Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Scenario Lab Static NAT
Caricato da
Rufino UribeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Scenario Lab Static NAT
Caricato da
Rufino UribeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lab ID: 9.9K114A018.SCI1.
Scenario Lab: Static NAT
Objective
Build a test lab to help you learn the basic commands needed to configure Network Address Translation
(NAT) on a Cisco network. Configure the routers with Routing Information Protocol version 2 (RIPv2) so
that all devices can ping any other device. Configure NAT on Router1.
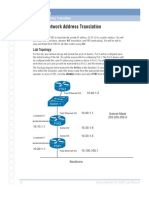
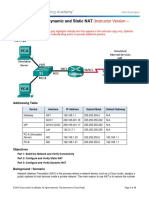
Lab Topology
The Topology diagram below represents the NetMap in the Simulator.
S0/0 Fa0/0
192.168.1.1/24 192.168.100.1/24
Router1 Router2
Fa0/0 S0/0
192.168.101.1/24 192.168.1.2/24
HostA HostB
Command Summary
Command Description
clock rate clock-rate sets the clock rate for a Data Communications Equipment
(DCE) interface
configure terminal enters global configuration mode from privileged EXEC mode
enable enters privileged EXEC mode
end ends and exits configuration mode
exit exits one level in the menu structure
hostname host-name sets the device name
interface type number changes from global configuration mode to interface
configuration mode
ip address ip-address subnet-mask assigns an IP address to an interface
ip nat inside defines the inside interface for NAT
ip nat inside source static inside- creates a static NAT translation
local-address inside-global-address
ip nat outside sets an interface to be an outside interface
network network-address activates RIP on the specified network
no shutdown enables an interface
ping ip-address sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo
request to the specified address
router rip enables RIP routing
show ip nat translations displays the NAT translation table
show running-config displays the active configuration file
version 2 enables RIPv2
1 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
The IP addresses and subnet masks used in this lab are shown in the tables below:
IP Addresses
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Router1 FastEthernet 0/0 192.168.101.1 255.255.255.0
Serial 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router2 FastEthernet 0/0 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
Serial 0/0 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
Device IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
HostA 192.168.101.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.101.1
HostB 192.168.100.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.100.1
Lab Tasks
1. Configure Router1 with a host name of Router1. Configure the appropriate IP addresses on the
interfaces; refer to the IP Addresses table. A DCE cable is connected to Router1. The Serial link
should have a speed of 64 Kbps. Enable the interfaces.
2. Configure Router2 with a host name of Router2. Configure the appropriate IP addresses on the
interfaces; refer to the IP Addresses table. Enable the interfaces.
3. Configure the routers with RIP; do not advertise Router1’s FastEthernet 0/0 interface network.
4. On Router1, configure NAT so that HostA appears as the IP address 192.168.1.100 to external
networks.
5. Ping from HostA to HostB (192.168.100.2) to populate the NAT translation table and to verify your
configuration of RIPv2. The ping should be successful.
6. On Router1, issue the show ip nat translations command to verify your NAT configuration.
2 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
Lab Solutions
1. On Router1, issue the following commands to configure a host name, to configure the appropriate IP
addresses, to configure a clock rate on the Serial 0/0 interface, and to enable the interfaces:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname Router1
Router1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
Router1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.101.1 255.255.255.0
Router1(config-if)#no shutdown
Router1(config-if)#interface serial 0/0
Router1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router1(config-if)#no shutdown
Router1(config-if)#exit
2. On Router2, issue the following commands to configure a host name, to configure the appropriate IP
addresses, and to enable the interfaces:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname Router2
Router2(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
Router2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
Router2(config-if)#no shutdown
Router2(config-if)#interface serial 0/0
Router2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
Router2(config-if)#no shutdown
Router2(config-if)#exit
3. On Router1 and Router2, issue the following commands to configure RIP, without advertising
Router1’s FastEthernet 0/0 interface network:
Router1(config)#router rip
Router1(config-router)#version 2
Router1(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
Router1(config-router)#exit
Router2(config)#router rip
Router2(config-router)#version 2
Router2(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
Router2(config-router)#network 192.168.100.0
Router2(config-router)#end
3 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
4. On Router1, issue the following commands to appropriate configure NAT:
Router1(config)#ip nat inside source static 192.168.101.2 192.168.1.100
Router1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
Router1(config-if)#ip nat inside
Router1(config-if)#interface serial 0/0
Router1(config-if)#ip nat outside
Router1(config-if)#end
5. A ping from HostA to HostB (192.168.100.2) should be successful.
6. On Router1, issue the show ip nat translations command to verify your NAT configuration. Sample
output is shown below:
Router1#show ip nat translations
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
--- 192.168.1.100 192.168.101.2 --- ---
Sample Configuration Script
Router1 Router1 (continued)
Router1#show running-config interface FastEthernet0/0
Building configuration... ip address 192.168.101.1 255.255.255.0
Current configuration : 866 bytes no ip directed-broadcast
! ip nat inside
Version 12.3 !
