Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions
Caricato da
yair cedillo jaramilloCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions
Caricato da
yair cedillo jaramilloCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP with IPv4
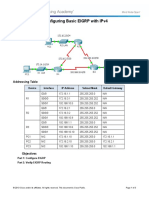
Topology
Addressing Table
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
G0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
R1 S0/0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.252 N/A
S0/0/1 192.168.10.5 255.255.255.252 N/A
G0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
R2 S0/0/0 172.16.3.2 255.255.255.252 N/A
S0/0/1 192.168.10.9 255.255.255.252 N/A
G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
R3 S0/0/0 192.168.10.6 255.255.255.252 N/A
S0/0/1 192.168.10.10 255.255.255.252 N/A
PC1 NIC 172.16.1.10 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1
PC2 NIC 172.16.2.10 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.1
PC3 NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Objectives
Part 1: Configure EIGRP
Part 2: Verify EIGRP Routing
Cisco and/or its affiliates Page 1 of 3
2017 . All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP with IPv4
Background
In this activity, you will implement basic EIGRP configurations including network commands, passive interfaces
and disabling automatic summarization. You will then verify your EIGRP configuration using a variety of show
commands and testing end-to-end connectivity.
Part 1: Configure EIGRP
Step 1: Enable the EIGRP routing process.
Enable the EIGRP routing process on each router using AS number 1. The configuration for R1 is shown.
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
What is the range of numbers that can be used for AS numbers? 1-65,535
Note: Packet Tracer currently does not support the configuration of an EIGRP router ID.
Step 2: Advertise directly connected networks.
a. Use the show ip route command to display the directly connected networks on each router.
How can you tell the difference between subnet addresses and interface addresses?
b. On each router, configure EIGRP to advertise the specific directly connected subnets. The configuration
for R1 is shown.
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.3.0 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.10.4 0.0.0.3
Step 3: Configure passive interfaces.
Configure the LAN interfaces to not advertise EIGRP updates. The configuration for R1 is shown.
R1(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0 Step
4: Disable automatic summarization.
The topology contains discontiguous networks. Therefore, disable automatic summarization on each router.
The configuration for R1 is shown.
R1(config-router)# no auto-summary
Note: Prior to IOS 15 auto-summary had to be manually disabled.
Step 5: Save the configurations.
Part 2: Verify EIGRP Routing
Step 1: Examine neighbor adjacencies.
a. Which command displays the neighbors discovered by EIGRP? Show ip protocol
b. All three routers should have two neighbors listed. The output for R1 should look similar to the following:
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1
Cisco and/or its affiliates Page 2 of 3
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
2013 . All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP with IPv4
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 172.16.3.2 Se0/0/0 14 00:25:05 40 1000 0
28
1 192.168.10.6 Se0/0/1 12 00:13:29 40 1000 0
31 Step 2: Display the EIGRP routing protocol parameters.
a. What command displays the parameters and other information about the current state of any active IPv4
routing protocol processes configured on the router? Show ip
b. On R2, enter the command you listed for 2a and answer the following questions:
How many routers are sharing routing information with R2? Dos routers
Where is this information located under? Dor routers
What is the maximum hop count? 100
Step 3: Verify end-to-end connectivity
PC1, PC2 and PC3 should now be able to ping each other. If not, troubleshoot your EIGRP configurations.
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Question Possible Earned
Location Points Points
Activity Section
Part 1: Configure EIGRP Step 1 2
Step 2a 2
Part 1 Total 4
Part 2: Verify EIGRP Step 1a 5
Routing
Step 2a 5
Step 2b 6
Part 2 Total 16
Packet Tracer Score 80
Total Score 100
Cisco and/or its affiliates Page 3 of 3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Advanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationDa EverandAdvanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationNessuna valutazione finora
- 13.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Communities PDFDocumento15 pagine13.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Communities PDFTrần Hoàng ThôngNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Stub Routing: TopologyDocumento9 pagineChapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Stub Routing: Topologyandres gomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Junos Release Notes 13.1Documento133 pagineJunos Release Notes 13.1anter1974Nessuna valutazione finora
- RacalDocumento537 pagineRacalengineer_3100% (1)
- 7.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 - ILM PDFDocumento17 pagine7.4.3.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv6 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov97% (31)
- 2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4tatic and Default Routes Instructions1Documento4 pagine2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4tatic and Default Routes Instructions1Rafiullah RustamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 (Service Accessibility) - WCDMA RAN Opt - EgitimDocumento200 pagineChapter 3 (Service Accessibility) - WCDMA RAN Opt - EgitimOkan IlkerNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions IGDocumento5 pagine7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions IGkarenNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes InstructionsDocumento4 pagine2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes InstructionsVivekanandan Kandasamy0% (1)
