Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
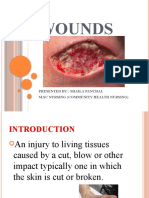
RLE 110 Causes and Types of Wounds
Caricato da
Choi Gong JuCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
RLE 110 Causes and Types of Wounds
Caricato da
Choi Gong JuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Causes and Types of Wounds
Depending on the healing time of a wound, it can be classified as acute or chronic. Those classified
as acute wounds heal uneventfully (with no complications) in the predicted amount of time. Those
classified as chronic wounds take a longer time to heal and might have some complications.
Wounds can be open or closed. Open wounds are wounds with exposed underlying tissue and/or
organs that are open to the outside environment (like penetrating wounds). Closed wounds have
damage that occurs without exposing the underlying tissue and organs (non-penetrating wounds).
Another way to classify wounds is to determine if the wound is clean or contaminated. Clean
wounds have no foreign materials or debris inside, whereas contaminated wounds or infected
wounds might have dirt, fragments of the causative agent, bacteria or other foreign materials.
Wound origin can be either internal or external. Internal wounds result from impaired immune and
nervous system functions and/or decreased supply of blood, oxygen or nutrients to that area; such
as in cases of chronic medical illness (diabetes, atherosclerosis, deep vein thrombosis). External
wounds are usually caused by penetrating objects or non-penetrating trauma, and other
miscellaneous causes as follows:
Non-penetrating wounds: These are usually the result of blunt trauma or friction with other
surfaces; the wound does not break through the skin, and may include:
Abrasions (scraping of the outer skin layer)
Lacerations (a tear-like wound)
Contusions (swollen bruises due to accumulation of blood and dead cells under skin)
Concussions (damage to the underlying organs and tissue on head with no significant external
wound)
Penetrating wounds: These result from trauma that breaks through the full thickness of skin;
reaching down to the underlying tissue and organs, and includes:
Stab wounds (trauma from sharp objects, such as knives)
Skin cuts
Surgical wounds (intentional cuts in the skin to perform surgical procedures)
Gunshot wounds (wounds resulting from firearms)
Miscellaneous wounds may include:
Thermal wounds: Extreme temperatures, either hot or cold, can result in thermal injuries (like
burns, sunburns and frostbite)
Chemical wounds: These result from contact with or inhalation of chemical materials that
cause skin or lung damage
Bites and Stings: Bites can be from humans, dogs, bats, rodents, snakes, scorpions, spiders
and tick
Electrical wounds: These usually present with superficial burn-like or sting-like wounds
secondary to the passage of high-voltage electrical currents through the body, and may include
more severe internal damage.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Different Types of WoundsDocumento1 paginaDifferent Types of WoundsJohn Levi P. CalinawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Types & Causes of Open WoundsDocumento3 pagineTypes & Causes of Open WoundsmArLoNNessuna valutazione finora
- Wound Types, Classification and Healing ProcessDocumento23 pagineWound Types, Classification and Healing ProcessKCN Anitha MNessuna valutazione finora
- Wound AssessmentDocumento14 pagineWound AssessmentMah ShawdNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Types of Wounds: Dr. Jaimenito C. GoDocumento33 pagineDifferent Types of Wounds: Dr. Jaimenito C. GoLea UnderscoreNessuna valutazione finora
- First Aid - Wound CareDocumento18 pagineFirst Aid - Wound CareKristine BillonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasmid Curing Response of Staphylococcus Aureus From Wound and High Vaginal SwabDocumento94 paginePlasmid Curing Response of Staphylococcus Aureus From Wound and High Vaginal SwabElufisan TemidayoNessuna valutazione finora
- WOUNDSDocumento45 pagineWOUNDSshaila100% (1)
- Wound CareDocumento16 pagineWound CareJohn FredNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Skills - First Aid To The InjuredDocumento20 pagineClinical Skills - First Aid To The InjuredAb RahNessuna valutazione finora
