Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
System Design Civil Uml
Caricato da
Mukesh Lavan0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
26 visualizzazioni11 paginehghgjhgjhg'
ug
uuuh'
guhg
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentohghgjhgjhg'
ug
uuuh'
guhg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
26 visualizzazioni11 pagineSystem Design Civil Uml
Caricato da
Mukesh Lavanhghgjhgjhg'
ug
uuuh'
guhg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 11
SYSTEM DESIGN
4.1 GENERAL
Design Engineering deals with the various UML
[Unified Modeling language] diagrams for the implementation of project.
Design is a meaningful engineering representation of a thing that is to be
built. Software design is a process through which the requirements are
translated into representation of the software. Design is the place where
quality is rendered in software engineering. Design is the means to
accurately translate customer requirements into finished product.
4.1.1 ACTIVITY DIAGRAM
Activity diagram are a loosely defined diagram to show workflows
of stepwise activities and actions, with support for choice, iteration and
concurrency. UML, activity diagrams can be used to describe the business
and operational step-by-step workflows of components in a system. UML
activity diagrams could potentially model the internal logic of a complex
operation. In many ways UML activity diagrams are the object-oriented
equivalent of flow charts and data flow diagrams (DFDs) from structural
development.
4.1.2 USE CASE DIAGRAM
A use case diagram is a type of behavioral
diagram created from a Use-case analysis. The purpose of use case is to
present overview of the functionality provided by the system in terms of
actors, their goals and any dependencies between those use cases.
4.1. 3. SEQUENCE DIAGRAM
A sequence diagram in UML is a kind of interaction diagram
that shows how processes operate with one another and in what order. It
is a construct of a message sequence chart. Sequence diagrams are
sometimes called Event-trace diagrams, event scenarios, and timing
diagrams.
4.1.4. CLASS DIAGRAM
A class diagram in the UML is a type of static structure
diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system’s
classes, their attributes, and the relationships between the classes. Private
visibility hides information from anything outside the class partition.
Public visibility allows all other classes to view the marked information.
Protected visibility allows child classes to access information they
inherited from a parent class.
4.1.5. E-R DIAGRAM
In software engineering, an entity-relationship model (ERM) is an
abstract and conceptual representation of data. Entity-relationship
modeling is a database modeling method, used to produce a type
of conceptual schema or semantic data model of a system, often
a relational database, and its requirements in a top-down fashion.
Diagrams created by this process are called entity-relationship
diagrams, ER diagrams, or ERDs.
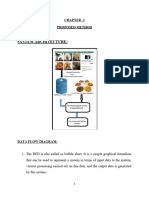
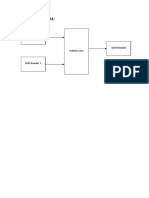
4.1.7. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
The users or nodes involved in our projects are
Sender, Intermediate and Receiver. In order to send file, the sender has to
find out the list of nodes which are connected with the sender. From that
available list he can choose receiver. Then the sender has to analyze the
performance of each and every node which is connected with the sender.
The performance analysis list will return the priority based result so that
sender can choose the intermediate to send the file. The Intermediate will
receive the file from sender then it will analyze the performance so that it
can send data to another intermediate or receiver. In the receiver side, the
receiver has to select the file path to receive the file from sender or
intermediate. Then the receiver can view the file received file.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Case Study In OOAD and UML: Case Studies in Software Architecture & Design, #1Da EverandCase Study In OOAD and UML: Case Studies in Software Architecture & Design, #1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Explanetion For OOAD DiagramsDocumento7 pagineExplanetion For OOAD Diagramsmsccs2nd2024Nessuna valutazione finora
- SDA Lab ManualDocumento17 pagineSDA Lab ManualBINARY TRADERNessuna valutazione finora
- Examination Seating and Invizilation Automation System DesignDocumento41 pagineExamination Seating and Invizilation Automation System Design19-1296 VASHISTA REDDYNessuna valutazione finora
- Uml DiagramsDocumento22 pagineUml DiagramsPavan KalyanNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 Overview: Chapter-Four DesignDocumento15 pagine4.1 Overview: Chapter-Four DesignAyush SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment Details - 1-4Documento13 pagineExperiment Details - 1-4Anonymous Sje7HJWNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Flow DiagramDocumento8 pagineData Flow DiagramMadhanDhonianNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.system DesignDocumento11 pagine4.system DesignSANDEEP KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Null 1Documento6 pagineNull 1ajaydanish012Nessuna valutazione finora