- 3g Kpi Formula Alu EricssonDocumento18 pagine3g Kpi Formula Alu Ericssonanupwadhwani0% (1)
- Data Communication and Networking 3 - Final Quiz 1 - Attempt ReviewDocumento6 pagineData Communication and Networking 3 - Final Quiz 1 - Attempt ReviewJan Warry BaranueloNessuna valutazione finora
- RSE v6 Instructor Packet Tracer ManualDocumento145 pagineRSE v6 Instructor Packet Tracer ManualRicardo Jose Rojas VilledaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path ManipulationDocumento14 pagine12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path ManipulationjoseNessuna valutazione finora
- 4G RF Planning and Optimization (Day One) 02 Jan 2014 PDFDocumento153 pagine4G RF Planning and Optimization (Day One) 02 Jan 2014 PDFThanh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- TBF Drop Improvement Tips in Huawei GSMDocumento5 pagineTBF Drop Improvement Tips in Huawei GSMbrunoNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsNicky Villa50% (2)
- 6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsMiguel AngelNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsArfian HaryonoNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsJessica Gregory100% (1)
- 2.2.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic EIGRP With IPv4Documento3 pagine2.2.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic EIGRP With IPv4venkteshmmoger13Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic EIGRP With IPv4 - ITExamAnswersDocumento4 pagine2.2.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic EIGRP With IPv4 - ITExamAnswersIwanNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.3.4.4 Packet Tracer - Investigating DUAL FSM InstructionsDocumento4 pagine6.3.4.4 Packet Tracer - Investigating DUAL FSM InstructionsJessica Gregory0% (1)
- KLoaiza 6.4.3.3 Packet TracerDocumento5 pagineKLoaiza 6.4.3.3 Packet TracerKevin LoaizaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.3.4.4 Packet Tracer - Investigating DUAL FSM InstructionsPHDocumento4 pagine6.3.4.4 Packet Tracer - Investigating DUAL FSM InstructionsPHPedro HernanNessuna valutazione finora
- Finals Activity 1 - 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocumento5 pagineFinals Activity 1 - 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANjaxmain1750Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDocumento3 pagine7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 InstructionsDaniel Osorio100% (2)
- Lab 2 - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Documento9 pagineLab 2 - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Shrey AnchalwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic Eigrp With Ipv4: ObjectivesDocumento2 paginePacket Tracer - Configuring Basic Eigrp With Ipv4: ObjectivesMehdi SultaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Documento10 pagine6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Ana DianaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.1.3.6 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features 1Documento9 pagine7.1.3.6 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features 1белимNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 FinalDocumento13 pagine6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 FinalJoseph Ryan WolfNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab: Topology DiagramDocumento4 pagineLab 3: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab: Topology DiagramDat LCNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes InstructionsDocumento4 pagine2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes InstructionsMuhammad Nabil12Nessuna valutazione finora
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Documento16 pagine11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Deux AmisNessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan Configuring Basic Eigrp For Ipv4Documento18 pagineLaporan Configuring Basic Eigrp For Ipv4sumar tiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features - ILMDocumento22 pagineLab - Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features - ILMEl ProfaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path Manipulation - ITExamAnswersDocumento22 pagine12.1.2 Lab - Implement BGP Path Manipulation - ITExamAnswersiqmalkuaciNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes Instructions PDFDocumento4 pagine6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes Instructions PDFzulnorainaliNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4 - ILMDocumento22 pagine11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4 - ILMlokuras de la vidaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Documento20 pagine11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Lilifilm OfficialNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes Instructions1Documento4 pagine2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes Instructions1master master0% (1)
- 2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2Documento2 pagine2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2-- JokerNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2 - ILMDocumento4 pagine2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2 - ILMEsteban TapiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP AuthenticationDocumento3 pagine2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP AuthenticationLayla KettlewellNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - Implement Eigrp For Ipv4: TopologyDocumento15 pagineLab - Implement Eigrp For Ipv4: TopologyyoursweetseptemberNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3.2a - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - 2.3.2.6Documento3 pagineLab 3.2a - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - 2.3.2.6MR ANessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Lab 2-3, EIGRP For IPv6Documento31 pagineChapter 2 Lab 2-3, EIGRP For IPv6leoNessuna valutazione finora