- First Aid: First Aid Is The Provision of Initial Care For AnDocumento3 pagineFirst Aid: First Aid Is The Provision of Initial Care For AnSharry StylesNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Wound: Knife RazorDocumento1 paginaTypes of Wound: Knife RazorKryztalGhail LlanoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Wound Management (11111)Documento40 pagineWound Management (11111)Shireen QaiserNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 3 - NCM112Documento1 paginaActivity 3 - NCM112JAY LORENZ CARIDONessuna valutazione finora
- Open WoundDocumento2 pagineOpen WoundReshiel RubioNessuna valutazione finora
- BMLS Pathology of Injuries & Type of Injuries OverviewDocumento40 pagineBMLS Pathology of Injuries & Type of Injuries Overviewwillisonjohn155Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fracture: Signs and SymptomsDocumento6 pagineFracture: Signs and SymptomsKaran MauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bullet Exsanguination Strangulation Myocardial InfarctionDocumento5 pagineBullet Exsanguination Strangulation Myocardial InfarctionGenevieve TersolNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5Documento3 pagineLecture 5Shakil MahmodNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Jurisprudence - Iat IiDocumento2 pagineMedical Jurisprudence - Iat IiAadhithya KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgery, General, Wounds and Wound HealingDocumento15 pagineSurgery, General, Wounds and Wound HealingRhazes78100% (1)
- Or/Dr/Nicu/Pacu Requirements: Open Wound TypesDocumento6 pagineOr/Dr/Nicu/Pacu Requirements: Open Wound TypesAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Answer of Surgery Mbbs Supplementary 1st Paper CDocumento296 pagineQuestion Answer of Surgery Mbbs Supplementary 1st Paper CShivam AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- D9 TraumatologyDocumento6 pagineD9 TraumatologyJoey Loh Hui WenNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety (Wounds)Documento32 pagineSafety (Wounds)kay_genius252Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Wounds and Wound CareDocumento25 pagine4 Wounds and Wound Caredoc-fahad aftabNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 TraumaDocumento10 pagine15 TraumaHarsh BarikNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 - Physiological Reaction To InjuryDocumento90 pagineUnit 2 - Physiological Reaction To InjuryFabian Chapima100% (1)
- Forensic TraumatologyDocumento113 pagineForensic TraumatologyYasir Latif Chauhdhary100% (1)
- Mapeh 9 (Health) On WoundsDocumento19 pagineMapeh 9 (Health) On WoundsVj TolentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Wounds: Prof - Işıl Pakiş Acıbadem University, School of Medicine, Forensic Medicine DepartmentDocumento56 pagineWounds: Prof - Işıl Pakiş Acıbadem University, School of Medicine, Forensic Medicine DepartmentKerem SAYARNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical and Emergency ResponseDocumento37 pagineMedical and Emergency ResponseMAGARRO ANLOUISE JAY M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Polytrauma Lesson PlanDocumento32 paginePolytrauma Lesson PlanSwapnil MahapureNessuna valutazione finora
- CDI 22 Midterm Chapter 5 Injuries and WoundsDocumento23 pagineCDI 22 Midterm Chapter 5 Injuries and WoundsFrank Davin BiraoNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicolegal Aspects of Hurt, Injury and Wound: Review ArticleDocumento5 pagineMedicolegal Aspects of Hurt, Injury and Wound: Review ArticleAbdul Samad Shaikh0% (1)
- Lecture 2Documento19 pagineLecture 2Dr. Rabail MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Introduction To WOUNDDocumento22 pagine2 Introduction To WOUNDkat garciaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Wound Is A Break in The Continuity of A Tissue of The BodyDocumento6 pagineA Wound Is A Break in The Continuity of A Tissue of The BodyChristine Katherine LibuitNessuna valutazione finora
- Vetero-Legal WoundsDocumento26 pagineVetero-Legal WoundsAhmadx Hassan100% (4)
- Wound and InjuryDocumento3 pagineWound and InjurySahil sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Forensic PathologyDocumento3 pagineForensic PathologyjmosserNessuna valutazione finora
- Injury Skin Trauma Contusion Pathology DermisDocumento2 pagineInjury Skin Trauma Contusion Pathology DermisMelvin Lopez SilvestreNessuna valutazione finora
