Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
NCP Impaired Cerebral Tissue Perfussion
Caricato da
Yvonne Ronamae100%(2)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (2 voti)
243 visualizzazioni4 pagineThe document outlines goals and interventions for a patient with altered consciousness and decreased GCS score. The short term objectives were for the patient to maintain consciousness, reorient to time/place/person, and have normal tissue perfusion. Interventions included monitoring vitals, labs, and mental status. The long term goals were for the patient to display tolerance to activity, have normal sensations/movement, and improve consciousness. Success would be seen through maintained consciousness, reorientation, and warmth/dryness; failure from decreased consciousness or need for full assistance.
Descrizione originale:
Sample NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe document outlines goals and interventions for a patient with altered consciousness and decreased GCS score. The short term objectives were for the patient to maintain consciousness, reorient to time/place/person, and have normal tissue perfusion. Interventions included monitoring vitals, labs, and mental status. The long term goals were for the patient to display tolerance to activity, have normal sensations/movement, and improve consciousness. Success would be seen through maintained consciousness, reorientation, and warmth/dryness; failure from decreased consciousness or need for full assistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(2)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (2 voti)
243 visualizzazioni4 pagineNCP Impaired Cerebral Tissue Perfussion
Caricato da
Yvonne RonamaeThe document outlines goals and interventions for a patient with altered consciousness and decreased GCS score. The short term objectives were for the patient to maintain consciousness, reorient to time/place/person, and have normal tissue perfusion. Interventions included monitoring vitals, labs, and mental status. The long term goals were for the patient to display tolerance to activity, have normal sensations/movement, and improve consciousness. Success would be seen through maintained consciousness, reorientation, and warmth/dryness; failure from decreased consciousness or need for full assistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 4
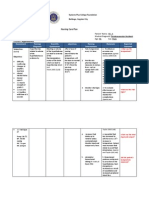
CUES EXPLANATION OF GOALS AND INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION ACTUAL EVALUATION
THE PROBLEM OBJECTIVES CRITERIA
SUBJECTIVE: Blood is a STO: DIAGNOSTICS: FULLY MET
connective tissue After 8 hours of If the patient
composed of a liquid appropriate nursing 1. Monitored respirations and Cardiac pump maintains an alert
extracellular matrix interventions, the absence of work of malfunction and/or level of
OBJECTIVE: called blood plasma patient will be able breathing. ischemic pain may result consciousness
Altered level of that dissolves and to: in respiratory distress. throughout the
consciousness suspends various a) Maintain usual Nevertheless, abrupt or shift
Confusion cells and cell or improved continuous dyspnea If the patient was
Decreased GCS fragments. Blood level of may signify kept reoriented to
score transports oxygen consciousness thromboembolic time, place, and
Language deficits from the lungs and b) Verbalize pulmonary person.
As of August 18, nutrients from the reorientation to complications. If the patient
2017 gastrointestinal time, place, and maintains a warm
CT-scan result shows tract. The oxygen person. 2. Checked rapid changes or Electrolyte/acid-base and dry skin
significant regression and nutrients c) Maintain continued shifts in mental variations, hypoxia, and during the shift.
of bilateral subdural subsequently diffuse maximum tissue status. systemic emboli If the patient
hematomaoverlying from the blood into perfusion to vital influence cerebral displays tolerance
both cerebral the interstitial fluid organs, as perfusion. In addition, it during activities.
hemisphere as and then into the evidenced by is directly related to If the patient
described, with body cells. warm and dry cardiac output. maintains usual or
associated mass Circulating blood skin. normal sensations
effect. helps maintain and motor
--recent note of the homeostasis of all LTO: activity.
following: acute left body fluids. Blood After 4 days of 3. Monitored oxygen Pulse oximetry is a
temporal epidural helps adjust body appropriate nursing saturation useful tool to detect PARTIALLY MET
hematoma, temperature interventions, the changes in oxygenation. If the patient
pneumocephalus, through the heat patient will be able maintains usual
craniotomy defects, absorbing and to: level of
bilateral parietal coolant properties a) Display growing 4. Checked Hemoglobin levels Low levels reduce the consciousness
bones with overlying of the water in tolerance to uptake of oxygen at the If the patient still
soft tissue swelling. blood plasma and its activity alveolar-capillary has events of
variable rate of flow confusion a few
--Atherosclerotic through the skin, b) Verbalize or membrane and oxygen hours after
intracranial arteries. where excess heat demonstrate delivery to the tissues. reorientation to
can be lost from the normal time, place, and
blood to the sensations and person.
