Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Modular Worksheet Final
Caricato da
Jouichiro MasamuneCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Modular Worksheet Final
Caricato da
Jouichiro MasamuneCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cells Acrostic Poem
An acrostic poem is one where you choose a word or name and use each letter in the name as the
beginning of a word or line that tells something about that person or topic.
Example: An acrostic poem using the word "Sun."
Sometimes when we go to the beach, I will get sun burn.
Usually if I put Sun block on my skin I will not burn.
Noon is when I'm really prone to burning.
Write an Acrostic Poem using the word below.
C- lassified as one of the small parts that
together formed all living
E- ach one made out from division
L-iving biological structure found in a
L-iving organism that is also created
S-urely every individual is aware of that
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 1
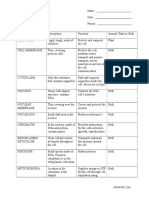
CELL ORGANELLES
Directions: Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or
organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the
left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once.
Structure/Function Cell Part
Stores material within the cell Vacuole
Closely stacked, flattened sacs (plants only) Chloroplasts
The sites of protein synthesis Ribosomes
Transports materials within the cell Vesicles
The region inside the cell except for the nucleus Cytoplasm
Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a
Nucleus
eukaryotic cell
Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from
Chloroplast
sunlight and gives plants their green color
Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and
Lysosome
invading viruses or bacteria
Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic
Ribosome
reticulum
Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste
Vacuole
products
Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in
Cell wall
plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists
Produces a usable form of energy for the cell Mitochondria
Packages proteins for transport out of the cell Golgi Apparatuses
Protective covering of the nucleus Nuclear envelope
Site where ribosomes are made Reticulum
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 2
The membrane surrounding the cell Cell membrane
Provides support for the cell, has two subparts Lipid bilayer
Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic
Nucleolus
cells
Consist of hollow tubes which provide support for the cell Cytoskeleton
Small hair-like structures used for movement or sensing
Cilia
things
Composed of a phospholipid bilayer Cell membrane
Longer whip-like structures used for movement Flagellum
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
Directions: Put a check in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the following
organelles are found in plant cells, animal cells or both.
Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Golgi body
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Vacuoles
Vesicles
Chloroplast
Cytoplasm
Chromatin
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 3
Cytoskeleton
Centrioles
Nuclear Envelope
Cytosol
CELL CITY ANALOGY
In a far city called Grant City, the main export and production product is the steel
widget. Everyone in the town has something to do with steel widget making and the
entire town is designed to build and export widgets. The town hall has the instructions
for widget making, widgets come in all shapes and sizes and any citizen of Grant can get
the instructions and begin making their own widgets. Widgets are generally produced in
small shops around the city, these small shops can be built by the carpenters union
(whose headquarters are in town hall).
After the widget is constructed, they are placed on special carts which can deliver
the widget anywhere in the city. In order for a widget to be exported, the carts take the
widget to the postal office, where the widgets are packaged and labeled for export.
Sometimes widgets don't turn out right, and the "rejects" are sent to the scrap yard where
they are broken down for parts or destroyed altogether. The town powers the widget
shops and carts from a hydraulic dam that is in the city. The entire city is enclosed by a
large wooden fence, only the postal trucks (and citizens with proper passports) are
allowed outside the city.
Match the parts of the city (underlined) with the parts of the cell.
1. Mitochondria Hydrolic dam
2. Ribosomes Small Shops
3. Nucleus Town Halls
4. Endoplasmic Reticulum Special Carts
5. Golgi Body Postal Office
6. Protein Steel widget
7. Cell Membrane Large wooden fence
8. Lysosomes Scrap yard
9. Nucleolus Carpenters Union
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 4
DRAWING AN ANIMAL CELL
Directions: In the space provided below, draw an animal cell. Make sure to draw and
label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the color of your
choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 5
DRAWING A PLANT CELL
Directions: In the space provided below, draw a plant cell. Make sure to draw and
label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the color of your
choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 6
DRAWING A BACTERIA CELL
Directions: In the space provided below, draw a bacteria cell. Make sure to draw
and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the color of
your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 7
HOW DOES AN ORGANELLE RELATE TO YOUR SCHOOL?
Directions: In the space provided below describe the function of each cell
organelle and then state what person in your school serves a similar
function in your school.
Who at your school has a similar
Plant Organelle Function within the cell
job?
An outer lipid layer for
mechanical protection
Cell Wall Guidance Counselors
Controls the entrance and
Plasma (Cell) exit of molecules and ions
School Guards
Membrane
It is known as the control
center
Nucleus Bus driver
Is the site of
photosynthesis
Cytoplasm Canteen staff
Are large membranous
storage sacs
Chloroplast(s) Janitor
They produce energy
Mitochondrion Maintenance staff
Are large membranous
storage sacs
Vacuole(s) Janitor
Long term storage of
Chromosomes information
Secretaries
(DNA)
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 8
Are cell structures that
Ribosome(s) Teachers
makes protein
CELLS WORD SEARCH
Directions: All words are positioned left to right.
P O N T Z E J U I N N B M B R H R D B T B J D
A T I S C P M F B T J S Z D F P A J O A B A X
C J N Y T Z C H U N Z N U C L E O L U S B N C
E C H L O R O P L A S T G I X N R A Z H E D O
D W H R A Z P B C M N P F R L G H P X Z H N M
I P Y O C H R O M O S O M E Y C I T D C S Y X
N T A D G M Y W E M N L J X O R G A N S H X S
R T Z C I W D S Z E V K A J B L M V C A U K I
D E M P K A K R W J O D C J C W V F D I X I F
B F X O P I G S T I S S U E S V D Z L J G M R
Z W P I C H L O R O P H Y L L V B P I A H D W
L W I G E B J I D D E H V A C U O L E M O R L
T R Z I E O J G V S M P Y X L N U C L E U S E
E V H V P M M M U Q U B E A M O H W N T S G C
S N I D Y N Z M X C Y Q D Y O F L Y S M A L S
B M I T O C H O N D R I A V O C C F S A Y V I
C Y T O P L A S M W K L F L L A K U F O C G V
P B K T R R R Q T A M U T J W U R J B W G G G
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 9
MITOCHONDRIA CHLOROPHYLL TISSUES CHROMOSOME
CYTOPLASM NUCLEOLUS ORGANS CHLOROPLAST
NUCLEUS VACUOLE
Comprehensive Questions:
1. In what organelle does cellular respiration take place?
-Mitochondria
2. Name two storage organelles?
-Vacuoles and Vesicles
3. What are the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesis?
-Nucleus
-Ribosomes
-Endoplasmic reticulum
-Golgi Apparatuses
-Vesicles
-Export
4. How is the nucleus involved in protein synthesis?
-The nucleus is involved in protein synthesis because this contains the
directions for making proteins.
