Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nu Day 3
Caricato da
Jan Tiangco100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
251 visualizzazioni2 pagineTitolo originale
NU DAY 3.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
251 visualizzazioni2 pagineNu Day 3
Caricato da
Jan TiangcoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
BRAKES factor.
The spring outside
diameter is 9.66 cm and wire
1. A band brake is installed on a diameter is 0.65 cm.
drum rotating at 250 rpm, and a
diameter of 900 millimeters. The 3. Compute the maximum deflection of
angle of contact is 1.5pi radians a 22-coil helical spring having a
and one end of the brake band is load of 120 kg. The spring has
fastened to a fixed pin while the squared and ground ends with
other end to the brake arm 150 modulus of elasticity in shear of
millimeter from the fixed pin. The 80 GPa, outside diameter of 8 cm
coefficient of friction is 0.25 and wire diameter of 8 mm.
and the straight brake arm is 1000
millimeters long and is placed 4. The load on a helical spring is
perpendicular to the diameter 1600-lb and the corresponding
bisecting the angle of contact. deflection is to be 4 in. Rigidity
Determine the minimum force in modulus is 11 million psi and the
Newton applied as the power (50 maximum intensity of safe
kW) is being absorbed. torsional stress is 60,000 psi.
Design the spring for the total
2. A simple band brake has a 76 cm number of turns if the wire is
drum and fitted with a steel band circular in cross section with a
2/5 cm thick lined with a brake diameter of 5/8 in. and a center
lining having a coefficient of line radius of 1 ½ in. The spring
friction of 0.25. The arc of is squared and ground ends.
contact is 245 degrees. The drum
is attached to a 60 cm hoisting 5. All four compression coil spring
drum that sustains a rope load of support one load of 700 kg/mm. All
820 kg. The operating force has a four springs are arranged in
moment arm of 1.50 m and the band parallel and rated same at 0.609
is attached 12 cm from the pivot kg/mm. Compute the deflection in
point. Find the width of a steel mm.
band for a tensile stress of 50
MPa. 6. A Mercedes Benz gas engine valve
spring is to have a mean diameter
SPRINGS of 3.81 cm. The maximum load it
will have to sustain is 45.45 kg
1. A coiled spring with 1¾ in. with corresponding deflection of
outside diameter is required to 1.27 cm. The spring is to be made
work under load of 140 lb. Wire of tempered steel wire. Since the
diameter used is 0.192 in., spring material is to be subjected to
is to have seven active coils, and repeated loading, and fatigue must
the ends are to be closed and be considered, a low working
ground. Determine the safe stress of 2820 kg/sq.cm will be
shearing stress and the unit used. Determine the size of wire.
deflection. Assume G equal to 12
million psi and mean radius to be 7. A body weighing 1000 lb falls 6
0.779 in. inches and strikes a 2000 lb per
in. spring. The deformation of the
2. A high alloy spring having squared spring is:
and ground ends has a total of 16
coils and modulus of elasticity in 8. Determine the width and thickness
shear of 85 GPa. Compute the Wahl of the leaves of a six-leaf steel
cantilever spring 13 in. long to
carry a load of 375 lb with a 15. A flywheel has a mean diameter of
deflection of 1¼ in. The maximum 4 ft and is required to handle
stress in this spring is limited 2250 ft-lb of kinetic energy. The
to 50,000 psi. flywheel has a width of 8 in.
Normal operating speed is 300 rpm
FLYWHEELS and the coefficient of fluctuation
is to be 0.05. Find the weight of
9. A flywheel weighing 457 kg has the rim assuming that the arms and
radius of 375 mm. How much energy hub are equivalent to 10% of the
in N-m does the flywheel loss from rim weight.
