottom of the ramp. ____________________________________
10. Describe the skater’s potential energy at the bottom of the ramp. ________________________________
11. What happens when the skater is dropped onto the ramp from above the ramp? ___________________________________
Go to the friction tab. Take some time and play with the skater. Turn on the Bar Graph, Pie Chart, Friction, and Speed
options.
12. How is the skater’s movement different with friction compared to without friction? ________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
13. What does the potential and kinetic energy get converted into? Why do you think that is? ___________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
PART B: Conclusion Questions: (circle the correct answers)
1. At the highest point kinetic energy is zero / maximum while the potential energy is zero / maximum.
2. At the lowest point kinetic energy is zero / maximum while potential energy is zero / maximum.
3. Mass affects / does not affect the amount of energy.
4. As an object falls in gravity, kinetic energy increases / decreases / remains the same.
Simulations at http://phet.colorado.edu/
5. As an object falls in gravity, potential energy increases / decreases / remains the same.
6. As an object falls in gravity, total energy increases / decreases / remains the same.
7. An object travelling faster and faster has a kinetic energy that increases / decreases / remains the same.
8. An object travelling faster and faster has a potential energy that increases / decreases / remains the same.
9. As an object speeds up, the total energy increases / decreases / remains the same.
10. As an object slows down, the total energy increases / decreases / remains the same.
PART C: The Skate Park – Intro to Energy and Work PhET Lab
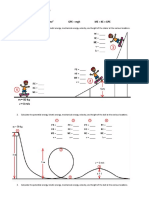
1. Create the skate paths as shown. If the skater starts on the left side, will he have
enough energy to make it all the way to the right side? _________ Why? / Why not?
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
A E If the skater starts on the left on the path here, match the letter here with
C the following conditions:
2. Maximum kinetic energy __________
D 3. Maximum potential energy _________
4. Two locations where the skater has about the same speed_______
B
5. Design your own skate track. BE CREATIVE. Draw your track below and answer the following questions.
If the skater starts on the left side, will he have enough energy to make it all the way to the right side? _________ Why? / Why
not? __________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
PART D: Conclusion Questions: use g = 9.8 m/s2
1. How much potential energy does the 60. kg skater have before she starts her ride, 12 m above the ground?
2. How much kinetic energy does a 60.0 kg skater have traveling with a velocity of 4 m/s?
3. How high must a 2.0 kg basketball be thrown so it has a potential energy of 160 J?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Marvelous Motion Computer Webquest 4 4 17Documento2 pagineMarvelous Motion Computer Webquest 4 4 17api-262586446100% (1)
- FanCart Acceleration 2017-1 PDFDocumento4 pagineFanCart Acceleration 2017-1 PDFAreej RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Engage: "Phet John Travoltage" Into Your BrowserDocumento4 pagineI. Engage: "Phet John Travoltage" Into Your BrowserEdgarAnwarGonzalezCafuentes0% (1)
- How objects fall in air and vacuumDocumento7 pagineHow objects fall in air and vacuumDylan Pond100% (1)
- Lesson Plan For Energy Skate Park1Documento2 pagineLesson Plan For Energy Skate Park1Arseniojakejr FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Skate Park - UsedDocumento5 pagineEnergy Skate Park - UsedUntold StoriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Exploration: Measuring MotionDocumento3 pagineStudent Exploration: Measuring MotionalexNessuna valutazione finora
- Moving Man Lab ActivityDocumento5 pagineMoving Man Lab ActivityAndy MontesNessuna valutazione finora
- My Weight On Other PlanetsDocumento1 paginaMy Weight On Other Planetsapi-3720073100% (1)
- KineticandPotentialEnergyWorksheetName 1 PDFDocumento3 pagineKineticandPotentialEnergyWorksheetName 1 PDFFerlyn PascuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Goals: Students Will Be Able To:: Energy Skate ParkDocumento3 pagineLearning Goals: Students Will Be Able To:: Energy Skate ParkPayje MisegadisNessuna valutazione finora
- Phet Force and Newton's Laws ReviewDocumento5 paginePhet Force and Newton's Laws ReviewkhairatuddinariNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Power Debate Project PacketDocumento6 pagineNuclear Power Debate Project Packetapi-252900678Nessuna valutazione finora
