Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
New Microsoft Word Document 1
Caricato da
api-385694647Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
New Microsoft Word Document 1
Caricato da
api-385694647Copyright:
Formati disponibili
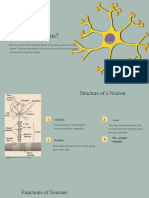
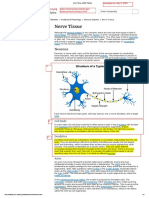
How do neuron works?
Vocabs / Keywords
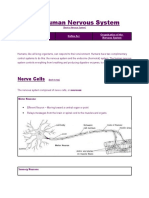
Neuron — Type of nerve cell
Basic principle
Axon — The long end of nerve cell, use to
transmit data
A neuron (also known as nerve cell) is an electrically excitable cell that takes up, processes and
transmits information through electrical and chemical signals. It is one of the basic elements of the Dendrites — The branch- looking end, receive
nervous system. data
Organelles — Organ of the cell
In order that a human being can react to his environment, neurons transport stimuli. The stimulation, for
example the burning of the finger at a candle flame, is transported by the ascending neurons to the Stimuli — a thing or event that evokes a
specific function
central nervous system and in return, the descending neurons stimulate the arm in order to remove the
finger from the candle. Transmits - Sent
Excitable—responding
A simple structure designed for a complex task Electrical impulse — The way that nerve cell
communicate
A typical neuron is divided into three parts: the cell body, the dendrites and the axon. The cell body Contact — to communicate
(green color), the center of the neuron, extends its processes called the axon and the dendrites to other
Synapse — a junction between two nerve cells
cells. Dendrites typically branch profusely, getting thinner with each branching (blue color). The axon is
thin but can reach enormous distances (violet color).
Summary
To make a comparable scale, the diameter of a neuron is about the tenth size of the diameter of a human
A neuron or nerve cells is a type of cell
hair. that process and transmits information
through electrical and chemical
Getting really into it signals. When you come in contact
with an environment, the neuron
The cell body is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell (that carries all the
transmit electrical signal which is
genetic material) and numerous organelles that allow protein synthesis (endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi,
etc. ) and energy production (mitochondria). send to your brain to react to different
stimuli, such as touching burning
candles. The neuron itself is divided
The axon is a fine, cable-like projection that can extend over enormous distances. At its final tip, the
axon contacts other cells (nerve- or muscle cells), through structures named synapses. into three parts, the cell body, the
The cell body and the axon are supported by a complex network of structural proteins called dendrites and the axon. The dendrites
microtubules. is an branch-looking shape, then the
body is where organelles located, then
Transmitting information
the axon is the long thin end of the cell
All neurons are electrically excitable. The electrical impulse mostly arrives on the dendrites, gets body. The cell body is the central
processed into the cell body to then move along the axon. On its all length an axon functions merely as parts, which is where the nucleus of
an electric cable, simply transmitting the signal. Once the electrical reaches the end of the axon, at the the cell is located, process similar task
synapses, things get a little more complex. as the normal cell, the axon is a fine
cable-like the stretch out over
The key to neural function is the synaptic signaling process, which is partly electrical and partly enormous distances. The tip of the
chemical. Once the electrical signal reaches the synapse, a special molecule called neurotransmitter is released by the neuron. This axon communicate with others cell,
neurotransmitter will then stimulate the second neuron, triggering a new wave of electrical impulse, repeating the mechanism described above.
while the dendrites received the
electrical impulse from others cell.
The process works by both electrical
and chemical reaction. when the
electrical signal reach the synapse, its
release the special molecule called
neurotransmitter is released by the
neuron, triggering the new wave
electrical impulse repeating the
mechanism again.
