Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Science Reviewer
Caricato da
ryle34Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Science Reviewer
Caricato da
ryle34Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Science Reviewer 2.
Neural
5. It is triggered by a signal
3rd Quarter
Nerves stimulates the
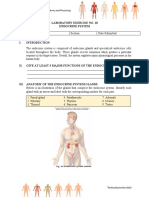
I. Endocrine Systems hormones.
Produces hormones From the nervous system.
It includes the
Nervous System - Adrenal medulla
Produces NEUROTRANSMITTERS - Hypothalamus.
6. Hormonal
Hormones It receives hormones from
Act slower than neurotransmitters another endocrine gland to
1. It creates long – lasting effect release their own hormones.
chemical messengers
secreted (released) from glands into the blood II. Different locations of glands in our body.
and affect cells in another part of the body. A. Glands found in the head and the neck.
Functions: 1. Hypothalamus
Small part of the brain
1. Regulate growth and Hormones
Has a role of controlling the
2. Regulate Metabolism
secretions.
3. Influence Behavior
It also controls the activities of
4. Influence reproductive processes
the nervous system.
5. Maintain Homeostasis
A. Thyrotropin – releasing (TRH)
6. Allow response to Stimuli
Release of THYROID stimulating hormone
7. Balance Water and Minerals
B. Dophamine (DA)
The release of Prolactin
2 Types of Glands
a. Produces milk for women
Exocrine
1. Duct C. Somatostatin(SS)
2. Transport substances to specific b. Inhibits the Release of the growth
locations in the body. hormone and the thyroid.
Endocrine
1. Do not have any Ducts (Canal) D. Growth hormone (GHRH)
2. It releases hormones c. Stimulates the release of the growth
Directly to the bloodstream hormone.
The fluid tissues going to the
brain. E. Gonatotropin (GnRH)
d. The release of follicle releasing
hormone
3 modes of Action: i. Luteinizing Hormone.
1. Humoral F. Corticotropin (CRH)
3. Release hormones e. The release of adrenocorticotropic
Sensing its immediate hormone.
surrounding
- Blood 2. Pituitary Gland
4. It includes Attached to base of the Hypothalamus
Parathyroid Considered as a Neuroendocrine gland.
Pancreatic Glands
1. Receives neuronal input Posterior Pituitary lobe
Divided into two parts 1. Oxytocin
1. Anterior Pituitary Lobe Stimulates uterine contraction
2. Posterior Pituitary Lobe Lactation
2. Vasopressin (ADH)
Increases water permeability in
Anterior Pituitary Lobe the NEPHRONS
- Secretes the following hormones Promoting water reabsorption
It also increase blood volume.
a. Growth Hormone
- Stimulates growth and cell
reproduction. 3. Pineal Gland
b. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
- Stimulates corticosteroid Small endocrine gland in the brain
- Androgen Synthesis Produces melatonin.
- Release from the adrenal cortex 1. It is involved in the circadian rhythm
Daily sleep – wake cycles
c. Beta – Endorphin It induces drowsiness by
lowering the body temperature.
- Inhibits perception of Pain
4.Thyroid Gland
d. Follicle - stimulating hormone (FSH)
i. Stimulates the production of One of the largest endocrine glands found in
Sex Cells. the neck
1. Both male and female. Secretes the following hormones
ii. Stimulates maturation of 1. Tri-iodothyronine (T3)
1. Ovaries follicles in Stimulates oxygen
females Energy consumption
2. Activation of SERTOLI - Increasing a person’s
CELLS basal metabolic rate
a. Males Also promotes protein
e. Luteinizing Hormone synthesis.
i. Stimulates ovulation in Females 2. Thyroxine (T4)
ii. Testosterone synthesis in males Serves as
Reservoir of
- T3
f. Prolactin T4 is converted to T3 through
i. Stimulates the synthesis removal of IODINE.
ii. Stimulates the release of milk in 3. Calcitonin
female’s breast. Stimulates Osteoblasts
g. Melanocyte – stimulating hormone - BONE CONSTRUCTION
(MSH).
5.Parathyroid Glands
i. Stimulates the synthesis and
release of the skin pigment
melanin.
Small endocrine glands
Found at the back of the thyroid gland
4 PARATHYROID GLANDs
1. It secretes the parathyroid hormone 8. Hepcidin
(PTH), Inhibits
Stimulates the release of - Intestinal Iron
CALCIUM IONS FROM THE absorption.