service timestamps debug uptime interface FastEthernet0/1
service timestamps log uptime no ip address
no service password-encryption no ip directed-broadcast
! shutdown
hostname Router1 !
ip cef router rip
! version 2
ip subnet-zero network 192.168.1.0
! !
interface Serial0/0 ip nat inside source static 192.168.101.2
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.100
no ip directed-broadcast !
clock rate 64000 ip classless
ip nat outside no ip http server
! !
interface Serial0/1 line con 0
no ip address line aux 0
no ip directed-broadcast line vty 0 4
shutdown !
! no scheduler allocate
end
Copyright © 1996–2014 Boson Software, LLC. All rights reserved. NetSim software and documentation are protected by copyright law.
4 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Da EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Nessuna valutazione finora
- DNS ConfigurationDocumento11 pagineDNS ConfigurationAsad Ul HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Del Operador altec-AM50-55-50E-55E-O PDFDocumento110 pagineManual Del Operador altec-AM50-55-50E-55E-O PDFFabian Andres Cely67% (3)
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationDa EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2. Connecting Two LANs Using Multi-Router Topology With Static RoutesDocumento8 pagine1.2. Connecting Two LANs Using Multi-Router Topology With Static Routesராஜ்குமார் கந்தசாமி100% (1)
- BS en Iso 9606-4 - 1999Documento26 pagineBS en Iso 9606-4 - 1999jesoneliteNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 11-5-1 Basic Cisco Device ConfigurationDocumento20 pagineLab 11-5-1 Basic Cisco Device ConfigurationNhật HồNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Quick ReferenceDocumento10 pagineCisco Quick Referencegotek145Nessuna valutazione finora
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityDa EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNessuna valutazione finora
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkDa EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplemental Lab CHAP and RIPDocumento4 pagineSupplemental Lab CHAP and RIPRufino UribeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Command Summary: Cisco Router Configuration CommandsDocumento13 pagineCisco Command Summary: Cisco Router Configuration CommandsGUnndiNessuna valutazione finora
- Series 0+-MODEL D: Connection ManualDocumento124 pagineSeries 0+-MODEL D: Connection ManualCristobal PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 7 Configuring and Verifying Static NATDocumento5 pagineLab 7 Configuring and Verifying Static NATrehsif nam100% (1)
- Cisco Router Configuration CommandsDocumento17 pagineCisco Router Configuration CommandsBazir AhamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 - Static RoutingDocumento5 pagineLab 4 - Static RoutingdaveNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1: Basic Cisco Device Configuration: Topology DiagramDocumento16 pagineLab 1: Basic Cisco Device Configuration: Topology DiagramNhựt LưuNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning PandasDocumento171 pagineLearning PandasMadhu MandavaNessuna valutazione finora
- IP Access Lists: Objective Lab TopologyDocumento5 pagineIP Access Lists: Objective Lab TopologyTomas Rodriguez RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- USP 2010 SWS: Ballast Distributing and Profiling MachineDocumento1 paginaUSP 2010 SWS: Ballast Distributing and Profiling MachineRohit BaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyDocumento26 pagineChapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyAhmed AlmussaNessuna valutazione finora
- NEC Product Brief InstructionDocumento15 pagineNEC Product Brief InstructionAHMEDKAMAL2011Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Linux Managing DNS Servers Lpic 2 m7 SlidesDocumento5 pagine7 Linux Managing DNS Servers Lpic 2 m7 SlidesАлександр ПяткинNessuna valutazione finora
- 19-Troubleshooting Basic Network Services IDocumento17 pagine19-Troubleshooting Basic Network Services Imansoorali_afNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication - 2500 Series: ObjectiveDocumento14 pagineLab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication - 2500 Series: Objectiveabdoulaye barryNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.7.2 Lab - Configure Single Area Ospfv2 EditadoDocumento4 pagine2.7.2 Lab - Configure Single Area Ospfv2 EditadoMaría ArmijosNessuna valutazione finora
- PracticeDocumento7 paginePracticeLiam PattersonNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Lab 3 Network Address TranslationDocumento8 pagine08 Lab 3 Network Address TranslationCaro CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- RIPv2 Part 2Documento10 pagineRIPv2 Part 2nurinNessuna valutazione finora