5. What organelle is considered a factory, because it takes in raw materials
and converts them to cell products that can be used by the cell?
-Ribosomes
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 10
6. How does the membrane of the cell differ from the nuclear membrane?
What advantages does this difference have for the nucleus?
-Cell membrane protects the cell; controls what goes in and out of the cell,
communication. Nuclear membrane protects the nucleus. Cell membrane is
only single bi-layer, and the nuclear membrane is double bi-layer. The
nuclear membrane is double bi-layer, it could provide better protection.
7. What is the function of the ribosomes? Are they found freely floating in the
cytoplasm? OR are they found attached to another organelle? OR both.
Explain why this occurs.
-The function of the ribosomes is to produce proteins. They are found freely
floating in the cytoplasm and it is attached in the endoplasmic reticulum.
8. What does the endoplasmic reticulum do?
-It helps move protein and other materials around within the cell.
9. What is the difference between rough ER and smooth ER? What is the ER
doing that is different in each case?
-The rough ER has ribosomes attached to it and produces proteins while the
smooth ER has no ribosomes and produces lipids.
10.What are lysosomes? What types of molecules would be found inside a
lysosome?
-Small, round organelles, containing enzymes that digest old worn out cell
parts, enzymes, and produces lipids.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 11
11.Why might a lysosome fuse with or link up with a food vacuole?
-In order to digest the food in the vacuole.
12.In what organelle do molecules move from the ER to the Golgi bodies?
-Within the vesicles
13.What is a centriole? In what type of cell (plant or animal) is it found?
What does it do for the cell?
-Centrioles is a part of the cytoskeleton found in animal cells only. It helps
separate the chromosomes in cell division.
Directions: Identify the following items below by writing the correct answer on
the second hand column.
Questions Answer
Laboratory Apparatuses
Used to crush and grind materials Mortar and Pestle
Used for drawing out fluids or gases Pippete
Quick source of heat and light Bunsen Burner
Gives support to beaker while heating Tripod
Used to hold, mix and heat liquids Beaker
Used to heat liquids for evaporation Dish
Used to measure temperature Thermometer
Used as pH or acid-base indicator Litmus Paper
Used to heat a small amount of a solid
Crucible and Cover
substance at a very high temperature
Used to hold several test tubes at one time Test tube rack
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 12
Used to measure a precise volume of a liquid Graduated Cylinder
Used for culturing bacteria Petri Dish
Used to separate fine solids from liquids Filter Paper
Holds chemical solutions Florence flask
Holds the test tube while heating Test tube holder
Parts of the Microscope
Supports the entire microscope Arm
Source of light that makes the specimen easier
Light or mirror
to use
Support the upper parts and carry the
Head or body
microscope
Component that magnifies the images of the
Objective lenses
specimen to form an enlarge image
Holds the glass slide and specimen in place Stage clips
Table of the microscope, where the microscope
Stage
slide is placed
The rotating part at the bottom of the body
Revolving nosepiece
tube; it holds the objectives
The long tube that holds the eyepiece and
Body tube
connects it to the objectives
Where you look through to see the image of
Eye piece lens
your specimen
Round knob on the side of the microscope
Coarse focus knob
used for focusing the specimen
Discovery of the Cell, Cell Theory and Cell Parts
Basic unit of life Cell
Group of cells Tissue
Group of organs Organ system
Group of organisms Population
Group of tissues Organs
Group of community Ecosystem
Group of population Community
Group of molecules Cells
Group of organ system Organism
Filipino translation of the word cell Sihay
Discovered nucleus Robert Brown
Discovered cytoplasm Rudolf Albert Von Kolliker
Discovered protoplasm Johannes Purkinje
Coined the term sarcode Felix Dujardin
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 13
Coined the term cell Robert Hooke
Coined the statement omnis cellula e cellula Rudolph Virchow
Discovered that plants are composed of cells Matthias Schleiden
Discovered that animals are composed of cells Theodore Schwann
Discovered tiny animals called animalcules Anton Van Leewenhoek
Proponent of the Theory of Spontaneous
Aristotle
Generation
Proponent of the Theory of Biogenesis Luis Pasteur
Did an experiment with flies and wide-mouth
Francisco Redi
jars containing meat
The only scientist who supported the Theory of
John Needham
Spontaneous Generation of Aristotle
Did an experiment on sealing a flask and
Lazzaro Spallanzani
boiled a chicken broth in it
Protein factories of the cell Ribosomes
Guard of the cell Cell
Powerhouse of the cell Mitochondria
Packaging of the cell Golgi Body
Food manufacturer of the cell Chloroplasts
Water tank of the cell Vacuole and Vesicle
Manufacturer of the cell Endoplasmic reticulum
Waste disposal of the cell Lysosomes and Peroxisome
Framework of the cell Cytoskeleton
Brain of the cell Nucleus
Water loving Hydrophilic
Afraid of water Hydrophobic
Not everything can enter or pass through the
Semi-permeability
cell membrane
Specialized finger like folds in the cell
Microvilli
membrane
Glycerol and charged
Joined to form the head of a phospholipid
phosphate group
Make up the tail of a phospholipid Fatty acid chain
Attached to membrane proteins that serves as
Carbohydrates
identification tags
Helps strengthen the cell membrane and
Cholesterol Molecules
making it more flexible and less fluid
Form tunnels that help cell to import or export
Channel proteins
needed materials and wastes
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 14
Extend from the phospholipid layer to help
Transport proteins
materials cross the membrane
Assist cell to cell adhesion and communication