3.0 rev/sec to 2.8 rev/sec? 16. A shearing machine requires 150
kg-m of energy to shear a steel
10. A flywheel weighing 6 kN has a sheet and has a normal speed of 3
mean diameter of 90 cm. The rev/sec, slowing down to 2.8
maximum speed of the flywheel is rev/sec during the shearing
7 rev/sec slowed down to 4 rev/sec process. The flywheel of the
during the shearing process. machine has a mean diameter of 75
Determine the energy released by cm and weighs 0.0155 kg/cm3. The
the flywheel. width of the rim is 30 cm. If the
hub and arms of the flywheel
account for 15% of its total
11. A flywheel rotates at 220 rpm
weight, find the weight of the
slowed down to 65% of its
flywheel.
revolution during the three -
fourth second punching portion of
the cycle. Compute the angular 17. A punch punches a 1-in diameter
acceleration of the flywheel in hole in a steel plate ¾ inch thick
radian per second squared. every 10 sec. The actual punching
takes 1 sec. The ultimate shear
strength of the plate is 60,000
12. A flywheel has a diameter of 1.5
psi. The flywheel of the punch
m, and mass of 800 kg. What torque
press has a mass moment of inertia
in N-m, is needed to produce an
of 500 in-lb-sec2 and rotates at a
angular acceleration of 100
mean speed of 150 rpm. What is the
revolutions per minute, per
horsepower required for the punch
second?
operation?
13. A cast iron flywheel with a mean
18. What pressure is required for
diameter of 36 inches changes
punching a hole 3 inches in
speed from 300 rpm to 280 rpm
diameter through ¼ inch steel
while it gives up 8000 ft-lb of
stock?
energy. What is the coefficient of
fluctuation?
19. What pressure is required for
punching a 1.5 inch square hole in
14. What would be the weight of a
a ¼ inch thick plate steel?
flywheel in kg if the weight of
the rim is 3 times the sum of the
weight of the hub and arms? Given 20. What pressure is required for
the outside diameter and inside punching a 1.5 inch by 2 inch
diameter to be 24 in and 18 in rectangular hole in a ¼ inch thick
respectively and the rim width is brass?
4.5 in. (assume steel flywheel).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Audio Reality Bruce Rozenblit PDFDocumento124 pagineAudio Reality Bruce Rozenblit PDFmehdi_mohebi2009100% (7)
- Module 3 - Lubrication & Journal Bearings: Isat U Me - Me 413A Machine Design 2 - Lecture Notes OnlyDocumento6 pagineModule 3 - Lubrication & Journal Bearings: Isat U Me - Me 413A Machine Design 2 - Lecture Notes OnlyGeoffrey GolbequeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear PrimeDocumento7 pagineGear PrimeEjNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 05 PDFDocumento7 pagineLab 05 PDFAbdul Rehman AfzalNessuna valutazione finora
- ProgressiveDocumento160 pagineProgressiveLuisgarciaBerlangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power and Industrial Plant Engineering: Lookslam Part 2Documento101 paginePower and Industrial Plant Engineering: Lookslam Part 2Eep JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Me Final Preboard Pipe PRC Format Set A No AnsDocumento9 pagineMe Final Preboard Pipe PRC Format Set A No AnsGerald EspanillaNessuna valutazione finora
- MD in House Set 1 4 1Documento12 pagineMD in House Set 1 4 1Mark Juren AlbaoNessuna valutazione finora
- IJIRAE::Seismic Pounding Between Adjacent Building StructuresDocumento4 pagineIJIRAE::Seismic Pounding Between Adjacent Building StructuresIJIRAE- International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate No RaDocumento5 paginePlate No RaEdelleNessuna valutazione finora
- MDSP August 2019Documento6 pagineMDSP August 2019Mark John DiolosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tamang Upload LangDocumento9 pagineTamang Upload Langrenz magatNessuna valutazione finora
- FLYWHEELDocumento5 pagineFLYWHEELEj0% (1)
- Coaching Machine DesgnDocumento4 pagineCoaching Machine DesgnJerome Isaac KatigbakNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcdes 1Documento7 pagineMcdes 1JerdNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample ProblemsDocumento8 pagineSample ProblemsKenn Earl Bringino VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
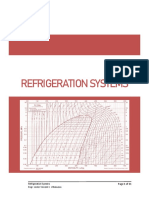
- Refrigeration-Systems Part 1Documento11 pagineRefrigeration-Systems Part 1Sean GuanzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Sentence A Is CorrectDocumento14 pagineSentence A Is CorrectLister NambatacNessuna valutazione finora