- CS 1.4 Skate Park Energy ActivityDocumento3 pagineCS 1.4 Skate Park Energy Activitysha catsNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity Web Quest 5 11 17Documento4 pagineElectricity Web Quest 5 11 17api-2625864460% (1)
- Newton's Three Law of MotionDocumento3 pagineNewton's Three Law of MotionArlyn Pong Pling PioNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Systems Phet WorksheetDocumento5 pagineEnergy Systems Phet Worksheetapi-203432401Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bill Nye Energy WorksheetDocumento2 pagineBill Nye Energy Worksheetapi-55809756100% (1)
- Covalent Bonding WebquestDocumento4 pagineCovalent Bonding Webquestapi-3031203990% (1)
- Force Fan Cart WorksheetDocumento4 pagineForce Fan Cart WorksheetIshaan SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Review Rock and Fossil RecordDocumento5 pagineChapter Review Rock and Fossil RecordRonaldo ManaoatNessuna valutazione finora
- How The Tiger Got Its StripesDocumento2 pagineHow The Tiger Got Its StripesCassie Ronald AvaAshNessuna valutazione finora
- Bill Nye, The Science Guy! EnergyDocumento2 pagineBill Nye, The Science Guy! EnergyTrevor RivardNessuna valutazione finora
- 6A Changing CircuitsDocumento5 pagine6A Changing CircuitsSSNessuna valutazione finora
- Newton Laws of Motion ReviewDocumento3 pagineNewton Laws of Motion Reviewapi-417027192Nessuna valutazione finora
- Counting Atoms WorksheetDocumento3 pagineCounting Atoms WorksheetDeysi LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.5 Final Review Key PDFDocumento4 pagine8.5 Final Review Key PDFAlex VongNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Work Power WebquestDocumento4 pagineEnergy Work Power Webquestapi-3299787630% (2)
- Test - Unit 3 - Energy and MomentumDocumento4 pagineTest - Unit 3 - Energy and Momentumascd_msvuNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction-To-Energy KeyDocumento2 pagineIntroduction-To-Energy KeyAngel JaimesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Test FORCEDocumento5 pagineChapter Test FORCEArnulfo Villasfer SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Energy And Momentum Practice TestDocumento11 pagineChapter 2 Energy And Momentum Practice TestMohamad SotoudehNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Bang WebquestDocumento4 pagineBig Bang WebquestblackwellbertNessuna valutazione finora
- PHET Magnetism - Lab Grade: NameDocumento4 paginePHET Magnetism - Lab Grade: NameAyhan AbdulAzizNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Skatepark Student GuideDocumento4 pagineEnergy Skatepark Student GuideZilvinas Griskevicius GriskeviciusNessuna valutazione finora
- Work Power and EnergyDocumento8 pagineWork Power and Energyapi-275290316Nessuna valutazione finora
- Part A: Thermal Energy: Name Elisabeth Albert Class General Science Page 1Documento11 paginePart A: Thermal Energy: Name Elisabeth Albert Class General Science Page 1RHEAMAE GALLEGO50% (2)
- Egg Drop Day 1 PDF CombinedDocumento13 pagineEgg Drop Day 1 PDF CombinedDaniel BissotNessuna valutazione finora
- Torque Web QuestDocumento3 pagineTorque Web QuestRex FortezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bohr Models Worksheet 2Documento4 pagineBohr Models Worksheet 2Amiyah ThompsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet For WorkDocumento3 pagineWorksheet For Workreielleceana07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Logistic VsDocumento5 pagineLogistic Vsapi-242868690Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetic - Potential Energy (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingDocumento2 pagineKinetic - Potential Energy (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingMOHDFADZLY84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Waves LabDocumento6 pagineWaves Labsamarghai0% (1)
- Atmosphere and Heat Transfer Web QuestDocumento2 pagineAtmosphere and Heat Transfer Web Questapi-237049863Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide Ionic Compounds and Metals Student Editable PDFDocumento8 pagineStudy Guide Ionic Compounds and Metals Student Editable PDFNicolyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.4 Power & EfficiencyDocumento2 pagine3.4 Power & EfficiencyCurtis Collins50% (2)
- HR DiagramDocumento7 pagineHR Diagramapi-237113285Nessuna valutazione finora
- Active Transport Worksheet: Exo-EndoDocumento3 pagineActive Transport Worksheet: Exo-EndoMargie OpayNessuna valutazione finora
