Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
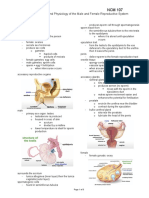
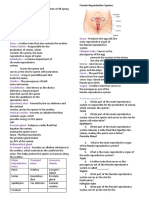
Sexual Reproduction: Male Reproductive System
Caricato da
cyprianDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sexual Reproduction: Male Reproductive System
Caricato da
cyprianCopyright:
Formati disponibili
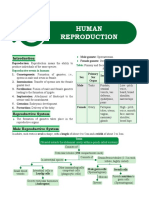
Sexual Reproduction: Male Reproductive System:
Reproduction
Fusion two gametes (egg and sperm)
Male deposit sperm cells into vagina of female
sexual intercourse
Zygote develop 9 months uterus
Plants asexual
- New plant formed existing plant
Plants Sexual
- Pollen grain and ovule form seed
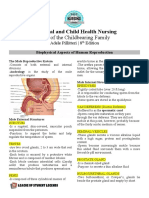
Have copulatory system to transfer sperm
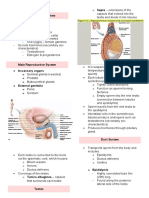
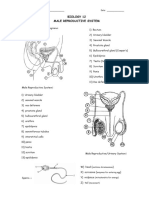
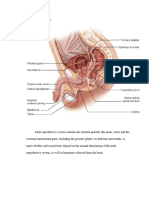
Scrotum
- Thin skinned sac houses testes
- Temperature regulation (36 degrees Celsius to produce fertile sperm)
- Cold: Smooth muscle contract move testes closer to abdomen warmth
- Warm: Testes loose and suspended well away body
- Protect
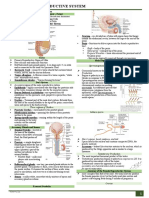
Testes
- Oval structures, suspended outside body
- Situated in a scrotum
- Consists many compartment/lobules, contain highly convoluted tubules:
seminiferous tubules
- Germinal epithelium lines seminiferous tubules
- Group endocrine cells, interstitial cells (cells of leydig) found in tubules
- Produce sperm (germinal layer) and hormone testosterone (interstitial cells)
Ducts: Epididymis
- Seminiferous tubules join to form, highly convoluted
- Immature sperm enter Epididymis where they mature become motile/fertile
- Stored several months
- Sperm viable approximately 3 months, broken down by epithelial cells of
epididymis and reabsorbed body
Sperm duct (vas deferens) Three glands contribute fluids to sperm to form semen: Reproduction
- Muscular sperm duct continuation of epididymis
Two seminal vesicles
- Leaves scrotum pass through prostate gland and
- lie between bladder/rectum
enter urethra
- Join vas deferens to form ejaculatory duct enter urethra
- Push mature sperm forward by strong peristaltic
- Secretion provide sperm nutrients/enzymes
wave from epididymis to urethra = ejaculation
- Provide sugary substance to give ATP to mitochondria in neck of sperm
Urethra
Prostate gland
- Common duct of semen and urine
- Located below bladder
- No worry contamination, muscle sphincter so
- Secrete milky, alkaline fluid (buffer against women’s acidic environment of
urine and sperm cant mix
vagina) that increases mobility of sperm
Penis
Two Cowper’s glands
- Transfer of sperm from male into vagina female
- Located either side urethra below prostate
- Made of tissue and huge sinuses that fill with
- Secretions stimulate mobility of sperm
blood
- during intercourse act as hydrostatic force as
blood push against sinuses to enlarge penis so fit
inside female reproductive system
Main role male reproductive system to produce sperm and
Tip of Penis hormone testosterone
- External skin close over urethra
- Foreskin protection against bacteria (moist-HIV) Sperm combine egg-half genetic material
- Lots of nerve endings (heightened awareness Male gonads (testes) develop abdominal cavity, descend
sex) into external sac (scrotum) just before birth
Define:
Sperm: male gametes
Semen: seminal fluid
Erection: stiffening penis (dilation arteries supplying blood to penis, more blood fill three spongy
erectile tissue chambers so penis stiffens and lengthens)
Ejaculation: the expulsion of semen
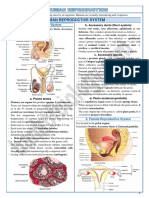
Female Reproduction System:
Uterus
- Muscular sac like structure where foetus Reproduction
develops
- Lower part project into vagina=cervix
(mucous plug prevent bacteria)
- Sphincter muscles keep uterus closed
- Uterus lined with endometrium
- Ovulation endometrium thicken to prepare
blastocyst
Ovaries - If not fertilized upper layer detaches
Layer of germinal epithelium surrounding each Female gonads suspended by
(smooth muscle) and passed out with
ovary ovarian ligaments in abdominal
egg=menstruation
Primary follicles contain immature egg cavity
- Organ in which blastocyst implants,
Primary follicle develop mature follicle Outside made of germinal
develops, grows
After ovulation Graafian follicle form corpus epithelium, divide from ova in
luteum
- Provide oxygen/nutrient and remove
foetal stages
Ovaries release eggs wastes and carbon dioxide from baby
Produce oestrogen, progesterone Vagina
Fallopian Tubes - Elastic folded walls allow to stretch during
lead from each ovary to uterus pregnancy
extensions called frimbia - pH of vagina is acidic healthy/free from
provide pathway between uterus, ovary, egg, infection