environment. Blood movement as 5. Assessed for presence of Nonexistence of If the patient
can clot, which appropriate. pallor, cyanosis, mottling, peripheral pulses must maintains a warm
protects against its cool or clammy skin. Assess be reported or and dry skin, but
excessive loss from quality of every pulse. managed immediately. have episodes of
the cardiovascular Systemic cold extremities.
system after an vasoconstriction If the patient still
injury. In addition, its resulting from reduced needs full
white blood cells cardiac output may be assistance to
protect against manifested by some activities,
disease by carrying diminished skin but can move on
on phagocytosis. perfusion and loss of his own when
Several types of pulses. Therefore, turning or
blood proteins assessment is required repositioning on
including antibodies, for constant bed.
interferons, and comparisons. If the patient
complement, help shows slight
protect against 6. Maintained optimal cardiac This ensures adequate improvement on
disease in a variety output. perfusion of vital sensations and
of ways. However, organs. motor activity.
conditions such as
conditions such as 7. Controled environmental Fever may be a sign of
amputation, temperature as necessary. damage to UNMET
cerebrovascular Perform tepid sponge bath hypothalamus. Fever If the patient does
accident, stroke, when fever occurs. and shivering can not show any
crainiocerebral further increase ICP. improvement in
trauma, disk his level of
surgery, myocardial 8. Reviewed laboratory result To know the type of consciousness
infarction, sepsis, interventions given to If the patient is
thrombophebitis, patient. confused during
deep vein the whole shift,
thrombosis, upper even after
gastrointestinal THERAPEUTICS: reorientation to
bleeding and time, place, and
atherosclerosis 1. Promoted passive ROM Exercise prevents person.
causes reduction in exercises. venous stasis and If the patient has
arterial blood flow further circulatory cold, clammy
that leads to compromise. extremities.
deprived nutrition If the patient still
and oxygenation at 2. Administered medications These medications needs full
the cellular level. as prescribed to treat facilitate perfusion for assistance in all
Decreased tissue underlying problem. Note most causes of activities and is
perfusion can be the response. impairment. dependent to
transient with few another person.
or minimal Antiplatelets/anticoagulants If the patient
consequences to the --These reduce blood viscosity shows no
health of the and coagulation. improvement in
patient. If the Peripheral vasodilators sensations and
decreased perfusion --These enhance arterial dilation movement.
is acute and and improve peripheral blood
protracted, it can flow.
have devastating Antihypertensives
effects on the --These reduce systemic vascular
patient. Diminished resistance and optimize cardiac
tissue perfusion, output and perfusion.
which is chronic in Inotropes
nature, invariably --These improve cardiac output.
results in tissue or
organ damage or 3. Provided oxygen therapy as This saturates
death. necessary. circulating hemoglobin
and augments the
efficiency of blood that
is reaching the ischemic
tissues.
4. Positioned patient properly
in a semi-Fowler’s to high- Upright positioning
Fowler’s as tolerated. promotes improved
alveolar gas exchange.
5. Elevated edematous legs as
ordered and ensure that Elevation improves
there is no pressure under venous return and helps
the knee. minimize edema.
Pressure under the knee
limits venous
circulation.
6. Applied support hose as Wearing support hose
ordered. helps decrease edema.
EDUCATIVE:
1. Encouraged the family Flexion exercises helps
members to do passive to enhance circulation.
