Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Publication
Caricato da
Anshuman TagoreTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Publication
Caricato da
Anshuman TagoreCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The atomic packing factor [A.P.
F]:
It can be defined as the ratio between the volume of the basic
atoms of the unit cell (which represent the volume of all atoms
in one unit cell ) to the volume of the unit cell it self.
For cubic crystals,
A.P. F its depends on the riadus of atoms and characrtiziation of
chemical bondings .
Atomic Packing Factor for Simple Cubic :-
no. of atoms = 1
volume of one atom = π
volume of unit cell (cubic) = a3
when , )a = 2r (
Filling Factor =
( )
Atomic Filling Factor for BCC:-
no of atoms =2
volume of tow atoms =2* π
University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed
volume of unit cell (cubic) = a3
√
when
Filling Factor =
√
( )
√ √
Atomic Filling Factor for FCC:-
no of atoms = 4
volume of four atoms = 4* π
volume of unit cell (cubic) = a3
√
when
√
Filling Factor =
√
( √ ) √
University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed
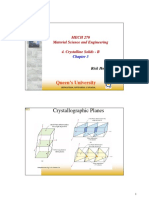
Miller Indices:
• Miller Indices are used to refer to specific lattice planes of
atoms.
• They are reciprocals of the fractional intercepts (with fractions
cleared) that the plane makes with the crystallographic x,y and z
axes of three nonparallel edges of the cubic unit cell.
Miller Indices – Procedure:
1. Choose a plane that does not pass through origin
2. Determine the x,y and z intercepts of the plane
3. Find the reciprocals of the intercepts
4. Fractions?
a. If Yes, Clear fractions by multiplying by an integer to
determine smallest set of whole numbers, then go to b
b. If No, Place a „bar‟ over the Negative indices
5. Enclose in parenthesis (hkl) where h,k,l are miller indices of
cubic crystal plane for x,y and z axes.
Note / if the one of axies value was negative then move the
center of cubic to negative value direction .
Example 1
Draw the follwing plances in the cubic crystal ?
)0 ̅ 0( -5 ، ) ̅ 00( -4 ، )001 ( -3 ، )010 ( -2 ، ) 100( - 1
)00 ̅ ( -6 ،
Ans.
1 - ) 100(
University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed
then miller indices are )1∞∞(
2- )010 (
then miller indices are )∞ ∞(
3- )001 (
University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed
then miller indices are)∞ ∞ (
Example 2 :-
Draw the follwing plances in the cubic crystal ?
، )1 ̅ 0 ( -5 ، )10 ̅ ( -4 ، )011 ( - 3 ، )110 ( - 2 ، )101( - 1
) 01 ̅ ( -6
1-)101(
University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed
then miller indices are ) ∞ (
2- )110 (
then miller indices are) ∞(
3- )011 (
then miller indices are )∞ (
University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed
Interplaner Distance between paraalls plances
The space lattice consist from many crystall plances which
separated by interplaner smallest distance
The distance can be calcalated by using x- ray diffraction , by
using the law below :-
Where dhkl = interplanar spacing between parallel closest planes
with Miller indices h, k, and l
a = lattice constant (edge of unit cube).
h, k, l = Miller indices of cubic planes being considered.
University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed
Angles between crystal planes :-
The crystal consist many from plance which contact with them
in vairty angles , The angle between crystal planes can be
calculated by using the following equation :-
√( ) √( )
Example :-
Find the angle between the plances )1 ̅ 1( & )111(?
√( ) √( )
( )
√ √
University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed
Example 2
Find the interplaner distance for plane (220) , which have FCC
Craystal and raidus of atom (1.414 A) ?
Solution:-
The crystal is FCC then
√
( ) ( )
√
Example: (H.W)
Copper has an FCC crystal structure and a unit cell with a lattice constant
of 0.361 nm. What is its interplanar spacing d220?