- Power, Work and Force IIDocumento4 paginePower, Work and Force IIchpwalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Science Worksheet Conservation of Energy #2: KE MV GPE MGH Me Ke + GpeDocumento4 paginePhysical Science Worksheet Conservation of Energy #2: KE MV GPE MGH Me Ke + GpeJudy MelegritoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pasay S9LT Q1 W3 4 04Documento6 paginePasay S9LT Q1 W3 4 04Frederick EspejoNessuna valutazione finora
- F=ma practice problemsDocumento2 pagineF=ma practice problemsreielleceana07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alternative Energy Project - ModifiedDocumento8 pagineAlternative Energy Project - Modifiedapi-241402391Nessuna valutazione finora
- 04 - Classwork - Types of EnergyDocumento6 pagine04 - Classwork - Types of Energyapi-293092810100% (1)
- Chicken DissectionDocumento2 pagineChicken Dissectionllatham100% (1)
- g485 5 3 4 Fission and FusionDocumento14 pagineg485 5 3 4 Fission and Fusionapi-236179294Nessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Skate Park WorksheetDocumento4 pagineEnergy Skate Park WorksheetKiLlmEEEplz XD100% (1)
- Skate Park and Roller Coaster Physics SimsDocumento4 pagineSkate Park and Roller Coaster Physics SimsKobiXDNessuna valutazione finora
- Skate Park Simulations Explore Energy TransferDocumento4 pagineSkate Park Simulations Explore Energy TransferGrace Angel FallariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Webquest Conduction Convection RadiationDocumento1 paginaWebquest Conduction Convection Radiationapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Webquest Conduction Convection RadiationDocumento1 paginaWebquest Conduction Convection Radiationapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vocab ThermoDocumento1 paginaVocab Thermoapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide Work Power and EnergyDocumento4 pagineStudy Guide Work Power and Energyapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 1 Work and PowerDocumento39 pagineDay 1 Work and Powerapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Density Worksheet: Helpful HintsDocumento1 paginaDensity Worksheet: Helpful Hintsapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 1 Density and Fluids IntroDocumento28 pagineDay 1 Density and Fluids Introapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vocab DensityDocumento1 paginaVocab Densityapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sub Work Mixed Work Power Pe KeDocumento1 paginaSub Work Mixed Work Power Pe Keapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pogil - Ke PeDocumento4 paginePogil - Ke Peapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- BalloonracecarlabDocumento1 paginaBalloonracecarlabapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 4 Ke and PeDocumento38 pagineDay 4 Ke and Peapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 2 Drawing Free Body DiagramsDocumento32 pagineDay 2 Drawing Free Body Diagramsapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 7 MomentumDocumento11 pagineDay 7 Momentumapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vocab WorkDocumento1 paginaVocab Workapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 6 Acceleration Due To GravityDocumento10 pagineDay 6 Acceleration Due To Gravityapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide ForcesDocumento4 pagineStudy Guide Forcesapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Newtons Review IssDocumento2 pagineNewtons Review Issapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- H Study Guide Velocity and AccelerationDocumento2 pagineH Study Guide Velocity and Accelerationapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 2 Drawing Free Body DiagramsDocumento32 pagineDay 2 Drawing Free Body Diagramsapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drawing Free Body DiagramsDocumento2 pagineDrawing Free Body Diagramsapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 4 F Ma Newtons Laws ReviewDocumento22 pagineDay 4 F Ma Newtons Laws Reviewapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 1 Intro To ForcesDocumento25 pagineDay 1 Intro To Forcesapi-259781257100% (1)
- Stations MotionDocumento2 pagineStations Motionapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vocab ForcesDocumento1 paginaVocab Forcesapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 4 Quiz Manipulating V and A Speed LabDocumento11 pagineDay 4 Quiz Manipulating V and A Speed Labapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide Velocity and AccelerationDocumento2 pagineStudy Guide Velocity and Accelerationapi-259781257100% (1)