flexion exercises in bed.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Nanda NCP BasedDocumento14 pagineNanda NCP Baseddeliejoyce100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 pagineDecreased Cardiac OutputRizalyn QuindipanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP NeuroDocumento20 pagineNCP NeuroNica Gaborne Navarro100% (3)
- NCPDocumento9 pagineNCPKarell Eunice Estrellado Gutierrez100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 pagineDecreased Cardiac OutputCristina L. JaysonNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP StrokeDocumento2 pagineNCP StrokeEtienne NinxNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) : Patient & Family Centered (In Priority Order)Documento1 paginaNursing Care Plan (NCP) : Patient & Family Centered (In Priority Order)WorodNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemothorax HandoutsDocumento2 pagineHemothorax HandoutsJunathan L. DelgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP AneurysmDocumento4 pagineNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 pagineNursing Care PlanCindy Mae Quinga100% (2)
- CRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocumento3 pagineCRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPchubbielitaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento4 pagineNCPElbert Vierneza100% (2)
- NCPDocumento17 pagineNCPbalongetzNessuna valutazione finora
- Head InjuryDocumento5 pagineHead InjuryJames Jayson Liberto100% (3)
- NCP ShockDocumento5 pagineNCP ShockJanina Patricia BuddleNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP1 CHFDocumento2 pagineNCP1 CHFapi-27015740100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan: Precipitating FactorDocumento8 pagineNursing Care Plan: Precipitating FactorJe Zal100% (1)
- CVA NCP'sDocumento45 pagineCVA NCP'sgenesis lucas100% (6)
- NCP HCVD (Final)Documento8 pagineNCP HCVD (Final)khrizaleeh100% (1)
- Myocardial Infarction Concept MapDocumento7 pagineMyocardial Infarction Concept Mapkarelclarke629280% (5)
- Soapie Charting: Date/ Time/ ShiftDocumento2 pagineSoapie Charting: Date/ Time/ Shiftspain michaelisNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP MiDocumento4 pagineNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Aortic Aneurysm - FinalDocumento67 pagineAortic Aneurysm - FinalJonathan DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Vehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPDocumento6 pagineVehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPCHRISTIE MONTANONessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For StrokeDocumento4 pagineNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCONessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment: Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocumento3 pagineAssessment: Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDelaine Mae MierNessuna valutazione finora
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDocumento2 pagineDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathySoniaMarieBalanayNessuna valutazione finora
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyDocumento7 pagineNueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyKym RonquilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Velez College of Nursing F. Ramos Street, Cebu CityDocumento57 pagineVelez College of Nursing F. Ramos Street, Cebu Cityinah krizia lagueNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineIneffective Tissue PerfusionMary Hope BacutaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionjamiemapanaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Case StudyDocumento10 pagineNCP For Case StudySarah BenjaminNessuna valutazione finora
- CHD With NCPDocumento10 pagineCHD With NCPJohanna Kirsten F. DaguioNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento5 pagineNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan CVADocumento6 pagineNursing Care Plan CVAessevyNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeDocumento22 pagineNCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeAnnNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For CHFDocumento11 pagineNCP For CHFqingwen100% (5)
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDocumento3 pagineImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (NCP)Documento4 pagineBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (NCP)24 PAULINO ALDRIN MUJARNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Acquired PneumoniaDocumento56 pagineCommunity Acquired Pneumoniashiean06Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP EpilepsyDocumento1 paginaNCP EpilepsyManpreet ToorNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 pagineNCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputErienne Lae Manangan - CadalsoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento11 pagineNCPRyan Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocumento6 pagineDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Pulmonary Edema PDFDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan For Pulmonary Edema PDFAsmaa100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotMikko Enoc100% (1)
- NCP CvaDocumento4 pagineNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeNessuna valutazione finora
- Soapie Charting: Patient X 50 Yrs Old Myocardial InfarctionDocumento1 paginaSoapie Charting: Patient X 50 Yrs Old Myocardial InfarctionKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco100% (1)