- Enterprise Network Design Part 2Documento3 pagineEnterprise Network Design Part 2Salim HassenNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Configuration StepsDocumento5 pagineCisco Configuration StepsMcDominiNessuna valutazione finora
- LabDocumento11 pagineLableonora KrasniqiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area Ospfv2 and Ospfv3 With Stub AreaDocumento29 pagineChapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area Ospfv2 and Ospfv3 With Stub AreaYafeth De Jesús Ramos CañizaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Switching LabDocumento17 pagineSwitching LabGabby100% (1)
- Expl2 IOS CmdsDocumento4 pagineExpl2 IOS CmdsJoey JanclaesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseDocumento4 pagineLab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprisemohammad_shahzad_iiuiNessuna valutazione finora
- OSPF Authentication II: Objective Lab TopologyDocumento9 pagineOSPF Authentication II: Objective Lab TopologyTomas Rodriguez RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative Access - ILMDocumento22 pagine4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative Access - ILMRony Schäfer JaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Configure Single-Area OSPFv2Documento12 pagineConfigure Single-Area OSPFv2Mohammed AkeelNessuna valutazione finora
- COMMANDS - Handout - 4 May 2015Documento35 pagineCOMMANDS - Handout - 4 May 2015Anup MukerjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4-Configuring RIPv1 and V2-ExampleDocumento4 pagineLab 4-Configuring RIPv1 and V2-ExampleOpenda mitchNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area Ospfv2 and Ospfv3 With Stub AreaDocumento19 pagineChapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area Ospfv2 and Ospfv3 With Stub AreaAhmed AlmussaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocumento11 pagine6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesCesar Lazo DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- RIP v2 - Lab 8Documento10 pagineRIP v2 - Lab 8nurinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Lab 3Documento39 pagineChapter 3 Lab 3luis vladimir cubillos sanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 2 OSPFv2 - MUHAMMAD IZWAN BIN NAZRI - CS2555ADocumento7 pagineExercise 2 OSPFv2 - MUHAMMAD IZWAN BIN NAZRI - CS2555Aezone8553Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocumento11 pagine6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesntutaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2 10 4aDocumento3 pagineLab 2 10 4asilindeanNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF Authentication - ILMDocumento11 pagine6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF Authentication - ILMRony Schäfer JaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocumento11 pagine6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesHani GoytomNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA1 - H2/H6: Cheat SheetDocumento7 pagineCCNA1 - H2/H6: Cheat SheetBart De ZaeytydtNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyDocumento26 pagineChapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyGuruparan PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Nat & PatDocumento5 pagineNat & Patrdj2rakibNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab5 3 5Documento10 pagineLab5 3 5ijot 76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Configure Cisco RouterDocumento9 pagineConfigure Cisco Routerfahmi0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab1: Simple Network: 1 TopologyDocumento5 pagineLab1: Simple Network: 1 TopologyfgherNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Configuration Demo I PDFDocumento8 pagine1 - Configuration Demo I PDFPriyanka BeheraNessuna valutazione finora
- H On F Study GuideDocumento5 pagineH On F Study GuideLeo F. Thomas Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nat - CcnaDocumento25 pagineNat - Ccnablue.jupiter9x154Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationDocumento7 pagine6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationGISTSalehuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocumento10 pagine4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessHector De Jesus Tapia GorgonioNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 2 2 6 Lab ConfiguringDynamicandStaticNAT PDFDocumento14 pagine9 2 2 6 Lab ConfiguringDynamicandStaticNAT PDFZersh EthioNessuna valutazione finora
