Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
SVRphy10 PDF
Caricato da
anoetaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SVRphy10 PDF
Caricato da
anoetaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
*01 Forces&Energy (8-45).
qxd 25/1/07 5:06 pm Page 10
Newton’s third law of
Key words
force
motion
momentum
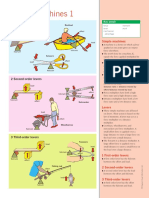
1 Example 1
Newton’s third law
● Newton’s third law of motion states
that when two objects, A and B,
interact, the force exerted by A on B is
equal in magnitude to the force
exerted by B on A, but the forces act
in opposite directions.
1 Example 1
● When a person steps forward from rest force exacted by
their foot pushes backwards on Earth force exacted on the the foot on the
foot by the Earth Earth
and Earth exerts an equal and
opposite force forward on the person.
Two bodies and two forces are
involved. 2 Example 2
● The small force that a person exerts
on Earth gives no noticeable
acceleration to Earth because of its
large mass. The equal force exerted on
the person, who has a much smaller
mass, causes them to accelerate.
force exacted on the
foot by the boat
2 Example 2 force exacted on the
● When a person steps out of a rowing boat by the foot
boat they push backwards on the boat,
and the boat pushes them forwards
with an equal but opposite force.
● The friction between the boat and the
water is slight and, as the person
pushes on the boat, it starts to move
backwards reducing the forward
motion of the person, who will tend to
fall in the water between boat and 3 Example 3 force exacted by the
land. bullet on the gun
3 Example 3
● When a bullet is fired from a gun, force exacted by gun
on the bullet
equal and opposite forces are exerted
on the bullet and the gun as the bullet
passes down the barrel. Bullet and gun
acquire equal momentum but in
© Diagram Visual Information Ltd.
opposite directions.
mass of bullet x bullet velocity = mass
of gun x gun velocity
● Since the mass of the bullet is much
less than that of the gun, the bullet
will move forward at a much higher
velocity than the gun will move
backwards.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Simple Machines 2: 1 Pulley SystemsDocumento1 paginaSimple Machines 2: 1 Pulley SystemsanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy19 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy19 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy13 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy13 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy9 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy9 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy17 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy17 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy8 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy8 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy15 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy15 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy18 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy18 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy16 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy16 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy14 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy14 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy11 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy11 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRphy12 PDFDocumento1 paginaSVRphy12 PDFanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Archimedes' Pump: Martin Gardner, Hendersonville, NC 28792Documento1 paginaArchimedes' Pump: Martin Gardner, Hendersonville, NC 28792anoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Fall and Terminal Velocity: 1 Gravity: Action at A DistanceDocumento1 paginaFree Fall and Terminal Velocity: 1 Gravity: Action at A DistanceanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRbio112 - Nematoda Life CycleDocumento1 paginaSVRbio112 - Nematoda Life CycleanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHIJKatong Convent 2011Documento7 pagineCHIJKatong Convent 2011anoetaNessuna valutazione finora
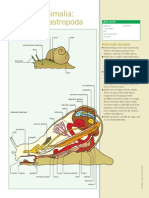
- SVRbio115 - GastropodaDocumento1 paginaSVRbio115 - GastropodaanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Newton's First Law of MotionDocumento1 paginaNewton's First Law of MotionanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRbio114 - MolluscaDocumento1 paginaSVRbio114 - MolluscaanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRbio126 MammaliaDocumento1 paginaSVRbio126 MammaliaanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRbio107 - CnidariaDocumento1 paginaSVRbio107 - CnidariaanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
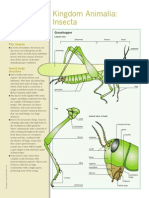
- Kingdom Animalia: Insecta: The InsectsDocumento1 paginaKingdom Animalia: Insecta: The InsectsanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
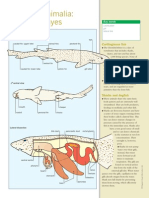
