Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
University 2 Marks Ans DTSSP
Caricato da
santh_213Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
University 2 Marks Ans DTSSP
Caricato da
santh_213Copyright:
Formati disponibili
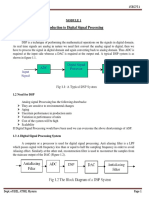
unit i
1. What are energy and power signals? (APR/MAY 17)
Energy signal: A finite energy signal is periodic sequence, which has a finite energy but zero
average power.
Power signal: An Infinite energy signal with finite average power is called a power signal.
2.Describe sampling theorem. (APR/MAY 17)
According to the sampling theorem, a band limited signal x(t) having a finiter energy,which has no
frequency components higher than fm hertz,can completely described and reconstructed from its
samples taken at the rate of 2fm samples per second.Also, the sampling rate of 2fm samples per
second is called the nyquist rate and its reciprocal 1/2πfm is called nyquist period.
1. Distinguish between digital signal & discrete-signal representation.(NOV/DEC 16)
2.IF x(n)=x(n+1)+x(n-2),is the system causal system? (NOV/DEC 16)
3.Determine wheather the system is causal system y(n)=x(n)+1/(x(n-1))
4. what is anti-aliasing filter. (MAY/JUNE 16)
A filter is used to reject frequency signals before it is sampled to reduce the
aliasing is anti-aliasing filter
5.Given a continuous time signal x(t)= 2cos500πt. What is the Nyquist rate
and fundamental frequency of the signal? (NOV/DEC 15)
ω =500π
2πf= 250π
f= 250Hz
Nyquist rate Fs=2fm= 2x250= 500Hz.
6. Determine whether x[n]=u[n] is a power signal or an energy signal.
The energy of a discrete time signal x(n) is defined as
The average power of a discrete time signal x(n) is defined as
Here E= and P= Finite. Therefore the given signal is a power signal.
unit II
1. What are THE properties of (ROC) region of convergence? (APR/MAY 17)
ROC contains strip lines parallel to jω axis in s-plane.
If x(t) is absolutely integral and it is of finite duration, then ROC is entire s-plane.
If x(t) is a right sided sequence then ROC : Re{s} > σo.
If x(t) is a left sided sequence then ROC : Re{s} < σo.
If x(t) is a two sided sequence then ROC is the combination of two regions.
2.Find the convalution of the input signal {1,2,1} and its impulse is {1,1,1} using Z transform?
(APR/MAY 17)
1. Find the system transfer function H(z) if y(n)=x(n)+y(n-1). (NOV/DEC 16)
2. Explain the relationship between S-plane & Z-plane. (NOV/DEC 16)
3. DETERMINE ROC & Z-transform OF THE FOLLOWING FINITE DURATION SIGNALS?
(i)x(n)={3,2,2,3,5,0,1)
(ii)x(n)=δ(n-k)
5.What is meant by region of convergence(ROC) of Z transform?state its
properties.
The region of conve X(z) is the set of all values of z for which X(z) attains a
finite value.
PROPERTIES
The ROC is a ring or disk in the Z – plane centered at the origin.
The ROC cannot contains any poles.
The ROC of an LTI stable system contains the unit.
The ROC must be a connected region
6. State initial value theorem& final value theorem.
If x(n)and X(z) are z-Transform pairs, then the initial value of x(z) ,
provided that the first derivative of x(t) should be Laplace transformable.
If x(n)and X(z) are z-Transform pairs, then the final value of x(z) is given as
have no pole on or outside the unit circle.
unit III
1. Define twiddle factor. Write its magnitude & phase angle. (APR/MAY 17)
The complex number N is called phase factor or twiddle factor.
2. Calculate the number of multiplications & additions for 32 point DFT and FFT.
(APR/MAY 17)
For the computation of N-point DFT, N^2 complex multiplications and N[N-1] Complex additions are
required.
For the computation of N-point FFT ,Complex multiplications = N/2 log2N &
Complex additions = N log2N
For N=32, the number of the complex multiplications is equal to 32/2log232=16*5=80.
1. Why is it required to do zero padding in DFT analysis? (NOV/DEC 16)
Let the sequence x (n) has a length L. If we want to find the N point DFT (N>L) of the
sequence x(n),we have to add (N-L) zeros to the sequence x(n). This is known as zero
padding. The uses of padding a sequence with zeros are (i) Better display of the frequency
spectrum.(ii) With zero padding, the DFT can be used in linear filtering.
