Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - Clinical Laboratory Testing From A Functional Perspective - Quick Reference Guide
Caricato da
jamesilluminareTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - Clinical Laboratory Testing From A Functional Perspective - Quick Reference Guide
Caricato da
jamesilluminareCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis
Clinical Laboratory Testing from a Functional Perspective
..
Quick Reference Guide
Dicken Weatherby, N.D.
Scott Ferguson, N.D.
Bear Mountain Publishing Ashland, OR
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 1 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 2 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis- Clinical Laboratory Testing from a Functional Perspective
Quick Reference Guide
2005 By Weatherby & Associates, LLC
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
recording, or by any information storage or retrieval system without written permission from the authors, except for the inclusion of quotations in a review.
Bear Mountain Publishing
1-541-482-3779
ISBN: 0-9761367-8-3
Warning - Disclaimer
Bear Mountain Publishing has designed this book to provide information in regard to the subject matter covered. It is sold with the understanding that the
publisher and the authors are not liable for the misconception or misuse of information provided. The purpose of this book is to educate. It is not meant to be a
comprehensive source for blood chemistry and CBC analysis, and is not intended as a substitute for medical diagnosis or treatment, or intended as a substitute
for medical counseling. Information contained in this book should not be construed as a claim or representation that any treatment, process or interpretation
mentioned constitutes a cure, palliative, or ameliorative. The interpretation is intended to supplement the practitioners knowledge of their patient. It should be
considered as adjunctive support to other diagnostic medical procedures.
Printed in the United States of America
How to Order
Order online at www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 3 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
BLOOD CHEMISTRY AND COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
Introduction
There are few diagnostic tests that are truly diagnostic all on their own. It is important to see the trends and patterns that exist
between various tests. This section is organized to provide that information, and is broken into two sections.
Section One
The first section of the Quick Reference Guide is a list of the individual components of the blood chemistry screen and complete
blood count. Beside each component, organized by high or low values, is a list of the most common conditions seen with deviations
from normal.
COMPONENT HIGH LOW
Insulin resistance Hypoglycemia- reactive
Early stage hyperglycemia/Diabetes Hypoglycemia- Liver glycogen problem
Syndrome X/Metabolic Syndrome Hyperinsulinism
Glucose Thiamine Need Adrenal hypofunction
Cortisol resistance
Fatty liver
Liver congestion
Diabetes mellitus Hypoglycemia
Hemoglobin A1C
Insulin resistance
Syndrome X/Metabolic Syndrome Liver/biliary dysfunction
Fatty liver Thyroid hyperfunction
Liver congestion Autoimmune processes
Insulin resistance Adrenal hyperfunction
Cardiovascular disease
Atherosclerosis
Poor metabolism and utilization of fats
Triglycerides
Early stage hyperglycemia/Diabetes
Hyperlipidemia/ Hyperlipoproteinemia
Primary hypothyroidism
Adrenal cortical dysfunction
Secondary hypothyroidism- anterior pituitary
dysfunction
Alcoholism
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 4 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
COMPONENT HIGH LOW
Primary hypothyroidism Oxidative stress
Adrenal cortical dysfunction Heavy metal body burden
Cardiovascular disease Liver/biliary dysfunction
Atherosclerosis Diet- malnutrition
Biliary stasis Thyroid hyperfunction
Insulin resistance Autoimmune processes
Cholesterol
Poor metabolism and utilization of fats Adrenal hyperfunction
Fatty liver
Early stage hyperglycemia/Diabetes
Syndrome X/Metabolic Syndrome
Hyperlipoproteinemia
Multiple sclerosis
Diet- high in refined carbohydrates
Syndrome X/Metabolic Syndrome
LDL Atherosclerosis
Fatty liver/Hyperlipidemia
Oxidative stress
