Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tenses 130625073753 Phpapp01
Caricato da
pwpw0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
59 visualizzazioni30 pagineTenses are verb forms that indicate time and can be used to show if an action has already occurred, is ongoing, or is yet to happen. There are three main tenses - present, past, and future. Each tense can be expressed through indefinite, continuous, perfect, or perfect continuous forms. The document then proceeds to define each tense and form, providing examples of affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences for each.
Descrizione originale:
ingles
Titolo originale
tenses-130625073753-phpapp01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoTenses are verb forms that indicate time and can be used to show if an action has already occurred, is ongoing, or is yet to happen. There are three main tenses - present, past, and future. Each tense can be expressed through indefinite, continuous, perfect, or perfect continuous forms. The document then proceeds to define each tense and form, providing examples of affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences for each.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
59 visualizzazioni30 pagineTenses 130625073753 Phpapp01
Caricato da
pwpwTenses are verb forms that indicate time and can be used to show if an action has already occurred, is ongoing, or is yet to happen. There are three main tenses - present, past, and future. Each tense can be expressed through indefinite, continuous, perfect, or perfect continuous forms. The document then proceeds to define each tense and form, providing examples of affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences for each.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 30
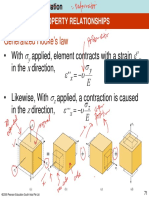
Tenses are the form taken by a verb to show the
time of an action or the state of an event.
There are three tenses :
The Present Tense
The Past Tense
The Future Tense.
Each of the three tenses has four forms or sub-
divisions to show continuity or completeness of
the action and time. These are :
1. Indefinite
2. Continuous or Imperfect
3. Perfect
4. Perfect Continuous
Table Of English
Tenses
Tense Indefinite Continuo Perfect Perfect
us Continuo
us
Present Play (s) Is / Am / Are Has / Has / Have
Playing Have been Playing
Played
Past Played Was / Were Had Had been
Playing Played Playing
Future Will / Shall Will / Shall Will / Will / Shall
Play be Playing Shall have been
Have Playing
Played
o The Indefinite Tense does not indicate whether the
action is complete or not.
o The Continuous (Imperfect) Tense that the action is
still going on.
o The Perfect Tense indicates that the action is
complete , finished or perfect.
o The Perfect Continuous Tense indicates that the
action began in the past and is still continuing.
Subject + Verb1 + Object
Expresses a general truth or an action that is
occurring now
Eg : The sun rises from the east.
Expresses an action that occurs regularly or
habitually
Eg : She goes to the school regularly.
Affirmative Sentences : They play.
Negative Sentences : They do not play.
Interrogative Sentences : Do they play ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Do they not
play ?
Subject + Is/Am/Are + V1 + ing +
Object.
The present continuous tense is
used to express an action which is
happening at a particular time in
the present or extending over a
period of present time.
Affirmative Sentences : You are playing.
Negative Sentences : You are not playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Are you playing ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Are you not
playing ?
Subject+ has/have + V3 + Object.
Has -> Singular , Have -> Plural.
The present perfect tense denotes an action
that was started in the past and has just been
completed.
Affirmative Sentences : I have played.
Negative Sentences : I have not played.
Interrogative Sentences : Have I played ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Have I not
played ?
Subject + has/have + been + V1 + ing + Object
The present perfect tense is used when an
action that started in the past is still
continuing.
Affirmative Sentences : We have been playing.
Negative Sentences : We have not been playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Have we been playing
?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Have we not
been playing ?
Subject + V2 + Object.
The simple past tense
is used for an action
which happened at a particular time in the past.
Affirmative Sentences : I played.
Negative Sentences : I did not play.
Interrogative Sentences : Did I play ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Did I not
played ?
Subject + was/were + V1 + ing + Object.
The past continuous tense
is used for an action
which was happening at a particular time in the
past.
Affirmative Sentences : Boys were playing.
Negative Sentences : Boys were not playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Were boys playing ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Were boys
not playing ?
Subject + had + V3 + Object.
The past perfect tense is used to express an
action that was completed before another
action started in the past. It is used with the
earlier of the two actions. The simple past tense
is used with the other action.
Affirmative Sentences : Sheila had played.
Negative Sentences : Sheila had not played.
Interrogative Sentences : Had Sheila played?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Had Sheila
not played ?
Subject + had + been + V1 + Object.
The past perfect continuous tense is used for an
action that began before a certain point in the
past and continued up to that point.
Affirmative Sentences : Ria had been playing.
Negative Sentences : Ria had not been playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Had Ria been playing?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Had Ria not been
playing ?
Subject + will/shall + V1 + Object.
The simple future tense is used for an action
that will take place at particular time in the
future.
Affirmative Sentences : Ravi will play.
Negative Sentences : Ravi will not play.
Interrogative Sentences : Will Ravi play ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Will Ravi not
play ?
