Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 2
Caricato da
teceeeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 2
Caricato da
teceeeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
114 ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEMS
5.5 PARALLEL AND SERIES CONNECTION OF THYRISTORS
In case of HVDC transmission, the voltage and current levels are so high that a single thyristor
cannot meet these requirements. Under such circumstances, it is essential to use more than
one thyristors in parallel to obtain increased current requirements and, in series, to achieve
higher voltage.
Parallel Connections
When thyristors are connected in parallel, the current sharing between them may not be equal.
The thyristor with lower dynamic resistance will take more current resulting in further
reduction in resistance and further increasing the flow of current through it. The process is
cumulative till the thyristor gives way.
For parallel operation of thyristors, it is desirable that the finger voltage of various
devices should be same, the latching current level of all the devices is such that when gate
pulse is applied, all of them will turn on and remain on when the gate pulse is removed. Also,
the holding current of various devices should not differ much.
In order to nullify the difference in characteristics of the thyristors due to slightly different
turn-on time, finger voltage, holding current, latching current etc. which results in unequal
current sharing, it is desirable to insert suitable value of inductance in each thyristor circuit.
Series Connection of Thyristors
In order to obtain higher d.c. voltage for HVDC transmission, two or more than two thyristors
are to be connected in series. In case, the thyristors have different leakage resistances, the
thyristor with higher leakage resistance will have larger voltage drop across it. High resistances
of equal values are connected across the thyristors.
5.6 POWER FLOW IN 08,+ TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
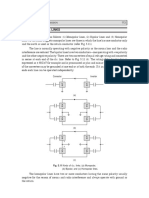
The equivalent circuit of a d.c. transmission system under steady state operating condition is
shown in Fig. 5.12.
Rcr RL Rci
Vor Voi
Vor Vdr Vdi Voi
cos a b
cos
d
Fig. 5.12 Equivalent circuit of a d.c. transmission link.
The current Id in the line is given by
Vor cos Voi cos ( or )
Id = (5.14)
Rcr + RL Rci
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- EENG611-7-Chapter 6-Part IDocumento45 pagineEENG611-7-Chapter 6-Part IbazzazNessuna valutazione finora
- Es173-Lecture 3-Dec-2020-10-12Documento135 pagineEs173-Lecture 3-Dec-2020-10-12shafyvonommyNessuna valutazione finora
- HVDC TRANSMISSION: ADVANTAGES AND APPLICATIONSDocumento14 pagineHVDC TRANSMISSION: ADVANTAGES AND APPLICATIONStaurus8055Nessuna valutazione finora
- Simultaneous Transmission of Ac and DC PowerDocumento6 pagineSimultaneous Transmission of Ac and DC PowermdayyubNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 7 AC Circuits: ObjectivesDocumento6 pagineExperiment 7 AC Circuits: ObjectivesMujtabaAliNessuna valutazione finora
- Exer 4Documento1 paginaExer 4RBNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Utility ApplicationsDocumento23 pagineElectric Utility Applicationssukhbat sodnomdorjNessuna valutazione finora
- Diodat PDFDocumento4 pagineDiodat PDFFatmir KelmendiNessuna valutazione finora
- Delta-Wye Circuit Transformation ExperimentDocumento6 pagineDelta-Wye Circuit Transformation ExperimentJohn Carlos MislangNessuna valutazione finora
- Group1 Experiment 4Documento6 pagineGroup1 Experiment 4John Carlos MislangNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 20 Electric Circuits PDFDocumento31 pagineCHAPTER 20 Electric Circuits PDFmasemola koketsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6Documento27 pagineChapter 6Abdirahman Elmi GureNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 16Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 16ragupaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kirchhoff' S Voltage LowDocumento2 pagineKirchhoff' S Voltage LowpriteshNessuna valutazione finora
- Triggering Methods For TriacsDocumento2 pagineTriggering Methods For Triacskencruz11Nessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 121 Circuit Theory 1: Circuit Theorems & Apllication To DC CircuitsDocumento29 pagineEEE 121 Circuit Theory 1: Circuit Theorems & Apllication To DC CircuitsKamarul Syaril AzzahariNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Chapter 2 Line ParametesDocumento28 pagine2 Chapter 2 Line ParametesPriyanshu GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding DC CircuitsDocumento12 pagineUnderstanding DC CircuitsEdoku IreneNessuna valutazione finora
- RC CircuitDocumento9 pagineRC CircuitRohishkumarReddy MittaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocumento4 pagineData Structures and AlgorithmsAbhishek RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit 7Documento5 pagineCircuit 7richy launcherNessuna valutazione finora
- Hcmos Oscillators: J. RuffellDocumento3 pagineHcmos Oscillators: J. RuffellAg CristianNessuna valutazione finora
- EDC 2 Marks Q ADocumento16 pagineEDC 2 Marks Q Akunaraj100% (3)
- NotesOnDiodes PDFDocumento4 pagineNotesOnDiodes PDFS D MajumderNessuna valutazione finora
- Section B4: Diode Equivalent Circuit ModelsDocumento3 pagineSection B4: Diode Equivalent Circuit ModelsCuevas ByronNessuna valutazione finora