- OctavoParaleloAAnrangoEdwin2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2 - ILMDocumento3 pagineOctavoParaleloAAnrangoEdwin2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2 - ILMrolando1991Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.6.6-Packet-Tracer - 19030313Documento8 pagine2.6.6-Packet-Tracer - 19030313Dante CamachoNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.1.5.5 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 FeaturesDocumento11 pagine8.1.5.5 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 FeaturesDaniel OsorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: TopologyDocumento5 paginePacket Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: TopologyShulav PoudelNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring Ipv4 Static and Default Routes: ND NDDocumento2 pagineConfiguring Ipv4 Static and Default Routes: ND NDNuwan ChamikaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 02-Implementing and Verifying EIGRPDocumento24 pagine02-Implementing and Verifying EIGRPPablo MotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity-6 Routing Informatio Protocol (RIP)Documento6 pagineActivity-6 Routing Informatio Protocol (RIP)raffy arranguezNessuna valutazione finora
- BGP Lab 4 - Implement BGP CommunitiesDocumento17 pagineBGP Lab 4 - Implement BGP CommunitiesSam A. SalmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMDocumento3 pagine2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMElectronica EdwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring EIGRP: BSCI Module 2-2 - Implementing and Verifying EIGRPDocumento24 pagineConfiguring EIGRP: BSCI Module 2-2 - Implementing and Verifying EIGRPHerlander FaloNessuna valutazione finora
- 16.1.2 Lab - Implement a GRE Tunnel - ITExamAnswersDocumento20 pagine16.1.2 Lab - Implement a GRE Tunnel - ITExamAnswershayltonmonteiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRPDocumento4 pagineLab - Configuring Basic EIGRPAisha MuhammedNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv6 Routing Instructions IG PDFDocumento3 pagine7.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv6 Routing Instructions IG PDFJESUSCAMPONessuna valutazione finora
- Transistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsDa EverandTransistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkDa EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNessuna valutazione finora
- Broadband Wireless Mobile: 3G and BeyondDa EverandBroadband Wireless Mobile: 3G and BeyondWillie W. LuNessuna valutazione finora
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingDa EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNessuna valutazione finora
- Routing Concepts and Packet Forwarding ProcessDocumento35 pagineRouting Concepts and Packet Forwarding ProcessNewton Dannie AbelNessuna valutazione finora
- ISDN Architecture and ServicesDocumento32 pagineISDN Architecture and ServicesSweqZNessuna valutazione finora
- Console OutputDocumento81 pagineConsole OutputManuel GermanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Center SolutionDocumento37 pagineData Center SolutionHumbulani D SioboNessuna valutazione finora
- Examples of Call FlowDocumento39 pagineExamples of Call FlowVivek YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1.3.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN RoutingDocumento10 pagine5.1.3.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN Routingfabio tovarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pepwave Max Hd2 DatasheetDocumento2 paginePepwave Max Hd2 DatasheetHendra AgustiaNessuna valutazione finora
- PPC 110097 1Documento2 paginePPC 110097 1Qamar Hassan IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ss 7 Fun 04Documento6 pagineSs 7 Fun 04Ajit RoutNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat4500E High Cpu Utilization TroubleshootingDocumento12 pagineCat4500E High Cpu Utilization TroubleshootingBhawna PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- SMS error codes and descriptionsDocumento2 pagineSMS error codes and descriptionsLokesh Ranjan KrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Special Kathrein CombinersDocumento22 pagineSpecial Kathrein Combinersstere_c23Nessuna valutazione finora
- MA BRKSEC-3006 284402 156-1 v1Documento110 pagineMA BRKSEC-3006 284402 156-1 v1Emmara SecondShopNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 3 v7.0 Modules 1 - 2: OSPF Concepts and Configuration Exam AnswersDocumento23 pagineCCNA 3 v7.0 Modules 1 - 2: OSPF Concepts and Configuration Exam AnswersElías Naranjo MejíaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Selection and Reselection in LTE UEDocumento3 pagineCell Selection and Reselection in LTE UESrotoswini SudhansuNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual - IP - Firewall - Connection Tracking - MikroTik WikiDocumento4 pagineManual - IP - Firewall - Connection Tracking - MikroTik WikiachainyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring VXLAN 16Documento16 pagineConfiguring VXLAN 16adroit itacademyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Framework of Multicast Transmission On MPLS Network Using PIM-SMDocumento6 pagineA Framework of Multicast Transmission On MPLS Network Using PIM-SMjackson8002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nodeb Data Configuration: InternalDocumento57 pagineNodeb Data Configuration: InternalOsama El MesalawyNessuna valutazione finora
- Missing 3G DB Cells MentorDocumento51 pagineMissing 3G DB Cells MentorMubashar khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mikrotik firewall and load balancing configurationDocumento1 paginaMikrotik firewall and load balancing configurationIskandar MustofaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccna 1 Module 7 v4.0Documento6 pagineCcna 1 Module 7 v4.0ccnatrainingNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet of Things (Cp5292) UNIT-1 Introduction To IotDocumento7 pagineInternet of Things (Cp5292) UNIT-1 Introduction To Iot2021 Batch First YearNessuna valutazione finora