BONE. IV. PANCREAS
It also STIMULATES Both for Exocrine and Endocrine Glands,
OSTEOCLASTS For Endocrine glands
- To breakdown the 8. Insulin
bone. ‘ a. Stimulate intake of
i. Glucose
1. From blood to form
Digestive System glycogen in liver and
I. Stomach muscle cells.
1. Gastrin 9. Glucagon
Stimulates secretion of a. Stimulate
- Hydrochloric Acid i. Gluconeogenesis in liver
2. Ghrelin 1. To release glucose
Stimulates Appetite 2. Increase blood glucose
3. Neuropeptide Y level.
Increases food intake 10. Somatostatin
a. Stimulates both
II. Duodenum i. Insulin
4. Secretin ii. Glucagon
Inhibits V. Kidneys
- Production of 11. Erythropoietin
- Hydrochloric Acid a. Stimulates
Stimulates secretion of i. Erythrocyte Production
- Bicarbonate 12. Calcitriol
A. Liver a. Increases the absorption of
B. Pancreas i. Calcium
C. Brunner’s ii. Phophate
Gland of 1. From the
Duodenum. GASTROINTESTINAL
5. Cholecystokinin TRACT
Stimulates the release of 2. KIDNEYS.
- Digestive enzymes b. Inhibits
- Bile i. Release of
Hunger suppressant 1. Parathyroid hormone.
III. Liver VI. Adrenal Glands
6. Angiotensinogen a. Located right above the kidney
Stimulates release of b. Hormones produced are from
- Aldosterone i. Adrenal Medulla
A. From the ii. Adrenal Cortex
Adrenal Cortex. 13. Adrenal Cortex
7. Thrombopoietin a. Glucocorticoids
Stimulates i. Stimulates
- Megakaryocytes 1. Gluconeogenesis
A. Produce (GLYCOGEN
platelets. BREAKDOWN).
ii. Inhibits Inhibits production of FSH
1. Protein Synthesis - To regulate the
b. Mineralocorticoids production of sperm.
i. Stimulates 2. Ovarian
1. Sodium Progesterone
2. Water - Helps in the
a. Reabsorption in development of the
the kidneys. FETUS
14. Adrenal Medula Estrogen
a. Ephinephrine (ADRENALINE) - Secondary
i. Increases Characteristics of
1. Heart rate Female
2. Force of heart Inhibin
contractions - Inhibits production of
ii. Help body to response from FSH
STRESSFUL ACTIVITIES. - To maintain the
female’s feedback
b. Norephinephrine (NORADRENALINE) mechanism.
i. Causes
1. Squeezing of the blood
vessels
a. To help
maintain
i. Blood
Pressur
e
b. Response to
Stress.
Reproductive System
1. Testis
Androgen
- Increase of
A. Muscle Mass
B. Strength
C. Bone Density
D. Maturation of
Sex organs
E. Deepening of
Voice
F. Growth of
Beard
- It is for Male Secondary
Characteristics.
Estradiol
- Prevents death of germ
cells
Inhibin
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Homework # 2 I. Tutorial On How To Install Mysql: Ryle Ibañez 2itbDocumento28 pagineHomework # 2 I. Tutorial On How To Install Mysql: Ryle Ibañez 2itbryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Homework # 2 I. Tutorial On How To Install Mysql: Ryle Ibañez 2itbDocumento28 pagineHomework # 2 I. Tutorial On How To Install Mysql: Ryle Ibañez 2itbryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- ContempDocumento4 pagineContempryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activity2 2623Documento14 pagineActivity2 2623ryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formative AssessmentDocumento1 paginaFormative Assessmentryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reflection of The WorldDocumento2 pagineReflection of The Worldryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- HW1 SolutionDocumento3 pagineHW1 Solutionryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- NAND-NAND and NOR-NOR Implementations: ObjectivesDocumento6 pagineNAND-NAND and NOR-NOR Implementations: Objectivesryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- IT2622 Ch2 - PrototypingDocumento42 pagineIT2622 Ch2 - Prototypingryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Needfinding & Participant ObservationDocumento34 pagineNeedfinding & Participant Observationempresscpy crackerNessuna valutazione finora
- IT2622 Design Thinking Act1 - VDocumento77 pagineIT2622 Design Thinking Act1 - Vryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prototyping & Storyboarding: IT2622 Chapter 4Documento16 paginePrototyping & Storyboarding: IT2622 Chapter 4empresscpy crackerNessuna valutazione finora
- IT2622 Ch1 Birth of HCIDocumento49 pagineIT2622 Ch1 Birth of HCIempresscpy crackerNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 2 Lecture 8 - Respiratory SystemDocumento24 pagineBiology 2 Lecture 8 - Respiratory Systemryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 101 PDFDocumento31 pagineChemistry 101 PDFryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Academic Writing Worksheet 2Documento5 pagineAcademic Writing Worksheet 2ryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 2 Lecture 7 - Circulatory SystemDocumento51 pagineBiology 2 Lecture 7 - Circulatory Systemryle34100% (1)