- Praktijk SamenvattingDocumento3 paginePraktijk SamenvattingNiels LoomansNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccna4-Lab 1: Nat & Pat: Scenario For NAT ConfigurationDocumento2 pagineCcna4-Lab 1: Nat & Pat: Scenario For NAT ConfigurationNhựt LưuNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocumento11 pagine4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessJesús EnriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- First Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolDa EverandFirst Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolNessuna valutazione finora
- Sequential Lab Trivial File Transfer ProtocolDocumento4 pagineSequential Lab Trivial File Transfer ProtocolRufino UribeNessuna valutazione finora
- Scenario Lab IP Addressing On Catalyst 2950 SwitchesDocumento4 pagineScenario Lab IP Addressing On Catalyst 2950 SwitchesRufino UribeNessuna valutazione finora
- Scenario Lab CDPDocumento2 pagineScenario Lab CDPRufino UribeNessuna valutazione finora
- Initial Security Incident Questionnaire For Responders PDFDocumento1 paginaInitial Security Incident Questionnaire For Responders PDFRufino UribeNessuna valutazione finora
- SANS Institute: Unix Security ChecklistDocumento9 pagineSANS Institute: Unix Security ChecklistRufino UribeNessuna valutazione finora
- Primo Rogerjr ITE292 2BSIT C1 1SDocumento4 paginePrimo Rogerjr ITE292 2BSIT C1 1SRoger PrimoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tacacs+ Server Project Reo/prtDocumento18 pagineTacacs+ Server Project Reo/prtAtul SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Substantial Changes To ANSI/AISC 360 in The 2022 Edition That Appear in Public Review One Draft Dated August 3, 2020Documento8 pagineSubstantial Changes To ANSI/AISC 360 in The 2022 Edition That Appear in Public Review One Draft Dated August 3, 2020phamminhquangNessuna valutazione finora
- 18/28/38P Series: High Pressure FiltersDocumento8 pagine18/28/38P Series: High Pressure FiltersChris BanksNessuna valutazione finora
- Rec. ITU-T G.650.3 PDFDocumento22 pagineRec. ITU-T G.650.3 PDFAngelo SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- EEPROM - m24c64-w PDFDocumento38 pagineEEPROM - m24c64-w PDFLodewyk KleynhansNessuna valutazione finora
- 1100 Series PerkinsDocumento2 pagine1100 Series PerkinsGilberto Diaz CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Engine Exhause Silencer and Accessories Catalog PDFDocumento32 pagineStandard Engine Exhause Silencer and Accessories Catalog PDFslow_bbNessuna valutazione finora
- Gap Analysis of Multispecialty Hospital in Bahadurgarh As Per NABH NormsDocumento1 paginaGap Analysis of Multispecialty Hospital in Bahadurgarh As Per NABH NormsSanjeev ChouguleNessuna valutazione finora
- FABRIANO Catalogo2010 - Ing PDFDocumento72 pagineFABRIANO Catalogo2010 - Ing PDFS Antoni De RotiNessuna valutazione finora
- R48 3500e Rectifier UM1R483500e PDFDocumento28 pagineR48 3500e Rectifier UM1R483500e PDFHythamMidani100% (1)
- Back Ups Bx950u MsDocumento3 pagineBack Ups Bx950u MsLuthfi AthoriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual de Utilizare Concasor BB300Documento20 pagineManual de Utilizare Concasor BB300lucianchiritaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Instrumentation & MeasurementsDocumento35 pagineElectronic Instrumentation & MeasurementsMuhammad Sohaib ShahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Management & Ethics Lecture Notes 4. Production & Operations Management (Quality Management) (20.03.17)Documento36 pagineEngineering Management & Ethics Lecture Notes 4. Production & Operations Management (Quality Management) (20.03.17)Afranur ErenNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A324-73 (1992)Documento2 pagineAstm A324-73 (1992)FeteneNessuna valutazione finora
- 150 70-nm2 1Documento12 pagine150 70-nm2 1Eduardo JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgelogic NQPanelboards PDFDocumento6 pagineSurgelogic NQPanelboards PDFgramirezsalazar@yahoo.com.mxNessuna valutazione finora
- Changhong Chassis LS18 PDFDocumento34 pagineChanghong Chassis LS18 PDFJuan CoronelNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer CCNA Security Final Exam v1.2Documento30 pagineAnswer CCNA Security Final Exam v1.2Darius LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Balometer PH730 731 - 6005724 PDFDocumento78 pagineBalometer PH730 731 - 6005724 PDFImran HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Unleashing The Power of iLO, IPMI and Other Service ProcessorsDocumento16 pagineUnleashing The Power of iLO, IPMI and Other Service Processorsdnayak1Nessuna valutazione finora
- KY5 MNTP 3 RNDocumento40 pagineKY5 MNTP 3 RNJuan Carlos Trucios MitmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Central de Incendios Edificio 43 Notifier AFP-100Documento142 pagineManual Central de Incendios Edificio 43 Notifier AFP-100haedo86Nessuna valutazione finora