Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
X Integrals 24
Caricato da
MasudRanaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
X Integrals 24
Caricato da
MasudRanaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
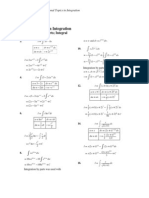
x−2
I = − 4 x − x 2 + 4sin −1 +c
2
x+2
21. Let I = ∫ x + 2x + 3
2
dx
Let Linear = A
d
dx
(Quadratic) + B ⇒ x+2= A
d 2
dx
( x + 2 x + 3) + B
⇒ x + 2 = A ( 2x + 2) + B ……(ii) ⇒ x + 2 = 2Ax + 2A + B
1
Comparing coefficients of x, 2A = 1 ⇒ A=
2
Comparing constants, 2A + B = 2
1
On solving, we get A= , B=1
2
1
Putting the values of A and B in eq. (ii), x+2= ( 2x + 2) + 1
2
1
( 2x + 2) + 1
Putting this value of x + 2 in eq. (i), I= ∫ 2 dx
x2 + 2 x + 3
1 2x + 2 1 1
I=
2 ∫ x + 2x + 3
2
dx + ∫
x + 2x + 3
2
dx ⇒ I = I1 +I 2
2
……….(iii)
2x + 2
Now I1 = ∫ dx
x + 2x + 3
2
dt
Putting x 2 + 2 x + 3 = t ⇒ 2x + 2 = ⇒ ( 2x + 2) dx = dt
dx
−1 1
dt t 2
∴ I1 = ∫ = ∫ t 2 dt = = 2 t = 2 x2 + 2 x + 3 ……….(iv)
t 1
2
1 1 1
Again I2 = ∫ dx = ∫ =∫ dx
x2 + 2x + 3 x2 + 2x + 1 + 2 ( x + 1) + ( 2)
2 2
= log x + 1 + ( x + 1) + ( 2 )
2 2
= log x + 1 + x 2 + 2 x + 3 ……….(v)
Putting values of I1 and I2 in eq. (iii),
I= x 2 + 2 x + 3 + log x + 1 + x 2 + 2 x + 3 + c
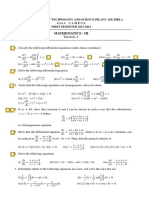
x+3
22. Let I = ∫x 2
− 2x − 5
dx ……….(i)
Let Linear = A
d
dx
(Quadratic) + B ⇒ x+3= A
d 2
dx
( x − 2 x − 5) + B
⇒ x + 3 = A ( 2 x − 2 ) + B ……(ii) ⇒ x + 3 = 2Ax − 2A + B
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- X Integrals 23Documento1 paginaX Integrals 23MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- X Integrals 21Documento1 paginaX Integrals 21MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lemh 2 SMDocumento10 pagineLemh 2 SMmamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maclaurin Series Timed Practice Exam Questions SolutionsDocumento4 pagineMaclaurin Series Timed Practice Exam Questions SolutionsRichard WaltonNessuna valutazione finora
- X Integrals 30Documento1 paginaX Integrals 30MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2006Documento46 pagineDifferential Equations - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2006Muhammad UmairNessuna valutazione finora
- 29 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بDocumento2 pagine29 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بMina AlbertNessuna valutazione finora
- X Integrals 22Documento1 paginaX Integrals 22MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- X Integrals 27Documento1 paginaX Integrals 27MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths 1B Integration of Partial FractionsDocumento2 pagineMaths 1B Integration of Partial FractionsSTHEMBILE MthethwaNessuna valutazione finora
- 37 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بDocumento2 pagine37 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بMina AlbertNessuna valutazione finora
- Integration of Rational Fractions: 4.3 Integration For None Repeated Quadratic FactorsDocumento6 pagineIntegration of Rational Fractions: 4.3 Integration For None Repeated Quadratic FactorsJamie MedallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Integration of Integrals Involving Quadratic FunctionsDocumento12 pagineIntegration of Integrals Involving Quadratic FunctionsNaseeb AliiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicio 1Documento2 pagineEjercicio 1JOSE ALBERTO QUINTANA SOLISNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 3 Exercise 3.8Documento6 pagineNotes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 3 Exercise 3.8shahidNessuna valutazione finora
- 25 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بDocumento2 pagine25 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بMina AlbertNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise # 9.2: B.Sc. Mathematics (Mathematical Methods) Chapter # 9: First-Order Differential EquationsDocumento12 pagineExercise # 9.2: B.Sc. Mathematics (Mathematical Methods) Chapter # 9: First-Order Differential EquationsMuhammad Haseeb RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- X Integrals 17Documento1 paginaX Integrals 17MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Math CH 3 Exercise 3.8Documento17 pagine12 Math CH 3 Exercise 3.8Aman rathiNessuna valutazione finora