Autoimmune processes Hyperlipidemia/Fatty Liver
Atherosclerosis
Syndrome X/Metabolic Syndrome
HDL Oxidative stress
Heavy metals
Hyperthyroidism
Lack of exercise/sedentary lifestyle
Renal disease Diet- low protein
Renal insufficiency Malabsorption
Dehydration Pancreatic insufficiency
Hypochlorhydria Liver dysfunction
BUN Diet- excessive protein intake
Adrenal hyperfunction
Dysbiosis
Edema
Anterior pituitary dysfunction
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 5 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
COMPONENT HIGH LOW
BPH Muscle atrophy
Urinary tract congestion Protein insufficiency or impaired digestion
Creatinine Renal disease
Renal insufficiency
Uterine hypertrophy
Bun/Creatinine Renal disease Diet- low protein
ratio Posterior pituitary dysfunction
Gout Molybdenum deficiency
Atherosclerosis/Oxidative stress Anemia- B12/folate deficiency
Arthralgias Copper deficiency
Uric Acid
Renal insufficiency/Renal disease
Circulatory disorders
Leaky gut syndrome
Adrenal hypofunction Adrenal hyperfunction
Dehydration Drug diuretics
Potassium
Tissue destruction Benign essential hypertension
Metabolic acidosis
Adrenal hyperfunction Adrenal hypofunction
Cushings disease Addisons disease
Sodium
Dehydration Edema
Drug diuretics
Metabolic acidosis Hypochlorhydria
Chloride Adrenal hyperfunction Metabolic alkalosis
Adrenal hypofunction
Metabolic alkalosis Metabolic acidosis
Adrenal hyperfunction Thiamine need
CO2
Hypochlorhydria Respiratory alkalosis
Respiratory acidosis
Thiamine need
Anion Gap
Metabolic acidosis
Dehydration Hypochlorhydria
Total Protein Digestive dysfunction and/or inflammation
Liver dysfunction
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 6 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
COMPONENT HIGH LOW
Dehydration Hypochlorhydria
Liver dysfunction
Albumin
Oxidative stress
Vitamin C need
Hypochlorhydria Digestive dysfunction and/or inflammation
Liver cell damage Immune insufficiency
Globulin
Oxidative stress
Heavy metal toxicity
Albumin/ Liver dysfunction
Globulin ratio Immune activation
Parathyroid hyperfunction Parathyroid hypofunction
Calcium
Thyroid hypofunction Calcium need
Impaired membrane health Hypochlorhydria
Parathyroid hypofunction Parathyroid hyperfunction
Bone growth and/or repair Hypochlorhydria
Phosphorous
Diet- excessive phosphorous consumption Hyperinsulinism
Renal insufficiency Diet- high in refined carbohydrates
Renal dysfunction Epilepsy
Magnesium
Thyroid hypofunction Muscle spasm
Biliary obstruction Zinc deficiency
Liver cell damage
Bone: loss/increased turnover or bone growth
Alkaline
and/or repair
phosphatase
Leaky gut syndrome
Herpes zoster
Metastatic carcinoma of the bone
Liver/biliary dysfunction Reactive hypoglycemia
Cardiovascular disease
Anemia- B12/folate deficiency, hemolytic
LDH
Non-specific tissue inflammation
Tissue destruction
Viral infection
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 7 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
COMPONENT HIGH LOW
Dysfunction located outside of the liver and Biliary B6 deficiency
tree Alcoholism
Developing Congestive Heart Failure
Acute MI
Cardiovascular dysfunction: Coronary artery
SGOT/AST
insufficiency
Liver cell damage
Liver dysfunction
Excess muscle breakdown or turnover
Infectious mononucleosis, EBV, CMV
Dysfunction located in the liver B6 deficiency
Fatty liver Fatty liver (early development)
Liver dysfunction Liver congestion
SGPT/ALT Biliary tract obstruction Alcoholism
Excessive muscle breakdown or turnover
Cirrhosis of the liver
Liver cell damage
Dysfunction located outside the liver and inside the B6 deficiency
biliary tree Magnesium need
Biliary obstruction
Biliary stasis/insufficiency
GGTP
Liver cell damage
Alcoholism
Acute/chronic Pancreatitis
Pancreatic insufficiency
Biliary stasis Spleen insufficiency
Oxidative stress
Thymus dysfunction
Total Bilirubin Biliary tract obstruction or calculi
Liver dysfunction
RBC hemolysis
Gilberts syndrome
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 8 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
COMPONENT HIGH LOW
Direct Bilirubin Biliary tract obstruction
Biliary calculi/obstruction (usually extra hepatic)
RBC hemolysis
Indirect Bilirubin
Gilberts syndrome
Liver dysfunction Anemia- iron deficiency
Hemochromatosis/hemosiderosis/iron overload Hypochlorhydria