2.What is the need for windowing techniques in Fourier transform signals ? (NOV/DEC 16)
3. Draw the basic butterfly diagram for radix -2 DIT -FFT
4. What are the applications of FFT algorithms?
1. Linear filtering 2. Correlation 3. Spectrum analysis
5. hat is the speed of improvement factor in calculating 256-point DFT of a sequence
using direct computation and computation and FFT algorithms? (NOV/DEC 15)
The number of complex multiplications required using direct computation is N^2=256^2= .
The number of complex multiplications required using FFT is = = . Speed improvement
factor = N^2/ = .
unit IV
1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of digital filters?
High thermal stability due to absence of resistors, inductors and capacitors.
Increasing the length of the registers can enhance the performance characteristics like
accuracy, dynamic range, stability and tolerance.
The digital filters are programmable.
Multiplexing and adaptive filtering are possible.
Highly immune to noise.
No problems in input or output impedance matching.
Disadvantages of digital filters:
The bandwidth of the discrete signal is limited by the sampling frequency.
The performance of the digital filter depends on the hardware used to implement the filter.
The quantization error arises due to finite word length of digital samples.
2. What is prewarping?
The effect of the non-linear compression at high frequencies can be compensated by Prewarping,
i.e the conversion of the digital frequencies to analog frequencies are called prewarping .
1.Why are digital filters more useful than analog filters? (NOV/DEC 16)
2.Name one method that converts the transfer function of a analog into the digital filter.
(NOV/DEC 16)
Unit V
1. What is meant by pipeline technique? How to determine depth?
A technique used in advanced microprocessors where the microprocessor begins executing a
second instruction before the first has been completed. That is, several instructions are in
the pipeline simultaneously, each at a different processing stage.
1. What is Gibb’s phenomenon (or Gibb’s Oscillation)? (NOV/DEC 16)
In FIR filter design by Fourier series method the infinite duration impulse response is truncated to
finite duration impulse response at n= . The abrupt truncation of impulse response introduces
oscillations in the passband and stopband. This effect is known as Gibb’s
phenomenon (or Gibb’s Oscillation).
2.State hoe the spectrum meter application can be designed with DS Processors. (NOV/DEC 16)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Gait AnalysisDocumento8 pagineGait AnalysisArief Azli100% (1)
- 2 Marks DSP Bits EceDocumento22 pagine2 Marks DSP Bits EceDustin GrahamNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento101 pagineDigital Signal ProcessingDheekshith ShettigaraNessuna valutazione finora
- IT 1252 - Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento22 pagineIT 1252 - Digital Signal Processinganon-384794100% (3)
- Laboratory 3 Digital Filter DesignDocumento8 pagineLaboratory 3 Digital Filter DesignModitha LakshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessDa EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Frequency Domain ProcessingDocumento42 pagineFrequency Domain ProcessingInJune YeoNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP 2 MaarksDocumento30 pagineDSP 2 MaarksThiagu RajivNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics For Machine Learning - Techniques For ExploringDocumento484 pagineStatistics For Machine Learning - Techniques For ExploringJuan Manuel Báez Cano100% (5)
- Ix Maths Chapter 8 QuadrilateralsDocumento20 pagineIx Maths Chapter 8 QuadrilateralsDVAC-SERVERNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM C403-16 Time of Setting of Concrete Mixtures by Penetration ResistanceDocumento7 pagineASTM C403-16 Time of Setting of Concrete Mixtures by Penetration ResistanceRajnikanth Gedhada50% (4)
- Digital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsDa EverandDigital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Integrating My Results in ChemStation - 121008Documento50 pagineIntegrating My Results in ChemStation - 121008William QuiroaNessuna valutazione finora
- Passive and Active RF-Microwave Circuits: Course and Exercises with SolutionsDa EverandPassive and Active RF-Microwave Circuits: Course and Exercises with SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Processing of Remotely-Sensed Images: An IntroductionDa EverandComputer Processing of Remotely-Sensed Images: An IntroductionNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Bit Sigma Delta ADC DesignDocumento10 pagine1 Bit Sigma Delta ADC DesignNishant SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento25 pagineDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Digital Signal ProcessingSETNHILNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 HRTHDocumento22 pagine9 HRTHNithindev GuttikondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Marks DSPDocumento16 pagineTwo Marks DSPReeshma.GogulaNessuna valutazione finora