sperm, zygote - exposed outside environment so stratified
site of fertilization epithelium good protection
initial cell division of zygote - sperm deposited
enable egg or developing zygote to move - birth canal
towards uterus (action smooth muscles/cilia)
vulva
- two outer and inner folds of skin
- outer folds have external surfaces covered
hair, inner surface moist/smooth
- inner folds delicate and form clitoris
- clitoris small erectile structure similar male
penis, many nerve endings, sexual
sensation
Puberty Note:
- Female 400 000 potential eggs Reproduction
Mitosis: result two cells, each same number (2n) of
- Males no sperm cells produced until boy chromosomes as mother cell, genetic info in both same
reaches puberty
- Puberty occur earlier in girls (11-14) than Meiosis: result four cells, half number (n) of
boys (14-16) chromosomes as mother cell, genetic info different due
to crossing over
- Puberty initiated by three hormones
(protein molecule, secreted in blood,
travel target organ, chemical messenger
control specific processes)
- LH, FSH, HGH
Female
Spermatogenesis
- Ovaries produce oestrogen, trigger
- Haploid spermatozoa produced from germinal epithelium in seminiferous tubules of testes
changes - Testosterone essential making sperm
- Rapid growth height Phases of spermatogenesis
- Hair: underarms, pubic - Multiplying phase
- Breasts - Diploid spermatogonia (2n) of germinal epithelium divide repeatedly mitosis to form new
- Hips widen spermatogonia (2n)
- Fat layer deposited - Growth phase
- Metabolic rate-settle slow - Spermatogonia mature (grow, develop into primary spermatocytes)
- Ovaries develop produce ova - Reduction phase
Males - Primary spermatocytes undergo first meiotic division, each forming two haploid secondary
spermatocytes (n)
- Testes produce testosterone, trigger
- These undergo the second meiotic division= four haploid spermatids
changes
- Sperm production balanced supply/demand
- Rapid, sustained growth height - Spermatogenesis take 72 days from primary spermatocyte to immature sperm
- Hair: underarms, pubic - Immature sperm moved to epididymis where mature, become motile/fertile
- Skin oiler, pimples - Mature sperm cells streamlined, high rate metabolism, propel selves long distance reach egg
- Moustache, beard
- Voice deepen (break-squeaky)
- Shoulders/chest broader
- Fat replaced defined/large muscles
- Penis/testes increase size
- Testes make sperm
Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle
Occurs every 28 days Reproduction
- Production haploid, mature eggs in follicles of
ovaries Series of changes in endometrium
- Number eggs determined before birth Menstrual and development of Graafian follicle/Follicular phase (Day 1-5):
- Multiplying phase Breakdown shedding endometrium of uterine wall
- Before birth germ cells from germinal No progesterone maintain endometrium
Detached tissue and blood out through vagina as menstrual flow
epithelium (surround ovary) sink in and divide
FSH is secreted from pituitary gland, target ovaries, to stimulate follicle to
mitosis to form primary follicles
mature/develop (others dormant), egg mature, follicle start release more oestrogen
- Each follicle has large central oogonium (2n)
Building phase/Ovulatory phase (Day 6-14):
- Growth phase
Wall of ovarian follicle become additional endocrine gland, follicle release oestrogen,
- Puberty FSH released cause follicles periodically target pituitary gland and uterus
grow/develop to form Graafian follicles Inhibit FSH release (stop maturing follicles less mature)
- Oogonium grow into primary oocytes Stimulate repair of endometrium
- Reduction and maturity phase NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
- Primary oocytes (2n) undergo meiosis form egg Oestrogen reach critical high stimulate release LH
(n) LH produced from pituitary gland, target ovary/follicle
- Mature Graafian follicle move periodically to Cause Graafian follicle to rupture (ovulation) releasing ovum
surface ovary, burst, release mature egg, Approximately day 14
surrounding follicle cells Luteal and secretory gland (after day 14):
Still under influence of LH empty follicle fill with yellow cells to form corpus luteum
(start produce progesterone) (endocrine gland)
Progesterone inhibit FSH/LH to stop another ovulation
Corpus luteum produce lots of progesterone in good condition maintain pregnancy
(thicken uterus, enough nutrients supply oxygen and nutrients baby)
Corpus luteum not viable for long, shrink down (get to critical low cannot maintain
endometrium, breakdown, inhibitory effect get weaker-LH/FSH)
Next cycle
Pregnancy
HCG produced in fertilized egg cell target corpus luteum
As cell divides more produce more HCG, implantation produce enough HCG