Junction proteins
between cells
Act as muscle and skeleton to maintain shape
Cytoskeleton proteins
and motility
Facilitate exchange of signals with other cells
by changing shape to allow a specific molecule Receptor proteins
to bind it
Participate in metabolic reactions such as
Enzymatic proteins
degradative and synthetic reactions
Enable cells to distinguish own cells from that
of other organisms, such as pathogens that may Cell recognition proteins
invade the body
One sugar molecule Monosaccharides
Two sugar molecule Disaccharide
Two or more sugar molecule Polysaccharide
Stored carbohydrates in plants Starch
Glucose + Glucose Maltose
Glucose + Galactose Lactose
Glucose + Fructose Sucrose
The sweetest sugar Fructose
Sugar found in milk Lactose
Malt sugar Maltose
Stored carbohydrates in animals Glycogen
Forms the cell wall of plants Cellulose
Support the exoskeleton of fungi and
Chitin
crustaceans
Present in plants, fungi, algae and bacteria Cell wall
A substance which is a primary component of
Lignin
wood
Channels in the cell wall that allow the
Plasmodesma
exchange of substances between adjacent cells
Composition of the cell wall of bacteria Peptidoglycan
Composition of the cell wall of plants and
Polysaccharide cellulose
algae
Composition of the cell wall of fungi Chitin
Those bacteria that are darker in color when
Gram-positive bacteria
viewed in the microscope
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 15
Those bacteria that are lighter in color when
Gram-negative bacteria
viewed in the microscope
Appendages attached to the plasma membrane;
Flagella and cilia
for movement
The semisolid, semiliquid, gel-like substance
Cytoplasm
that hold the internal structures of the cell
Semi-fluid substance where the different
Cytosol
organelles are suspended
Substances that produce electrically
Electrolytes
conducting solutions
Substances produced during metabolism Metabolytes
Conversion of glucose into another form Glycolysis
Little organs that perform specific functions
Organelles
inside the cell
Refers to the group of organelles that produce
and transport substances on the cytoplasm Endomembrane system
through the use of vesicles
Energy currency of the cell Adenosine triphosphate
Just floating free in the cytoplasm Free ribosomes
Attached with the rough endoplasmic
Attached ribosomes
reticulum
Circular containers from the Golgi Body that is
Transport vesicle
used for shipping
Hydrolytic enzymes that digests and destroys
molecules and organelles that are not needed Lysozyme
anymore by the cell
Breaks down long chains of fatty acids and
Oxidative enzyme
lipids (fats)
Produce spindle fibers that pull away the
Centrioles
chromosomes at the end of each pole
Green pigment in plants Chlorophyll
A denser, darker sphere in the center of the
Nucleoulus
nucleus
Cell Transport
Spreading of molecules Diffusion
Molecules that are permeable to pass through
Oxygen and water
the cell membrane
Diffusion of water Osmosis
Molecules that are impermeable to pass
Glucose and salt
through the cell membrane
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 16
Two types of transport under small particles Passive and active transport
Two types of transport under large particles Edocytosis and exocytosis
Diffusion and facilitated
Two types of transport under passive transport
diffusion
Pattern of concentration for passive transport High to low concentration
Pattern of concentration for active transport Low to high concentration
Internal balance of the cell Homeostasis
Chance of the position or movement of
Concentration gradient
molecules
A pocket that capture molecules from the
Carrier protein
outside going to the inside of the cell
A special protein embedded in the membrane
Channel protein
helps molecules move across
Cells have to move a substance against the
concentration gradient or from an area of low Active transport
to high concentration
Occurs when large particle(s) are captured by a
Endocytosis
pocket in the membrane
Occurs when a large bit of material needs to be
Exocytosis
removed from a cell
Directions: Compare and contrast a prokaryotic cell from a eukaryotic cell in
terms of their characteristics listed below.
c Characteristics Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
Presence of nucleus
Nuclear Membrane
Lack of nucleus
It consists of a DNA-
Chromosomes protein complex stored in
It is stored in the nucleoid
the nucleus.
It is found freely in the It is contained within a
DNA
cytoplasm. nucleus
mRNA molecules are mRNA molecules are
polycistronic. Protein monocistronic. Protein
RNA and Protein synthesis occurs in the synthesis occurs before the
cytoplasm. transcription of mRNA
molecule.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 17
It does not contain Eukaryotic cells contain a
Endoplasmic lysosomes, golgi body and numerous membrane-
reticulum, Golgi ER but instead it has enclosed organelles
body and mesosomes that perform the (lysosomes, golgi body and
Lysosomes role of the golgi body. endoplasmic reticulum)
The mitochondria produces
The mesosomes also energy in the form of ATP.
Mitochondria perform the role of the
mitochondria
Ribosomes are smaller Ribosomes are larger (80 s)
Ribosomes (70s)
It has cytoskeleton that Microtubules maintain
Microtubules maintain shape and stability shape
It encompses everything It is everything between the
within the plasma plasma membrane and the
Cytoplasm
membrane nuclear envelope
It is able to be structurally It has a variety of
Cellular moved simple because of its specialized internal
organization small size organelles
Photosynthetic
Apparatus
Cell size
DRAWING A PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER
Directions: In the space provided below, draw a phospholipid bilayer. Make sure
to draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the
color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 18
PASSIVE VS. ACTIVE TRANSPORT
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the process of diffusion, facilitated
diffusion and active transport. Make sure to draw and label it properly.