Bhumrapee Soonjun 1002
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 2 ReadingDocumento13 pagineChapter 2 ReadingYousef Ahmad2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Central Nervous System: NeuronsDocumento1 paginaBrain Central Nervous System: NeuronsMares InliwanNessuna valutazione finora
- PSYC 30043 Cognitive Psychology - Cognitive NeuroscienceDocumento10 paginePSYC 30043 Cognitive Psychology - Cognitive NeuroscienceAngelica TumlodNessuna valutazione finora
- BRAIN LECTURE and ACTIVITYDocumento5 pagineBRAIN LECTURE and ACTIVITYRussel Cyrus SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- CerebrumDocumento5 pagineCerebrumShiella Barroga LorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemDocumento19 pagineNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Invertebrate Nervous Systems: Thomas MathesonDocumento6 pagineInvertebrate Nervous Systems: Thomas MathesonMax MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 - The NeuroneDocumento17 pagineLesson 4 - The NeuroneArgie M. EspinosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain AnatomyDocumento2 pagineBrain AnatomyÖzge ŞenNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 1Documento12 paginePresentation 1Maryam KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemDocumento17 pagineNervous SystemZairene Jane del RosarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureDocumento7 pagineHistology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureAli HayderNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento51 pagineUnit 5JAYANT CH (RA2111004010265)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 11 Nervous SystemDocumento117 pagineUnit 11 Nervous SystemChandan Shah100% (1)
- The Human Nervous System A2Documento33 pagineThe Human Nervous System A2Melody PamireNessuna valutazione finora
- Central NervousDocumento8 pagineCentral NervousDamian MaferiNessuna valutazione finora
- Botan's Cns and The Brain 2023Documento115 pagineBotan's Cns and The Brain 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Psychology Module 9Documento29 pagineAP Psychology Module 9Klein ZhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurons. The Building Blocks of Nervous SystemDocumento3 pagineNeurons. The Building Blocks of Nervous SystemGinelQuenna De VillaNessuna valutazione finora
- MC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSDocumento7 pagineMC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSFrancine Dominique CollantesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 The Nervous SystemDocumento58 pagineLesson 1 The Nervous SystemBeck YepsenaNessuna valutazione finora
- GenBio2 Lesson 1 Muscular and Nervous TissuesDocumento5 pagineGenBio2 Lesson 1 Muscular and Nervous TissuesAnne BeatrizNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are NeuronsDocumento16 pagineWhat Are NeuronsJaebeom's Best FriendNessuna valutazione finora
- (w14) Nervous Tissue and Nervous SystemDocumento7 pagine(w14) Nervous Tissue and Nervous Systemden mNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.3 Neurons - Biology LibreTextsDocumento3 pagine11.3 Neurons - Biology LibreTextsDandy MarayagNessuna valutazione finora
- NeuronsDocumento9 pagineNeuronsMuhammad Junaid SialNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 7 Full HBDocumento56 pagineTopic 7 Full HBazankha1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemDocumento9 pagineNervous SystemChristine Joanne CelendroNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5-Immune SystemDocumento51 pagineUnit 5-Immune SystemAnih Kishor (RA1911002010062)Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A NeuronDocumento5 pagineWhat Is A NeuronJason StevetimmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ns-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemDocumento14 pagineNs-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- IPG 9 - Nervous System ChangesDocumento50 pagineIPG 9 - Nervous System ChangesdeviNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurology Assignment 1Documento9 pagineNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Inside Out Anatomy NervousDocumento3 pagineInside Out Anatomy NervousJonathan LlanilloNessuna valutazione finora
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocumento10 pagineG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurons 974802Documento3 pagineNeurons 974802james kahiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System - Histology - CompressedDocumento15 pagineNervous System - Histology - Compressedadlin munirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuron:: Fundamentals of Psychology Fundamentals of PsychologyDocumento3 pagineNeuron:: Fundamentals of Psychology Fundamentals of PsychologyChaudhary Muhammad Talha NaseerNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 6 DLP 11 The Nerves - RepairedDocumento9 pagineScience 6 DLP 11 The Nerves - RepairedMonica Morales MaañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ns-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemDocumento14 pagineNs-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination and Response in Animals - 052037Documento8 pagineCoordination and Response in Animals - 052037MosesNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Assignment Draft Copy Minna and AishDocumento7 pagineBiology Assignment Draft Copy Minna and AishAish ThangalNessuna valutazione finora
- Nerve Cell PPT 1Documento16 pagineNerve Cell PPT 1Zhen ObelidorNessuna valutazione finora
- SEER 2023 NerveTissueDocumento2 pagineSEER 2023 NerveTissueShweta KhannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Nervous SystemDocumento63 pagineOverview of Nervous SystemMAHARANI100% (1)
- Module 5 Nervous TissueDocumento8 pagineModule 5 Nervous TissueHermione MalfoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationDocumento26 pagineBilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationMuhammad UsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination and ResponseDocumento8 pagineCoordination and ResponseEnaya MajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning & The BrainDocumento7 pagineLearning & The BrainLara GreyjoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec Activity8 Jbillones 101221Documento15 pagineLec Activity8 Jbillones 101221Jayvee BillonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Class NotesDocumento4 pagineClass Notesdaniel holmesNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of NeuronsDocumento6 pagineStructure of NeuronsMusdiqJavedNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Bases of BehaviorDocumento8 pagineBiological Bases of BehaviormysterioushumaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Fifth Grade Nervous SystemDocumento9 pagineHomework Fifth Grade Nervous Systemmed.visionschoolNessuna valutazione finora
