Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
TRB SYLLABUS
Caricato da
Mechanical Engineering0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
27 visualizzazioni3 pagineelectrical
Titolo originale
trb SYLLABUS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoelectrical
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
27 visualizzazioni3 pagineTRB SYLLABUS
Caricato da
Mechanical Engineeringelectrical
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
TRB POLYTECHNIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
UNIT 2: ELECTRIC CIRCUITS AND FIELDS [10 TOPICS]
1. KCL, KVL, node and mesh analysis,
2. transient response of dc and ac network,
3. sinusoidal steady – state analysis,
4. resonance, ideal current and voltage sources,
5. Thevenin's Norton's and Superposition and Maximum Power Transfer
theorems,
6. Three phase circuits.
7. Gauss Theorem,
8. electric field and potential due to point, line, plane and spherical charge
distributions,
9. Ampere's and Biot-Savart's laws,
10.inductance, dielectrics, capacitance.
UNIT 3: DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING [6 TOPICS ]
1. Representation of continuous and discrete-time signals,
2. shifting and scaling operations,
3. linear, time-invariant and causal systems,
4. Fourier series representation of continuous periodic signals,
5. sampling theorem,
6. Fourier, Laplace and Z transforms.
UNIT 4: ELECTRICAL MACHINES [ 9 TOPICS]
1. Single phase transformer – equivalent circuit, phase diagram, tests,
regulation and efficiency,
2. three phase transformers - connections, parallel operation,
3. auto- transformer, energy conversion principles,
4. DC machines - types, windings,
5. generator characteristics, armature reaction and commutation,
6. starting and speed control of motors,
7. three phase induction motors - principles, types, performance
characteristics, starting and speed control,
8. single phase induction motors, synchronous machines - performance,
regulation and parallel operation of generators, motor starting,
characteristics and applications,
9. Special Electrical machines.
UNIT 5: POWER SYSTEMS [8 TOPICS]
1. Basic power generation concepts,
2. transmission line models and performance,
3. cable performance insulation,
4. corona and radio interference,
5. distribution systems, per – unit quantities,
6. bus impedance and admittance matrices,
7. load flow, voltage control, power factor correction,
8. Economic operation, symmetrical components, fault analysis.
UNIT 6: PROTECTION AND SWITCHGEAR [6 TOPICS]
1. Principle of over - current,
2. differential and distance protection,
3. solid state relays and digital protection, circuit breakers,
4. system stability concepts,
5. swing curves and equal area criterion.
6. High voltage generation and measurements.
UNIT 7: CONTROL SYSTEM [4 TOPICS]
1. Principle and feedback, transfer function, block diagrams,
2. steady – state errors,
3. Routh and Nyquist techniques,
4. Bode plots, root loci, lag, lead and lead-leg compensation.
UNIT 8: ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS MEASUREMENTS [6 TOPICS]
1. Bridges and potentiometers,
2. PMMC, moving iron,
3. dynamometer and induction type instruments,
4. measurement of voltage, current, power, energy and power factor,
5. instruments transformers, phase, time and frequency measurement,
6. Q-meters, Oscilloscopes, Transducers and Data acquisition systems.
UNIT 9: ANALOG AND DIGITAL ELECTRONICS [11 TOPICS]
1. Characteristics of diodes, BJT, FET, amplifiers - biasing.
2. equivalent circuit and frequency response,
3. oscillators and feedback amplifiers,
4. operational amplifiers- characteristics and applications,
5. simple active filters,
6. VCOs' and timers,
7. combinational and sequential logic circuit,
8. multiplexer, Schmitt trigger, multi Vibrators,
9. sample and hold circuit,
10.A/D and D/A convertors,
11.8085 and 8086 - microprocessor and 8051 microcontroller basics,
architecture, programming and interfacing.
