Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
A Silicon Controlled Rectifier Reviewer
Caricato da
ian jheferCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
A Silicon Controlled Rectifier Reviewer
Caricato da
ian jheferCopyright:
Formati disponibili
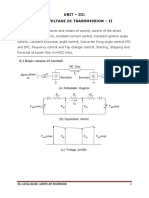
A Silicon Controlled Rectifier (or Semiconductor Three terminals are taken;
Controlled Rectifier) -is a four layer, three-terminal 1. Anode(A)-one from the outer p-type material
2. Cathode(K)-second from the outer n-type material
solid state device used to control rather large currents 3. Gate(G)-the third from the base of transistor Section
to a load.
The name “silicon controlled rectifier” is a trade name The silicon controlled rectifier is a solid state equivalent of
for the type of thyristor commercialized at General thyratron.
Electric in 1957 There are two ways to turn on the SCR:
1. first method is to keep the gate open and make the
SCR has three states: supply voltage equal to the breakover voltage.
2. second method is to operate SCR with supply voltage
1. Reverse blocking mode, less than breakover voltage and then turn it on by
2. forward blocking mode, and means of a small voltage ( typically 1.5 V, 30 mA)
3. forward conducting mode applied to the gate.
(i) Breakover voltage. It is the minimum forward voltage,
In SCR is fired by a short burst of current into the gate. gate being open, at which SCR starts conducting heavily i.e.
This gate current Ig flows through the junction between turned on.
(ii) Peak reverse voltage (PRV). It is the maximum reverse
the gate and cathode and exits from the SCR on the voltage (cathode positive w.r.t.
cathode lead. anode) that can be applied to an SCR without conducting in
the reverse direction.
Igt = 0.1 – 50 mA is the amount of gate current needed
to fire a particular SCR (iii) Holding current. It is the maximum anode current, gate
being open, at which SCR is turned off from ON conditions.
Voltage between gate and cathode (Vgk) ranges from
Forward current rating. It is the maximum anode current
0.6-0.8 V for a standard PN junction. that an SCR is capable of passing without destruction.
Circuit fusing (I2t) rating. It is the product of square of
forward surge current and the time of duration of the surge
i.e., Circuit fusing rating = I2t
reverse breakdown voltage -This maximum reverse voltage at
which SCR starts conducting heavily.
SCR turn-off method
1. (i) Anode current interruption
2. (ii) Forced commutation
SCR WAVEFORMS: Application of SCR:
1. Conduction angle- is the number of degrees of 1. (i) SCR as static contactor- As SCR has no moving
an ac cycle during which the SCR is turned ON. parts, therefore, when it is used as a switch,
2. (ii) SCR for power control.
2. Firing delay angle- is the number of degrees of
3. (iii) SCRs for speed control of d.c. shunt motor
an ac cycle that elapses before the SCR is turned 4. (iv) Overlight detector
ON. 5. (v) SCR Crowbar
SCR- is essentially a diode with an extra terminal added
This extra terminal is called the gate, and it is used to
trigger the device into conduction by the application of
a small voltage
silicon controlled rectifier (abbreviated as SCR) is a three-
terminal semiconductor switching device which is probably
the most important circuit element after the diode and the
transistor.
The SCR has appeared in the market under different names
such as thyristor, thyrode transistor.