- CS6511case Tools Lab Manual UpdatedDocumento96 pagineCS6511case Tools Lab Manual UpdatedSelva Kanmani100% (1)
- Uml ModelsDocumento25 pagineUml ModelsNorife Z GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- TALHA NADEEM 11610 CS 5thDocumento15 pagineTALHA NADEEM 11610 CS 5thtalhanadeem02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Function Point Analysis Example PDFDocumento4 pagineFunction Point Analysis Example PDFPranav Sanjeev kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- SE Term PaperDocumento8 pagineSE Term PaperAkash BagchiNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Diagram?Documento13 pagineWhat Is A Diagram?John Kenneth HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Uml Diagrams For TambolaDocumento5 pagineUml Diagrams For Tambolaansh100% (1)
- App Dev Module 20 CopiesDocumento8 pagineApp Dev Module 20 CopiesArjay BalberanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Four 4. System DesignDocumento21 pagineChapter Four 4. System DesignGetenet ZigaleNessuna valutazione finora
- SYSTEM DESIGN (WomenSaftey)Documento11 pagineSYSTEM DESIGN (WomenSaftey)Sandesh RameshNessuna valutazione finora
- DMDTDocumento4 pagineDMDTnaveenath12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Systems Integration & Architecture IT312Documento36 pagineSystems Integration & Architecture IT312RobijhinNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagrams Used in SrsDocumento2 pagineDiagrams Used in SrsBuggineni Vamsi Ram100% (1)
- Sepm Updated 6Documento11 pagineSepm Updated 6Hanumanth Rao MareeduNessuna valutazione finora
- System Modeling: Existing and Planned System ModelsDocumento5 pagineSystem Modeling: Existing and Planned System ModelsMaricar SucalditoNessuna valutazione finora
- SDM-Assignment2-Depyloment DiagramDocumento4 pagineSDM-Assignment2-Depyloment DiagramSiddarth PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- CASE STUDyDocumento20 pagineCASE STUDyTRAIL BLAZERNessuna valutazione finora
- OOAD LAB ManualDocumento187 pagineOOAD LAB ManualsangeethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Green University of BangladeshDocumento11 pagineGreen University of Bangladeshishrakh bari১৮১০০২০২৭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ooad Unit3 NotesDocumento15 pagineOoad Unit3 NotesplutopopNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Analysis: UML DiagramsDocumento16 pagineDesign Analysis: UML DiagramsTejaNessuna valutazione finora
- OO Analysis and Design and UMLDocumento9 pagineOO Analysis and Design and UMLMayank SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4+1 View in UMLDocumento4 pagine4+1 View in UMLsanketskumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Se Model 4Documento8 pagineSe Model 4Praveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sequence TutorialDocumento5 pagineSequence TutorialMoheb Adly YoussefNessuna valutazione finora
- Chappter 2 Introduction To UmlDocumento20 pagineChappter 2 Introduction To UmlgitanjalipandaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.ijaest Vol No 7 Issue No 2 Designing Aspects Using Various Uml Diagrams in Resource Pool Management 228 233Documento6 pagine8.ijaest Vol No 7 Issue No 2 Designing Aspects Using Various Uml Diagrams in Resource Pool Management 228 233helpdesk9532Nessuna valutazione finora
- UmlDocumento19 pagineUmlSwati Sharma100% (1)
- What Is UMLDocumento6 pagineWhat Is UMLseelan15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Use Case DiagramsDocumento24 pagineUse Case DiagramsJigar ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Asgnmt5 (522) Idress SirDocumento11 pagineAsgnmt5 (522) Idress SirDil NawazNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5-Modeling Component DesignDocumento27 pagineUnit 5-Modeling Component DesignAsif ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- UML Lab Week-1Documento24 pagineUML Lab Week-1Sumanth_YedotiNessuna valutazione finora
- Component Engineering - UMLDocumento131 pagineComponent Engineering - UMLSouvikNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Engineering Principles and Practices 20CS44P: WEEK-6: Requirement Engineering & ModelingDocumento9 pagineSoftware Engineering Principles and Practices 20CS44P: WEEK-6: Requirement Engineering & ModelingManjunatha OkNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No 1Documento3 pagineExperiment No 1Shreyas JadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Unified Modeling LanguageDocumento13 pagineUnified Modeling Languagepuja786Nessuna valutazione finora