Identify each stage by coloring it with the color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 19
ENDOCYTOSIS
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the process of endocytosis. Make
sure to draw and label it properly. Identify each stage by coloring it
with the color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 20
EXOCYTOSIS
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the process of exocytosis. Make
sure to draw and label it properly. Identify each stage by coloring it
with the color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 21
MITOCHONDRIA
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the mitochondria. Make sure to
draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the
color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 22
RIBOSOMES
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the ribosomes. Make sure to draw
and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the color of
your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 23
CHLOROPLAST
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the chloroplast. Make sure to draw
and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the color of
your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 24
GOLGI APPARATUS
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the golgi apparatus. Make sure to
draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the
color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 25
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the endoplasmic reticulum. Make
sure to draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with
the color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 26
LYSOSOMES
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the lysosomes. Make sure to draw
and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the color of
your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 27
PEROXISOMES
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the peroxisomes. Make sure to
draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the
color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 28
CENTRIOLES
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the centrioles. Make sure to draw
and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the color of
your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 29
CYTOSKELETON
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the cytoskeleton. Make sure to
draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the
color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 30
MICROTUBULES
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the microtubules. Make sure to
draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the
color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 31
INTERMEDIATE FILAMENT
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the intermediate filament. Make
sure to draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with
the color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 32
ACTIN FILAMENT
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the actin filament. Make sure to
draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the
color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 33
VACUOLES AND VESICLES
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the vacuoles and vesicles. Make
sure to draw and label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with
the color of your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 34
Nucleus
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the nucleus. Make sure to draw and
label all its part. Identify each part by coloring it with the color of your
choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 35
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS BY LEVEL
Directions: Refer to any biology books/ any reference materials and complete the
table using the classification of living things by level.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 36
Level Human Cat Dog
Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia
Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata
Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia
Order Primates Carnivora Carnivora
Family Hominidae Felidae Canidae
Genus Homo Felis Canis
Species Sapiens Catus Lupus familliaris
Scientific Name Homo sapiens Felis catus C. lupus familliaris
Level Housefly Carabao Milk Fish
Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia
Phylum Arthopoda Chordata Chordata
Class Insecta Mammalia Actinopterygli
Order Diptera Artiodactyla Gonoryn chiformes
Family Muscidae Bovidae Chanidae
Genus Musca Bubalus Chanos
Species Domestica B.bubalis Chanos chanos
Scientific Name Musca domestica Bubalus bubalis Chanos chanos
casabanesis
Level Spider Chicken Eagle
Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia
Phylum Arthropoda Chordata Chordata
Class Arachnida Aves Aves
Order Araneae Galliformes Falconiformes
Family Si cariida Phasianidae Accipitidae
Genus Loxosceles Gallus Haliaetus
Species L. reclusa Gallus Leucocephalus
Scientific Name L. reclusa Gallus gallus Haliaetus
domesticus leucocephalus
Level Onion Sampaguita Mango
Kingdom Plantae Plantae Plantae
Phylum Magnoliophyta Magnoliophyta Magnoliophyta
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 37
Class Lilioida Magnoliopsida Magnoliopsida
Order Asparagales Lamiales Sapindale
Family Liliaceae Oleaceae Anacardiaceae
Genus Allium Jasminum Mangifera
Species A. cepa J. sambac M. indica
Scientific Name Allium cepa Jasminum sambac Mangifera indica
Level Squash Bitter Gourd Orchid
Kingdom Plantae Plantae Plantae
Phylum Magnoliophyta Spermatophyta Magnoliophyta
Class Magnoliopisda Magnoliopisda Liliopsida
Order Cucurbitales Violales Asparagales
Family Cucurbitaceae Cucurbitaceae Orchidaceae
Genus Cucurbita Mormordica Aerides
Species C. maxima Charantia
Scientific Name Cucurbita Momordica Orchidaeae
charrantia
Level Snake Lizard Turtle
Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia
Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata
Class Reptilia Reptilia Reptilia
Order Squamata Squamata Testudines
Family Pythinidae Agamidae Cheloniidae
Genus Phython Pogona Chelonio
Species P. reticulatus Vitticeps Chelonian mydas
Scientific Name Serpentes Lacertia Testudines
Level Narra Star Apple Rat
Kingdom Plantae Plantae Animalia
Phylum Magnoliophyta Angiosperms Chordata
Class Magnoliopsida Magnoliopsida Mammalia
Order Fabales Ericales Rodentia
Family Fabaceae Sapotaceae Muridae
Genus Pterocarpus Chysophylum Rattus
Species P. indicus C. cainito R. norvergicus
Scientific Name Pterocarpus Chysophylum Rattus norvergicus
indicus cainito
Level Carrot Bougainvillaea Crocodile
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 38
Kingdom Plantae Plantae Animal
Phylum Magnoliophyta Magnoliophyta Chordata
Class Magnoliopsida Magnoliopsida Reptilia
Order Apiales Caryphyllates Crocodilia
Family Apiaceae Nytaginaceae Crcodylidae
Genus Daucus Bougainvillea Ccodylus
comm. ex Jucs
Species Daucus carota Bougainvillea Crocodylus acutus
glabra choisy
Scientific Name Daucus carota Bougainvillea Crocodylus acutus
subsp. sativus glabra choisy
Level Dolphin Tomato Eggplant
Kingdom Animalia Plantae Planta
Phylum Chordata Magnoliophyta Magnoliopsida
Class Mammalia Magnoliopsida Magnoliopsita
Order Cetacea Solonales Solanales
Family Delphinidae Solanaceae Solanaceae
Genus Stella Solanum Solanum
Species Stenella S. lycopessicum S.melongena
longirustris
Scientific Name Delphinus delphis Solanum Solanum
lycopersicum melongena
Level Shrimp Earthworm Leech
Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia
Phylum Arthropoda Annelidia Annelidia
Class Malacostraca Clitellata Clitellata
Order Decapoda Haplotaxida Arhyncodbaellida
Family Penaeidae Cambricidae Hinudidae
Genus Penaeus Lumbricus Hirudo
Species P. setiferus Terrrestris H. medicinalis
Scientific Name Penaeus setiferus Lumbricina Hirudinea
Level Snail Octopus Butterfly
Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia
Phylum Mollusca Mollusca Arthopoda
Class Gastropoda Cephalopoda Insecta
Order Achatiniodea Octopoda Lepidotera
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 39
Family Polygyridae Octopodidae Lycaenidae
Genus Allogona Octopus Polyommatus
Species A.profunda V.vulgaris Icarus
Scientific Name Comu apersum Octopoda Phopolocera
Level Grasshopper Scorpion Beetle
Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia
Phylum Arthopoda Arthopoda Arthopoda
Class Insecta Arachnida Insecta
Order Orthoptera Scorpiones Coleoptera
Family Acrididae Scorpionoidae Carabidae
Genus Chloeatis Pandinus Cicindela
Species C. conspersa P. imperator Tranguebarica
Scientific Name Caelifera Pandinus imperator Coleoptera
Level Dragonfly Sea Urchin Frog
Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia
Phylum Arthopoda Echinodermata Chordata
Class Insecta Echinoidea Amphibian
Order Odonata Arbacoida Anura
Family Libellulidae Arbaciidae Ranidae
Genus Libellula Arbacra Rana
Species Fiavida Punctulata R. pipiens
Scientific Name Anisoptera Echinoidea Anura
Level Pea Plant Corn Cheetah
Kingdom Plantae Plantae Animalia
Phylum Anthophyta Magnoliophyta Chordata
Class Eudiotyledoned Magnoliopsida Mammalia
Order Fabales Poales Carnivora
Family Fabaceae Poaceace Fellidae
Genus Pisum Zea Acinonyx
Species P. sativum Zea mays A. jubatus
Scientific Name Pisum sativum Zea mays Acinonyx jubatus
Level Guava Watermelon Cucumber
Kingdom Plantae Plantae Plantae
Phylum Magnoliophyta Magnoliophyta Magnoliophyta
Class Magnoliopsida Magnoliopsida Magnoliopsida
Order Mytales Cucurbitales Cucurbitales
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 40
Family Mytaceae Cucurbitaceae Cucurbitaceae
Genus Psidium Citrullus Cucumis
Species P. guajava C. lanatus C. sativus
Scientific Name Psidium guajava Citrullus lanatus Cucumis sativus
SCIENTIFIC NAMES OF PLANTS
Directions: Give the correct scientific names of the following plants.
Common Name of Plants Scientific Name of Plants
Apple Pyrus malus
Bamboo Bamboosa aridinarifolia
Brinjal Solanum melongena
Banana Musa acuminate/ paradisicum
Black Gram Vigna/ Plasoes mungo
Banyan Ficus benghalensis
Barley Hordeum vulgare
Black Pepper Piper nigrum
Carrot Daucas carota
Cashew Nut Anacardium occidentale
Cotton Gossypium herbaceum
Curry Leaf Murraya koenigii
Coriander Coriandrum sativum
Clove Syzygium aromaticum
Capsicum Capsicum annum/ fruitscence
Chiku Achras sapota
Cucumber Cucumis sativas
Dragon Fruit Hylocereus undutus
Finger Millet Eleusine coracana
Guava Psidium guajava/ guava
Garlic Allium sativum
Ginger Zingiber officinale
Green Gram Phaseolies auicus
Jowar Sorghum vulgare
Jack Fruit Artocarpus integra
Kadamb Anthocephalus indicus
Lemon Citrus limonium
Mango Mangifera indica
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 41
Maize Zea mays
Neem Azadirachta indica
Orange Citrus aurantium
Onion Alluim cepa
Papaya Carica papaya
Pomegranate Punica granatum
Peepal Ficus religiosa Linn
Pineapple Ananus sativus
Pea Pisum sativam
Potato Solanum tubersum
Peacock Flower Delonix regia rafin
Purple Orchid Tree Bauhinia purpurea
Radish Raphanus sativus
Rice Oryza sativa
Red Maple Acer rubrum
Rose Rosa
Silver Oak Grevillea robusta
Soya Bean Glycine max
Spinach Lactuca sativa
Sunflower Helianthus annuus
Sandalwood Santalum album
Turmeric Curcuma longa
Tabacco Nicotina tobaccum
Tulsi Ocimum sanctum
Teak Tectona grandis Linn
Tamarind Tree Tamarindus indica
Tomato Lycopersican esculentum
Watermelon Citrullus vulgaris
Wheat Triticum aestivum
Tangerine Citrus reticulate
Lime Citrus aurantifolia
Limeberry Triphasia trifolia
Soursop Annona muricata
Custard Apple Annona reticulate
Sweetsop Annona squamosal
Sugarcane Saccharum officinarum
Avocado Persea Americana
Asparagus Asparagus officinalis
Santol Sandoricum koetjape
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 42
Cassava Abelmoschus esculentus
Grapes Manihot Esculenta
Starfruit Vitis vinifera
Swamp Cabbage Averrhoa carambola
Okra Ipornoea aquatic Forsk
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 43
SCIENTIFIC NAMES OF ANIMALS
Directions: Give the correct scientific names of the following animals.