- Biology 2 Lecture 6 - Digestive SystemDocumento39 pagineBiology 2 Lecture 6 - Digestive Systemryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- SCAMPER WorksheetDocumento2 pagineSCAMPER Worksheetryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 2 Lecture 9 - Urinary SystemDocumento29 pagineBiology 2 Lecture 9 - Urinary Systemryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- LE2 CMDDocumento1 paginaLE2 CMDryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- AnswersDocumento8 pagineAnswersryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Crossword Annotating, Outlining, SummarizingDocumento2 pagine2 - Crossword Annotating, Outlining, Summarizingryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 20120 00 Safety and Laboratory Rules NamanDocumento45 pagine2019 20120 00 Safety and Laboratory Rules Namanryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine MythologyDocumento1 paginaPhilippine Mythologyryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Respect To Human Sexuality - Notes For SHSDocumento10 pagineRespect To Human Sexuality - Notes For SHSryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine MythologyDocumento8 paginePhilippine Mythologyryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 2 Answer SheetDocumento1 paginaQuiz 2 Answer Sheetryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Handout On Piecewise Functions PDFDocumento2 pagineHandout On Piecewise Functions PDFryle34100% (1)
- Popcorn RecitationDocumento1 paginaPopcorn Recitationryle34Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- ATAR Human Biology 12 Units 3Documento13 pagineATAR Human Biology 12 Units 3FireAwayNessuna valutazione finora
- BP502TPDocumento2 pagineBP502TPraj royel100% (2)
- 1st MBBS Past QuestionsDocumento10 pagine1st MBBS Past Questionsdajisafe829Nessuna valutazione finora
- Body CordinationDocumento13 pagineBody CordinationmaryamsyuhadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Homeostasis: Dr.P.HamambuluDocumento15 pagineHomeostasis: Dr.P.HamambuluDevina SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflection On Simon Sinek VideoDocumento1 paginaReflection On Simon Sinek Videoizzain15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal 101 PDFDocumento28 pagineAnimal 101 PDFJoaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Primal Hormones Made by Aesthetic Primal 1Documento59 paginePrimal Hormones Made by Aesthetic Primal 1enzopark776Nessuna valutazione finora
- Star Seed Activation I PDFDocumento11 pagineStar Seed Activation I PDFGurpreet Kaur50% (4)
- Chapter 9 Cell Communication Part 1Documento40 pagineChapter 9 Cell Communication Part 1MARK BRIAN FLORESNessuna valutazione finora
- Inter 2nd Year ZoologyDocumento7 pagineInter 2nd Year ZoologyRsp Srinivas100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocumento20 pagineEndocrine SystemK8Y KattNessuna valutazione finora
- Course PlanDocumento17 pagineCourse PlanDelphy VargheseNessuna valutazione finora
- Manifest From The HeartDocumento25 pagineManifest From The HeartTuta Velesije Bg100% (2)
- Lab Exercise10 Endocrine SystemDocumento3 pagineLab Exercise10 Endocrine SystemMary Danica MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 10: Quarter 3 - Module 1 (Week 1)Documento8 pagineScience 10: Quarter 3 - Module 1 (Week 1)Kent Joshua Garcia Tangan100% (3)
- Biokimia Kelompok 5 Revisi (Enzim, Hormon Dan Vitamin)Documento50 pagineBiokimia Kelompok 5 Revisi (Enzim, Hormon Dan Vitamin)Uni NadhilaNessuna valutazione finora
- TEST - Parasite EbookDocumento34 pagineTEST - Parasite EbookDrNicole BarssoumNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO220Documento6 pagineBIO220imma haznaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology QuestionsDocumento37 pagineAP Biology QuestionsRaci DesovskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Doctor of Veterinary Medicine: Scheme of Study of Five Years Composit Degree ProgrammeDocumento62 pagineDoctor of Veterinary Medicine: Scheme of Study of Five Years Composit Degree ProgrammeAhmed Hassan SamatarNessuna valutazione finora
- ZOO502-Animal-Physiology-and-Behavior Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Documento13 pagineZOO502-Animal-Physiology-and-Behavior Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Awais BhuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Encyclopedia of Hormones PDFDocumento2.120 pagineEncyclopedia of Hormones PDFWisnu Adryanto0% (2)
- Consumer Chemistry NotesDocumento2 pagineConsumer Chemistry Notestres gian de guzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocumento8 pagineChemical Coordination and IntegrationsuryababaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Successful Aging (Flood)Documento4 pagineTheory of Successful Aging (Flood)Chinnie Nicole RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 15 16 Module Biochem Lec EndocrinologyDocumento19 pagineWeek 15 16 Module Biochem Lec EndocrinologyLy xyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Project Not CompleteDocumento13 pagineBio Project Not Completekaushik17yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocumento41 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)