Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Gensoc (Midterms)
Caricato da
aly0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
28 visualizzazioni3 pagineSocialization is the lifelong process by which individuals develop their human potential and learn the culture of their society. It involves acquiring social statuses, roles, and a sense of self or personality. Key factors that influence personality development include biological inheritance, environment, and social interaction. Several theories view culture and social interaction as most influential. Socialization occurs through various agencies such as family, school, peers, media and workplace, which transmit social norms and expectations to individuals.
Descrizione originale:
g
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoSocialization is the lifelong process by which individuals develop their human potential and learn the culture of their society. It involves acquiring social statuses, roles, and a sense of self or personality. Key factors that influence personality development include biological inheritance, environment, and social interaction. Several theories view culture and social interaction as most influential. Socialization occurs through various agencies such as family, school, peers, media and workplace, which transmit social norms and expectations to individuals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
28 visualizzazioni3 pagineGensoc (Midterms)
Caricato da
alySocialization is the lifelong process by which individuals develop their human potential and learn the culture of their society. It involves acquiring social statuses, roles, and a sense of self or personality. Key factors that influence personality development include biological inheritance, environment, and social interaction. Several theories view culture and social interaction as most influential. Socialization occurs through various agencies such as family, school, peers, media and workplace, which transmit social norms and expectations to individuals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
Socialization - Process by which individual acquires a status, plays
children become participating and a corresponding role and emerges
functioning members of society and fit with a personality
into an organized way of life as mature
adults Social status - refers to the social
portion of a person in the group
- refers to life long process of
learning and relearning. Two types of status
1.) Ascribed - determined by births
- refers to the lifelong experience 2.) Achieved - refers to the status which
by which individuals develop the person attains through his efforts,
their human potentials and learn intelligence, and choice
culture
Social Role - refers to the functions,
- the process by which we acquire duties, responsibilities, and behavioral
those modes of thinking, feeling, expectations attached to the social status
and acting that are necessary to
participate effectively in the Personality - A persons consistent
larger community patterns of acting, thinking and feeling
- process by which we acquire - the organization of the
social identities and internalize biological, psychological, social,
the values and roles of our social cultural, and moral factors which
world underlie a persons behavior.
- process by which a society - Refers to a more or less enduring
transmits its cultural values to organization of forces within an
individuals in order that they can individual, associated with a
function properly as its members complex of fairly consistent
attitudes, values, and modes of
- Its a process whereby a person perception which account for the
acquires and internalizes the individuals consistency of
behavior, concept, knowledge behavior
and skills that are essential for
social living - Refers to the sum total of all the
physical or biological,
- Process of fitting into an psychological, or mental, social
organized way of life and or cultural, emotional, and
established cultural tradition spiritual traits of a person which
underlie his behavior and makes
- It includes the complementary him distinct
process of transmission of the
culture and social heritage and - the way by which the individual
the development of personality is interrelated through ideas,
actions, and attitudes to the non-
- The learning process where the human aspects of his
environment and biological
heritage Symbol interactionism - This theory
poses that self-identity is developed
Factors that affect personality through the social interaction with
development others, mediated by language in the
1.) Biological inheritance or heredity process of socialization
Heredity - Refers to the physical
and mental traits transmitted by the Culture and personality - This
parents to their offspring through the personality theory held by anthropologist
germ plasma views the cultural environment as the
main factor for determining human
2.) Environment - refers to geographic, behavior
cultural, and social environment
Franz Boas - views that personality is
3 major systems of personality: found in the culture and that significant
1.) Id - the reservoir of sexual and differences in personality are learned
aggressive urges.
- Its centered on the Charles Darwin - human behavior was
satisfaction of basic needs like food and instinctive, simple or nature
sex and dominated by the pleasure
principle. John B Watson - Behaviorism; which
held that behavior is not instinctive but
2.) Ego - The rational part of the self and learned
interprets information obtained through
the sense and that finds realistic and Culture and Personality -Cultural
acceptable ways of satisfying biological determinism
cravings. The cognitive and intellectual -Personality development theory
processes are controlled by the ego held by anthropologist views the cultural
environment as the main factor for
3.) Superego - conscience stands for the determining human behavior
internalized ideas of right and wrong, the
traditional values and morals of the Franz Boas - View that personality
society development results from learning what
is found in the culture and that
Theories of personality development significant difference in personality are
and the social self learned.