University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lecture 4 - Lattice Position PlaneDocumento10 pagineLecture 4 - Lattice Position Plane杨致远Nessuna valutazione finora
- Subject: Engineering of Metallurgy: Theoretical Density ComputationsDocumento13 pagineSubject: Engineering of Metallurgy: Theoretical Density ComputationskdNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials of Science and Structure of Matter - Section of The FE Supplied-Reference Handbook - NCEESDocumento4 pagineMaterials of Science and Structure of Matter - Section of The FE Supplied-Reference Handbook - NCEESjazz fraire bernalNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystallography (M)Documento57 pagineCrystallography (M)Michael Vincent MirafuentesNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structure of SolidsDocumento15 pagineCrystal Structure of SolidsZack KingNessuna valutazione finora
- MLE 1101 Fall 2008 Tutorial IIDocumento23 pagineMLE 1101 Fall 2008 Tutorial IIAlexander ZeusNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystallograpic PlanesDocumento13 pagineCrystallograpic PlanesMd Mehrab Alam ShayikhNessuna valutazione finora
- On Crystal StructureDocumento32 pagineOn Crystal StructureDeathEaterReturnNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 MillerIndicesDocumento19 pagine3 MillerIndicesyasin yttNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDocumento51 pagine3 The Structure of Crystalline SolidsNeko-neko CasugaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEN4235 - Lecture - Surface StructureDocumento31 pagineCHEN4235 - Lecture - Surface StructureAmadeus HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Crystal StructureDocumento38 pagineChapter 2 Crystal StructureAbo Abdo100% (1)
- Structure of Materials-Part1Documento60 pagineStructure of Materials-Part1KaitoNessuna valutazione finora
- #Solutions: UCK215E - Aerospace Materials Quiz 1Documento5 pagine#Solutions: UCK215E - Aerospace Materials Quiz 1jose antonio villena medinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sci Mat Crystal - StructuresDocumento21 pagineSci Mat Crystal - StructuresAPNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystallography and Structure: ME 2105 R. R. LindekeDocumento66 pagineCrystallography and Structure: ME 2105 R. R. LindekeMohammad RameezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cation Vs AnionDocumento16 pagineCation Vs AnionnobleskyNessuna valutazione finora
- Symmetry & Crystal StructuresDocumento37 pagineSymmetry & Crystal StructuresNurnajihah Sukimi JiehaNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal and Amorphous Structure in MaterialsDocumento57 pagineCrystal and Amorphous Structure in MaterialsAmir AyobNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3-9 OctDocumento27 pagineLecture 3-9 OctPrakash KonanakeriNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystalline SolidsDocumento28 pagineCrystalline SolidsAyush ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- IAS Mains Physics 2005Documento11 pagineIAS Mains Physics 2005RATNADEEP BANERJEENessuna valutazione finora
- Atom Position in A Cubic CellDocumento17 pagineAtom Position in A Cubic CellAhmed EssamNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal StructureDocumento78 pagineCrystal StructureSukhwinder Singh GillNessuna valutazione finora
- 5Documento31 pagine5M Rajesh NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Crystal Structure: Palak Desai Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocumento44 pagineUnit 1 Crystal Structure: Palak Desai Mechanical Engineering DepartmentPalak NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- 256 MAT ShortNotesJan26-Feb7 06Documento5 pagine256 MAT ShortNotesJan26-Feb7 06gombossandorNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structures and SymmetriesDocumento18 pagineCrystal Structures and SymmetriesZrusNessuna valutazione finora
- IAS Mains Physics 2005Documento11 pagineIAS Mains Physics 2005ajay70233Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 - Crystalline Structure of MetalsDocumento25 pagineLecture 2 - Crystalline Structure of MetalsAkerkeMami100% (1)
- Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100Documento1 paginaTime: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100Yatheesh KCNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystallographic Planes: Queen's UniversityDocumento10 pagineCrystallographic Planes: Queen's Universityeng20072007Nessuna valutazione finora
- MTE 583 - Class - 17 PDFDocumento13 pagineMTE 583 - Class - 17 PDFPorfirio HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Planes and Miller IndicesDocumento12 pagineCrystal Planes and Miller IndicesUpender DhullNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystallography and Structure - Ch3F10-2Documento66 pagineCrystallography and Structure - Ch3F10-2Syeda Fatima FarzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear and Planar Densities: Assist. Prof. Dr. Ahmed Mudhafar HashimDocumento8 pagineLinear and Planar Densities: Assist. Prof. Dr. Ahmed Mudhafar Hashimklashklash527Nessuna valutazione finora
- #Solutions: 1. Fill The Blanks. (8pts)Documento5 pagine#Solutions: 1. Fill The Blanks. (8pts)Fatih KESKİNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems Set 2Documento2 pagineProblems Set 2Govindanunni PadmakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Vibration Analysis of Beams Considering Different Geometric Characteristics and Boundary ConditionsDocumento7 pagineFree Vibration Analysis of Beams Considering Different Geometric Characteristics and Boundary ConditionsMaría Del Carmen Cedeño QuijadaNessuna valutazione finora
