Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids (Practice Problems) : Important Formulae
Caricato da
Sarunkumar BalathTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids (Practice Problems) : Important Formulae
Caricato da
Sarunkumar BalathCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dated On: 22/11/2017
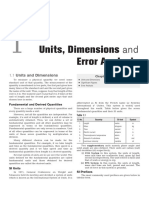
PHYSICS
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS (PRACTICE PROBLEMS)
Important Formulae:
𝐹 𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑑𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛
𝑆𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠 = ; 𝑆𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛 =
𝐴 𝑂𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝐷𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛
′ 𝐹𝐿 𝑚𝑔𝐿
𝑌𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑔 𝑠 𝑀𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑙𝑢𝑠 𝑌 = 𝐴∆𝐿 = 𝜋𝑟 2 ∆𝐿
𝑃𝑉
𝐵𝑢𝑙𝑘 𝑀𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑙𝑢𝑠 𝐵 = ∆𝑉
∆𝑥
Rigidity Modulus 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃 ≈ 𝜃 =
𝐿
1. A load 2 kg produces an extension of 1.5mm in a wire of length 4.5m. The radius of the wire is 0.3 mm. Calculate the
Young’s Modulus of the material of the wire.
2. The diameter of a brass rod is 2 mm. Brass has Young’s Modulus 8.8 x 1010 Pa. Calculate the stress and strain when it
extended by 0.2 % of its length. Also calculate the force exerted.
3. Calculate the percentage increase in the length of a wire of diameter 10-3 m stretched by a force of 10 N. Y of the
material of the wire is 2 x 10 11 Pa.
4. A glass rod has a diameter 1 cm and is 10 cm long. Calculate the largest mass that can be hung from it without
breaking it. Y of glass =6.5 x10 10 Pa and breaking stress for this glass = 5 x 10 7 Pa.
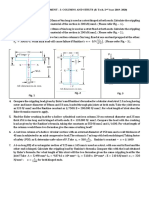
5. Two wires of diameter 0.25 cm, one made of steel and the other made of brass are loaded as
shown in the figure. The unloaded length of steel wire is 1.5 m and that of brass is 1.0 m.
Compute the elongation of the steel and brass wire.
Assume Young’s Modulus of steel 2 x10 11 Pa
Young’s Modulus of brass 9.2 x 10 10 Pa. [NCERT]
6. A metal cube of side 10 cm is subjected to a shear stress 10 4 Nm -2 . Calculate the rigidity
modulus if the top the cube is displaced by 0.05 cm with respect to its bottom.
7. A spherical ball contracts by a volume 0.01 % , when subjected to a normal uniform pressure of 10 7 Pa. Calculate the
bulk modulus of the material of the ball.
8. The stress-strain graph for wires of two materials A and B are given below.
(a) Which material in more ductile?
(b) Which material has greater value of young modulus?
(c) Which of the two is stronger material?
(d) Which material is more brittle?
9. When a spring balances are continuously used for long time, they show wrong reading. Explain why
10. Select the material from the table, which shows more elasticity.
11. Draw the stress-strain graph of a rubber band.
12. Calculate the stress developed in a metal wire when it is strained by 30%. Given young’s modulus of material is
200 GPa.
13. The wire has an unstretched length of 2.40 m and an area of cross section of 3.90 x 10 – 7 m 2 . Determine the
Young’s modulus Y of the material.
14. If the bulk modulus of water is 2 x 10 9 N/m 2, find its compressibility.
15. Which is more elastic, steel or rubber?
16. Between steel and diamond, which is more elastic?
17. What is the necessary condition for the Hooke’s law to be valid?
18. Draw the stress – strain graph of a loading wire.
Mark the following points:
i. Elastic limit ii. Fracture point
iii. Plastic region iv. Elastic region
19. If the young’s moduli of iron and glass are 190 x 109 Nm -2 and 65 x 10 9 Nm -2 respectively. Which is more elastic?
Justify your answer.
20. When the pressure on a sphere is increased by 80 atmospheres, its volume decreases by 0.01%. Find the bulk
modulus of elasticity of the material of the sphere.
21. Young’s modulus for a perfectly rigid body is ---------
22. One end of a rope of a length 4.5 m and diameter 6 mm is fixed to the branch of a tree. A monkey weighing 100 N
jumps to catch the free end and stays there. Find the elongation of the rope. (Young’s modulus = 4.8x10 11 N/ m 2).