UNIT 10: POWER ELECTRONICS AND DRIVES [6 TOPICS]
1. Semiconductor power diodes, transistors, thyristors, TRIACs, MOSFETs and
IGBTs- static characteristics and principles of operation
2. triggering circuits,
3. phase control rectifiers,
4. bridge converters – fully controlled and half controlled,
5. principles of choppers and inverters,
6. basic concepts of adjustable speed dc and ac drives.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- AI 16 UV C Flux 401Documento1 paginaAI 16 UV C Flux 401Mechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
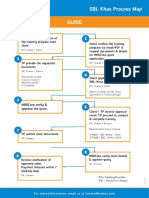
- SBL Khas Process MapDocumento1 paginaSBL Khas Process MapMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
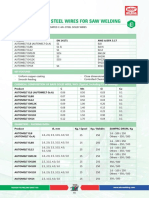
- C-MN STEEL WIRES FOR SAW WELDINGDocumento1 paginaC-MN STEEL WIRES FOR SAW WELDINGMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Ba EnglishDocumento15 pagineBa EnglishMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- M85ECB2892ED2005A82D24000Documento1 paginaM85ECB2892ED2005A82D24000Mechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Alagappa University: History of Indian National Movement From 1885 To 1947 A.DDocumento9 pagineAlagappa University: History of Indian National Movement From 1885 To 1947 A.DMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifemember-ship-ISME-25 SeptDocumento1 paginaLifemember-ship-ISME-25 SeptMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Our Pasts-1 Ch-1 What Where How and When: BC) Some of The Earliest Cities Flourished On These BanksDocumento1 paginaOur Pasts-1 Ch-1 What Where How and When: BC) Some of The Earliest Cities Flourished On These BanksMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Gdce Je Tmo Pway For SR NotificationDocumento4 pagineGdce Je Tmo Pway For SR NotificationMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Qualification CSTS Advt 01Documento4 pagineEssential Qualification CSTS Advt 01Mechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- BHEL Exam Pattern: 50% of Questions Shall Be From Subject/Discipline, While Remaining 50% WouldDocumento1 paginaBHEL Exam Pattern: 50% of Questions Shall Be From Subject/Discipline, While Remaining 50% WouldMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus For Written Examinaiton: A. General Knowledge - Both For Open and Departmental CandidatesDocumento3 pagineSyllabus For Written Examinaiton: A. General Knowledge - Both For Open and Departmental CandidatesMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Day Guide To InfosysDocumento3 pagine10 Day Guide To InfosysMechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Chandran Resume-1 1Documento2 pagineChandran Resume-1 1Mechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Electronic Timer - Series Micon 225-4Documento3 pagineElectronic Timer - Series Micon 225-4Rohit chavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Deber 3Documento9 pagineDeber 3Ale ZamNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei 3g Counters and Kpis PDFDocumento4 pagineHuawei 3g Counters and Kpis PDFsatya vara prasad ballaNessuna valutazione finora
- SeminarDocumento13 pagineSeminar17K41A0 440Nessuna valutazione finora
- Waveform Digitizers: Digitizer Families Waveform Recording Digital Pulse Processing (DPP) ToolsDocumento38 pagineWaveform Digitizers: Digitizer Families Waveform Recording Digital Pulse Processing (DPP) ToolsScarduelliNessuna valutazione finora
- LG 32lc7d 32lc55 32lc56 Chassis Ld73aDocumento44 pagineLG 32lc7d 32lc55 32lc56 Chassis Ld73awillorikerNessuna valutazione finora
- Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Thevenin's and Norton TheoremDocumento132 pagineNodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Thevenin's and Norton Theoremkarra veera venkata prasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Casa Datasheet RCNDocumento6 pagineCasa Datasheet RCNdiegoh_silvaNessuna valutazione finora
- MARANTZ SR5009 Service ManualDocumento195 pagineMARANTZ SR5009 Service ManualToni TonevNessuna valutazione finora
- ChartsDocumento17 pagineChartsHoàng Minh ThịnhNessuna valutazione finora
- Fujitsu Amilo Xi 1526Documento3 pagineFujitsu Amilo Xi 1526alelujaNessuna valutazione finora
- M571 LMR21 ADocumento50 pagineM571 LMR21 Aapi-3704830Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cables, Adapters, Accessories - 1Documento8 pagineCables, Adapters, Accessories - 1Nguyen Danh HuyNessuna valutazione finora
- DS-K1T804AMF Fingerprint Access Control TerminalDocumento3 pagineDS-K1T804AMF Fingerprint Access Control TerminalLuis RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei Improve SDSRDocumento9 pagineHuawei Improve SDSRAhmadArwani88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Del 2kva Liebert PDFDocumento44 pagineManual Del 2kva Liebert PDFVictor GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- CMO 24 s2008 Annex IVB List of LABORATORY Requirements For ECEDocumento31 pagineCMO 24 s2008 Annex IVB List of LABORATORY Requirements For ECEcathyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware Troubleshooting NotesDocumento11 pagineHardware Troubleshooting Notessimha23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate G59/3: Engineering RecommendationDocumento4 pagineCertificate G59/3: Engineering RecommendationNguyen VansuNessuna valutazione finora
- RGB Control SwitchDocumento1 paginaRGB Control SwitchLucian LupaşcoNessuna valutazione finora
- KY-031 Knock-Sensor ModuleDocumento3 pagineKY-031 Knock-Sensor Modulegabusmdq60Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual QuartusIIDocumento73 pagineManual QuartusIIoperezNessuna valutazione finora
- Temperature Control Design For The Substrate Holder of A High Vacuum Chamber, To Produce Semiconductor Films2 PDFDocumento7 pagineTemperature Control Design For The Substrate Holder of A High Vacuum Chamber, To Produce Semiconductor Films2 PDFcalchavNessuna valutazione finora
- Nptel Electrical MachinesDocumento7 pagineNptel Electrical MachinesVinodkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 128 Pid 102Documento2 pagine128 Pid 102Naing Min Htun60% (5)
- BITS HD ECE QuestionsDocumento10 pagineBITS HD ECE QuestionsLokesh Ceg100% (3)
- Addpac GSM CLI Manual Guide - EngDocumento56 pagineAddpac GSM CLI Manual Guide - EngNoltonNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis NewDocumento55 pagineThesis NewHasan juwelNessuna valutazione finora
- LT-493 FA-1025T Installation and Operation ManualDocumento22 pagineLT-493 FA-1025T Installation and Operation ManualpaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Efyxnov 2020Documento84 pagineEfyxnov 2020Subhash ThakerNessuna valutazione finora