Corpus luteum stimulate grow larger, progesterone maintain thick endometrium
After 12 weeks corpus luteum shrivel up as placenta produce enough progesterone (can
have withdrawals)
Fertilization Implantation Reproduction
Copulation Zygote transported along fallopian tube cilliary
- Sperm deposited in females action, start dividing mitosis within 12 hours to
Sexual intercourse semen forced out penis powerful contraction form cluster cells= morula within 4-5 days
urethra (ejaculation) Morula change shape form blastula (hollow ball
Enter vagina not exposed air cells)
Force ejaculation force sperm into cervix, swim along walls of
Blastula grow tiny extensions-villi
uterus
Day 7 enter cavity uterus sufficiently developed
Choose one of two fallopian tubes (no chemical attraction,
sink in attach to endometrium
randomness of which sperm fertilises which egg)
Egg surrounded by follicle cells sucked into fallopian tube action Human chorionic gonadothrophin (HCG)
fimbriae stimulate corpus luteum in ovary continue
Spermatozoa get to top uterus in 8 seconds if female have orgasm secretion progesterone maintain endometrium
(muscular contraction cervix) Stimulation continue at least 12 weeks
If sperm reach top uterus in two days rest gain small amounts of Implantation complete by about day 14 after
nourishment before swimming to ovum in fallopian tube (released ovulation (should start next period)
during ovulation) HCG and progesterone inhibit FSH release so
Ovum metabolically inactive dies within 3 days preventing a new menstrual cycle
Sperm dies within 6 days
Millions sperm surround egg
Digestive enzymes release from acrosome break down
glycoprotein layer envelopes ovum
One spermatozoon will penetrate fertilization membrane
immediately depolarize/toughens to prevent sperm from entering
ovum
Only head region of sperm enters egg (leave mitochondria neck
piece and tail outside)
Ovum complete meiosis 2
Contents sperm nucleus fuse egg nucleus form diploid zygote=
contraception
Extra Embryonic Membrane and Placenta: Umbilical cord
Outer layer cells of blastula develop embryonic membranes Form extension chorion, allantois and yolk Reproduction
sac
Allantois and yolk sac develop become incorporated umbilical cord Long flexible chord extending from abdomen
Chorion outer membrane embryo (responsible successful implantation) Two foetal arteries carry wastes and carbon dioxide away foetus to
Produce chorionic villi placental surface
Increase surface area of chorion ensure huge contact endometrium, embryonic One umbilical vein bring nutrients, oxygen and maternal antibodies
membranes from placental surface into foetus
Link where maternal nutrients, oxygen, antibodies exchanged with foetal wastes and
Rich store embryonic stem cells
carbon dioxide during pregnancy
Chorion produce progesterone 12th week (vital)
- Used to form any type of cell
Corpus luteum shrivels up and dies no longer producing progesterone - Can be harvested stored for person
If chorion not produce progesterone=spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) Placenta
Yolk sac Disc shaped organ made of rich supply connective tissue
Initial storage site for blood production as no transport system for few weeks Weighs about 1kg
Maintain integrity embryo site where exchanges mother and foetus take place
Amnion
foetal blood mothers blood DO NOT MIX
Thin very strong membrane surround embryo/foetus
transfer of substances occurs through very thin layers chorion and
Secrete amniotic fluid
Fluid produced recycled continuously during pregnancy so always clean, right balance material capillaries
substances in villi unite into foetal arteries and vein (very close maternal blood
99% water also foetal cells, microorganisms, foetal wastes vessels/sinuses)
Isotonic with tissue fluid of foetus prevent too much absorption water allow for very efficient rapid diffusion of substances from mother to
Constant 37 degrees Celsius foetus and from foetus to mother
Functions: produce progesterone (maintain endometrium)
- Cushion developing foetus any injuries
act as micro-filter prevent pathogenic bacteria in mother enter
- Shock absorber
- Support to foetus (buoyancy) freedom move foetus
- Prevent malformations gravity pressure following pass across placental barrier
- Hold urine - water (osmosis), carbon dioxide, urea (away foetus)
- Prevent dehydration - nutrients (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids essential ions/vit,
- Rupture beginning labour lubricate birth passage (vagina) pregnancy move active transport)
Allantois
- antibodies (mother to foetus)
Store metabolic wastes (nitrogenous waste poisonous)
- cigarette smoke, alcohol, illegal drugs, medicine, viruses (German
Store increase in size fuse chorion (common membrane), move through chorio-