23. The stress-strain graph for two materials A and B are given:
(a) Which is more elastic?
(b) Which is stronger?
Additional Problems
1. A load of 2 kg produces an extension of 1 mm in a wire of length 3 m and diameter 1 mm. Calculate the Young’s
Modulus of the material of the wire. [Ans : 7.5 x 10 10N/m2 ]
2. Calculate the percentage increase in length of a wire of diameter 2.5 mm, when stretched by a force of 1000 N. Y of
the material of wire is 12.5 x 1010 N/m2. [Ans : 0.16% ]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresDa EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Assignment No. 1 Materials Science and MetallurgyDocumento2 pagineAssignment No. 1 Materials Science and MetallurgySamruddhi MirganeNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ CH 4 and 5 - 2019 - 20Documento3 pagineMCQ CH 4 and 5 - 2019 - 20Patel 0786Nessuna valutazione finora
- ME6601Documento28 pagineME6601Sridiwakaran ParameswaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Neet Current Electricity Important Questions PDFDocumento28 pagineNeet Current Electricity Important Questions PDFVINOD KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Rot Motion MCQ PDFDocumento2 pagine11 Rot Motion MCQ PDFtanmayNessuna valutazione finora
- CADMDocumento3 pagineCADMSaravana Kumar MNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbse - Grade 7 - Science - CH-1 - Nutrition in PlantsDocumento5 pagineCbse - Grade 7 - Science - CH-1 - Nutrition in PlantsjayeshmananiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.thermal (500+0Documento52 pagine1.thermal (500+0ajayNessuna valutazione finora
- DMM-2 Second Mid Bit PaperDocumento2 pagineDMM-2 Second Mid Bit PaperYeswanth Kumar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pahal ChemistryDocumento98 paginePahal ChemistryMahesh BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Angular Momentum MCQsDocumento2 pagineAngular Momentum MCQsTrue LoverNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 1 Part - 1Documento122 pagineUNIT 1 Part - 1Ysv PavuluriNessuna valutazione finora
- Em WaveDocumento4 pagineEm WavethinkiitNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid State Physics: Unit IVDocumento20 pagineSolid State Physics: Unit IVReddyvari VenugopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9th MCQDocumento6 pagineClass 9th MCQprachi pundhirNessuna valutazione finora
- MF7203-Dec 16 THEORY-OF-METAL-FORMINGDocumento3 pagineMF7203-Dec 16 THEORY-OF-METAL-FORMINGupender100% (1)
- ICSE Class 9 Physics Important QuestionsDocumento2 pagineICSE Class 9 Physics Important QuestionsSagnik MajumderNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective QuestionsDocumento40 pagineObjective QuestionsManohar WaghmodeNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallurgy Question Bank Quize Metals 2Documento31 pagineMetallurgy Question Bank Quize Metals 2abhishek_m_more67% (3)
- Emm MCQ of All Six UnitDocumento121 pagineEmm MCQ of All Six UnitSantosh100% (2)
- Class 9 (Surface Areas and Volumes)Documento3 pagineClass 9 (Surface Areas and Volumes)alvina dhalaitNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Type Questions Chapter # 1 The Scope of Physics: Compiled By: Faizan AhmedDocumento2 pagineObjective Type Questions Chapter # 1 The Scope of Physics: Compiled By: Faizan AhmedSindhu JattNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Type Questions For Material ScienceDocumento44 pagineObjective Type Questions For Material Sciencepiyush138090Nessuna valutazione finora
- Question Paper For Class 12 PhysicsDocumento5 pagineQuestion Paper For Class 12 PhysicsShubham AsthanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Environmental ScienceDocumento4 pagine07 Environmental ScienceRaghavendra SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook 300 General Science Questions PDFDocumento33 pagineEbook 300 General Science Questions PDFDeep Trend100% (1)
- Eamcet Grand Test - 5 Date 06-08-2021Documento20 pagineEamcet Grand Test - 5 Date 06-08-2021M.MUKESH KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Dimension Chapter PDFDocumento25 pagineUnit Dimension Chapter PDFAbhishek100% (1)
- Surface Area 10Documento2 pagineSurface Area 10Smaranil GuchaitNessuna valutazione finora
- Fractional Value SDocumento11 pagineFractional Value SKarim AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- AEC361 2019 Question BankDocumento10 pagineAEC361 2019 Question BankVenky GollavelliNessuna valutazione finora
- Find The Volume of The Given Rectangular Glass Plate Using Vernier Calipers and Screw GaugeDocumento5 pagineFind The Volume of The Given Rectangular Glass Plate Using Vernier Calipers and Screw GaugeGyanRaj Chavan100% (1)