- X-Ray Diffraction by CrystalsDocumento5 pagineX-Ray Diffraction by CrystalsBaseeji BaseejiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stationary Self-Organized Fractal Structures in An Open, Dissipative Electrical SystemDocumento7 pagineStationary Self-Organized Fractal Structures in An Open, Dissipative Electrical SystemOscar Lemus RamírezNessuna valutazione finora
- Microelectronics TechDocumento33 pagineMicroelectronics TechmailstonaikNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 03Documento39 pagineCH 03AbdulslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Lecture 2 - AnnotatedDocumento62 pagineChapter 2 - Lecture 2 - AnnotatedAhmed TamerNessuna valutazione finora
- A Curved Finite Element For Thin ElasticDocumento38 pagineA Curved Finite Element For Thin ElasticJosé Cléber Rodrigues da SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tight BindingDocumento5 pagineTight BindingalkeroneNessuna valutazione finora
- Universal Functional Formula of Atomic Elastic CroDocumento2 pagineUniversal Functional Formula of Atomic Elastic CroIsaac MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Prolog::, "Introduction To Solid State Physics", 8th Ed.,wiley (2005)Documento19 pagineProlog::, "Introduction To Solid State Physics", 8th Ed.,wiley (2005)mahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structure (21!10!2011)Documento71 pagineCrystal Structure (21!10!2011)Swetha PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- XRDDocumento42 pagineXRDkaushik4208100% (3)
- The Crack Tip Strain Field of AISI 4340: Experimental MeasurementsDocumento9 pagineThe Crack Tip Strain Field of AISI 4340: Experimental Measurementsfrederico wlassakNessuna valutazione finora
- EP UNIT NewDocumento20 pagineEP UNIT Newtejav2468Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structures and X-Ray DiffractionDocumento5 pagineCrystal Structures and X-Ray DiffractionV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tables of Similar Solutions To Equations of Momentum, Heat and Mass TransferDocumento340 pagineTables of Similar Solutions To Equations of Momentum, Heat and Mass TransferZoro JoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structures and X-Ray Diffractions: Point Coordinates and DirectionsDocumento9 pagineCrystal Structures and X-Ray Diffractions: Point Coordinates and DirectionsSamyabrata ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IV CrystallographyDocumento17 pagineUnit IV Crystallographyswapniljawadwar1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ex ExpPhys V WS2006 07ENDocumento15 pagineEx ExpPhys V WS2006 07ENSatyam AgrahariNessuna valutazione finora
- MP Chapt 4 SolDocumento19 pagineMP Chapt 4 SolFirdha FauziyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial ReportDocumento3 pagineFinancial ReportAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- SOP of Avaya Workplace ApplicationDocumento36 pagineSOP of Avaya Workplace ApplicationAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- 110 MailDocumento1 pagina110 MailAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Template - Senior Stakeholder EmailDocumento1 paginaActivity Template - Senior Stakeholder EmailAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Evaluation FindingsDocumento4 paginePresent Evaluation FindingsAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Completing Project Charter - Stephen Ardey MensahDocumento3 pagineCompleting Project Charter - Stephen Ardey MensahAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Precaseread Nirmalya 17jul MrMehtaDocumento2 paginePrecaseread Nirmalya 17jul MrMehtaAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Template - Project CharterDocumento3 pagineActivity Template - Project CharterAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Template - Project-Charter - Sause and SpoonDocumento2 pagineTemplate - Project-Charter - Sause and SpoonAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Survey QuestionsDocumento50 pagineSurvey QuestionsAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- NP - Gantt Chart - Gantt ChartDocumento1 paginaNP - Gantt Chart - Gantt ChartAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity - Write An Email To A Senior StakeholderDocumento1 paginaActivity - Write An Email To A Senior StakeholderAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Draft Influential EmailsDocumento1 paginaDraft Influential EmailsAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Refine Your Time EstimatesDocumento134 pagineRefine Your Time EstimatesAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rebirth of Container Shipping: An Example of Disruptive InnovationDocumento18 pagineThe Rebirth of Container Shipping: An Example of Disruptive InnovationAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Template - Meeting AgendaDocumento2 pagineActivity Template - Meeting AgendaAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal SuccessDocumento4 paginePersonal SuccessAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Sprint Backlog - Sprint BacklogDocumento1 paginaSprint Backlog - Sprint BacklogAnshuman Tagore100% (2)