allantoic membrane to mother endometrial tissue-kidney
measles) (some substances damage foetus/cause addiction born)
- HIV/Flu not cross placental barrier
Chorion Antenatal care
Reproduction
Formed sufficiently successful pregnancy Healthy diet
Chorion villi (extensions) - protein
Fuse allantois form placenta - extra calcium iron for bone and teeth
Cells produce HCG - maternal, foetal haemoglobin
- Stimulate corpus luteum Avoid drugs
Villi embed, anchor implantation - Aspirin (reduce ability blood clot cause bleeding/miscarriage)
Greater surface area across which oxygen and nutrients can be Do not smoke or drink alcohol
exchanged - Nicotine slow down oxygen delivery to foetus
Time after fertilization: - Foetal Alcohol Syndrome
- 7 days: embryo in uterus Avoid contact German Measles
- 8-14 days: implantation - Pass through placental barrier (first trimester)
- 6 weeks: embryo (complete fingers, eyelids, ears) - Affect foetal nervous system cause blindness, deafness, cardiac defects (hole in
- 8 weeks: foetus heart)
- 6 months: eyebrows and lashes Exercise lightly
- 280 days: birth - Stimulate circulatory system mother
Ectopic pregnancy:
Embryo implants fallopian tubes
Not form placenta or accommodate growth
Abort
Foetus foreign tissue mother
Carry antigens that are foreign
Mother produce antibodies against any proteins cross placenta baby to mother
Birth (parturition): Multiple births:
Reproduction
Expulsion of foetus, surrounding membranes, placenta from uterus Fraternal (non identical)
End gestation period levels progesterone drop coincide rise oestrogen - Two or more eggs released same time during ovulation
- Two eggs fertilized and implanted uterus
levels cause uterus muscles contract
Identical
False labour-Braxton-Hicks contractions
- Inner cell mass of blastcyst divides mitosis form to identical separate
Dilation of cervix (12 hours)
embryos develop into identical twins
Progesterone levels reach critical low threshold and oestrogen reach a
high threshold Post natal care:
Oxytocin released pituitary gland mother-start labour Oxytocin continue to be released
- Sustained rhythmic contractions uterus wall - Uterus contract down normal size
- Oxytocin respond positive feedback-increase amounts - Stimulate release prolactin
Baby descends head first into pelvic girdle (head engaged) Combined effect hormones and sucking of baby on nipple cause mammary
Mucous plug cervix comes away (show) gland produce milk
Strong regular contractions of uterus get closer together - Breast milk contain nutrients ideal proportions
Cervix dilates - Valuable antibodies
- Correct temperature
Amniotic fluid trapped by babies head, increase pressure cause amnion
- Cannot cause allergies in baby
to break release amniotic fluid “breaking of waters”
- Deep bond mother child
Delivery of baby (1 hour) - Cheap easy
Very strong contractions uterus forces baby through birth canal Mothers poor communities go back to work almost immediately
Head of baby emerges first (crowning) - Bottle feeding start early
Short rest-right then left shoulders delivered - Water contaminated germs
Rest baby emerges - Cheap milk powder lack essential nutrients needed by baby
Umbilical cord clamped two places prevent bleeding, then cut between - Over dilute and still too expensive
- No immunological protection
clamps
New born babies not able look after themselves
- Painless no nerves placenta
Need a lot of attention
Separation mother baby inflates lungs take first breath
- Keep warm cannot regulate own body temp
Afterbirth - Stop breast feeding lose protection mothers antibodies, need to be
Contractions uterine wall continue until placenta detached uterine wall protected against disease
Placenta rest umbilical cord pass out vagina (afterbirth) - Immunization projects clinics worst illness (some compulsory before
Note: Episiotomy incision vagina towards uterus to ease expulsion baby school)
and avoid uneven tearing
Birth control
Reproduction
Most people cannot afford large families
Natural
- Withdraw penis before ejaculation
- Intercourse not occur between day 8 and
18 menstrual cycle
Mechanical
- Male condom (place over erect penis
before intercourse)
- Female condom (inserted into vagina
before intercourse)
- Diaphragm (inserted over cervix by
doctor)
- IUD Intrauterine Device (inserted into
uterus medical person)
Chemical
- Pill one per day, taken orally
- Injection (administered medical person
last 90 days)
Surgical
- Ligation (Female: fallopian tubes cut and
tied)
- Vasectomy (Male: sperm ducts cut and