- Practice Assignment Work Energy and PowerDocumento3 paginePractice Assignment Work Energy and PowerAyush GogiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Placid Vidya Vihar Sr. Sec. School: PhysicsDocumento11 paginePlacid Vidya Vihar Sr. Sec. School: PhysicsGouri VandanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test - Chapter 7 - Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms - QuizletDocumento3 pagineTest - Chapter 7 - Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms - QuizletAbhinandan AdmutheNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 8 Icse Board Chemistry Atomic Structure PDFDocumento2 pagineClass 8 Icse Board Chemistry Atomic Structure PDFAgrim VarshneyNessuna valutazione finora
- BAJA SAEINDIA 2020 - POSTER FORMAT FOR GO GREEN EVENT (mBAJA Pithampur)Documento1 paginaBAJA SAEINDIA 2020 - POSTER FORMAT FOR GO GREEN EVENT (mBAJA Pithampur)Akash PavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Transmission System Question BankDocumento18 pagineDesign of Transmission System Question BankAravind50% (2)
- Assignment - 1: C) Excitation Reduction at SourceDocumento2 pagineAssignment - 1: C) Excitation Reduction at Sourcemanoranjan0% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Worksheet - Areas Related To CirclesDocumento2 pagineCBSE Class 10 Mathematics Worksheet - Areas Related To CirclesSandyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Chemical Engg. UET PeshawarDocumento2 pagineDepartment of Chemical Engg. UET PeshawarZakaria UsafxaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class 10 Chapter 13 Exercise 13.1 Surface Areas and Volumes Ncert QaDocumento2 pagineMaths Class 10 Chapter 13 Exercise 13.1 Surface Areas and Volumes Ncert QaJyoti tyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Workbook Exercise of Motion and TimeDocumento7 pagineWorkbook Exercise of Motion and Timesmi_santhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis On Conversion Efficiency of Homojunction and Heterojunction Solar Cell Using Semiconductor MaterialsDocumento4 pagineAnalysis On Conversion Efficiency of Homojunction and Heterojunction Solar Cell Using Semiconductor MaterialsAnonymous izrFWiQNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Engineering Test Assignment: Solution Numerical 1Documento9 pagineMechanical Engineering Test Assignment: Solution Numerical 1Raj PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFDocumento22 pagineCBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFHrithik RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper For ChemistryDocumento23 pagineSample Paper For ChemistryAmit joshiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Year Physics All in One NotesDocumento151 pagine1st Year Physics All in One NotesNabeel Riasat Riasat Ali100% (3)
- Basic Electrical Engineering MCQs PDF 3 PDFDocumento9 pagineBasic Electrical Engineering MCQs PDF 3 PDFAdnan QadeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank BE and B TECH First YearDocumento138 pagineQuestion Bank BE and B TECH First YearRukman Divya SNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - X Science (Electricity and Its Effects)Documento5 pagineCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - X Science (Electricity and Its Effects)Megha SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbse Mixed Test Paper-01Documento12 pagineCbse Mixed Test Paper-01kamalkantmbbsNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in A Plane With AnswersDocumento31 pagineMCQ Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in A Plane With Answerskirki pNessuna valutazione finora
- ZrO2-CaO Phase DiagramDocumento1 paginaZrO2-CaO Phase DiagramJohn Joseph100% (2)
- 2016Documento896 pagine2016Someshwar KoreNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs PTDocumento4 pagineMCQs PTMohsin AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical On ElectrostaticsDocumento2 pagineNumerical On ElectrostaticsAshok PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Mechanics (ME 14.101) Tutorial Sheet-6: (Tension, Compression & Shear)Documento1 paginaApplied Mechanics (ME 14.101) Tutorial Sheet-6: (Tension, Compression & Shear)atulkumargaur26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Henament Physics Exercise Young ModulisDocumento2 pagineHenament Physics Exercise Young ModulisMohamed JameelNessuna valutazione finora
- New Doc 2018-01-21Documento1 paginaNew Doc 2018-01-21Sarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled DocumentDocumento1 paginaUntitled DocumentSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Kas Notification 2019Documento12 pagineKas Notification 2019sun shineNessuna valutazione finora
- Plustwo 2019Documento2 paginePlustwo 2019Sarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- FebruaryDocumento26 pagineFebruarySarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsDocumento101 paginePhysicsSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Sineesh Chettanncurrent BillDocumento1 paginaSineesh Chettanncurrent BillSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- SSCDocumento1 paginaSSCSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Sanoop ChauDocumento1 paginaSanoop ChauSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- 1881653868-Sylabus in EnglishDocumento5 pagine1881653868-Sylabus in EnglishSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- CheDocumento2 pagineCheSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Ak 37Documento2 pagineAk 37Sarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- DFT TablesDocumento6 pagineDFT TablesgalaxystarNessuna valutazione finora