Freuds Theory of socialization - A form
of biological determinism which holds Symbolic Interactionism - This theory
that socialization is a process poses that self-identity is developed
characterized by the internal struggle through the social interaction with
between the biological components and others, mediated by language in the
the social-cultural environment. process of socialization (Cooley &
Mead)
-Freud proposed the personality
consisted of three major systems; id, Cooley and the Looking-Glass Self -
ego, and superego The ability of children to visualize
themselves through the eyes of others, to Mass media - informs, educates, and
imagine how they appear to others is entertains
what Cooley calls the looking-glass self Workplace - the individual gets
or the social self socialized to its norms and values and
finds his or her place in its hierarchy of
Mead and the Development of the self statuses
- George Herbert Mead expanded Gender socialization - an interaction
Cooleys idea of social self by relating with the family and other agencies of
the idea of the self concept to role socialization
talking. He believed that the behavior Sex - refers to the biological or
and perception held by individuals are anatomical differences between males
influenced by the social groups of which and females. Certain behavior patterns,
they are members. attitudes, and motivations are considered
appropriate for males or females of a
Erving Goffman and the particular culture
dramaturgical approach - Erving made
use of the use of dramaturgical approach
with his expression, All the world is a
stage. He said that individuals are
performing and acting for their audience
in everyday life
Role - refers to acting in accordance
with the expected norms attached to a
particular position
Role performance - the actual conduct
of the role in accordance with the
position
Human infant - born helps and has no
concept of self. At age 2, she/he acquires
a crude self awareness
Agencies of Socialization
Family - first and most influential social
group in the childs life
Peer Group - the individual is more or
less in cooperative interaction with
people of the same age group, and is
influenced by its norms, interest, values
Church - provides spiritual guidance,
norms of conduct, and rules of behavior
School - formal agency for weaning the
child from home and introducing him or
her into the society
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Summary Of "Behavioral Psychology" By José Bleger: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESDa EverandSummary Of "Behavioral Psychology" By José Bleger: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Of "The Interpretation Of Cultures" By Clifford Geertz: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESDa EverandSummary Of "The Interpretation Of Cultures" By Clifford Geertz: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Peronality and Socialization SemiFinal3.1Documento36 paginePeronality and Socialization SemiFinal3.1Ran CamallereNessuna valutazione finora
- Socialization and PersonalityDocumento14 pagineSocialization and PersonalityAlfonse Sarmiento100% (1)
- Personality and SocializationDocumento9 paginePersonality and SocializationRhazellaCuasayNessuna valutazione finora
- Becoming A Member of SocietyDocumento5 pagineBecoming A Member of SocietyPelayo ElyzherNessuna valutazione finora
- Becoming A Member of SocietyDocumento26 pagineBecoming A Member of SocietyBro. Khyean Gabriel C. SilvestreNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Behavior and Social Environment: "The Individual Is A Biopsychosocial Being" Means That There IsDocumento104 pagineHuman Behavior and Social Environment: "The Individual Is A Biopsychosocial Being" Means That There IsJerson GozarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sociology and The Study of SocietyDocumento2 pagineSociology and The Study of SocietyMae BalacanaoNessuna valutazione finora
- UTS ReviewerDocumento19 pagineUTS ReviewerJohn Philip ParasNessuna valutazione finora
- Diffun Campus: College of Teacher EducationDocumento4 pagineDiffun Campus: College of Teacher EducationMaden betoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sociology Series 4Documento24 pagineSociology Series 4Saleha ZainNessuna valutazione finora
- Socialization and Personality DevelopmentDocumento17 pagineSocialization and Personality Developmentmeck josephNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1. W8. Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocumento12 pagineQ1. W8. Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsNatsumiGraceNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 UCSP Module Chapter 6Documento9 pagine2 UCSP Module Chapter 6jannprems01Nessuna valutazione finora