tied)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reproduction NotesDocumento2 pagineReproduction NotesNerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive System TransesDocumento5 pagineReproductive System Transesadrielvamos28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes Introduction To Reproductive SystemDocumento8 pagineLecture Notes Introduction To Reproductive SystemKirstie Goc-ongNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Internal Male Reproductive OrgansDocumento2 pagineA. Internal Male Reproductive OrgansMacchi MagsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 NCM 107: Review of The Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Prof. Dymphna CasquejoDocumento3 pagineLesson 2 NCM 107: Review of The Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Prof. Dymphna CasquejoLynnelljhyen MALUBAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocumento6 pagineMaternal and Child Health NursingRoanne DivinagraciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ana ReproDocumento4 pagineAna ReproFIONA DANE MAURERANessuna valutazione finora
- Human Male and Female Reproductive System (Reviewer)Documento8 pagineHuman Male and Female Reproductive System (Reviewer)Justine Yuan DoradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive Systems ReviewerDocumento4 pagineReproductive Systems ReviewerAustin LaurenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pnle Obstetric NursingDocumento15 paginePnle Obstetric Nursingcanetem1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- A. Internal Male Reproductive OrgansDocumento2 pagineA. Internal Male Reproductive OrgansDel Enriquez RiboNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes in ScienceDocumento4 pagineNotes in ScienceKate NicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Male Gametes: OvariesDocumento5 pagineMale Gametes: OvariesJasper OrilNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 Reproductive SystemDocumento6 pagine19 Reproductive SystemEugene HerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ca ObDocumento23 pagineCa ObDonald SebidanNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocumento6 pagineScience 3rd Quarter ReviewerAmbika PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Science ReviewerDocumento7 pagineScience ReviewerGilvert PanganibanNessuna valutazione finora
- Human ReproductionDocumento5 pagineHuman ReproductionHimanshu Harsh 12th ANessuna valutazione finora
- (Week 17) Reproductive SystemDocumento3 pagine(Week 17) Reproductive SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- G10 3RD Quarter ScienceDocumento15 pagineG10 3RD Quarter ScienceRaven MayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive SystemDocumento5 pagineReproductive SystemkhakimagdalenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive SystemDocumento7 pagineReproductive SystemshaniaericaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Human Reproduction-Sample Notes 2021Documento2 pagine3 Human Reproduction-Sample Notes 2021shahd elmaghraby (user206)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive SystemDocumento7 pagineReproductive SystemAngelica JovenNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento9 pagineSimple Anatomy and PhysiologyPatrick ValerioNessuna valutazione finora
- Female and Male Reproductive OrgansDocumento2 pagineFemale and Male Reproductive OrgansPink EaintNessuna valutazione finora
- Human ReproductionDocumento19 pagineHuman ReproductionSantosh JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCE Lecture b516Documento2 pagineSCIENCE Lecture b516Justine Mae FeranilNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproducrive SystemDocumento15 pagineReproducrive SystemEfren GuinumtadNessuna valutazione finora
- MATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsDocumento10 pagineMATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsJill Margarett BongatoNessuna valutazione finora
- TH THDocumento12 pagineTH THchn pastranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive SystemDocumento5 pagineReproductive Systemmuli.michaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer Unit 5 by Adelle PilliteriDocumento3 pagineReviewer Unit 5 by Adelle PilliteriMaria Luisa VillalunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ob Notes Normal 1Documento41 pagineOb Notes Normal 1pinpindalgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 12 Worksheet Male Reproductive SystemDocumento4 pagineBiology 12 Worksheet Male Reproductive SystemMJ VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDocumento12 pagineScience 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDyaan TrajicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Human ReproductionDocumento9 pagineHuman Reproductionarnavkataria22Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCN COMPILED 2ndyrnsgDocumento43 pagineMCN COMPILED 2ndyrnsgquincy fajardoNessuna valutazione finora