SCR combines the features of a rectifier and a transistor.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityDa EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical InstallationsDocumento48 pagineElectrical InstallationsSyed Muzammil AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Manual STR 155 RL-1Documento24 pagineInstruction Manual STR 155 RL-1VENDI100% (3)
- Experiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDocumento6 pagineExperiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDeepak BansalNessuna valutazione finora
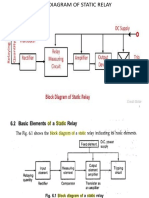
- Static Relays: Prepared byDocumento56 pagineStatic Relays: Prepared byLavanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Over Voltage ProtectionDocumento15 pagineOver Voltage ProtectionSridharan MNessuna valutazione finora
- Ac DrivesDocumento36 pagineAc Drivesaswardi50% (2)
- EASA Part 66 Module 7 MCQ and Essay QuestionsDocumento4 pagineEASA Part 66 Module 7 MCQ and Essay QuestionsazadairNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.feeder Analysis & ModelingDocumento117 pagine10.feeder Analysis & ModelingNamiraNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW - Incar.tw-Kobelco SK 75 Service ManualDocumento5 pagineWWW - Incar.tw-Kobelco SK 75 Service Manualpurnomo0% (1)
- SCR Operation, Characteristics, & ApplicationsDocumento38 pagineSCR Operation, Characteristics, & ApplicationsPaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Solve Process Problems Quickly with Simulation TrainingDocumento6 pagineSolve Process Problems Quickly with Simulation TrainingAnonymous qPt2MHzXTNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical Machines (Eceg132) Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocumento132 pagineBasic Electrical Machines (Eceg132) Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringRonan RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- PSG Two Marks With AnswersDocumento21 paginePSG Two Marks With AnswersKRCT EEE HODNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced clutter options for radio propagation modelingDocumento40 pagineAdvanced clutter options for radio propagation modelingLaura VillarrealNessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of Waste Management in Philippines AgricultureDocumento8 pagineImportance of Waste Management in Philippines Agricultureian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A02602 Power System AnalysisDocumento4 pagine9A02602 Power System Analysissivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- Power System ProtectionDocumento38 paginePower System ProtectionMuhd WariNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic TestingDocumento55 pagineUltrasonic Testingdhasdj100% (1)
- Matlab Finite Element Modeling For Materials Engineers Using MATLABDocumento74 pagineMatlab Finite Element Modeling For Materials Engineers Using MATLABPujara ManishNessuna valutazione finora
- Voltage and Frequency ControlDocumento12 pagineVoltage and Frequency ControlKhawarAminNessuna valutazione finora
- Emeng 3131 Electrical Power Systems: Fundamentals of Power System Yoseph MekonnenDocumento36 pagineEmeng 3131 Electrical Power Systems: Fundamentals of Power System Yoseph MekonnenmichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Oblique SphericalDocumento5 pagineOblique SphericalInriko Rico Castillo100% (1)
- Pe Final Ex SS 2010-2011Documento8 paginePe Final Ex SS 2010-2011Saif Uddin100% (1)
- Power Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesDocumento24 paginePower Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesTapobroto ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- RACTIFIERDocumento19 pagineRACTIFIERDhananjay Aghara100% (1)
- HVDC Unit IIIDocumento22 pagineHVDC Unit IIISreenivas Reddy BodimallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip TestDocumento3 pagineExperiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip Test61EEPrabhat PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Resonant TransformerDocumento15 pagineResonant TransformerfelogonzaNessuna valutazione finora
- DC GeneratorDocumento38 pagineDC Generatoraswardi8756Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microprocessor Based Impedance RelayDocumento11 pagineMicroprocessor Based Impedance RelayS Bharadwaj ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto Selection of Any Available PhaseDocumento16 pagineAuto Selection of Any Available PhaseRyan HarrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Speed Control of 3-Phase IMDocumento19 pagineSpeed Control of 3-Phase IMpramana_gmritNessuna valutazione finora
- Machies Singly ExcitedDocumento15 pagineMachies Singly ExcitedMohamed ElfekyNessuna valutazione finora
- DNT 354 - Control Principle: Steady-State AnalysisDocumento25 pagineDNT 354 - Control Principle: Steady-State AnalysisNiranjan BeheraNessuna valutazione finora
- Simplified Analysis of Graetz CircuitDocumento42 pagineSimplified Analysis of Graetz CircuitKaran Singhania100% (3)
- Brushless DC MotorDocumento3 pagineBrushless DC MotorSourav KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Multi-Step Back-To-Back Capacitor Bank Switching On 115 KV SubstationDocumento5 pagineMulti-Step Back-To-Back Capacitor Bank Switching On 115 KV SubstationAnonymous j5apk2AumNessuna valutazione finora
- Parallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesDocumento9 pagineParallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesJayant Kirpekar100% (1)
- Unit-2-Converter and HVDC System ControlDocumento13 pagineUnit-2-Converter and HVDC System Controlravikumar_ranganNessuna valutazione finora
- EEEE2201: Electrical and Electronic Measurement Lecture Notes Chap 3: Instruments Transformers IDocumento11 pagineEEEE2201: Electrical and Electronic Measurement Lecture Notes Chap 3: Instruments Transformers IFataahu Nyuydze KehkimokiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sphere GapDocumento10 pagineSphere GapAnonymous gbaQBP100% (1)
- 360 Topic 6 DC MachineDocumento33 pagine360 Topic 6 DC MachineAchsan ArfandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics 2 MarkDocumento5 paginePower Electronics 2 MarkPrakash Mahendran100% (2)
- HVDC SlidesDocumento25 pagineHVDC SlidesAreeb ZulkifleNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Sharing of Synchronous GeneratorDocumento16 pagineLoad Sharing of Synchronous GeneratorSalma AkterNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyristors PDFDocumento41 pagineThyristors PDFAvegeil Faye Rubio GamitNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Intelligence SF6 Circuit Breaker Health AssessmentDocumento9 pagineArtificial Intelligence SF6 Circuit Breaker Health AssessmentClaudia TrujilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Static RelayDocumento62 pagineStatic Relayannamalaiasmani1551Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chopper Notes1Documento7 pagineChopper Notes1Ruthra DeviNessuna valutazione finora
- Arcing Phenomenon and Arc InterruptionDocumento9 pagineArcing Phenomenon and Arc Interruptionprabahsh anand100% (1)
- Emf Equation of AlternatorDocumento2 pagineEmf Equation of AlternatorThe Engineers EDGE, CoimbatoreNessuna valutazione finora
- PLC & 8051Documento22 paginePLC & 8051Sunil Patel100% (1)
- Lecture # 3 (Thyristors)Documento25 pagineLecture # 3 (Thyristors)UsmanIbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Series & Shunt CapacitorsDocumento5 pagineSeries & Shunt Capacitorsneo100% (3)
- Chapter 3 Transformer Connections, Operation, and Specialty TransformersDocumento38 pagineChapter 3 Transformer Connections, Operation, and Specialty TransformersSihamaSihamNessuna valutazione finora
- 120 Degree Mode of ConductionDocumento5 pagine120 Degree Mode of ConductionAyshwar Venkatesh75% (4)
- Wien Bridge Oscillator Using OpampDocumento4 pagineWien Bridge Oscillator Using OpampVishesh Kumar SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Rectifier Circuit BasicsDocumento26 pagineRectifier Circuit BasicsShiny SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 - Static Relays and Numerical Protection 4.1 Static RelaysDocumento18 pagineUnit 4 - Static Relays and Numerical Protection 4.1 Static RelaysRushikesh KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronic Circuits Question BankDocumento48 pagineAnalog Electronic Circuits Question BankchaitanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment IIIDocumento2 pagineAssignment IIIPrasenjit DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Godown Wiring - MechatroficeDocumento2 pagineGodown Wiring - MechatroficeKush SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wave Shaping CircuitsDocumento56 pagineWave Shaping CircuitsWaltas KariukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis Proposal For 2021Documento4 pagineSynopsis Proposal For 20212k18-EE-243 Vethushan VinnayagamoorththiNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Outline-TICIDocumento1 paginaCourse Outline-TICISajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties-Of-Matter - of - Matter-And-Change - of - CK-12-Chemistry-Basic S v4 TVB s1Documento6 pagineProperties-Of-Matter - of - Matter-And-Change - of - CK-12-Chemistry-Basic S v4 TVB s1ian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS 221 Herrera-Siklody Nicholas PHYS221 16-04-2009Documento2 paginePHYS 221 Herrera-Siklody Nicholas PHYS221 16-04-2009ian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Absolute Entropy and Its Increase in Disordered SubstancesDocumento13 pagineAbsolute Entropy and Its Increase in Disordered Substancesian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Cooling Coke with Ice Physics QuestionDocumento1 paginaCooling Coke with Ice Physics Questionian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Navigation Fundamentals: Jonathan F. Carrillo, ECEDocumento16 pagineNavigation Fundamentals: Jonathan F. Carrillo, ECEian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Author Rajkumar SharmaDocumento1 paginaAuthor Rajkumar Sharmaian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions: AnswersDocumento1 paginaQuestions: Answersian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Positioning SystemDocumento24 pagineGlobal Positioning Systemian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- HW 02Documento4 pagineHW 02Tabitha HowardNessuna valutazione finora