- CSP Mod4&5 Notes g11Documento23 pagineCSP Mod4&5 Notes g11Louise TeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Explains The Development of One's Self & Others As A Product of Socialization & EnculturationDocumento25 pagineExplains The Development of One's Self & Others As A Product of Socialization & Enculturationdarlene jane maynesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ucsp WK3 IplanDocumento3 pagineUcsp WK3 IplanJosephine May PitosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethics WEEKS 1 9Documento17 pagineEthics WEEKS 1 9Jhann Lei DapitilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento3 pagineChapter 2Ken CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Ucsp Notes Chapter 4Documento5 pagineUcsp Notes Chapter 4Jacinthe Angelou D. PeñalosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual: of Self in Everyday Life, Tried To Show How Certain Social ProcessesDocumento3 pagineIndividual: of Self in Everyday Life, Tried To Show How Certain Social ProcessesLawrence Sean MotinNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2: Culture in Moral Behavior and Developing Virtue As A HabitDocumento6 pagineModule 2: Culture in Moral Behavior and Developing Virtue As A HabitMina M. SumaoangNessuna valutazione finora
- PHL 1B ETHICS 2 Module 2 Without EvaluationDocumento11 paginePHL 1B ETHICS 2 Module 2 Without EvaluationRommel Soliven EstabilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Ucsp 2Documento10 pagineUcsp 2christine abilaNessuna valutazione finora
- UCSP - ReviewerDocumento2 pagineUCSP - ReviewernjlexbackupaccNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento26 pagineUntitledApril CananeaNessuna valutazione finora
- GE 1 - 5 - Anthropological View of SelfDocumento3 pagineGE 1 - 5 - Anthropological View of SelfJarixa BalbuenaNessuna valutazione finora
- BROCHUREDocumento2 pagineBROCHUREFeane LamasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Becoming A Member of Society - Handout 11 PDFDocumento4 pagineBecoming A Member of Society - Handout 11 PDFHaron BusranNessuna valutazione finora
- Uts Midterms ReviewerDocumento7 pagineUts Midterms ReviewerRegie BayaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding The Self PPT Presentation 2018a Chapter 1Documento16 pagineUnderstanding The Self PPT Presentation 2018a Chapter 1Marshall TeachNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Behavior and Victimology: Elma Jane M BorjaDocumento190 pagineHuman Behavior and Victimology: Elma Jane M BorjaCounter IntelligenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Telos Signifying Something Infinite Toward TheDocumento2 pagineTelos Signifying Something Infinite Toward TheChristine Isabel BaclitNessuna valutazione finora
- Ucsp Reviewer FinalsDocumento15 pagineUcsp Reviewer FinalsMigaeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Becoming A Member of A SocietyDocumento53 pagineBecoming A Member of A SocietyHenry BuemioNessuna valutazione finora
- Uts ReviewerDocumento15 pagineUts ReviewerVivien TaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- UNDERSTANDING CULTURE SOCIETY AND POLICY ReviewerDocumento12 pagineUNDERSTANDING CULTURE SOCIETY AND POLICY ReviewerAlexia SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Social PsychologyDocumento17 pagineSocial PsychologyKzghnNessuna valutazione finora
- Socialization PresentationDocumento44 pagineSocialization Presentationsidrosaurus100% (1)
- SocialisationDocumento23 pagineSocialisationakshita upadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Socio, Anthro, Psychological PerspectiveDocumento89 pagineSocio, Anthro, Psychological PerspectiveAngelicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Have A Nice Day ClassDocumento30 pagineHave A Nice Day ClassMira EgarNessuna valutazione finora
- UTS ReviewerDocumento4 pagineUTS Reviewerjaninasachadelacruz0119Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm ModuleDocumento5 pagineMidterm ModuleArah Lyn ApiagNessuna valutazione finora
- UTS Module2NotesDocumento5 pagineUTS Module2NotesKorina RocasNessuna valutazione finora
- Udself Midterm NotesDocumento22 pagineUdself Midterm NotesmrnxakeiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Socialization: Quarter 1 - Module 5Documento5 pagineSocialization: Quarter 1 - Module 5Johanna Gultiano100% (1)
- Orca Share Media1662297772350 6972182195761793320Documento7 pagineOrca Share Media1662297772350 6972182195761793320Risavina Dorothy CondorNessuna valutazione finora
- Sociological Views of The SelfDocumento3 pagineSociological Views of The SelfRechiel Joy Espulgar LactaoenNessuna valutazione finora
- Education and SocializationDocumento29 pagineEducation and Socializationshaira alliah de castro100% (1)
- UCSP ReviewerDocumento3 pagineUCSP ReviewerKarl SiaganNessuna valutazione finora
- SOCIOLOGYDocumento49 pagineSOCIOLOGYStephanie Ann MARIDABLENessuna valutazione finora
- C1 Intro To CultureDocumento20 pagineC1 Intro To CultureYong ZhenNessuna valutazione finora