- EC2302 QB PDFDocumento22 pagineEC2302 QB PDFokhtayaNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP Solved Question BankDocumento19 pagineDSP Solved Question Banksakshi_kapuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing Two MarksDocumento11 pagineDigital Signal Processing Two MarksDelphin ShibinNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP and Power System ProtectionDocumento11 pagineDSP and Power System ProtectionsegamegaNessuna valutazione finora
- EC8553 2marksDocumento20 pagineEC8553 2marksSNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Marks Questions & Answers: Cs-73 Digital Signal Processing Iv Year / Vii Semester CseDocumento18 pagine2 Marks Questions & Answers: Cs-73 Digital Signal Processing Iv Year / Vii Semester CseprawinpsgNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP Two Marks - Unit I-IVDocumento27 pagineDSP Two Marks - Unit I-IVDhariniNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Converters1Documento30 pagineData Converters1Vidyanand PattarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Marks Questions & Answers: Cs-73 Digital Signal Processing Iv Year / Vii Semester CseDocumento18 pagine2 Marks Questions & Answers: Cs-73 Digital Signal Processing Iv Year / Vii Semester CsehariharankalyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dspa Word FileDocumento82 pagineDspa Word FilenithinpogbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee 6403 - Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing (April/ May 2017) Regulations 2013Documento4 pagineEe 6403 - Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing (April/ May 2017) Regulations 2013selvakumargeorg1722Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Introduction To Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento15 pagineUnit 1 Introduction To Digital Signal ProcessingPreetham SaigalNessuna valutazione finora
- Elec9123 DSP DesignDocumento7 pagineElec9123 DSP DesignSydney FinestNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP - Ece - 5th Sem (2mark Q&A)Documento21 pagineDSP - Ece - 5th Sem (2mark Q&A)vinothNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP)Documento0 pagineDigital Signal Processing (DSP)www.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- 07a Fourier AnalysisDocumento20 pagine07a Fourier AnalysisPersonOverTwoNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Material (Question Bamk)Documento4 pagineCourse Material (Question Bamk)Guna PriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP 2 MarksDocumento20 pagineDSP 2 MarksSanthosh SandyNessuna valutazione finora
- It6502 2m-1 RejinpaulDocumento12 pagineIt6502 2m-1 RejinpaulTejaswini PydiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wavelet Transform Approach To Distance: Protection of Transmission LinesDocumento6 pagineWavelet Transform Approach To Distance: Protection of Transmission LinesthavaselvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kings: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocumento5 pagineKings: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringA RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- DTSP 2marks PDFDocumento20 pagineDTSP 2marks PDFishuNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing Two Mark Question With Answer Unit IIIDocumento4 pagineDigital Signal Processing Two Mark Question With Answer Unit IIIsarathbabumjNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece Odd9Documento17 pagineEce Odd9Venkat MuruganNessuna valutazione finora
- Adaptive Variable: Window Algorithm For Transformer Differential Protection RelayDocumento5 pagineAdaptive Variable: Window Algorithm For Transformer Differential Protection RelayproteccionesNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Material (Question Bamk)Documento4 pagineCourse Material (Question Bamk)lakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP) - Jeppiar CollegeDocumento22 pagineDigital Signal Processing (DSP) - Jeppiar CollegeKarthi KeyanNessuna valutazione finora
- B.Suresh Kumar Ap/Ece Tkec Ec6502 PDSP Two MarksDocumento14 pagineB.Suresh Kumar Ap/Ece Tkec Ec6502 PDSP Two MarksSuresh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP Algorithm and Architecture PDFDocumento199 pagineDSP Algorithm and Architecture PDFBheemareddiNessuna valutazione finora
- CRT MaterialDocumento33 pagineCRT MaterialSaiChandraNNessuna valutazione finora