- S10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREDocumento35 pagineS10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREREGLOS, Marie Nhelle K.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cmca 1Documento5 pagineCmca 1Erika Mae Sta. MariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 17: ReproductionDocumento29 pagineTopic 17: ReproductionEva SidhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 3q ScienceDocumento5 pagine3q Sciencemariefranchescadevelos.imcNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive SystemDocumento8 pagineReproductive SystemaynNessuna valutazione finora
- Ob Notes NormalDocumento41 pagineOb Notes NormalLyra Penelope OliquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Reproductive SystemDocumento87 pagine08 Reproductive SystemcelynjasminegNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento2 pagineChapter 2青Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocumento16 pagineLesson 4 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionAngel AsisNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary QuestionDocumento4 pagineSummary QuestionwagkangtangaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st TERM BIOLOGY NotesDocumento24 pagine1st TERM BIOLOGY NotesPenta GonNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewers 3rd Qrtr.Documento33 pagineReviewers 3rd Qrtr.Kim Jay Ann HalongongNessuna valutazione finora
- MCA (107) T - Module 1, 2, 3Documento27 pagineMCA (107) T - Module 1, 2, 3Gulayan, Renz Bryelle T.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive System ReproductionDocumento9 pagineReproductive System ReproductionDaBestMusicNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 10 Reviewer 3RDDocumento12 pagineScience 10 Reviewer 3RDaltheaburgas9Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Monthly Test ReviewerDocumento5 pagine3rd Monthly Test ReviewerLaxen JunioNessuna valutazione finora
- G.R. Pitts, J.R. Schiller, and James F. Thompson, PH.DDocumento91 pagineG.R. Pitts, J.R. Schiller, and James F. Thompson, PH.DrerenNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburDocumento24 pagineReproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburOKTAVIANI HAPSARINessuna valutazione finora
- MC I Modular Reviewer Reproductive SystemDocumento20 pagineMC I Modular Reviewer Reproductive SystemSteiner LimNessuna valutazione finora
- SXSXDocumento27 pagineSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Reproductive SystemDocumento26 pagineHuman Reproductive SystemAlmario DacalcapNessuna valutazione finora
- Good Neighbour 2Documento1 paginaGood Neighbour 2cyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio NotesDocumento1 paginaBio NotescyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Xie XieDocumento1 paginaXie XiecyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- AaronDocumento1 paginaAaroncyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes QuestionsDocumento1 paginaDiabetes QuestionscyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- XEIDocumento1 paginaXEIcyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Heartstructurenotes PDFDocumento3 pagineHeartstructurenotes PDFcyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Good NeighbourDocumento1 paginaGood NeighbourcyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Good Neighbour 1 PDFDocumento1 paginaGood Neighbour 1 PDFcyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- EDEXCEL Chemistry IGCSE Student BookDocumento243 pagineEDEXCEL Chemistry IGCSE Student BookFilipa Rosa77% (48)
- BiologyWorkbook AnswersDocumento30 pagineBiologyWorkbook AnswersStudent Research50% (2)
- IGCSE Biology Notes PDFDocumento46 pagineIGCSE Biology Notes PDFmayaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Good Neighbour 1Documento1 paginaGood Neighbour 1cyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- ANAT - Unit 3 - Heart Anatomy and Function - NotesDocumento15 pagineANAT - Unit 3 - Heart Anatomy and Function - NotescyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Reservoiur For NotesDocumento1 paginaReservoiur For NotescyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 8 PDFDocumento2 pagineBiology 8 PDFcyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Trinidad 6Documento11 pagineBiology Trinidad 6cyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 1Documento4 pagineChemistry 1cyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography 2011 Paper 3 Red Sec PDFDocumento27 pagineGeography 2011 Paper 3 Red Sec PDFcyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- 0610 s07 Ms 2Documento7 pagine0610 s07 Ms 2Hubbak KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 6Documento1 paginaBiology 6cyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Biology Notes