- Kingdom Animalia: Chondrichthyes: DogfishDocumento1 paginaKingdom Animalia: Chondrichthyes: DogfishanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRbio120 EchinodermataDocumento1 paginaSVRbio120 EchinodermataanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kingdom Animalia: ClassificationDocumento1 paginaKingdom Animalia: ClassificationanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kingdom Animalia: ClassificationDocumento1 paginaKingdom Animalia: ClassificationanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRbio117 - CrustaceaDocumento1 paginaSVRbio117 - CrustaceaanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRbio118-Chilopoda and DiplopodaDocumento1 paginaSVRbio118-Chilopoda and DiplopodaanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- SVRbio125 AvesDocumento1 paginaSVRbio125 AvesanoetaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- 9781919780382Documento22 pagine9781919780382Jeannot MpianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling of Surface-Mounted PMSM in Different Frames of ReferenceDocumento19 pagineModeling of Surface-Mounted PMSM in Different Frames of ReferenceAnonymous XKlkx7cr2INessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization Efficiency Dampers: of The of Aeolian VibrationDocumento3 pagineOptimization Efficiency Dampers: of The of Aeolian VibrationServando LozanoNessuna valutazione finora
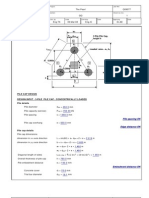
- Pile Cap Design 1Documento6 paginePile Cap Design 1kjpatel2100% (2)
- Control of Inverted PendulumDocumento5 pagineControl of Inverted PendulumAhmed HwaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- John Dirk Walecka - Introduction To Classical Mechanics-WSPC (2020)Documento184 pagineJohn Dirk Walecka - Introduction To Classical Mechanics-WSPC (2020)Saiyad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Tunnel SupportDocumento19 pagineTunnel Supportabhaysinghpratap2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Physics PDFDocumento20 pagineModern Physics PDFPrathm MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- January 2016 (IAL) QP - Unit 2 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocumento24 pagineJanuary 2016 (IAL) QP - Unit 2 Edexcel Physics A-LevelAshish MashruNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Structural Calculation of 2-Barrel Box CulvertDocumento51 pagineSummary of Structural Calculation of 2-Barrel Box CulvertPutri Lambok LubisNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Introduction To Structural Steel Design-Chapter 1Documento3 pagine1 - Introduction To Structural Steel Design-Chapter 1Abera DeressaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Fluid StaticsDocumento6 pagineChapter 3 - Fluid StaticsKristine Joy BagaporoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics Practice Problems SolvedDocumento3 pagineKinematics Practice Problems SolvedAbhinandan KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Aeletters 2023 8 2 2Documento8 pagineAeletters 2023 8 2 2miskoscribdNessuna valutazione finora
- (Environmental Science and Engineering) Jaime Klapp, Leonardo Di G. Sigalotti, Abraham Medina, Abel López, Gerardo Ruiz-Chavarría (Eds.)-Recent Advances in Fluid Dynamics With Environmental ApplicatioDocumento509 pagine(Environmental Science and Engineering) Jaime Klapp, Leonardo Di G. Sigalotti, Abraham Medina, Abel López, Gerardo Ruiz-Chavarría (Eds.)-Recent Advances in Fluid Dynamics With Environmental ApplicatioKyler GreenwayNessuna valutazione finora
- BSC Syllabus 2014Documento63 pagineBSC Syllabus 2014kcameppadi123Nessuna valutazione finora
- v11.0.1 System DocumentationDocumento4.258 paginev11.0.1 System DocumentationJOSE LUIS HDZNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical ChemistryDocumento3 paginePhysical ChemistrySeleneArthur25% (4)
- Excitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFDocumento2 pagineExcitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFRobNessuna valutazione finora
- Center of GravityDocumento7 pagineCenter of GravityAnonymous QiMB2lBCJLNessuna valutazione finora
- THERMODYNAMICS 1 Rev 2Documento62 pagineTHERMODYNAMICS 1 Rev 2Jads Cayabyab100% (2)
- Projectile and Circular Motion GuideDocumento10 pagineProjectile and Circular Motion GuideBryanHarold BrooNessuna valutazione finora
- 22303-2019-Winter-Model-Answer-Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Documento24 pagine22303-2019-Winter-Model-Answer-Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Nilesh LankeNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Design ProjectDocumento35 pagineMachine Design ProjectDũng PhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. (3) Experiment Name: Forced Convection Heat Transfer. Objective: To Determine The Heat Transfer Coefficient of Forced Convection of AirDocumento3 pagineExperiment No. (3) Experiment Name: Forced Convection Heat Transfer. Objective: To Determine The Heat Transfer Coefficient of Forced Convection of Airwrya hussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Slug Tracking Simulation of Severe Slugging Experiments: Tor Kindsbekken Kjeldby, Ruud Henkes and Ole Jørgen NydalDocumento6 pagineSlug Tracking Simulation of Severe Slugging Experiments: Tor Kindsbekken Kjeldby, Ruud Henkes and Ole Jørgen NydalAyauwu LovedayNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermoacoustic CoolingDocumento10 pagineThermoacoustic CoolingElisabeth MorseNessuna valutazione finora
- HEB200Documento1 paginaHEB200giulioNessuna valutazione finora
- Funds of Inertial Navigation Satellite Based Positioning and Their Integration PDFDocumento44 pagineFunds of Inertial Navigation Satellite Based Positioning and Their Integration PDFCaehhsegffNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix B Design Example Lifting LugDocumento6 pagineAppendix B Design Example Lifting LugfernandoNessuna valutazione finora