Serum Iron Iron conversion problem Internal/microscopic bleeding
Viral infection
Excess iron consumption
Hemochromatosis/hemosiderosis/iron overload Anemia- iron deficiency
Ferritin Excess iron consumption
Inflammation/liver dysfunction/oxidative stress
Anemia- iron deficiency Hemochromatosis/hemosiderosis/iron overload
TIBC Internal bleeding Microscopic bleeding
Diet- protein malnutrition
% Transferrin Hemochromatosis/hemosiderosis/iron overload Anemia- iron deficiency
Saturation
Primary hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism
Secondary hypothyroidism- anterior pituitary
TSH dysfunction
Tertiary hypothyroidism- hypothalamic dysfunction
Heavy metal body burden
Hyperthyroidism Primary hypothyroidism
T-3
Iodine deficiency Selenium deficiency
Hyperthyroidism Primary hypothyroidism
T-4
Thyroid hormone replacement Iodine deficiency
Hyperthyroidism Primary hypothyroidism
Thyroid hormone replacement Secondary hypothyroidism- anterior pituitary
T-3 Uptake dysfunction
Selenium deficiency
Iodine deficiency
ESR Non-specific tissue inflammation or destruction
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 9 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
COMPONENT HIGH/LOW CONDITION
Childhood diseases (Measles, Mumps, Rubella, Chronic viral infections
Chicken pox etc.) Chronic bacterial infections
White Blood Cell Acute bacterial infection Leukocytic auto-digestion
Count Acute viral infection Systemic Lupus Erythematosis (SLE)
Stress Decreased production from bone marrow
Diet- High in refined carbohydrates Diet- raw food diet
Respiratory distress: Asthma or emphysema Anemia- Iron deficiency
Polycythemia (relative or absolute) Anemia- B12/folate deficiency
Red Blood Cell
Dehydration Anemia- Copper deficiency
Count
Internal bleeding
Vitamin C need
Respiratory distress: Asthma or emphysema Anemia- iron deficiency
Polycythemia (relative or primary) Anemia- B12/folate deficiency
Dehydration Anemia- B6 deficiency anemia
Hemoglobin Anemia- Copper deficiency
Internal bleeding
Digestive inflammation
Vitamin C need
Respiratory distress: Asthma or emphysema Anemia
Polycythemia (relative or primary) Anemia- Iron deficiency
Spleen hyperfunction Anemia- B12/folate deficiency
Dehydration Anemia- B6 deficiency
Hematocrit
Anemia- Copper deficiency
Internal bleeding
Digestive inflammation
Thymus hypofunction
Vitamin C need
Anemia- B12/folate deficiency Anemia- Iron deficiency
MCV Vitamin C need Anemia- B6 deficiency
Internal bleeding
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 10 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
COMPONENT HIGH LOW
Anemia- B12/folate deficiency Anemia- Iron deficiency
Hypochlorhydria Anemia- B6 deficiency
MCH Internal bleeding
Heavy metal body burden
Vitamin C need
Anemia- B12/folate deficiency Anemia- Iron deficiency
Hypochlorhydria Anemia- B6 deficiency
MCHC
Heavy metal body burden
Vitamin C need
Anemia- Iron deficiency Childhood diseases (Measles, Mumps, Rubella,
Anemia- B12/folate deficiency Chicken pox)
RDW
Pernicious anemia Acute or chronic bacterial infection
Inflammation
Blood diseases (aplastic anemia, pernicious
Neutrophils anemia etc.)
Chronic viral infection
Recovery phase of infection
Liver dysfunction
Monocytes
Intestinal parasites
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)
Childhood diseases Chronic viral or bacterial infections
Acute and chronic viral infection Free radical activity
Lymphocytes Infectious mononucleosis Active bacterial infection
Inflammation Suppressed bone marrow function
Systemic toxicity
Intestinal parasites Increased adrenal steroid production
Eosinophils Food and environmental allergies/sensitivities
Asthma
Tissue inflammation
Basophils
Intestinal parasites
Atherosclerosis Idiopathic thrombocytopenia
Platelet count Heavy metal body burden
Free radical pathology
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 11 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
Section Two
The second section presents the common patterns arranged by conditions. Beside each condition is a list of the patterns organized
by which components of the blood chemistry screen and complete blood count are high or low for any given condition. The optimal
value changes are given for both the Standard US Units and Standard International Units.