- Livingstone International UniversityDocumento4 pagineLivingstone International Universityopolot PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- UML Lab ManualDocumento56 pagineUML Lab ManualAnonymous M9NDXtI5dNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4a - High Level DesignDocumento26 pagineChapter 4a - High Level DesignsagniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ooad Unit3 Notes PDFDocumento15 pagineOoad Unit3 Notes PDFVidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- SEPM FileDocumento44 pagineSEPM Fileaasthamahajan2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- OOAD Unit 5 - Traffic Management SystemDocumento20 pagineOOAD Unit 5 - Traffic Management Systemlilooooooooooo100% (2)
- Cs2357-Ooad Lab ManualDocumento199 pagineCs2357-Ooad Lab ManualMohammed Thawfeeq0% (1)
- OOAD Unit 5 - Traffic Management SystemDocumento20 pagineOOAD Unit 5 - Traffic Management SystemSowmya SNessuna valutazione finora
- SE Assignment IIIDocumento5 pagineSE Assignment IIIShilpa chaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Describing Software Architecture With UML: Siemens Corporate Research, Princeton, New Jersey, USADocumento15 pagineDescribing Software Architecture With UML: Siemens Corporate Research, Princeton, New Jersey, USASwetha ManchikantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect-20-21-UML - SW Engineering 1Documento11 pagineLect-20-21-UML - SW Engineering 1Al YarNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is UML? What're The Purposes of UML?: UML Use Case DiagramDocumento4 pagineWhat Is UML? What're The Purposes of UML?: UML Use Case DiagramqwertyuiopNessuna valutazione finora
- 165 AutomaticDocumento7 pagine165 AutomaticMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Santhana Lakshmi New Cleared PaperDocumento7 pagineSanthana Lakshmi New Cleared PaperMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- TheTransistorAmplifier P1Documento63 pagineTheTransistorAmplifier P1Marcelo Napoleão BarrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Compressed MinDocumento2 pagineCompressed MinMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Image Saliency Analysis Based On Retina Simulation: 2017 IEEE Third International Conference On Multimedia Big DataDocumento4 pagineImage Saliency Analysis Based On Retina Simulation: 2017 IEEE Third International Conference On Multimedia Big DataMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- HM1100 UM EU E Rev.1.1 131101 Screen PDFDocumento8 pagineHM1100 UM EU E Rev.1.1 131101 Screen PDFMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- 43.sensor Fusion-Based Vacant Parking SlotDocumento4 pagine43.sensor Fusion-Based Vacant Parking SlotMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- HM1100 UM EU E Rev.1.1 131101 Screen PDFDocumento8 pagineHM1100 UM EU E Rev.1.1 131101 Screen PDFMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Doctor Appoinment SystemDocumento30 pagineDoctor Appoinment SystemMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unsupervised Learning - Text Clustering Machine Learning For NLPDocumento51 pagineUnsupervised Learning - Text Clustering Machine Learning For NLPravigobiNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On Student Information Management System Php-MysqlDocumento87 pagineProject Report On Student Information Management System Php-MysqlKapil Kaushik76% (72)
- I. Automatic Screening System - A ReviewDocumento6 pagineI. Automatic Screening System - A ReviewMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Retinal Image Analysis Using Morphological Process and Clustering TechniqueDocumento15 pagineRetinal Image Analysis Using Morphological Process and Clustering TechniquesipijNessuna valutazione finora
- Biometric System Based Electronic Voting Machine Using Arm9 MicrocontrollerDocumento9 pagineBiometric System Based Electronic Voting Machine Using Arm9 MicrocontrollerInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biometric System Based Electronic Voting Machine Using Arm9 MicrocontrollerDocumento9 pagineBiometric System Based Electronic Voting Machine Using Arm9 MicrocontrollerInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Implementation of Library Books Search and Management System Using RFID TechnologyDocumento6 pagineDesign and Implementation of Library Books Search and Management System Using RFID TechnologyMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Diagram:: RFID Reader 1Documento1 paginaBlock Diagram:: RFID Reader 1Mukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Fir Registration and Sos System: Prof. Anindita Khade, Sanket Yerigeri, Kaustubh Sonde, Shivaganesh PillaiDocumento5 pagineOnline Fir Registration and Sos System: Prof. Anindita Khade, Sanket Yerigeri, Kaustubh Sonde, Shivaganesh PillaiMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unsupervised Learning - Text Clustering Machine Learning For NLPDocumento51 pagineUnsupervised Learning - Text Clustering Machine Learning For NLPravigobiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 4Documento14 paginePresentation 4Mukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Librr AryyyyDocumento68 pagineLibrr AryyyyMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sundar PHDocumento3 pagineSundar PHMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Time Monitoring of Various Projects Funded by Ministry of Ayush (Ministry of Ayush)Documento37 pagineReal Time Monitoring of Various Projects Funded by Ministry of Ayush (Ministry of Ayush)Mukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Path Holes in All ProjecttDocumento26 paginePath Holes in All ProjecttMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.0 System Analysis and Design 5.1 Input DesignDocumento4 pagine5.0 System Analysis and Design 5.1 Input DesignMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