- Enculturation and SocializationDocumento21 pagineEnculturation and SocializationNikkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ucsp Unit Iii ReviewerDocumento7 pagineUcsp Unit Iii Reviewerslsuls.sheekainasalvaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fss Shashank JainDocumento5 pagineFss Shashank JainShashank JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4: Becoming A Member of The Society Lesson 1: Socialization and Enculturation Socialization B. ReligionDocumento17 pagineUnit 4: Becoming A Member of The Society Lesson 1: Socialization and Enculturation Socialization B. ReligionMichiiee BatallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Democracy and Education & Other Writings (A Collected Edition): My Pedagogic Creed, The School and Society, The Child and the Curriculum…Da EverandDemocracy and Education & Other Writings (A Collected Edition): My Pedagogic Creed, The School and Society, The Child and the Curriculum…Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Rural Mind and Social Welfare (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Da EverandThe Rural Mind and Social Welfare (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rec1967 124Documento70 pagineRec1967 124anaghaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.proceeding Snib-Eng Dept, Pnp-IndonesiaDocumento11 pagine7.proceeding Snib-Eng Dept, Pnp-IndonesiamissfifitNessuna valutazione finora
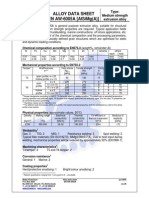
- Calculation of Load Capacity of Shafts and Axles: Supplementary 1 To DIN 743Documento8 pagineCalculation of Load Capacity of Shafts and Axles: Supplementary 1 To DIN 743Karthik VaidhyanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary School: Literature Review & Case StudyDocumento89 paginePrimary School: Literature Review & Case StudySresta100% (1)
- Data 6005ADocumento1 paginaData 6005AErick De La RoSaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ms. Merrick's CSEC Geography Crash Course Booklet-1Documento30 pagineMs. Merrick's CSEC Geography Crash Course Booklet-1shalini100% (4)
- Basic Color TheoryDocumento12 pagineBasic Color TheorysasankaNessuna valutazione finora
- Application For Petitioned Class: College of Engineering and ArchitectureDocumento2 pagineApplication For Petitioned Class: College of Engineering and ArchitectureJohn A. CenizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Image Filtering: Low and High FrequencyDocumento5 pagineImage Filtering: Low and High FrequencyvijayNessuna valutazione finora
- Layout Proposal CSD 17 5613Documento1 paginaLayout Proposal CSD 17 5613Cesar Garay RangelNessuna valutazione finora
- Rubric For Use When Evaluating Lesson Plan PresentationsDocumento1 paginaRubric For Use When Evaluating Lesson Plan PresentationsSajid AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Lakes White Paper PDFDocumento16 pagineData Lakes White Paper PDFRKNessuna valutazione finora
- Concurrent Manager ConceptDocumento9 pagineConcurrent Manager Conceptnikhil_cs_08Nessuna valutazione finora
- EDUC5271 Week 3 Written Assignment Unit 3Documento7 pagineEDUC5271 Week 3 Written Assignment Unit 3Meleisa GordonNessuna valutazione finora
- Acumuladores de AP Atlas CopcoDocumento32 pagineAcumuladores de AP Atlas CopcovictorhernandezregaNessuna valutazione finora
- On-the-Job Training Blueprint - ConciergeDocumento28 pagineOn-the-Job Training Blueprint - ConciergeRHTi BDNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 1 HTDocumento57 pagineUnit - 1 HTSoham PendseNessuna valutazione finora
- Expansion Joint SpecsDocumento1 paginaExpansion Joint SpecsFaisal MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynasylan BSM 40%Documento3 pagineDynasylan BSM 40%Francois-Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Psychology of Worldviews: Mark E. Koltko-RiveraDocumento56 pagineThe Psychology of Worldviews: Mark E. Koltko-RiveraPablo SeinerNessuna valutazione finora
- Akash IntenshipDocumento28 pagineAkash IntenshipAkash TaradaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpersonal and Interapersonal Communication6Documento20 pagineInterpersonal and Interapersonal Communication6abh ljknNessuna valutazione finora
- Aravindhan PT CV CSWIP TrainerDocumento4 pagineAravindhan PT CV CSWIP TrainerGanesan RamamoorthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety PledgeDocumento3 pagineSafety Pledgeapi-268778235100% (1)
- E Katalog 2019Documento15 pagineE Katalog 2019Dwi Putri BastiyantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Finding The Right Materials ESPDocumento8 pagineFinding The Right Materials ESPEdison Dela Cruz Jr.100% (1)
- Aster 30 Sampt PDFDocumento2 pagineAster 30 Sampt PDFmig29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Form No. NTC 1 22 Application For Tvro Renewal SignedDocumento1 paginaForm No. NTC 1 22 Application For Tvro Renewal SignedAmor LicudoNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit1 Topic1 Digital Logic IntroductionDocumento33 pagineUnit1 Topic1 Digital Logic IntroductionHari Kumar N CNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of The Rebound Hammer Method-1Documento26 pagineReview of The Rebound Hammer Method-1Mr. Jitender KumarNessuna valutazione finora