- NCPDocumento2 pagineNCPJonathan LiscanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocumento2 pagineDecreased Cardiac Output NCPmicah1318100% (2)
- CroupDocumento20 pagineCroupFariezuan HamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Anxiety R:T Death ThreatDocumento8 pagineAnxiety R:T Death ThreatAlfredo BaulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGDocumento11 pagineAssessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGGrape JuiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Pleural EffusionDocumento9 pagineNursing Care Plan For Pleural EffusionJoseph Angelo Fortuna Carmona100% (1)
- NCP CPDocumento7 pagineNCP CPAllyzah Faith BernalesNessuna valutazione finora
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocumento6 pagineROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Post PartumDocumento2 pagineNCP Post PartumsteffiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Voltmeter (DVM) : Elementary Measurement SystemDocumento4 pagineDigital Voltmeter (DVM) : Elementary Measurement SystemRounakNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuñez Survey InstrumentDocumento3 pagineNuñez Survey InstrumentAnna Carmela NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Detector Bump Test Record Log Sheet: Bump Test Result Test Date Time Pass Fail Retest Pass Retest Fail Tester NameDocumento2 pagineGas Detector Bump Test Record Log Sheet: Bump Test Result Test Date Time Pass Fail Retest Pass Retest Fail Tester NameAndry Kurnia100% (2)
- Learning Activity 4 Evidence: My View On Colombia: 1. Write A Composition Describing What The LifestyleDocumento2 pagineLearning Activity 4 Evidence: My View On Colombia: 1. Write A Composition Describing What The LifestyleYenifer PatiñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Schumpeter CaseDocumento1 paginaAssignment Schumpeter CaseValentin Is0% (1)
- Mr./Ms. Anshu Yadav Dear Anshu,: DateDocumento3 pagineMr./Ms. Anshu Yadav Dear Anshu,: DateAnshu YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma Asia-PasificDocumento13 pagineSoft Tissue Sarcoma Asia-PasificHayyu F RachmadhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) Faqs: Why Is TKN Important?Documento4 pagineTotal Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) Faqs: Why Is TKN Important?dsbishtNessuna valutazione finora
- Epsom Salt ClassDocumento7 pagineEpsom Salt ClassSofia marisa fernandesNessuna valutazione finora
- Masculine Scents SpicyDocumento2 pagineMasculine Scents SpicyGabrielle May LacsamanaNessuna valutazione finora
- MIP17-HSE-JSA-JUB-39 JSA For Piping Works (Flanged Installation, - Gasket Installation Welding & Bolt Tightening) - 2023 Rev 0Documento13 pagineMIP17-HSE-JSA-JUB-39 JSA For Piping Works (Flanged Installation, - Gasket Installation Welding & Bolt Tightening) - 2023 Rev 0AmeerHamzaWarraichNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter To The GuardianDocumento3 pagineLetter To The GuardianBelle Princess DuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide in Filling Up The Competency Assessment FormDocumento5 pagineGuide in Filling Up The Competency Assessment FormJOSEPH CAJOTENessuna valutazione finora
- Agreement To Care For and Return Company EquipmentDocumento1 paginaAgreement To Care For and Return Company EquipmentUbuntu Linux100% (2)
- PPLS Seri A Februari 2020 PDFDocumento33 paginePPLS Seri A Februari 2020 PDFhedriansyah edNessuna valutazione finora
- Applicationformpdf COLUMBANDocumento1 paginaApplicationformpdf COLUMBANRIMANDO LAFUENTENessuna valutazione finora
- Micro InsuranceDocumento27 pagineMicro Insurancedrishya3Nessuna valutazione finora
- ALP 9th Bio. Ch. 3 MCQs - Nauman SadafDocumento2 pagineALP 9th Bio. Ch. 3 MCQs - Nauman SadafSohail AfzalNessuna valutazione finora
- Recent Advances in Natural Polymer-Based Drug Delivery SystemsDocumento18 pagineRecent Advances in Natural Polymer-Based Drug Delivery SystemsTelmoNessuna valutazione finora
- Neither This Nor That by Jean KleinDocumento6 pagineNeither This Nor That by Jean KleinTarun Patwal60% (5)
- (V) Disaster Management by Vaishali MamDocumento7 pagine(V) Disaster Management by Vaishali Mamnvn.2130Nessuna valutazione finora
- ForwardInvoice ORD660948335Documento4 pagineForwardInvoice ORD660948335Nitin GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A: Jawab Semua SoalanDocumento3 pagineSection A: Jawab Semua SoalanAzreen IzetNessuna valutazione finora
- Green Energy BricksDocumento8 pagineGreen Energy BricksSriram NandipatiNessuna valutazione finora
- PEDOSPHEREDocumento32 paginePEDOSPHEREKENT YNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolyte & Acid Base Disturbances in Diabetes MellitusDocumento12 pagineElectrolyte & Acid Base Disturbances in Diabetes MellitusAla SoroceanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Apply Health, Safety and Security Procedures in The WorkplaceDocumento9 pagineApply Health, Safety and Security Procedures in The WorkplaceRene EspenocillaNessuna valutazione finora
- New Tenant Welcome LetterDocumento1 paginaNew Tenant Welcome Letterkristen uyemuraNessuna valutazione finora
- CUP 04 BOIN USA 02 WebDocumento2 pagineCUP 04 BOIN USA 02 WebMajid abdulNessuna valutazione finora
- AcknowledgementDocumento2 pagineAcknowledgementSonali SinghNessuna valutazione finora