CONDITION HIGH LOW
Adrenal Sodium (>142) Potassium (<4.0)
hyperfunction Chloride (>106) Cholesterol (<150 or 3.9mmol/L)
CO2 (>30) Triglyceride (<70 or 0.79mmol/L)
BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L)
Adrenal hypofunction Potassium (>4.5) Sodium (<135)
Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L) Chloride (<100)
Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L) Blood Glucose (<80 or 4.44 mol/L)
MCH (>31.9) RBCs (<3.9, <4.2)
MCV (>89.9) HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
Anemia- B12/folate RDW (>13) HGB (<13.5 or 135g/L in and <14 or 140 in )
deficiency MCHC (>35) WBCs (<5.0)
Serum iron (>100 or >17.91 mol/L) Neutrophils (<40)
LDH (>200) Uric acid (<3.5 or 208 mol/dL)
LDH (>200)
Anemia- hemolytic
Reticulocytes (>1 or 00.1)
TIBC (>350) Serum iron (<50 or <8.96 mol/L)
Transferrin Ferritin (<10 in and <33 in )
If hypochlorhydria is present: % transferrin saturation (<20%)
Globulin (>2.8 or 28 g/L) or N RBCs (<3.9, <4.2)
Anemia- Iron
HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in and <14 or140 in )
deficiency
or N HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
MCV MCV (<82), MCH (<28), MCHC (<32)
Globulin (<2.4 or 24 g/L)
Phosphorous (<3.0 or 0.97 mmol/L)
Anterior Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L) TSH (<2.0)
pituitary/secondary Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L) T-3 uptake (<27)
thyroid hypofunction BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L)
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 12 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
ESR (> 10 in and > 5 in ) or N albumin (<4.0 or 40 g/L)
C-reactive protein
Arthralgias or N albumin (>5.0 or 50 g/L)
Globulin (>2.8 or 28 g/L)
Platelet (>385)
HGB (>14.5 or 145 g/L in and >15 or 150 in ) Lymphocytes
Eosinophils (>3%) Plasma and salivary cortisol in the chronic phase.
Asthma HCT (>44 or 0.44 in and >48 or 0.48 in )
Neutrophils (>60%)
or N Total WBC (>7.5)
Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L) HDL (<55 or 1.42 mmol/L)
or N Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L)
LDL (>120 or 3.1 mmol/L)
Atherosclerosis
Uric acid (>5.9 or 351 mol/dL)
Platelet (>385)
C reactive protein
Autoimmune HDL (>70 or 1.81 mmol/L) Triglyceride (<70 or 0.79 mmol/L)
processes- tissue LDH (>200) or N Cholesterol (<150 or 3.9 mmol/L)
destruction
N Serum iron or N SGPT/ALT (<10)
B6 deficiency SGOT/AST (<10)
(confirm with a serum GGTP (<10)
or urinary MCV (<82), MCH (<28)
homocysteine) MCHC (<32)
HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in and <14 or 140 in )
Alkaline phosphatase (>100) Triglyceride (<70 or 0.79 mmol/L)
GGTP (>30) Cholesterol (<150 or 3.9 mmol/L)
Biliary dysfunction
SGPT/ALT (>30)
LDH (>200)
Alkaline phosphatase (>100)
SGPT/ALT (>30)
Biliary GGTP (>30)
obstruction/calculi
Bilirubin (>1.2 or 20.5 mol/dL)
Direct bilirubin (>0.2 or 3.4 mol/dL)
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 13 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69 mmol/L)
Biliary GGTP (>30)
stasis/insufficiency Bilirubin (>1.2 or 20.5 mol/dL)
Alk Phos (>100)
Creatinine (>1.1 or 97.2 mmol/L)
BPH PSA (may be normal)
Monocytes (>7%)
Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L) HDL (<55 or 1.42 mmol/L)
Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L)
Cardiovascular
LDL (>120 or 3.1 mmol/L)
disease
LDH (>200)
SGOT/AST (>30)
Total WBC (>7.5) Neutrophils (<40%) (later)
Childhood diseases Neutrophils (>60%) (early) Lymphocytes (<24%) (early)
Lymphocytes (>44%)(later)
Low high MCV (>89.9) Uric acid (<3.5 or 208 mol/dL)