- WT1SDocumento2 pagineWT1SSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- My HomeDocumento1 paginaMy HomeSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- ADocumento2 pagineASarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- My HomeDocumento1 paginaMy HomeSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- FHDDocumento68 pagineFHDSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- BSNL JE SyllabusDocumento2 pagineBSNL JE SyllabusSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Q CHTFRGJDocumento1 paginaQ CHTFRGJSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- IT SyllabusDocumento75 pagineIT SyllabusFiroz FizzNessuna valutazione finora
- DeoDocumento7 pagineDeoSanjay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- GATE Signals and Systems by KanodiaDocumento128 pagineGATE Signals and Systems by Kanodiakaran11383% (6)
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Electronics & Communication General ApitudeDocumento16 pagineNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Electronics & Communication General ApitudeSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Rief IstoryDocumento12 pagineRief Istoryyamz111Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1406211403352941QS ADocumento12 pagine1406211403352941QS ASarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Rate Profile: Bluetooth®Documento21 pagineHeart Rate Profile: Bluetooth®Sarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- C ProgramsDocumento10 pagineC ProgramsSarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Punjab InsurgencyDocumento10 paginePunjab InsurgencySarunkumar BalathNessuna valutazione finora
- Kel 6Documento8 pagineKel 6LalangNessuna valutazione finora
- Sandwich Construction 1. Basic Design PrinciplesDocumento12 pagineSandwich Construction 1. Basic Design PrinciplesKûmãr PrabakaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Material Nonlinear Problems Using Pseudo-Elastic Finite Element MethodDocumento5 pagineAnalysis of Material Nonlinear Problems Using Pseudo-Elastic Finite Element MethodleksremeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Som-I: Assignment - I: Columns and Struts (B. Tech. 2 Year: 2019 - 2020)Documento1 paginaSom-I: Assignment - I: Columns and Struts (B. Tech. 2 Year: 2019 - 2020)Prince SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Varela & Hasbani Arma2017 Rock Mechanics Laboratory Characterization of Vaca Muerta FormationDocumento10 pagineVarela & Hasbani Arma2017 Rock Mechanics Laboratory Characterization of Vaca Muerta Formationandmol5796Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sabine Glas-Peters, Angela Pude, Monika Reimann - Menschen. A1.1 - Deutsch Als Fremdsprache. Arbeitsbuch (2014, Hueber)Documento9 pagineSabine Glas-Peters, Angela Pude, Monika Reimann - Menschen. A1.1 - Deutsch Als Fremdsprache. Arbeitsbuch (2014, Hueber)Mert sefasefeNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete 17 - Autogenous Shrinkage 1Documento8 pagineConcrete 17 - Autogenous Shrinkage 1Robert CoelhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Testing LabDocumento79 pagineMaterial Testing LabBrijesh VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- AISC 360-22 Specification For Structural Steel Buildings PUBLIC REVIEWDocumento329 pagineAISC 360-22 Specification For Structural Steel Buildings PUBLIC REVIEWjackcan501100% (3)
- 1 58503 227 1 2 PDFDocumento22 pagine1 58503 227 1 2 PDFDavor IlicNessuna valutazione finora
- RTM Nagpur University Mechanical Engineering Machining Processes Syllabus (Theory) Course code-BEME401TDocumento27 pagineRTM Nagpur University Mechanical Engineering Machining Processes Syllabus (Theory) Course code-BEME401TxaloliNessuna valutazione finora
- NASTRAN/PATRAN Intro ManualDocumento248 pagineNASTRAN/PATRAN Intro Manualjarzola11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 4Documento2 pagineAssignment 4sstibisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Stabilized Pavement MaterialsDocumento16 pagineChapter 6 Stabilized Pavement Materialsዳጊ ዳጊ ዳጊNessuna valutazione finora
- Ashby Method - SM - 2.1Documento25 pagineAshby Method - SM - 2.1Anand BhiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1: To Calculate The Deformations in A Bar Having Variable Cross-Sectional Area, Using 7 ElementsDocumento21 pagineExperiment 1: To Calculate The Deformations in A Bar Having Variable Cross-Sectional Area, Using 7 ElementsMaria MeharNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Parameters For Eps Geofoam v1Documento3 pagineDesign Parameters For Eps Geofoam v1Bao TruongNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequency Dependence of Complex Moduli of Brain Tissue Using A Fractional Zener ModelDocumento8 pagineFrequency Dependence of Complex Moduli of Brain Tissue Using A Fractional Zener Modellux_kingNessuna valutazione finora