- Stab Wound Heat Stroke Bone Fracture: First AidDocumento1 paginaStab Wound Heat Stroke Bone Fracture: First AidRenz Laurenciana HonradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Clostridium-Tetani Handout Group4Documento6 pagineClostridium-Tetani Handout Group4Raiden EiNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicolegal Aspects of Hurt Injury and WoundDocumento6 pagineMedicolegal Aspects of Hurt Injury and WoundSebin JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Blast Injuries 1Documento63 pagineBlast Injuries 1Doc On CallNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Surgery: by Kostychenko Anastasia, Zhurbenko Julia, Kolomiets Daniil 1fniiiDocumento35 pagineDepartment of Surgery: by Kostychenko Anastasia, Zhurbenko Julia, Kolomiets Daniil 1fniiiНастя КостюченкоNessuna valutazione finora
- WOUNDSDocumento30 pagineWOUNDSSachin KpNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Wounds, Soft Tissue Injuries: ClassificationDocumento64 pagineTypes of Wounds, Soft Tissue Injuries: ClassificationAli ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin Integrity and Wound CareDocumento28 pagineSkin Integrity and Wound Caregrazelantonette.calubNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus NoteDocumento4 pagineTetanus NoteTaufik KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- MedicoDocumento3 pagineMedicoATOLBA, Rizel D.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sports MedicineDocumento2 pagineSports MedicineShelby HooklynNessuna valutazione finora
- (Notes) MEDICOLEGAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL INJURIESDocumento20 pagine(Notes) MEDICOLEGAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL INJURIESChristian Edward CoronadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Forensic Classification of WoundsDocumento5 pagineForensic Classification of WoundsSoze KeyserNessuna valutazione finora
- Types WoundsDocumento21 pagineTypes WoundsPaulo Justin Tabangcora OropillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blast Injuries - From Triage To Critical Care 2003Documento16 pagineBlast Injuries - From Triage To Critical Care 2003Cris TobalNessuna valutazione finora
- HANDOUT Third Level Block 6 (Final)Documento119 pagineHANDOUT Third Level Block 6 (Final)abobaker solimanNessuna valutazione finora
- How to Survive a Nuclear Attack - PRACTICAL GUIDE (translated)Da EverandHow to Survive a Nuclear Attack - PRACTICAL GUIDE (translated)Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple Guide To Pressure Injuries, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandA Simple Guide To Pressure Injuries, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- New Treatments, Tests For Alzheimer'S in PipelineDocumento3 pagineNew Treatments, Tests For Alzheimer'S in PipelineChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Mni CP Wound-PechonDocumento26 pagineMni CP Wound-PechonChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- CopdDocumento11 pagineCopdChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Fidel V RamosDocumento6 pagineFidel V RamosChoi Gong Ju100% (1)
- Basic Principles of Delivery AsepsisDocumento20 pagineBasic Principles of Delivery AsepsisChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- New Treatments, Tests For Alzheimer'S in PipelineDocumento3 pagineNew Treatments, Tests For Alzheimer'S in PipelineChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- De Bride MentDocumento5 pagineDe Bride MentChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Citrate IntoxicationDocumento9 pagineCitrate IntoxicationChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- De Bride MentDocumento5 pagineDe Bride MentChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Genitourinary SurgeryDocumento2 pagineGenitourinary SurgeryChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Related To Adrenal Function: (Chapter 34)Documento8 pagineDrugs Related To Adrenal Function: (Chapter 34)Choi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Citrate IntoxicationDocumento9 pagineCitrate IntoxicationChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- A Reflection Paper On SuperbugsDocumento1 paginaA Reflection Paper On SuperbugsChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma Reporting PechonDocumento34 paginePharma Reporting PechonChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cervical CancerDocumento16 pagineCervical CancerChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Counter ReformationDocumento13 pagineCounter ReformationChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Facts and Definition of EclampsiaDocumento5 pagineFacts and Definition of EclampsiaChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Bronchial AsthmaDocumento14 pagineBronchial AsthmaChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Process SOAPIEDocumento33 pagineNursing Process SOAPIEChoi Gong Ju100% (4)