Common Name of Animals Scientific Name of Animals
Bat Chiroptera
Cat Felis catus
Cobra Elaphidae naja
Camel Camelus camelidae
Cheetah Acinonyx jubatus
Chimpanzee Pan troglodytes
Crocodile Crocodilia niloticus
Chameleon Chamaele ontidate
Dog Canis familiaris
Deer Artiodactyl cervidae
Dolphin Delphinidae delphis
Elephant Proboscidea elepahantidae
Frog Anura ranidae
Fox Cannis vulpes
Giraffe Giraffa horridus
Giant Panda Ailuropoda melanoleuca
Goat Capra hircus
Housefly Musca domestica
Hippopotamus Hippopotamus amphibious
Horse Equus ferus caballus
Hyena Hyaenidae carnivore
Kangaroo Macropus macropodidae
Lion Panthera leo
Lizard Sauria lacertidae
Mouse Mus musculus
Panther Panthera pardus
Pig Sus scrofa
Porcupine Hystricomorph hystricidae
Rabbit Oryctolagus cuniculus
Rhinoceros Perrissodanctyl rthinocerotidae
Scorpion Archinida scorpionida
Sea Horse Hippocampus syngnathidae
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 44
Squirrel Rodentia sciurus
Tiger Panthera tigris
Whale Cetacea, Balaenoptera musculus
Zebra Equidae burcheli
Leopard Panther pardus
Bear Ursidae carnivore
Crow Corvus splendens
Ant Hymenopetrous formicidae
Buffalo Bison bonasus
Ass Equs asinus
Beaver Castor Canadensis
Bison Bison Bison
Wild turkey Maleagris gallopavo
Black Bear Ursus americanus
Bighorn Sheep Ovis Canadensis
Elk Cervus Canadensis
Gray Wolf Canis lupus
Spotted Bat Euderma maculatum
Grizzly Ursus arctos horriblis
Javelina Tayassuidae, Tayassu tajacu, Pecari tajacu
Mule Deer Equus Mule, Odocoileus hemionus
White-tailed Deer Odocoileus virginianus
Pronghorn Antilocapra Americano
Mountain Lion Felis Concolor, Puma concolor
Green Humphead Parrotfish Bolbometopon muricatum
Flying Lemur Cynocephalus volarus
Flat-headed Frog Barbourula busuangesis
Binturong Arctictis binturong
Flying Fox Pteropus vampyrus, Pteropus samoensis
Streaked Reed-Warbler Acrocephalus sorghophilus
Blue-capped Kingfisher Actenoides hombroni
Banded Eagle Ray Aetomylaeus nichofii
Mindanao Pygmy Fruit Bat Alionycteris paucidentata
Palawan Hornbill Anthracoceros marchei
Philippine Duck Anas luzonica
Palawan Flycatcher Ficedula platenae
Dugong Dugong dugon
Sharpnose Guitarfish Glaucostegus granulatus, Rhinobatos granulatus
Blue Coral Heliopora coerulea
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 45
Palawan Stink Badger Mydaus marchei
Tawny Nurse Shark Nebrius ferrugineus
Directions: Classify the following organisms on to what kingdom do they belong.
Use the Five-Kingdom Scheme of Classification.
Organisms Kingdom
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Fungus
Platypus Animalia
Spiny Anteater Animalia
Penicillium Fungus
Paramecium Protista
Pityrosporum ovale Fungus
Aspergillus Fungus
Tarantula Animalia
Vanda sanderyana Plantae
Sponges Animalia
Corals Animalia
Clams animalia
Mangifera indica Plantae
Mucor Fungus
Rhizopus Fungus
Saccharomyces boulardii Fungus
Cryptococcus neoformans Fungus
Candida albicans Fungus
Butterfly Animalia
Paramecium Protista
Shrimp Animalia
Sting ray Animalia
Amoeba Animalia
Cucurbita maxima Plantae
Oleander Plantae
Momordica charantia Plantae
Custard apple Plantae
Malabar night shade Plantae
Solanum melongena Plantae
Ananas comosus Plantae
Fragrant screwpine Plantae
Abelmoschus esculentus L. Plantae
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 46
Parrot Animalia
Owl Animalia
Tapeworm Animalia
Leech Animalia
Planaria Animalia
Protozoa Fungus
Plasmodium Fungus
Chlamydomonas Protista
Sargassum Protista
Yellow bell Plantae
Allium cepa Plantae
Allium sativum Plantae
Papaya Plantae
Winged bean Plantae
Blue berry Plantae
Raspberry Plantae
Caulerpa Protista
Snake Animalia
Turtle Animalia
Elephant Animalia
Salamander Animalia
Godzilla Animalia
Crocodile Animalia
Carbs Animalia
Octopus Animalia
Squid Animalia
Spirogyra Protista
Volvox Protista
Eucheuma Protista
Gracilaria Protista
Escherichia coli Monera
Bacillus anthracis Monera
Klebsiella pneumoniae Monera
Listeria monocytogenes Monera
Arcanobacterium bemolyticum Monera
Rose Plantae
Button mushroom Plantae
Ascomycetes Fungus
Vibrio cholera Monera
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 47
Aeromonas hydrophila Monera
Treponema pallidum Monera
Borellia duttoni Monera
Truffles Fungus
Morels Fungus
Lichens Protista
Puffballs Fungus
Star gazer Plantae
Rhizopus stolonifer Fungus
Chytrids Animalia
Chanterelle Plantae
Portobello Plantae
Mussels Animalia
Snail Animalia
Shark Animalia
Panda Animalia
Oysters Animalia
Sea urchin Animalia
Oregano Plantae
Acapulco Plantae
Eucheuma Plantae
Gonyaulax Animalia
Dragonfly Animalia
Damselfly Animalia
Daisy Plantae
Gumamela Plantae
Jackfruit Plantae
Gracilaria Plantae
Gelidiella Plantae
Triconympha Protista
Zingiber officinale Plantae
Daucas carota Plantae
Cucumis sativas Plantae
Nicotina tobaccum Plantae
Zea mays Plantae
Oryza sativa Plantae
Psidium guava Plantae
Carica papaya Plantae
Pyrus malus Plantae
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 48
Raphanus sativus Plantae
Musa paradisicum Plantae
Citrus limonium Plantae
Directions: Classify the following organisms on to what phylum do they belong in
the Animal Kingdom.
Kingdom Animalia Phylum
Box jellyfish Cnidaria
Sponges Porifera
Venus flower basket Porifera
Spiders Arthropoda
Elephant Chordata
Pig Chordata
Kangaroo Chordata
Platypus Chordata
Crabs Arthropoda
Butterfly Arthropoda
Spiders Arthropoda
Mite Arthropoda
Cat Chordata
Dog Chordata
Lampreys Chordata
Corals Cnidaria
Tick Arthropoda
Earthworms Annelida
Centipede Annelida
Millipede Annelida
Lice Arthropoda
Silverfish Chordata
Mosquito Arthropoda
Planaria Platyhelmintes
Ascaris Nematoda
Liver fluke Platyhelmintes
Tapeworm Platyhelmintes
Ant Arthropoda
Grasshopper Arthropoda
Firefly Arthropoda
Termites Arthropoda
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 49
Sea urchin Echinodermata
Rat Chordata
Sea stars Echinodermata
Butanding Chordata
Sea cucumbers Echinodermata
Sting ray Chordata
Milk fish Chordata
Skate Chordata
Mudfish Chordata
Shark Chordata
Lungfish Chordata
Ostrich Chordata
Penguin Chordata
Doberman Chordata
Bees Arthropoda
Crocodile Chordata
Osprey Chordata
Fruit bat Chordata
Directions: Classify the following plants whether it is a monocot or dicot by
putting a check on the appropriate column below.