- 「9781337616249 - CalcMetric - 08 - CSM.pdf」複本 的副本Documento135 pagine「9781337616249 - CalcMetric - 08 - CSM.pdf」複本 的副本shawn wuNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Indefinite Integration15914392201591601451Documento5 pagine03 Indefinite Integration15914392201591601451meshramshrikant443Nessuna valutazione finora
- NYJC 2017 EOY Exam Paper Solutions 2Documento12 pagineNYJC 2017 EOY Exam Paper Solutions 2Low Jia YingNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Separable EquationDocumento7 pagine1.1 Separable EquationNasir AiyubNessuna valutazione finora
- Xii Maths Book-2 Based (Solutions) Self-Assessment Tests 2022-23 (Amit Bajaj)Documento32 pagineXii Maths Book-2 Based (Solutions) Self-Assessment Tests 2022-23 (Amit Bajaj)Dheeraj SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- CQF January 2014 Maths Primer Differential Equations ExercisesDocumento5 pagineCQF January 2014 Maths Primer Differential Equations ExercisesShravan VenkataramanNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.exercise#1.0Documento32 pagine7.exercise#1.0u.k.jashinthanNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Differential Equations and Areas Sheet MathonGo BITSATDocumento8 pagineQuestion Differential Equations and Areas Sheet MathonGo BITSATraghavchawdhryNessuna valutazione finora
- MAT060 - 27 Integration Involvin Quadratic FunctionsDocumento11 pagineMAT060 - 27 Integration Involvin Quadratic FunctionsHassan GandamraNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrals Wo WatermarkDocumento12 pagineIntegrals Wo Watermarkmeghashyam.raju1210Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ex2 1 PDFDocumento7 pagineEx2 1 PDFMeer MomiNessuna valutazione finora
- X Integrals 19Documento1 paginaX Integrals 19MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- FInal Project Dichoson&SonidoDocumento5 pagineFInal Project Dichoson&SonidoMark DichosonNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Equation 1.6Documento3 pagineDifferential Equation 1.6Vans HpNessuna valutazione finora
- GCE A' Level H2 Mathematics November 2017 Paper 1Documento8 pagineGCE A' Level H2 Mathematics November 2017 Paper 1Just MeNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise - 3 Motion SolutionDocumento12 pagineExercise - 3 Motion Solutionnainaradhey24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1Documento7 pagineNotes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1shahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Indefinite Integration - Short Notes - Prayas JEE 2024Documento2 pagineIndefinite Integration - Short Notes - Prayas JEE 2024Mohit YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- H2 Further Math ACJC-NJC-RVHS - H2 - FM - Prelim - 2022 - P2 - SolutionsDocumento10 pagineH2 Further Math ACJC-NJC-RVHS - H2 - FM - Prelim - 2022 - P2 - SolutionscamaralckinNessuna valutazione finora
- Prelim Paper 1 - 2022 - Solution (Comments)Documento17 paginePrelim Paper 1 - 2022 - Solution (Comments)Bryan TangNessuna valutazione finora
- Ass 2022Documento10 pagineAss 2022olemas1984Nessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Topics in Integration: 6.1 Integration by Parts Integral TablesDocumento32 pagineAdditional Topics in Integration: 6.1 Integration by Parts Integral TablesHaris Aman ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Solutions 1. (20 PTS.) Evaluate The Following Indefinite IntegralsDocumento15 pagineFinal Exam Solutions 1. (20 PTS.) Evaluate The Following Indefinite IntegralsАрхи́пNessuna valutazione finora
- Assorted Integration Exercise AnswerDocumento1 paginaAssorted Integration Exercise AnswermengleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrales 2.0Documento8 pagineIntegrales 2.0JOAQUIN MANUEL MENDOZA MONTIELNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 3 Exercise 3.3Documento6 pagineNotes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 3 Exercise 3.3shahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluate 1 LN D 2 Sin 3 Cos 4 D: X X X X XXDocumento18 pagineEvaluate 1 LN D 2 Sin 3 Cos 4 D: X X X X XXShereen LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheetlecture12 SolutionsDocumento9 pagineWorksheetlecture12 SolutionsEditha CuencoNessuna valutazione finora