- Variable Stresses With Stress ConcentrationsDocumento16 pagineVariable Stresses With Stress ConcentrationsBryan GounzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nit Mtech Course 1.1Documento61 pagineNit Mtech Course 1.1AbhishekVermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Transfer Problem SetDocumento6 pagineHeat Transfer Problem Setkim dianonNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Thermodynamics 01Documento1 pagina10 Thermodynamics 01Jhun BrionesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mikee EncodedDocumento2 pagineMikee EncodedjaysonNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No. 1 in PpeDocumento3 pagineAssignment No. 1 in PpeJenny Mae PomedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe Preboard 1Documento10 paginePipe Preboard 1Chyno Kang100% (1)
- PPE Coaching ProblemsDocumento37 paginePPE Coaching ProblemsYato QtNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Desig3Documento1 paginaMachine Desig3Francis John S. TanarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Strain Stress Sample ProblemsDocumento2 pagineStrain Stress Sample ProblemsPaul CatayongNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat TransferDocumento27 pagineHeat TransferLurking RogueNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No 1b - PPDDocumento1 paginaAssignment No 1b - PPDJerico Llovido0% (1)
- Ppe - Inhouse 2Documento27 paginePpe - Inhouse 2Samuel ArzadonNessuna valutazione finora
- HGFHFGHFGDocumento24 pagineHGFHFGHFGAljhon BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9-Hydroelectric Plant PDFDocumento118 pagineChapter 9-Hydroelectric Plant PDFsindyNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Design/Shop Practice Trivia: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento9 pagineMachine Design/Shop Practice Trivia: Multiple Choice QuestionsPaul EdwardNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe 02: by TRC - Tiger's Review CenterDocumento119 paginePipe 02: by TRC - Tiger's Review Centerkristan7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bsme 3-B: Me 114 - Heat Transfer Bachelor of Science in Mechanical EngineeringDocumento3 pagineBsme 3-B: Me 114 - Heat Transfer Bachelor of Science in Mechanical EngineeringJethro Briza GaneloNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Me155Documento1 paginaFinal Exam Me155Mr GreedyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Problems SPRINGSDocumento15 pagineSample Problems SPRINGSKara KruzNessuna valutazione finora
- MD ProbsetDocumento27 pagineMD ProbsetRicky AlamoNessuna valutazione finora
- Compressors: Isothermal - This Model Assumes That TheDocumento12 pagineCompressors: Isothermal - This Model Assumes That TheRenneil De PabloNessuna valutazione finora
- Melab1 Exp3Documento11 pagineMelab1 Exp3privateziel100% (1)
- Merged Refresher MESL Questions OCRDocumento22 pagineMerged Refresher MESL Questions OCRBernalynMalinaoNessuna valutazione finora
- ThermoDocumento6 pagineThermoE.G Boy GudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Compressor ProblemsDocumento2 pagineGas Compressor Problemskim dianon0% (1)
- Pumps Part 2Documento13 paginePumps Part 2Allen DagsilNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Design, Engineering Materials and Machine Shop Problem Solving Examination No. 4 / Second Semester, A.Y. 2008-2009Documento9 pagineMachine Design, Engineering Materials and Machine Shop Problem Solving Examination No. 4 / Second Semester, A.Y. 2008-2009maria katherine pantojaNessuna valutazione finora
- IPE Practice QuestionsDocumento49 pagineIPE Practice QuestionsLeslie CatindigNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample 03 Rev 1Documento5 pagineSample 03 Rev 1Dhenil ManubatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento8 pagineChapter 1Von A. Damirez0% (1)
- PDF Compre Special Project Ppe Ampipe DLDocumento92 paginePDF Compre Special Project Ppe Ampipe DLClint Baring ArranchadoNessuna valutazione finora
- PipeDocumento8 paginePipeVon A. DamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE 306 - Solved Problems-9Documento1 paginaCHE 306 - Solved Problems-9Garcia Raph100% (1)
- Power and Industrial Plant Engineering: INTRUCTION: Solve The Following Very Important ProblemsDocumento2 paginePower and Industrial Plant Engineering: INTRUCTION: Solve The Following Very Important ProblemsAnonymous zF4syKOrJNessuna valutazione finora