- Bee Papers SolutionDocumento60 pagineBee Papers Solution230860116023Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Comparision of Popular MV Motor DrivesDocumento11 pagineA Comparision of Popular MV Motor DrivesCristian Rene Orozco PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics DW Hart McGraw-Hill 2010 BBS 123Documento5 paginePower Electronics DW Hart McGraw-Hill 2010 BBS 123paul kioiNessuna valutazione finora
- HVDC Power Transmission BasicsDocumento20 pagineHVDC Power Transmission BasicsrichierichNessuna valutazione finora
- HVDC Transmission LinesDocumento12 pagineHVDC Transmission LinesDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (2)
- Half-Wave and Full-Wave RectifiersDocumento6 pagineHalf-Wave and Full-Wave RectifiersAditya KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformers and Rectifier Analysis in Power ElectronicsDocumento9 pagineTransformers and Rectifier Analysis in Power ElectronicsMehmet DALNessuna valutazione finora
- Re-Visiting Naturally Balanced Average Capacitor Voltages in Multilevel DC-DC ConvertersDocumento6 pagineRe-Visiting Naturally Balanced Average Capacitor Voltages in Multilevel DC-DC ConvertersHussain K. SayedNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3Documento39 pagineCH 3Hadis SyoumNessuna valutazione finora
- HVDC Control Schemes ExplainedDocumento9 pagineHVDC Control Schemes ExplainedSusmita AdhikaryNessuna valutazione finora
- BE8255 Notes PDFDocumento188 pagineBE8255 Notes PDFPragna SidhireddyNessuna valutazione finora
- HVDC Voltage ControlDocumento11 pagineHVDC Voltage ControlMd.Arifur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 24XDocumento26 pagineChapter 24Xchristian limaNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Documento1 pagina17 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNessuna valutazione finora
- EC-BASIC ELECTRONICs and InsDocumento6 pagineEC-BASIC ELECTRONICs and InsAshish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electric Engineering Unit 1 Notes RGPVDocumento11 pagineBasic Electric Engineering Unit 1 Notes RGPVMufaddal HamidNessuna valutazione finora
- The Laplace Transform in Circuit AnalysisDocumento79 pagineThe Laplace Transform in Circuit Analysis채정우Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3010Documento25 pagine3010Sandeep Babu VannempalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Stability Enhancement by SiDocumento8 paginePower System Stability Enhancement by SiUdaiveer SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 5 Full-Wave RectifierDocumento21 pagineCH 5 Full-Wave RectifierSYAFIQAH ISMAILNessuna valutazione finora
- Travelling Waves 1Documento12 pagineTravelling Waves 1Shareef ChampNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4Documento12 pagineLecture 4deepika yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Gate Triggering Ckts Resistance TriggeringDocumento6 pagineGate Triggering Ckts Resistance TriggeringAkhilrajscribdNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IV Transient AnalysisDocumento43 pagineUnit IV Transient AnalysisSaravana SelvanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 DiodeRectifiers HLDocumento10 pagine3 DiodeRectifiers HLRimsha pervaizNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 CurrentElectricityExe PCDocumento44 pagine2 CurrentElectricityExe PCAditya KapooorNessuna valutazione finora
- ESC201AT: Introduction To Electronics: Lecture-3: Tools For Circuit Analysis-1Documento34 pagineESC201AT: Introduction To Electronics: Lecture-3: Tools For Circuit Analysis-1Shubham KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1: RC Circuits: 1.1 Electrical Circuit DefinitionsDocumento12 pagineExperiment 1: RC Circuits: 1.1 Electrical Circuit DefinitionsBrice Ekobo AkoaNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE572 Homework 1 Solutions Inductor Waveform Analysis DC-DC Converter CircuitsDocumento6 pagineEEE572 Homework 1 Solutions Inductor Waveform Analysis DC-DC Converter Circuitsmitrax1pNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Chapter 26: Current and ResistanceDocumento8 pagineHomework Chapter 26: Current and ResistanceIvy RetuyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsDa EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 8Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 8teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 1Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 1teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 9Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 9teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 7Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 7teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 10Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 10teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 3Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 3teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- High Voltage DC Transmission ControlDocumento1 paginaHigh Voltage DC Transmission ControlteceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 6Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 6teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 4Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 4teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 9Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 9teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 11Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 11teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 8Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 8teceee100% (1)