- Integration by Partial FractionsDocumento2 pagineIntegration by Partial Fractionspalmer okiemuteNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment IIDocumento1 paginaAssignment IIAarush PitlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 334 Fall 2011 Homework 2 Solutions: Sept. 23, 2011Documento7 pagineMath 334 Fall 2011 Homework 2 Solutions: Sept. 23, 2011Tristan Joseph ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1Documento2 pagineTutorial 1baklolNessuna valutazione finora
- Cauchy DE Method 11Documento20 pagineCauchy DE Method 11ahmadshujaat99proNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 1 Tutorial 5Documento1 paginaMathematics 1 Tutorial 5hnafiul97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5-6 Exercise Double, Triple, Multiple (J) IntegralDocumento6 pagineWeek 5-6 Exercise Double, Triple, Multiple (J) IntegralLamiaNessuna valutazione finora
- CALA05 - Đào Nguyễn Nam - PS9Documento10 pagineCALA05 - Đào Nguyễn Nam - PS9Nguyễn NamNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1Documento3 pagineNotes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1shahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1Documento3 pagineExercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1Ajhd FvsgNessuna valutazione finora
- Order and Linearity: Faculty of Applied Sciences and Technology Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia BWM12303 Tutorial 1Documento1 paginaOrder and Linearity: Faculty of Applied Sciences and Technology Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia BWM12303 Tutorial 1Jojnojie DannyzNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsDa EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Data Compressions 37Documento1 paginaData Compressions 37MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 42Documento1 paginaData Compressions 42MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 39Documento1 paginaData Compressions 39MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 40Documento1 paginaData Compressions 40MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 38Documento1 paginaData Compressions 38MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 41Documento1 paginaData Compressions 41MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 27Documento1 paginaData Compressions 27MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 34Documento1 paginaData Compressions 34MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 36Documento1 paginaData Compressions 36MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 29Documento1 paginaData Compressions 29MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 30Documento1 paginaData Compressions 30MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 15Documento1 paginaData Compressions 15MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 35Documento1 paginaData Compressions 35MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 28Documento1 paginaData Compressions 28MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 19Documento1 paginaData Compressions 19MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 25Documento1 paginaData Compressions 25MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 26Documento1 paginaData Compressions 26MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 21Documento1 paginaData Compressions 21MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 22Documento1 paginaData Compressions 22MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 23Documento1 paginaData Compressions 23MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 18Documento1 paginaData Compressions 18MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 17Documento1 paginaData Compressions 17MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 16Documento1 paginaData Compressions 16MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 24Documento1 paginaData Compressions 24MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 20Documento1 paginaData Compressions 20MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 13Documento1 paginaData Compressions 13MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 14Documento1 paginaData Compressions 14MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 9Documento1 paginaData Compressions 9MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 12Documento1 paginaData Compressions 12MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Compressions 11Documento1 paginaData Compressions 11MasudRanaNessuna valutazione finora