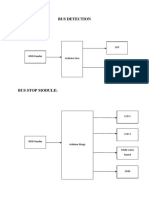
- Bus DetectionDocumento1 paginaBus DetectionMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bricks, Crushed Stone Per Ton: Database Name QualityDocumento3 pagineBricks, Crushed Stone Per Ton: Database Name QualityMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhee 2016Documento6 pagineRhee 2016Mukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Garbage Monitoring and Clearance System Using Internet of ThingsDocumento6 pagineSmart Garbage Monitoring and Clearance System Using Internet of ThingsMukesh LavanNessuna valutazione finora
- I Focus: Echnology For CSECDocumento3 pagineI Focus: Echnology For CSECChad McdonaldNessuna valutazione finora
- World Tourism Day by SlidesgoDocumento56 pagineWorld Tourism Day by SlidesgoLe Anh Quan B2105684Nessuna valutazione finora
- HTTP 111Documento18 pagineHTTP 111jayaprabasNessuna valutazione finora
- Logcat Prev CSC LogDocumento278 pagineLogcat Prev CSC LogValentina GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- PL-2000 - Packet Light NetworksDocumento2 paginePL-2000 - Packet Light NetworksIsrael ExporterNessuna valutazione finora
- Zemez Free Theme Documentation: How To Install Wordpress Free Theme Customizer Working With Theme Elementor PluginDocumento17 pagineZemez Free Theme Documentation: How To Install Wordpress Free Theme Customizer Working With Theme Elementor PluginDaviq MusholliniNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistem Tarantula I-NILAMDocumento1 paginaSistem Tarantula I-NILAMJazfrul FahmiNessuna valutazione finora
- CASE Tool IntroDocumento8 pagineCASE Tool Intromohanacute90Nessuna valutazione finora
- AS and A Level Business Studies Student's CD-ROM: Help NotesDocumento5 pagineAS and A Level Business Studies Student's CD-ROM: Help NotesMuhammad Salim Ullah KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hspice Download Full VersionDocumento3 pagineHspice Download Full Versionnishant205kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ciclo de Vida Del RansomwareDocumento1 paginaCiclo de Vida Del RansomwarerodrigoduocNessuna valutazione finora
- Ile CobolDocumento10 pagineIle Cobolप्रभाकर भट्टNessuna valutazione finora
- Java AssignmentDocumento55 pagineJava AssignmentAnanya BhagatNessuna valutazione finora
- (CS214P) Assembly Language Grade: Third Year (Computer Science)Documento41 pagine(CS214P) Assembly Language Grade: Third Year (Computer Science)Yahia ShahinNessuna valutazione finora
- Karl Dvorak, Geschichte Des K.K. Infanterie-Regiments Nr. 41, Vol. IIIDocumento322 pagineKarl Dvorak, Geschichte Des K.K. Infanterie-Regiments Nr. 41, Vol. IIIGiovanni Cerino-BadoneNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento23 pagineNew Microsoft Word DocumentHitesh BhatnagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Te2401 Part1Documento193 pagineTe2401 Part1Jami BurnettNessuna valutazione finora
- Sit774-9 1PDocumento4 pagineSit774-9 1PTanzeel MirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- OCR Computer Science A Level: 1.1.1 Structure and Function of The ProcessorDocumento471 pagineOCR Computer Science A Level: 1.1.1 Structure and Function of The ProcessorIncognitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Grade 11 & 12 (Day 2)Documento5 pagineLesson Plan Grade 11 & 12 (Day 2)HanessyNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Web Services I So Bra PrefDocumento43 pagineManual Web Services I So Bra Prefanon_211919506Nessuna valutazione finora
- HLD-FQZ-3Z Alternator and Starter Test Bench (Windows Computer)Documento2 pagineHLD-FQZ-3Z Alternator and Starter Test Bench (Windows Computer)Rocky Escudero GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- FBL 2360Documento14 pagineFBL 2360musarraf172Nessuna valutazione finora
- Template Access and EditingDocumento3 pagineTemplate Access and Editingxolaspor13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carungcong HciDocumento3 pagineCarungcong Hcibenedict carungcongNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Practices For Developing Apache Kafka Applications On Confluent CloudDocumento37 pagineBest Practices For Developing Apache Kafka Applications On Confluent CloudMuhammad Masood HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Security 210-260Documento2 pagineCCNA Security 210-260Chris BuenaventuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tafi40 en 46b FV Part1Documento472 pagineTafi40 en 46b FV Part1manoj14febNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Subdomain EnumDocumento17 pagineAutomatic Subdomain EnumPortia SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- SPL Series Scpi Programming Guide SB - GBDocumento16 pagineSPL Series Scpi Programming Guide SB - GBMihai CherechesNessuna valutazione finora