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 8Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 8teceee100% (1)
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 10Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 10teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 9Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 9teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power Systems Wadhwa 7Documento1 paginaElectrical Power Systems Wadhwa 7teceeeNessuna valutazione finora
- EM-CABLE Product CatalogDocumento96 pagineEM-CABLE Product Catalogm00h00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Induction Hardening - Interpretation of Drawing & Testing PDFDocumento4 pagineInduction Hardening - Interpretation of Drawing & Testing PDFrajesh DESHMUKHNessuna valutazione finora
- Mycbseguide: Cbse Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper - 08 (MCQ Based)Documento10 pagineMycbseguide: Cbse Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper - 08 (MCQ Based)Abdul MuqsitNessuna valutazione finora
- Abundance BlocksDocumento1 paginaAbundance BlockssunnyNessuna valutazione finora
- BS en 12201 5 2011Documento20 pagineBS en 12201 5 2011fatjon31100% (4)
- Elements of Plane and Spherical Trigonometry With Numerous Practical Problems - Horatio N. RobinsonDocumento228 pagineElements of Plane and Spherical Trigonometry With Numerous Practical Problems - Horatio N. RobinsonjorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- EVOLUTION Class Notes PPT-1-10Documento10 pagineEVOLUTION Class Notes PPT-1-10ballb1ritikasharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- My Medications ListDocumento5 pagineMy Medications Listhussain077Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fendering For Tugs: Mike Harrison, Trelleborg Marine Systems, UKDocumento5 pagineFendering For Tugs: Mike Harrison, Trelleborg Marine Systems, UKRizal RachmanNessuna valutazione finora
- ATEX Certified FiltersDocumento4 pagineATEX Certified FiltersMarco LoiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitchella Partridge Berry Materia Medica HerbsDocumento3 pagineMitchella Partridge Berry Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra GuerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Oil Corporation Limited: Bhubaneswar Divisional OfficeDocumento3 pagineIndian Oil Corporation Limited: Bhubaneswar Divisional OfficeBinay SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion Cat 2008Documento32 pagineCombustion Cat 2008Miguel LinaresNessuna valutazione finora
- POLIOMYELITISDocumento26 paginePOLIOMYELITISIzhra Margate100% (1)
- Desiderata: by Max EhrmannDocumento6 pagineDesiderata: by Max EhrmannTanay AshwathNessuna valutazione finora
- Hedging Techniques in Academic WritingDocumento11 pagineHedging Techniques in Academic WritingÛbř ÖňNessuna valutazione finora
- IITG MA101 Endsem Question PaperDocumento12 pagineIITG MA101 Endsem Question PaperNarravula Harshavardhan100% (2)
- SSX Diaphragm: Truextent® Replacement Diaphragms For JBL and RADIANDocumento2 pagineSSX Diaphragm: Truextent® Replacement Diaphragms For JBL and RADIANIvica IndjinNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Modernization Poster2Documento1 paginaGSM Modernization Poster2leonardomarinNessuna valutazione finora
- LIST Real Estate Contacts ListDocumento4 pagineLIST Real Estate Contacts ListChauhan Harshit100% (1)
- 500 Important Spoken Tamil Situations Into Spoken English Sentences SampleDocumento7 pagine500 Important Spoken Tamil Situations Into Spoken English Sentences SamplerameshdurairajNessuna valutazione finora
- True/False/Not Given Exercise 5: It Rains On The SunDocumento2 pagineTrue/False/Not Given Exercise 5: It Rains On The Sunyuvrajsinh jadejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Techniques for Studying FossilsDocumento11 pagineTechniques for Studying FossilsP. C. PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines On Dissolution Profile Comparison: Udrun ReitagDocumento10 pagineGuidelines On Dissolution Profile Comparison: Udrun ReitagRaju GawadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Function and Euqations - Quantitative Aptitude Questions MCQDocumento4 pagineFunction and Euqations - Quantitative Aptitude Questions MCQAnonymous v5QjDW2eHxNessuna valutazione finora
- DGPS Sensor JLR-4331W Instruction ManualDocumento42 pagineDGPS Sensor JLR-4331W Instruction ManualantonioNessuna valutazione finora
- JSW Energy Plant Maintenance BBPDocumento46 pagineJSW Energy Plant Maintenance BBPSandeep Kumar PraharajNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Quarter Summative Test in MusicDocumento2 pagine2nd Quarter Summative Test in MusicIverAlambraNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Names in English and IndonesianDocumento7 pagineAnimal Names in English and IndonesianAndi KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Schaeffler - Account Insights - Mar 2020Documento13 pagineSchaeffler - Account Insights - Mar 2020mohit negiNessuna valutazione finora