Subject + will/shall + be +V1 + ing + Object
The future continuous tense is used to express
an action which will be in progress at a
particular time in the future.
Affirmative sentences : I will be playing.
Negative sentences : I will not be playing.
Interrogative sentences : Shall I be playing?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Shall I not
be playing?
Subject + shall/will + have + V3 + Object.
Future perfecttense is used to indicate the
completion of an action by a certain period of
time in the future.
Affirmative Sentences : She will have played.
Negative Sentences : She will not have played.
Interrogative Sentences : Will she have played?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Will she not
have played?
Subject + shall/will +have been + V1 + ing +
Object.
The future perfect tense is used when an action
is to continue up to a certain point of time in
the future.
Affirmative Sentences : Raj will have been
playing.
Negative Sentences : Raj will not have been
playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Will Raj have been
playing ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Will Raj not
have been playing ?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Complex Numbers: Problem-SolvingDocumento2 pagineComplex Numbers: Problem-SolvingK TariNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep Glow v1.4.6 ManualDocumento6 pagineDeep Glow v1.4.6 ManualWARRIOR FF100% (1)
- Sambungan Chapter 2.2Documento57 pagineSambungan Chapter 2.2iffahNessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion Exp 2 Chm674Documento4 pagineDiscussion Exp 2 Chm674Eva Lizwina MatinNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockaura Token 3.1: Serial No. 2022100500012015 Presented by Fairyproof October 5, 2022Documento17 pagineBlockaura Token 3.1: Serial No. 2022100500012015 Presented by Fairyproof October 5, 2022shrihari pravinNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Rotary Pulse Encoder Operation Replacement SettingDocumento8 pagineStandard Rotary Pulse Encoder Operation Replacement SettingGuesh Gebrekidan50% (2)
- MetaLINK Info r456Documento5 pagineMetaLINK Info r456Milan AntovicNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Eligible Candidates Applied For Registration of Secb After Winter 2015 Examinations The Institution of Engineers (India)Documento9 pagineList of Eligible Candidates Applied For Registration of Secb After Winter 2015 Examinations The Institution of Engineers (India)Sateesh NayaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment03 PCM-DecodingDocumento10 pagineExperiment03 PCM-DecodingMary Rose P Delos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- AOAC BAX Assay Listeria Monocytogenes RT 121402Documento18 pagineAOAC BAX Assay Listeria Monocytogenes RT 121402Yesenia Borja ArroyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon FibreDocumento25 pagineCarbon Fibrejagadish.kvNessuna valutazione finora
- Norstar ICS Remote Tools, NRU Software Version 11Documento1 paginaNorstar ICS Remote Tools, NRU Software Version 11Brendan KeithNessuna valutazione finora
- Indigenous Microorganisms Production and The Effect On Composting ProcessDocumento5 pagineIndigenous Microorganisms Production and The Effect On Composting ProcessAldrin Baquilid FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP Table BufferingDocumento31 pagineSAP Table Bufferingashok_oleti100% (3)
- The Gist of NCERT General Science PDFDocumento148 pagineThe Gist of NCERT General Science PDFSatyajitSahooNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Altimetry 1Documento1 paginaWhat Is Altimetry 1miguel rosasNessuna valutazione finora
- CBIP draft meter standardsDocumento22 pagineCBIP draft meter standardslalit123indiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quizlet-Philippine Electrical CodeDocumento2 pagineQuizlet-Philippine Electrical Codena zafira0% (1)
- Astrology, Believe It or Not - OCRDocumento155 pagineAstrology, Believe It or Not - OCRShashwat Singh Pokharel100% (2)
- COP ImprovementDocumento3 pagineCOP ImprovementMainak PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Automobile Engg-UNIT-1Documento28 pagineAutomobile Engg-UNIT-1Muthuvel MNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes in Computational Science and EngineeringDocumento434 pagineLecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineeringmuhammad nurulNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Stability-Chapter 3Documento84 paginePower System Stability-Chapter 3Du TrầnNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5: Work, Energy and PowerDocumento4 pagineChapter 5: Work, Energy and PowerPriyaa JayasankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Massive Transfusion ProtocolDocumento2 pagineMassive Transfusion ProtocolmukriNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling, Testing, and Analysis of Asphalt Roll Roofing, Cap Sheets, and Shingles Used in Roofing and WaterproofingDocumento13 pagineSampling, Testing, and Analysis of Asphalt Roll Roofing, Cap Sheets, and Shingles Used in Roofing and WaterproofingLuigi HernándezNessuna valutazione finora
- Quasi VarianceDocumento2 pagineQuasi Varianceharrison9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daily production planning and capacity analysisDocumento27 pagineDaily production planning and capacity analysisahetNessuna valutazione finora
- SM Maintenance Instructions: Author: Lars Rydén, Konecranes AB, SwedenDocumento132 pagineSM Maintenance Instructions: Author: Lars Rydén, Konecranes AB, SwedenDan VekasiNessuna valutazione finora