- CNN Architectures For Large-Scale Audio ClassificationDocumento5 pagineCNN Architectures For Large-Scale Audio ClassificationRizki Jumadil PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- PcommsDocumento24 paginePcommsNeslynNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter1 PDFDocumento54 pagineChapter1 PDFdebojyotiNessuna valutazione finora
- Kalman FilterDocumento11 pagineKalman FilterSanjay Kumar GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- IFEM Ch28Documento6 pagineIFEM Ch28Yiling HeNessuna valutazione finora
- Signals and Systems Using Matlab Chapter 8 - Sampling TheoryDocumento14 pagineSignals and Systems Using Matlab Chapter 8 - Sampling TheoryDiluNessuna valutazione finora
- Generation of Quasi-Uniform Distributions and Verification of The Tightness of The Inner BoundDocumento18 pagineGeneration of Quasi-Uniform Distributions and Verification of The Tightness of The Inner Bounddauoodsaleem dauoodsaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Similarity Measures For Categorical DataDocumento12 pagineSimilarity Measures For Categorical DataNeti SuherawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer VisionDocumento6 pagineComputer Visionmd alamNessuna valutazione finora
- PID-Controller Tuning Optimization With Genetic Algorithms in Servo SystemsDocumento14 paginePID-Controller Tuning Optimization With Genetic Algorithms in Servo SystemsAurel GSNessuna valutazione finora
- Convex and Conic Optimization: Spring 2017Documento3 pagineConvex and Conic Optimization: Spring 2017akiscribd1Nessuna valutazione finora
- DAA Lab ManualDocumento49 pagineDAA Lab ManualsammmNessuna valutazione finora
- NR-311201-Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsDocumento8 pagineNR-311201-Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsSrinivasa Rao GNessuna valutazione finora
- Branch and BoundDocumento46 pagineBranch and BoundRAJASH89Nessuna valutazione finora
- Voronoi Diagrams 2Documento15 pagineVoronoi Diagrams 2api-220467405Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maths (041) Xii PB 1 QP Set CDocumento7 pagineMaths (041) Xii PB 1 QP Set Cup14604Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Test Topic: Normal Distribution: I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Letter of The Best Answer. (1 Point Each)Documento3 pagineChapter Test Topic: Normal Distribution: I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Letter of The Best Answer. (1 Point Each)Jessa Banawan EdulanNessuna valutazione finora
- Forecasting-Seasonal ModelsDocumento34 pagineForecasting-Seasonal Modelssuriani hamsahNessuna valutazione finora
- Curve25519 20060209 PDFDocumento22 pagineCurve25519 20060209 PDFbitcasabackup1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Convolution:: Impulse ResponseDocumento8 pagineConvolution:: Impulse ResponseEjaz ul Haq kakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Discrete Time Convolution PDFDocumento1 paginaDiscrete Time Convolution PDFDela Natalia MalauNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Failure Finding Maintenance: SectionDocumento4 pagine5 Failure Finding Maintenance: SectionRamzi BrkNessuna valutazione finora
- Automation KivaDocumento25 pagineAutomation KivaAnirudh KowthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Number Theory and CryptographyDocumento26 pagineNumber Theory and CryptographyanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Section N Notes With AnswersDocumento4 pagineSection N Notes With AnswersDeivid William TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Little PigsDocumento17 pagineThree Little PigsAbdul QaiyoumNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec-431 - Digitalcommunication: College of E&Me, Nust, RawalpindiDocumento10 pagineEc-431 - Digitalcommunication: College of E&Me, Nust, RawalpindiAffra NazirNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Electrodynamics by Imran AzizDocumento29 pagineQuantum Electrodynamics by Imran AzizDr.Imran Aziz0% (1)
- Assignment - ForecastingDocumento1 paginaAssignment - ForecastingVencint LaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfer Function - Poles and Zeros - StabilityDocumento9 pagineTransfer Function - Poles and Zeros - Stability666667Nessuna valutazione finora