- Anto ME463 Plate No. 3Documento18 pagineAnto ME463 Plate No. 3Eman Lampago AntoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 FansDocumento20 pagine1 FansEasy WriteNessuna valutazione finora
- HW 1 2Q1314 QuestionaireDocumento1 paginaHW 1 2Q1314 QuestionairejenninajubanNessuna valutazione finora
- GearDocumento14 pagineGearAnimesh ManiNessuna valutazione finora
- BrakesDocumento2 pagineBrakesAngielou SialanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems in Keys and CouplingsDocumento4 pagineProblems in Keys and CouplingsDaryl CalderonNessuna valutazione finora
- PUMPS Part 2Documento11 paginePUMPS Part 2Kaiser CarloNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 Activity No. 4Documento1 paginaModule 5 Activity No. 4dracarysNessuna valutazione finora
- BRAKESDocumento4 pagineBRAKESAjayBravo0% (1)
- Pointers For ReviewDocumento3 paginePointers For ReviewAdriel JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Board Problems - StemEZDocumento1 paginaBoard Problems - StemEZRey Danielle Taray NaveaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento2 pagineGujarat Technological Universityaxayzala778Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optical SourcesDocumento33 pagineOptical SourcesAmit VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shunt GeneratorDocumento6 pagineShunt GeneratorudhaiiNessuna valutazione finora
- C. de Koninck - Random Reflections On Science & CalculationDocumento37 pagineC. de Koninck - Random Reflections On Science & CalculationJoseph TrabbicNessuna valutazione finora
- Pat Form 4 2015 Kimia Paper2 Jawapan SebenarDocumento6 paginePat Form 4 2015 Kimia Paper2 Jawapan Sebenardasima83Nessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas Resueltos Del Reichl - TMPDocumento141 pagineProblemas Resueltos Del Reichl - TMPLuis Alberto Aliaga VásquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1: Basic Concepts: Eric G. PatersonDocumento17 pagineChapter 1: Basic Concepts: Eric G. PatersondongaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group1 ThermodynamicsDocumento4 pagineGroup1 ThermodynamicsMICHAEL ANGELO BRUFALNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Energy Field and AuraDocumento2 pagineHuman Energy Field and AuraMirea ClaudiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluent-Intro 14.5 L02 IntroCFDDocumento13 pagineFluent-Intro 14.5 L02 IntroCFDKarl-Andrew Kluge RudisileNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 VrabeyDocumento7 pagine04 VrabeyVictor Solis BrevisNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions Manual For Quantum Chemistry 7Documento10 pagineSolutions Manual For Quantum Chemistry 7Pablo GutembergNessuna valutazione finora
- Mole Fraction Volume FractionDocumento9 pagineMole Fraction Volume FractionameyckulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Techo GeneratorDocumento18 pagineTecho GeneratorBhola KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Breaker Timing - ZensolDocumento20 pagineBreaker Timing - ZensolIsmail Azad100% (1)
- Helical Antenna PDFDocumento20 pagineHelical Antenna PDFOmar F'KassarNessuna valutazione finora
- Examine2D VerificationDocumento13 pagineExamine2D VerificationmarckAntony12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Study and Modeling of Surge and Swab Pressures For Yield-Power-Law Drilling FluidsDocumento118 pagineExperimental Study and Modeling of Surge and Swab Pressures For Yield-Power-Law Drilling FluidsBui Thanh Binh0% (1)
- B. Tech: Uka Tarsadia UniversityDocumento3 pagineB. Tech: Uka Tarsadia UniversityHardikPrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of An Equilibrium Constant For A Complex IonDocumento6 pagineDetermination of An Equilibrium Constant For A Complex IonNur Rau'ah100% (1)
- Gate Question Papers Chemical Engineering 2007Documento17 pagineGate Question Papers Chemical Engineering 2007david_tomy_1Nessuna valutazione finora
- NIMS PosterDocumento1 paginaNIMS Posterアスリアナ イブラヒムNessuna valutazione finora
- PPA6 Lecture CH 16Documento49 paginePPA6 Lecture CH 16suhartojagoNessuna valutazione finora
- FSI Residential Eng Ind - Bifacial Update Approved-NewDocumento83 pagineFSI Residential Eng Ind - Bifacial Update Approved-NewDedy KcpNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Elastomeric Bearing System and AnalysisDocumento11 pagineDesign of Elastomeric Bearing System and Analysisabdelrahman emadNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion - Worksheet 2Documento4 pagineMotion - Worksheet 2Shrijeet SomaniNessuna valutazione finora