- Abruptio Placenta: By: Princess Grace A. Pechon, SNDocumento12 pagineAbruptio Placenta: By: Princess Grace A. Pechon, SNChoi Gong JuNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Animal Management Text SetDocumento8 pagineSmall Animal Management Text Setapi-281848945Nessuna valutazione finora
- End of The Line - wks01Documento4 pagineEnd of The Line - wks01mtp84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Heart: Padangusthasana (Big Toe Pose)Documento3 pagineHeart: Padangusthasana (Big Toe Pose)passion26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Intrusion With Mini ImplantDocumento13 pagineIntrusion With Mini Implantdrzana78100% (1)
- Rekam Anusha Et Al.Documento3 pagineRekam Anusha Et Al.International Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cartoon Fundamentals: How To Draw A Cartoon Body - Envato Tuts+ Design & Illustration ArticleDocumento21 pagineCartoon Fundamentals: How To Draw A Cartoon Body - Envato Tuts+ Design & Illustration ArticleAnonymous e49Vjy0100% (4)
- Single Document For InfrographicDocumento5 pagineSingle Document For Infrographicapi-457039397Nessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Horse QuestionsDocumento2 pagineIndian Horse Questionslee0% (1)
- Q2 DLL SCIENCE COMPLETE QUARTER 2 Inkay PeraltaDocumento24 pagineQ2 DLL SCIENCE COMPLETE QUARTER 2 Inkay PeraltaGlen GorgonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Reproductive Sexual Behavior in AnimalsDocumento8 pagineNon-Reproductive Sexual Behavior in AnimalsLeokadia ŻukowskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inguinal HerniaDocumento19 pagineInguinal HerniaArdham ChesukoruNessuna valutazione finora
- How Do We ReadDocumento3 pagineHow Do We ReadArgatha Alwinsyah50% (2)
- Modern Bio II - Nutrition Plant and AnimalsDocumento77 pagineModern Bio II - Nutrition Plant and AnimalsLavander BlushNessuna valutazione finora
- Vanoxerine: Cellular Mechanism of A New AntiarrhythmicDocumento10 pagineVanoxerine: Cellular Mechanism of A New Antiarrhythmicapi-26169290Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mr. Skeleton PDFDocumento6 pagineMr. Skeleton PDFniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles-Pelvic Limb 6-Craniolateral CrusDocumento2 pagineMuscles-Pelvic Limb 6-Craniolateral CrusR1pTid3Nessuna valutazione finora
- ALS1 - Listening Quiz 2 - Virtual 202209 Avanzado 7 21 - 15-22 - 45Documento3 pagineALS1 - Listening Quiz 2 - Virtual 202209 Avanzado 7 21 - 15-22 - 45Omar Sanchez0% (2)
- Biology B PDFDocumento9 pagineBiology B PDFJoTanlogonOcate-AmbongNessuna valutazione finora
- Monro-Kellie 2.0: The Dynamic Vascular and Venous Pathophysiological Components of Intracranial PressureDocumento12 pagineMonro-Kellie 2.0: The Dynamic Vascular and Venous Pathophysiological Components of Intracranial PressureDevi Hariyanti PramitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank Endocrine PDFDocumento29 pagineTest Bank Endocrine PDFWenzy Cruz100% (3)
- Forest and Wildlife ResourcesDocumento15 pagineForest and Wildlife ResourcesNazia NaushinNessuna valutazione finora
- AnalogyDocumento94 pagineAnalogyRizwan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- All About GIT PhysiologyDocumento79 pagineAll About GIT PhysiologySherwan R Shal91% (23)
- Study of The Ratio of Cross-Matching To Transfusio PDFDocumento7 pagineStudy of The Ratio of Cross-Matching To Transfusio PDFampratikna 14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acne Vulgaris: Abdul Alraiyes 5/7/08Documento22 pagineAcne Vulgaris: Abdul Alraiyes 5/7/08Abdul Hamid AlraiyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Brioche Cat Hat by Natasha SillsDocumento4 pagineBrioche Cat Hat by Natasha SillsMythili SHIVKUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Value Addition and Processing of Poultry ProductsDocumento25 pagineValue Addition and Processing of Poultry ProductsGourav Wagh0% (1)
- Panna Gecko, Issue 3 2012Documento50 paginePanna Gecko, Issue 3 2012pannageckoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Silkewormes and Their Flies by Thomas Moffat ("T.M.") @1599Documento107 pagineThe Silkewormes and Their Flies by Thomas Moffat ("T.M.") @1599TerryandAlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Molestation of Men by WomenDocumento15 pagineSexual Molestation of Men by WomenEstefanía Vela Barba100% (2)