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceDa EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleDa EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (16)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessDa EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNessuna valutazione finora
- Python for Beginners: A Crash Course Guide to Learn Python in 1 WeekDa EverandPython for Beginners: A Crash Course Guide to Learn Python in 1 WeekValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (7)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveDa EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNessuna valutazione finora
- Excel 2023 for Beginners: A Complete Quick Reference Guide from Beginner to Advanced with Simple Tips and Tricks to Master All Essential Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, Charts, Tools, & ShortcutsDa EverandExcel 2023 for Beginners: A Complete Quick Reference Guide from Beginner to Advanced with Simple Tips and Tricks to Master All Essential Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, Charts, Tools, & ShortcutsNessuna valutazione finora
- Clean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software CraftsmanshipDa EverandClean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software CraftsmanshipValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (13)
- Learn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Da EverandLearn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (34)
- Optimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesDa EverandOptimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesNessuna valutazione finora
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsDa EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (24)
- Fundamentals of Data Engineering: Plan and Build Robust Data SystemsDa EverandFundamentals of Data Engineering: Plan and Build Robust Data SystemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Once Upon an Algorithm: How Stories Explain ComputingDa EverandOnce Upon an Algorithm: How Stories Explain ComputingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (43)
- Microsoft 365 Guide to Success: 10 Books in 1 | Kick-start Your Career Learning the Key Information to Master Your Microsoft Office Files to Optimize Your Tasks & Surprise Your Colleagues | Access, Excel, OneDrive, Outlook, PowerPoint, Word, Teams, etc.Da EverandMicrosoft 365 Guide to Success: 10 Books in 1 | Kick-start Your Career Learning the Key Information to Master Your Microsoft Office Files to Optimize Your Tasks & Surprise Your Colleagues | Access, Excel, OneDrive, Outlook, PowerPoint, Word, Teams, etc.Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- How to Make a Video Game All By Yourself: 10 steps, just you and a computerDa EverandHow to Make a Video Game All By Yourself: 10 steps, just you and a computerValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Python Machine Learning - Third Edition: Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Python, scikit-learn, and TensorFlow 2, 3rd EditionDa EverandPython Machine Learning - Third Edition: Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Python, scikit-learn, and TensorFlow 2, 3rd EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Software Engineering at Google: Lessons Learned from Programming Over TimeDa EverandSoftware Engineering at Google: Lessons Learned from Programming Over TimeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Python Programming For Beginners: Learn The Basics Of Python Programming (Python Crash Course, Programming for Dummies)Da EverandPython Programming For Beginners: Learn The Basics Of Python Programming (Python Crash Course, Programming for Dummies)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Nine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersDa EverandNine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (7)
- Excel Dynamic Arrays Straight to the Point 2nd EditionDa EverandExcel Dynamic Arrays Straight to the Point 2nd EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Coders at Work: Reflections on the Craft of ProgrammingDa EverandCoders at Work: Reflections on the Craft of ProgrammingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (151)
- Microservices Patterns: With examples in JavaDa EverandMicroservices Patterns: With examples in JavaValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Product Operations: How successful companies build better products at scaleDa EverandProduct Operations: How successful companies build better products at scaleNessuna valutazione finora