- PCBDocumento1 paginaPCBian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- DescriptionDocumento2 pagineDescriptionian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- By: Kimberly P. ManaliliDocumento11 pagineBy: Kimberly P. Manaliliian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Img 20180702 0001Documento1 paginaImg 20180702 0001ian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- NB Ra 9163Documento5 pagineNB Ra 9163Vienna Mantiza - PortillanoNessuna valutazione finora
- ROTC Program Information SheetDocumento4 pagineROTC Program Information Sheetian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 10-9-2015Documento4 pagineChapter 1 10-9-2015ian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- MS 1 Handbook PDFDocumento184 pagineMS 1 Handbook PDFian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Refernces EconomicsDocumento13 pagineRefernces Economicsian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 5Documento14 pagine2 5ian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Waste Management in the PhilippinesDocumento3 pagineWaste Management in the Philippinesian jhefer100% (1)
- BibliographyDocumento1 paginaBibliographyian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Updated 1Documento15 pagineChapter 2 Updated 1ian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview of Waste Management in The Philippines Particularly in The Agricultural SectorDocumento1 paginaAn Overview of Waste Management in The Philippines Particularly in The Agricultural Sectorian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Accessories PartDocumento4 pagineAccessories Partian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- AmeconfigDocumento1 paginaAmeconfigMarlynne Vidal AldeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Great DealsDocumento1 paginaGreat Dealsian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- Cineminuto Application FormDocumento1 paginaCineminuto Application Formian jheferNessuna valutazione finora
- NPN Silicon Transistor: High Voltage Switch Mode ApplicationDocumento6 pagineNPN Silicon Transistor: High Voltage Switch Mode ApplicationManuel PradoNessuna valutazione finora
- PARTSDocumento10 paginePARTSTestrooteNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Sensors: Jiturvi Chokshi ENPM-808BDocumento27 pagineGas Sensors: Jiturvi Chokshi ENPM-808Banon_44955929Nessuna valutazione finora
- FST DFS Ge-EgdDocumento5 pagineFST DFS Ge-EgdEric DunnNessuna valutazione finora
- TF Section - MICET 2016Documento21 pagineTF Section - MICET 2016Eddie D SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Capacitor Banks - Schedules FILLEDDocumento11 pagineCapacitor Banks - Schedules FILLEDyahyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Saes N 004Documento5 pagineSaes N 004Mo'tasem SerdanehNessuna valutazione finora
- Solidworks SyllabusDocumento7 pagineSolidworks SyllabusArun SubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is AmplifierDocumento18 pagineWhat Is AmplifierEbayLunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vismat Material V-Ray For SketchupDocumento19 pagineVismat Material V-Ray For SketchupAmer GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Standardization of Welding ElectrodesDocumento8 pagineStandardization of Welding ElectrodesAqsa BanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Agentur H. Willems: Tel.: +49-421-52009-0 List of Manufacturers Fax: +49-421-545858Documento5 pagineAgentur H. Willems: Tel.: +49-421-52009-0 List of Manufacturers Fax: +49-421-545858Trần Minh NhậtNessuna valutazione finora
- FTS ScaleoEUserManualEN 10 1082177Documento2.044 pagineFTS ScaleoEUserManualEN 10 1082177JNessuna valutazione finora
- Argelith Lieferprogramm GBDocumento24 pagineArgelith Lieferprogramm GBmutyokaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatic and Electromagnetic Forces: Electronic Address: Tim - Henley@mail - Utoronto.caDocumento9 pagineElectrostatic and Electromagnetic Forces: Electronic Address: Tim - Henley@mail - Utoronto.caTimothy Murray HenleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurul Ain - nurulain@gmail.comDocumento32 pagineNurul Ain - nurulain@gmail.comMuhamad FarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Specification - EstimationDocumento4 pagineSpecification - EstimationVenkatesan VenkatNessuna valutazione finora
- Hybrid or Standard?: Why The Urge To "Go Green"Documento20 pagineHybrid or Standard?: Why The Urge To "Go Green"Tyler McPhersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Premium Swab Rigs Since 1925Documento8 paginePremium Swab Rigs Since 1925fabricio3fabricio-1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tli R3.0 PDFDocumento6.465 pagineTli R3.0 PDFz_sadiq25% (4)
- Fisher Poistioner CatalogueDocumento12 pagineFisher Poistioner CatalogueUsama IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- JV Punj Lloyd - SICIMDocumento9 pagineJV Punj Lloyd - SICIMBarock NaturelNessuna valutazione finora
- Tek 10-03Documento4 pagineTek 10-03Thai DamNessuna valutazione finora
- Signals and Systems - MjrobertsDocumento3 pagineSignals and Systems - Mjrobertspriyakanthr5883100% (1)