Plants Monocot Dicot
Mango
Banana
Papaya
Palmera
Gumamela
Yellow bell
Santan
Cassava
Okra
Eggplant
Daisy
Orchid
Rose
Sunflower
Chrysanthemum
Garlic
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 50
Onion
Lilies
Coconut
Bamboo
Squash
Camote
San Vicente
Ginger
Pineapple
Guava
Winged bean
Star apple
Lima bean
Jicama
Peanut
String bean
Hyacinth bean
Winter melon
Chinese okra
Bottle gourd
Radish
Mustard
Sesame
Tamarind
Sugar Apple
Madre de Cacao
Oregano
Acapulco
Peanut Grass
Corn
Santol
Narra
Acacia
Paper Tree
Tulips
Euphorbia
Dhalia
Carnation
Winged bean
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 51
Lima bean
INTERPHASE
Directions: In the space provided below, draw the three sub-phases of interphase:
(1 , , 2 ) ake sure to explain each sub-
phase.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 52
PROPHASE
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the prophase stage of
mitosis. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 53
METAPHASE
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the metaphase stage of
mitosis. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 54
ANAPHASE
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the anaphase stage of
mitosis. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 55
TELOPHASE
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the telophase stage of
mitosis. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 56
PROPHASE 1
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the prophase 1 stage of
meiosis 1. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 57
METAPHASE 1
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the metaphase 1 stage
of meiosis 1. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 58
ANAPHASE 1
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the anaphase 1 stage of
meiosis 1. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 59
TELOPHASE 1
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the telophase 1 stage of
meiosis 1. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 60
PROPHASE 2
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the prophase 2 stage of
meiosis 2. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 61
METAPHASE 2
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the metaphase 2 stage
of meiosis 2. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 62
ANAPHASE 2
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the anaphase 2 stage of
meiosis 2. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 63
TELOPHASE 2
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the telophase 2 stage of
meiosis 2. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 64
SPERMATOGENESIS
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the process of
spermatogenesis. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 65
OOGENESIS
Directions: In the space provided below, draw and explain the process of
oogenesis. Make it creative and color it by your choice.
Christian Jay Segador Agcaoili, LPT 66
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Organelles Cheat SheetDocumento8 pagineOrganelles Cheat Sheetapi-55809756Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento8 pagineCell Organelles Worksheet537777333% (3)
- Jayden Smith - Handout - Cell Organelle Review WorksheetDocumento2 pagineJayden Smith - Handout - Cell Organelle Review WorksheetJayden SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles Worksheet KEYDocumento9 pagineCell Organelles Worksheet KEYRonnieMaeMaullionNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartDocumento2 pagineCell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartKimora BrooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Documento2 pagineCell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Kirsten Troupe100% (1)
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento8 pagineCell Organelles WorksheetJohn OsborneNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Activity Sheet Biotechnology 8Documento11 pagineLearning Activity Sheet Biotechnology 8Jaeda BaltazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles Worksheet - Pgs 3-5Documento3 pagineCell Organelles Worksheet - Pgs 3-5Kawisara Raorung a roonNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant and Animal CellDocumento24 paginePlant and Animal CellMichel Jay Arguelles EspulgarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells Review Ws AnswersDocumento4 pagineCells Review Ws AnswersTongtun TuntunNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento8 pagineCell Organelles WorksheetVeer RamloghunNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles ReviewDocumento5 pagineCell Organelles ReviewvictoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology: Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento5 pagineBiology: Cell Organelles WorksheetАлександър Антоан НиколовNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocumento37 pagine2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelle Review WorksheetDocumento4 pagineCell Organelle Review WorksheetMae SilogNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento6 pagineCell Organelles WorksheetEdnalyn Cruzada SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento8 pagineCell Organelles WorksheetErika Mae LibangNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure WorksheetDocumento6 pagineCell Structure Worksheetafaflotfi_155696459Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bab 2 Tingkatan 1Documento58 pagineBab 2 Tingkatan 1azizahembong84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key - 2020 - Cell Organelles Worksheet ch2.2Documento7 pagineAnswer Key - 2020 - Cell Organelles Worksheet ch2.2Ria Cloe LavaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology For Engineers: 8.1 What Is A Cell?Documento3 pagineBiology For Engineers: 8.1 What Is A Cell?Sunidhi ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocumento45 pagine1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rajeem Outlaw Wright - Cell Organelle Review WorksheetDocumento3 pagineRajeem Outlaw Wright - Cell Organelle Review WorksheetRajeem Outlaw WrightNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocumento45 pagine1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and Function CW2Documento5 pagineCell Structure and Function CW2areej salimNessuna valutazione finora
- Kami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2Documento8 pagineKami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2bloomington369Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento7 pagineCell Organelles WorksheetKenneth ParungaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Module I-Cocepts in BiologyDocumento46 pagineModule I-Cocepts in BiologyManan MaheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Tour of The CellDocumento60 pagineTour of The Celladisty sncNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal and Plant CellDocumento41 pagineAnimal and Plant CellSabrina LavegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento8 pagineCell Organelles WorksheetJohn OsborneNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 - 02 - 17 1 - 58 PM Office LensDocumento20 pagine2021 - 02 - 17 1 - 58 PM Office Lensojaswi bhatiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2ND-TERM-General BiologyDocumento11 pagine2ND-TERM-General BiologyRaals Internet CafeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Yanga'S Colleges, Inc.: Name: Role: Course - Date Submitted: Group NoDocumento3 pagineDr. Yanga'S Colleges, Inc.: Name: Role: Course - Date Submitted: Group NoJamil Samira E. BuizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell & TissueDocumento11 pagineCell & TissuerahulpanditkgpNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio IpassDocumento15 pagineBio IpassmonreNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsDocumento52 pagineGrade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsFritzel NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Pidlaoan Coleen - Cell-Organelles WorksheetDocumento3 paginePidlaoan Coleen - Cell-Organelles WorksheetColeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 3Documento3 pagineActivity 3enaniacanoNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO Cell Structure Function UnChilled.8532Documento9 pagineBIO Cell Structure Function UnChilled.8532Anna WrightNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Cell?: Cells: Size & ShapeDocumento7 pagineWhat Is A Cell?: Cells: Size & ShapePedro SuyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Points To RememberDocumento5 pagineChapter 8 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1.new Unit 2-1Documento16 pagine1.new Unit 2-1Paramagurunathan YathusanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 (BioChem)Documento33 pagineModule 1 (BioChem)cariagatrishaclaireNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Structures and OrganellesDocumento5 pagine4 Structures and Organellessalmasadiq2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Use The Table Above To Fill in The ChartDocumento5 pagineCell Organelles Worksheet Use The Table Above To Fill in The ChartRachel Ann EstanislaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartDocumento2 pagineCell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartLJ ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure ASDocumento40 pagineCell Structure ASYasmine HadiastrianiNessuna valutazione finora
- SLM Biotech Wekk 1 2Documento7 pagineSLM Biotech Wekk 1 2Petronila LumaguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade Nine Biology Cell AnswersheetDocumento4 pagineGrade Nine Biology Cell AnswersheetHitakshi BhanushaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction CellDocumento48 pagineIntroduction CellabdNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryDocumento6 pagineWeek 2: September 20-25: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell - Structure, Function and OrganizationDocumento1 paginaCell - Structure, Function and Organization- adlina -100% (1)
- OliverosChristian Laboratory Activity No. 2Documento11 pagineOliverosChristian Laboratory Activity No. 2Christian OliverosNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Animal Cell DiagramsDocumento5 paginePlant Animal Cell Diagramssalagi28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartDocumento2 pagineCell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartCyril Mae MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Draw A Simple Eukaryotic Cell and Label All The Parts CompletelyDocumento3 pagineDraw A Simple Eukaryotic Cell and Label All The Parts CompletelyJan Edward Abarientos MandaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksDa EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- 19 - Lipid MetabolismDocumento35 pagine19 - Lipid MetabolismcheckmateNessuna valutazione finora
- RetinaDocumento12 pagineRetinagdudex118811Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gluconeogenesis + Evaluations 4/23/2003Documento30 pagineGluconeogenesis + Evaluations 4/23/2003Ajay Pal NattNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Active Reading GuideDocumento5 pagineChapter 10 Active Reading GuidedorothyNessuna valutazione finora
- MitosisDocumento8 pagineMitosisMilongy JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO1400 Test April 2020-3Documento17 pagineBIO1400 Test April 2020-3Mohammed NawwabNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology SummaryDocumento24 pagineHistology SummaryaelsehamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Article Collection Illuminating Cancer Mechanisms Through Confocal MicrosDocumento110 pagineArticle Collection Illuminating Cancer Mechanisms Through Confocal Microsskraja7534Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blood JournalDocumento12 pagineBlood Journaltammy_tataNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna Transparency TeacherDocumento12 pagineDna Transparency Teacherapi-445198464100% (1)
- Pathophysiologic Mechanism of Erythrocyte Morphological Alteration in Freshwater Fish Channa 2 A Tanning Industry Dye)Documento6 paginePathophysiologic Mechanism of Erythrocyte Morphological Alteration in Freshwater Fish Channa 2 A Tanning Industry Dye)Mamta AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Osmosis: 1 MechanismDocumento6 pagineOsmosis: 1 MechanismsnowflomanNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoker C23Documento15 pagineStoker C23Zahir Jayvee Gayak IINessuna valutazione finora
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocumento67 paginePHOTOSYNTHESISLujinelle FusinganNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle: Gerald Dale Giron MD Department of Human Structural BiologyDocumento23 pagineMuscle: Gerald Dale Giron MD Department of Human Structural BiologyMarx AsuncionNessuna valutazione finora
- Mito-Meiosis Test AnswersDocumento11 pagineMito-Meiosis Test Answersrosidin_551390Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Bio 1 Lesson 4Documento2 pagineGen Bio 1 Lesson 4Ric SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Open Book Exam, Aseel AlharbiDocumento6 pagine2nd Open Book Exam, Aseel Alharbiعبدالرحمن الحربيNessuna valutazione finora
- 9700 m16 Ms 22 PDFDocumento8 pagine9700 m16 Ms 22 PDFIG UnionNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Blood Power PointDocumento71 pagineChapter 10 Blood Power PointNurseReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are T Cells and B Cells - Google SearchDocumento8 pagineWhat Are T Cells and B Cells - Google Searchraj kishan srinivasanNessuna valutazione finora
- CLASS 12 BIO PROJECT SpermatogenesisDocumento19 pagineCLASS 12 BIO PROJECT Spermatogenesisanon_383524563Nessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To Eocqs: Notes About Mark SchemesDocumento2 pagineAnswers To Eocqs: Notes About Mark Schemeshshshs hshs sshdgNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch5. ST - Lecture4 FunctionDocumento50 pagineCh5. ST - Lecture4 Functionsultan khabeebNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Cell Organelles and Other Specialized Cell StructuresDocumento38 pagine2 Cell Organelles and Other Specialized Cell StructuresAnand Wealth JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotez Products & Services 2020Documento20 pagineBiotez Products & Services 2020skljoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Progress in PD-1 - PD-L1 Pathway Inhibitors - From Biomacromolecules To Small MoleculesDocumento30 pagineProgress in PD-1 - PD-L1 Pathway Inhibitors - From Biomacromolecules To Small MoleculesMario Andres JuradoNessuna valutazione finora
- GR 10 5.1 - 5.2 FormativeDocumento3 pagineGR 10 5.1 - 5.2 FormativeShaimaa SalamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 61 Sharma and Agarwal Spermiogenesis - An OverviewDocumento26 pagine61 Sharma and Agarwal Spermiogenesis - An Overviewjohairah merphaNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulation of The Cell TheoryDocumento4 pagineFormulation of The Cell Theoryapi-345209915Nessuna valutazione finora