- Lateral Stiffness Characteristics of Tall PDFDocumento19 pagineLateral Stiffness Characteristics of Tall PDFLaila Monteiro A MeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm d4065 PDFDocumento7 pagineAstm d4065 PDFradziNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Mechanical Properties Between PE80 and PE100 Pipe MaterialsDocumento8 pagineComparison of Mechanical Properties Between PE80 and PE100 Pipe MaterialsFields NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Member EI ValueDocumento4 pagineComposite Member EI ValueArjun RajaNessuna valutazione finora
- LE1 Problem Set PDFDocumento14 pagineLE1 Problem Set PDFJunhong BapNessuna valutazione finora
- Ov Ed: Type 1 M Asonry Support CalculationDocumento12 pagineOv Ed: Type 1 M Asonry Support Calculationshare4learnNessuna valutazione finora
- Fea To Study Effect of Basalt FRP On Flexural Behavior of ConcreteDocumento43 pagineFea To Study Effect of Basalt FRP On Flexural Behavior of ConcreteAya SalahNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Formet KumariniwasDocumento30 pagineReport Formet KumariniwasshaimenneNessuna valutazione finora
- MosDocumento20 pagineMosutsav_koshtiNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 3716 01 Durometer Hardness For SiliconesDocumento5 pagine11 3716 01 Durometer Hardness For SiliconesKiran ShetNessuna valutazione finora
- Rigid Pavement Design As Per IRC 58 2011 BUC and TDC AnalysisDocumento3 pagineRigid Pavement Design As Per IRC 58 2011 BUC and TDC Analysisarvind sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Limit State Design TheoryDocumento3 pagineLimit State Design TheoryEvans KishNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeDa EverandThe Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (52)
- Principles of Welding: Processes, Physics, Chemistry, and MetallurgyDa EverandPrinciples of Welding: Processes, Physics, Chemistry, and MetallurgyValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsDa EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (242)
- Waste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretDa EverandWaste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- How to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionDa EverandHow to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Building Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1Da EverandBuilding Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialDa EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedDa EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Building Physics -- Heat, Air and Moisture: Fundamentals and Engineering Methods with Examples and ExercisesDa EverandBuilding Physics -- Heat, Air and Moisture: Fundamentals and Engineering Methods with Examples and ExercisesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseDa EverandThe Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsDa EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- The Everything Woodworking Book: A Beginner's Guide To Creating Great Projects From Start To FinishDa EverandThe Everything Woodworking Book: A Beginner's Guide To Creating Great Projects From Start To FinishValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Civil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeDa EverandCivil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Art of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionDa EverandArt of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&ADa EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&ANessuna valutazione finora
- Estimating Construction Profitably: Developing a System for Residential EstimatingDa EverandEstimating Construction Profitably: Developing a System for Residential EstimatingNessuna valutazione finora
- Woodworking: 25 Unique Woodworking Projects For Making Your Own Wood Furniture and Modern Kitchen CabinetsDa EverandWoodworking: 25 Unique Woodworking Projects For Making Your Own Wood Furniture and Modern Kitchen CabinetsValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (4)
- History of Smart Textiles: A Comprehensive Guide To E-TextilesDa EverandHistory of Smart Textiles: A Comprehensive Guide To E-TextilesNessuna valutazione finora
- Exposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle Against DuPontDa EverandExposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle Against DuPontValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (18)
- Construction Project Management 101: For Beginners & New GraduatesDa EverandConstruction Project Management 101: For Beginners & New GraduatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics Diploma Interview Q&A: Career GuideDa EverandPower Electronics Diploma Interview Q&A: Career GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Life: Construction Management Guide from A-ZDa EverandReal Life: Construction Management Guide from A-ZValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)