- W02 AssessmentDocumento5 pagineW02 AssessmentShahid SdqshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Template - Email CoalitionDocumento2 pagineActivity Template - Email CoalitionAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- C1 Assessment WorkbookDocumento197 pagineC1 Assessment WorkbookAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Excel Skills For Business: Essentials: Week 6: ChartsDocumento3 pagineExcel Skills For Business: Essentials: Week 6: ChartsAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Tales From Mythology: Fact Is Everybody's Truth. Fiction Is Nobody's TruthDocumento15 pagineTales From Mythology: Fact Is Everybody's Truth. Fiction Is Nobody's TruthAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- W04-AssessmentDocumento71 pagineW04-AssessmentPooja KhinchiNessuna valutazione finora
- W03-AssessmentDocumento2 pagineW03-AssessmentAnshuman Tagore0% (1)
- C1 Assessment Workbook - Ejemplo PrácticoDocumento120 pagineC1 Assessment Workbook - Ejemplo PrácticolorenasanzbNessuna valutazione finora
- Single and Dedicated ECU For Each Function. Integrated ECU Networking of ECUDocumento12 pagineSingle and Dedicated ECU For Each Function. Integrated ECU Networking of ECUAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Test Results: Student No Teacher First Name Last NameDocumento3 pagineStudent Test Results: Student No Teacher First Name Last NameAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Deutsche Bank Group: Divisional Description-TechnologyDocumento2 pagineDeutsche Bank Group: Divisional Description-TechnologyAnshuman TagoreNessuna valutazione finora
- 87 Kerabondplus GB in PDFDocumento4 pagine87 Kerabondplus GB in PDFpankajNessuna valutazione finora
- Polishing and Etching Coal Samples For Microscopical Analysis by Reflected LightDocumento4 paginePolishing and Etching Coal Samples For Microscopical Analysis by Reflected LightGnanavel GNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 06Documento18 pagineCH 06Abdul Shokor Abd TalibNessuna valutazione finora
- DP FlowDocumento47 pagineDP FlowGustavo PuenteNessuna valutazione finora
- A General Review of The Causes and Acceptance of Shape ImperfectionsDocumento7 pagineA General Review of The Causes and Acceptance of Shape ImperfectionsMuhammed SulfeekNessuna valutazione finora
- Final - Basic Lasting TechnologyDocumento137 pagineFinal - Basic Lasting TechnologySumit Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Annex 2 - 20-Sample Template For EMoPDocumento2 pagineAnnex 2 - 20-Sample Template For EMoPHercie Jean Golfo50% (2)
- Chapter 6-Rainwater HarvestingDocumento20 pagineChapter 6-Rainwater HarvestingJpmega Civil StructuralNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Ideal Reactors: Deviations From Ideal Reactor BehaviorDocumento8 pagineNon-Ideal Reactors: Deviations From Ideal Reactor BehaviorrawadNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock 2-Chem SPMDocumento11 pagineMock 2-Chem SPMLyna JingomNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Lubricants For All MachineryDocumento3 pagineTypes of Lubricants For All MachineryLaxman Singh SankhlaNessuna valutazione finora
- BFC 3042 Chapter 4bDocumento10 pagineBFC 3042 Chapter 4bInahMisumiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mfhpb07 Eng ListeriaDocumento12 pagineMfhpb07 Eng ListeriaMarce LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Is Alcohol in Skincare Products Bad For Your Skin in The Long TermDocumento6 pagineIs Alcohol in Skincare Products Bad For Your Skin in The Long TermgaladrielinNessuna valutazione finora
- Roof Bolting AKMDocumento81 pagineRoof Bolting AKMNutan PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- User'S Manual: InstructionsDocumento46 pagineUser'S Manual: InstructionsNikola Markovski100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheets: 1. Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocumento6 pagineSafety Data Sheets: 1. Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingIgor IgorNessuna valutazione finora
- LaMotte 1756 Fluoride Tracer PockeTester InstructionsDocumento16 pagineLaMotte 1756 Fluoride Tracer PockeTester InstructionsPromagEnviro.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Manual FFETDocumento21 pagineProduct Manual FFETAan Sarkasi Amd100% (1)
- Environment VocabularyDocumento5 pagineEnvironment VocabularyJ Adrian HidrovoNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavior of Steel Under TensionDocumento6 pagineBehavior of Steel Under TensionAshNessuna valutazione finora
- Hempel Protective Infrastructure Corrosion Protection For Cargo Handling Equipment Low ResDocumento12 pagineHempel Protective Infrastructure Corrosion Protection For Cargo Handling Equipment Low Reskamardheen majithNessuna valutazione finora
- DJ 10 CM Plate: MJ MJDocumento9 pagineDJ 10 CM Plate: MJ MJredspidey13100% (2)
- Cu (II) Complex v3 011809Documento7 pagineCu (II) Complex v3 011809shahera rosdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Schemes Form 1Documento4 pagineChemistry Schemes Form 1NZURE NJOKANessuna valutazione finora
- Failure Analysis of Structural Steel Subjected To Long Term ExposureDocumento13 pagineFailure Analysis of Structural Steel Subjected To Long Term ExposureDeepak wadgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch3 SolutionsDocumento64 pagineCh3 Solutionsmohimran2002100% (1)
- CIP13 Concrete BlistersDocumento2 pagineCIP13 Concrete Blisters7774R105Nessuna valutazione finora
- 부식 en12944Documento10 pagine부식 en12944ksjin0226Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of Biodiesel Concentration in A Diesel Oil MixtureDocumento4 pagineMeasurement of Biodiesel Concentration in A Diesel Oil MixtureFredy Akenaton ArroyoNessuna valutazione finora