- Spread Spectrum Communications Using Chirp SignalsDocumento5 pagineSpread Spectrum Communications Using Chirp SignalsArkaprava MajeeNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview of FMCW Systems in MATLABDocumento7 pagineAn Overview of FMCW Systems in MATLABHenry TangNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance and Analysis of OFDM Signal Using Matlab SimulinkDocumento7 paginePerformance and Analysis of OFDM Signal Using Matlab SimulinkIJMERNessuna valutazione finora
- Kiings DSPDocumento4 pagineKiings DSPkar07indiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rajastan College of Engineering For Women: Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento7 pagineRajastan College of Engineering For Women: Digital Signal Processingchandra1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- National University of Modern Languages, Islamabad Communication System LabDocumento7 pagineNational University of Modern Languages, Islamabad Communication System LabImMalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsDa EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationDa EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDDa EverandRadio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Linearities in Passive RFID Systems: Third Harmonic Concept and ApplicationsDa EverandNon-Linearities in Passive RFID Systems: Third Harmonic Concept and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing Techniques and Applications in Radar Image ProcessingDa EverandDigital Signal Processing Techniques and Applications in Radar Image ProcessingNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Case Studies on Signal, Audio and Image Processing Using MatlabDa EverandSome Case Studies on Signal, Audio and Image Processing Using MatlabNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation Metrics For Data ClassificationDocumento12 pagineEvaluation Metrics For Data ClassificationelmannaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unbalanced Transportation ModelDocumento4 pagineUnbalanced Transportation ModelSunil Prasanna PatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Waling-Waling: San Isidro, Angono, RizalDocumento3 pagineGrade 9 Waling-Waling: San Isidro, Angono, RizalMark Cris Fabella FabaliñaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Hybrid Firefly Algorithm Approach For Job Shop Scheduling ProblemDocumento11 pagineA Hybrid Firefly Algorithm Approach For Job Shop Scheduling ProblemIJRASETPublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Latihan f2 Ratio 1Documento4 pagineLatihan f2 Ratio 1sifir1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Using of Taguchi Method To Optimize The Casting of Al-Si /al O CompositesDocumento8 pagineUsing of Taguchi Method To Optimize The Casting of Al-Si /al O Compositesarun_premnathNessuna valutazione finora
- CDocumento20 pagineCDoc NaziaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Exam Q3Wk1Documento5 pagineSummative Exam Q3Wk1Shaira ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- Mat Chapter 18Documento29 pagineMat Chapter 18hemant_durgawaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Mechanics ME 212 - Week 1 PDFDocumento39 pagineSolid Mechanics ME 212 - Week 1 PDFAlpha WolfNessuna valutazione finora
- Hill CodeDocumento2 pagineHill CodeVilhena FonsecaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wet-Bulb Temperature From RH and Air TemperatureDocumento3 pagineWet-Bulb Temperature From RH and Air TemperatureJorge Hernan Aguado QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- CS530 ApproximationDocumento12 pagineCS530 ApproximationShagunNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Review Technology Technology: Advancements AdvancementsDocumento9 pagineReview Review Technology Technology: Advancements AdvancementsFatih KarabacakNessuna valutazione finora
- Pi Systems MatlabDocumento32 paginePi Systems MatlabvervesolarNessuna valutazione finora
- THere's A Tree Plan GuideDocumento22 pagineTHere's A Tree Plan Guidemeiling_1993Nessuna valutazione finora
- Churn Prediction Using MapReduce and HBa PDFDocumento5 pagineChurn Prediction Using MapReduce and HBa PDF7565006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry XI Chapter No. 2Documento1 paginaChemistry XI Chapter No. 2Abdul Haleem PanhwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Protecting Portfolios Using Correlation DiversificationDocumento7 pagineProtecting Portfolios Using Correlation Diversificationselozok1Nessuna valutazione finora
- The GMAT SyllabusDocumento4 pagineThe GMAT SyllabusAnoop MuraliNessuna valutazione finora
- Measure TheoryDocumento39 pagineMeasure TheorySutapa BornaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tenta 20150610LDocumento2 pagineTenta 20150610LPedro Antonio Marrone GaudianoNessuna valutazione finora
- On The Burnside ProblemDocumento13 pagineOn The Burnside ProblemEpic WinNessuna valutazione finora
- Amin A 2014 PHD Thesis PDFDocumento197 pagineAmin A 2014 PHD Thesis PDFPedroNessuna valutazione finora