- Ps CH 11 Lab Phet Moving Man Activity2Documento4 paginePs CH 11 Lab Phet Moving Man Activity2api-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 3 Velocity and Acceleration PracticeDocumento34 pagineDay 3 Velocity and Acceleration Practiceapi-259781257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Final For WEBDocumento84 pagineJournal Final For WEBnormanwillowNessuna valutazione finora
- Balance and Stability PowerpointDocumento36 pagineBalance and Stability PowerpointCzarina Amor CabilleteNessuna valutazione finora
- Arithmetic SequencesDocumento3 pagineArithmetic SequencestuvvacNessuna valutazione finora
- Camote Tops Acid-BaseDocumento3 pagineCamote Tops Acid-BaseAldren BeliberNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make Partitions in Windows 10 - Windows 8 PDFDocumento6 pagineHow To Make Partitions in Windows 10 - Windows 8 PDFAbhrajyoti DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Master Thesis Natural Oil AbsorbentDocumento178 pagineMaster Thesis Natural Oil AbsorbentFaris Mat100% (1)
- Dubai Workshop RegistrationDocumento2 pagineDubai Workshop RegistrationmfkmughalNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of ThermodynamicsDocumento31 pagineLaws of ThermodynamicsPradeep Kumar Mehta100% (1)
- Pakistan Academy School Al-Ahmadi Kuwait Monthly Test Schedule Class: 9 FBISEDocumento16 paginePakistan Academy School Al-Ahmadi Kuwait Monthly Test Schedule Class: 9 FBISEapi-126472277Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scherrer Equation - WikipediaDocumento7 pagineScherrer Equation - WikipediaSilviu-Laurentiu BadeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Artefact 1Documento5 pagineArtefact 1api-405808158Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cluster Sampling: ProcedureDocumento12 pagineCluster Sampling: ProcedureAahil RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecturio The 40 Day Study Schedule USMLE Step 1Documento20 pagineLecturio The 40 Day Study Schedule USMLE Step 1Kimberly Kanemitsu50% (2)
- Playboy 2Documento12 paginePlayboy 2theraphimNessuna valutazione finora
- February 26 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 390 Fluid MechanicsDocumento6 pagineFebruary 26 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 390 Fluid Mechanicsshun84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Munir Ahmed: ObjectivesDocumento2 pagineMunir Ahmed: ObjectivesIrfan ALiNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Resource ManagementDocumento18 pagineHuman Resource Managementsamruddhi_khale67% (3)
- Excel Spreadsheet SoftwareDocumento22 pagineExcel Spreadsheet SoftwareJared Cuento TransfiguracionNessuna valutazione finora
- CERN Initial Letter For Yr 12Documento2 pagineCERN Initial Letter For Yr 12AlexFryNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual Image.: 1 (A) Fig. 8.1 Is A Ray Diagram of A Convex Lens Being Used As A Magnifying Glass To Produce ADocumento11 pagineVirtual Image.: 1 (A) Fig. 8.1 Is A Ray Diagram of A Convex Lens Being Used As A Magnifying Glass To Produce AahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Language and AttractionDocumento21 pagineBody Language and Attractionpoiqwe1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 ClimateDocumento21 pagineChapter 2 ClimateShahyan bilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary Classification MetricsDocumento6 pagineBinary Classification MetricssharathdhamodaranNessuna valutazione finora
- ICAO Annex 19 PresentationDocumento46 pagineICAO Annex 19 PresentationBenoit Paré100% (1)
- Notification JNTU Anantapur Assistant Professor Posts PDFDocumento7 pagineNotification JNTU Anantapur Assistant Professor Posts PDFNagabhushanaNessuna valutazione finora
- IE 404 Mathematical Methods EconomicsDocumento2 pagineIE 404 Mathematical Methods EconomicsNaveen GargNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 ECI 2015 Final ProgramDocumento122 pagine1 ECI 2015 Final ProgramDenada Florencia LeonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bresnen M. and Marshall N. 2000a Building Partnerships Case Studies of Client Contractor Collaboration in The UK Construction Industry'Documento14 pagineBresnen M. and Marshall N. 2000a Building Partnerships Case Studies of Client Contractor Collaboration in The UK Construction Industry'VivianeLeuchtenbergPEspositoNessuna valutazione finora
- KEY - Unit 12 Test ReviewDocumento4 pagineKEY - Unit 12 Test ReviewHayden MulnixNessuna valutazione finora
- Using The PNR Curve To Convert Effort To ScheduleDocumento2 pagineUsing The PNR Curve To Convert Effort To ScheduleRajan SainiNessuna valutazione finora