- (Oct 1) Nervous-SystemDocumento78 pagine(Oct 1) Nervous-SystemBea GualbertoNessuna valutazione finora
- ANAPHY - Nervous SystemDocumento5 pagineANAPHY - Nervous SystemMA. ANDREA NICOLE DURANNessuna valutazione finora
- Transes, Es + NsDocumento6 pagineTranses, Es + NsCristine Dominique E. DonaireNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture3 - (Chapter3.1) - Neuroscience and Behavior - Part1Documento42 pagineLecture3 - (Chapter3.1) - Neuroscience and Behavior - Part1EDA SEYDINessuna valutazione finora
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesDa EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.Da EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.Nessuna valutazione finora
- IsisDocumento26 pagineIsisapi-385694647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bhum RaftDocumento1 paginaBhum Raftapi-385694647Nessuna valutazione finora
- StoryDocumento2 pagineStoryapi-385694647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Body 1Documento1 paginaBody 1api-385694647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract 2Documento2 pagineAbstract 2api-385694647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Research PaperDocumento31 pagineResearch Paperapi-385694647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Peppered Moth File - Bhumrapee SoonjunDocumento5 paginePeppered Moth File - Bhumrapee Soonjunapi-385694647Nessuna valutazione finora
- International DayDocumento14 pagineInternational Dayapi-385694647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Summarizing A Reading TextDocumento5 pagineSummarizing A Reading Textapi-385694647Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento82 pagineChapter 2Kavitha Selvaraj50% (2)
- Magneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionDocumento18 pagineMagneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionIOSRjournalNessuna valutazione finora
- An Experimental Investigation On Abrasive Jet Machining by Erosion Abrasive GrainDocumento3 pagineAn Experimental Investigation On Abrasive Jet Machining by Erosion Abrasive GrainPkNessuna valutazione finora
- WRP Examination Extension 1 2012Documento12 pagineWRP Examination Extension 1 2012Belinda JadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Menstrupedia Comic: The Friendly Guide To Periods For Girls (2014), by Aditi Gupta, Tuhin Paul, and Rajat MittalDocumento4 pagineMenstrupedia Comic: The Friendly Guide To Periods For Girls (2014), by Aditi Gupta, Tuhin Paul, and Rajat MittalMy Home KaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Noxim MANUALDocumento5 pagineNoxim MANUALSAI NRUSIMHA DEEPAK BURRA SAI NRUSIMHA DEEPAK BURRANessuna valutazione finora
- Glacial Lakes of Himachal PradeshDocumento4 pagineGlacial Lakes of Himachal PradeshMonidipa DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Extrahepatic Biliary Tract Pathology - Cholidolithiasis, Cholidocholithiasis, Cholecystitis and CholangitisDocumento60 pagineExtrahepatic Biliary Tract Pathology - Cholidolithiasis, Cholidocholithiasis, Cholecystitis and CholangitisDarien LiewNessuna valutazione finora
- Med Chem Exam 2Documento24 pagineMed Chem Exam 2cNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng Pipe DesignDocumento12 pagineEng Pipe DesignEsapermana Riyan100% (1)
- AVR Brosure Basler Decs 100Documento2 pagineAVR Brosure Basler Decs 100NikolayNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 Work Energy TNDocumento2 pagine19 Work Energy TNAna DorueloNessuna valutazione finora
- ScilabDocumento4 pagineScilabAngeloLorenzoSalvadorTamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chuyên Đề ConjunctionDocumento5 pagineChuyên Đề ConjunctionKhánh Linh TrịnhNessuna valutazione finora
- 173 EvidenceDocumento6 pagine173 EvidenceSantiago RubianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Latihan Soal BlankDocumento8 pagineLatihan Soal BlankDanbooNessuna valutazione finora
- High Performance Dialysis GuideDocumento28 pagineHigh Performance Dialysis GuideRoxana ElenaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Influence of School Architecture and Design On The Outdoor Play Experience Within The Primary SchoolDocumento20 pagineThe Influence of School Architecture and Design On The Outdoor Play Experience Within The Primary SchoolAnca BalotaNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 WosDocumento6 pagine14 WosATUL KURZEKARNessuna valutazione finora
- Komatsu Technical BrochurDocumento7 pagineKomatsu Technical BrochurBenjamin MossoNessuna valutazione finora
- HardikDocumento21 pagineHardikGohil HardikNessuna valutazione finora
- In Truth To Mollusca According To New Studies by J RutherfordDocumento4 pagineIn Truth To Mollusca According To New Studies by J RutherfordbalaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 7 - Cocktail RecipiesDocumento20 pagineAssignment 7 - Cocktail RecipiesDebjyoti BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Zetor Crystal 150 170 Tractor Operator Manual PDFDocumento234 pagineZetor Crystal 150 170 Tractor Operator Manual PDFAntonNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary Three Exam Question.Documento17 paginePrimary Three Exam Question.ogidan preciousNessuna valutazione finora
- Tank Gauging TankvisionDocumento31 pagineTank Gauging Tankvisionkhangduongda3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sindarin-English Dictionary - 2nd EditionDocumento192 pagineSindarin-English Dictionary - 2nd EditionNea Tan100% (1)
- Fluid Solids Operations: High HighDocumento20 pagineFluid Solids Operations: High HighPriscilaPrzNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Poisoning: VocabularyDocumento9 pagineFood Poisoning: VocabularyHANG WEI MENG MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Amies A 114 - 3Documento17 pagineAmies A 114 - 3Syed Umar Farooq100% (1)