PDFDocumento46 pagineIGCSE Biology Notes PDFmayaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Reservoiur For Notes PDFDocumento1 paginaReservoiur For Notes PDFcyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Biology Notes PDFDocumento46 pagineIGCSE Biology Notes PDFmayaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Agriculture 2004Documento4 pagineAgriculture 2004cyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Agriculture 2004Documento4 pagineAgriculture 2004cyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 1Documento3 paginePhysics 1cyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics SyllabusDocumento6 paginePhysics SyllabuscyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography 2011 Paper 3 Red SecDocumento27 pagineGeography 2011 Paper 3 Red SeccyprianNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in Science 5Documento2 pagineLesson Plan in Science 5Dhalia ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Penis PDFDocumento9 pagineThe Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Penis PDFredderdatNessuna valutazione finora
- Gametogenesis Process in HumanDocumento13 pagineGametogenesis Process in HumanRiski UntariNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle IdentificationDocumento7 pagineMuscle Identificationhakdog hakdogNessuna valutazione finora
- MCHN OutlineDocumento15 pagineMCHN OutlineAngel Strauss KmpsnNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Forms of Infertility in MaleDocumento36 pagineDifferent Forms of Infertility in MaleSheikh QasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro - Male Reproductive System PDFDocumento4 pagineMicro - Male Reproductive System PDFKaren ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- Male Genitalia ExaminationDocumento6 pagineMale Genitalia ExaminationParthik PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Menstrual CycleDocumento46 pagineMenstrual CycleManilyn PenafloridaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Body Project Sperm Cell - Carabelle Abbas 1Documento6 pagineThe Human Body Project Sperm Cell - Carabelle Abbas 1api-359673554Nessuna valutazione finora
- InfertiityDocumento36 pagineInfertiityKavya S Mohan100% (1)
- Associate Level Material: Sexual Response CyclesDocumento4 pagineAssociate Level Material: Sexual Response CyclesdoinhairNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 5 - 2ND QuarterDocumento4 pagineScience 5 - 2ND QuarterRica VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual CycleDocumento26 pagineScience: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual CycleViktor InocNessuna valutazione finora
- ICD 10 GinekologiDocumento15 pagineICD 10 GinekologiMario Aphin NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 12 - The Reproductive System!: Name: Block: DateDocumento4 pagineBiology 12 - The Reproductive System!: Name: Block: DateLerr Real Relle100% (1)
- Checklist (PapSmear)Documento5 pagineChecklist (PapSmear)Sinung BawonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex at The Anatomical LevelDocumento46 pagineSex at The Anatomical LevelkavehNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelvic Examination: W - Newton LongDocumento3 paginePelvic Examination: W - Newton LongyuexinchongNessuna valutazione finora
- 7B Reproduction Test 2004Documento2 pagine7B Reproduction Test 2004api-3698146100% (3)
- Menstrual Cycle Physiology: - Dr. Atef AboodDocumento33 pagineMenstrual Cycle Physiology: - Dr. Atef AboodatefmaboodNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat ReproductionDocumento22 pagineCat ReproductionKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Jlgarcia,+gerente+da+revista,+27 39384Documento12 pagineJlgarcia,+gerente+da+revista,+27 39384gilson_pessoaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Powers of LaborDocumento12 pagineThe Powers of LaborElinor Faith V. Retita-CoronadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 ReproductionDocumento12 pagineChapter 4 ReproductionPraveena MoganNessuna valutazione finora
- Male Reproductive SystemDocumento16 pagineMale Reproductive SystemJeric FranzNessuna valutazione finora
- Labia Minora Reconstruction Using Clitoral Hood Flaps, Wedge Excisions, and YV Advancement FlapsDocumento8 pagineLabia Minora Reconstruction Using Clitoral Hood Flaps, Wedge Excisions, and YV Advancement FlapsHazel Vivian Soliz AlconzNessuna valutazione finora
- Science QUARTER 2 SummativeDocumento5 pagineScience QUARTER 2 SummativeMjel Kezhia BarrietaNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Biology - RheaDocumento8 pagineDetailed Lesson Plan in Biology - RheaJohn Paul Pasa88% (8)
- Seminal Fluid AnalysisDocumento11 pagineSeminal Fluid AnalysisKenneth Jake BatiduanNessuna valutazione finora