to N MCH (>31.9), HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
Copper deficiency
HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in and <14 or 140 in )
RBCs (<3.9, <4.2)
Deficient Red Blood Serum iron (>100 or >17.91 mol/L) RBCs (<3.9, <4.2)
Cell production HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
RBCs (>4.5 in and >4.9 in )
HGB (>14.5 or 145 g/L in and >15 or 150 in )
HCT (>44 or 0.44 in and >48 or 0.48 in )
Total protein (> 7.4 or 74 g/L) (Chronic)
Dehydration
Albumin (>5.0 or 50 g/L) (Chronic)
Sodium (>142)
Potassium (<4.0)
BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L) (Chronic)
Blood Glucose (>100 or 5.55 mmol/L) HDL (<55 or 1.42 mmol/L)
Hemoglobin A1C (>5.7% or 0.057)
Diabetes/hyperglyce Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69 mmol/L)
mia Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L)
BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L)
Creatinine (>1.1 or 97.2 mmol/dL)
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 14 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
Cholesterol (<150 or 3.9mmol/L)
Diet- fat deficient
Triglyceride (<70 or 0.79mmol/L)
Diet- high in refined LDL (>120 or 3.1 mmol/L) Phosphorous (<3.0 or 0.97 mmol/L)
carbohydrates Total WBC count (<5.0)
BUN (<10 or 3.57 mmol/L)
Total protein (< 6.9 or 69 g/L)
Diet- low protein
BUN-Creatinine ratio (<13)
Creatinine (<0.8 or 70.7 mmol/dL)
BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L) Total protein (< 6.9 or 69 g/L)
Digestive Basophils (>1%) Total Globulin (<2.4 or 24 g/L)
dysfunction/inflamma With Ulceration or erosion: Albumin (<4.0 or 40 g/L)
tion Alk Phos intestinal isoenzyme Phosphorous (<3.0 or 0.97 mmol/L)
Creatinine (<0.8 or 70.7 mol/dL)
BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L) Sodium (<135)
Edema
albumin (<4.0 or 40 g/L)
HCT (>44 or 0.44 in and >48 or 0.48 in ) Alpha I globulin
Emphysema RBCs (>4.5 in and >4.9 in ) or N serum chloride (<100)
or N C02 (>30)
Excess consumption Serum iron (>100 or >17.91 mol/L)
of iron Ferritin (>122 in and >236 in )
SGPT/ALT (>30)
Fatty Liver (steatosis) LDH (>200)
Alk Phos (>100)
Blood Glucose (>100 or 5.55 mmol/L) HDL (<55 or 1.42 mmol/L)
Fatty liver- Early Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L) SGPT/ALT (<10)
Stage Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L)
LDL (>120 or 3.1 mmol/L)
Bilirubin (>1.2 or 20.5 mol/dL)
Gilberts syndrome
Indirect bilirubin (>1.0 or 17.1 mol/dL)
Uric acid (>5.9 or 351 mol/dL) Phosphorous (<3.0 or 0.97 mmol/L)
Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L)
Gout
BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L)
or N Creatinine (>1.1 or 97.2 mmol/dL)
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 15 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
Uric acid (>5.9 or 351 mol/dL) MCHC (<32) and MCH (<28)
Heavy metal burden Total Bilirubin (>1.2 or 20.5 mol/dL) HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
(run a hair/urine BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L) HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in and <14 or 140 in )
analysis if this Cadmium toxicity: RBCs (<3.9, <4.2)
pattern comes up to Calcium (>10.5 or 2.5 mmol/L) 5th Isoenzyme of LDH
rule this out) Cadmium toxicity:
Phosphorous (<3.0 or 0.97 mmol/L)
Total globulin (>2.8 or 28 g/L) Uric acid (<3.5 or 208 mmol/L)
Cholesterol (<150 or 3.9mmol/L)
Heavy HDL (<55 or 1.42 mmol/L)
metals/chemical MCH (<28)
toxicity MCHC (<32)
TSH (<2.0)
Platelets (<155)
Serum iron (>100 or >17.91 mol/L) TIBC (<250 or 44.8 mol/dL)
Ferritin (>1000)
Hemochromatosis
% transferrin saturation (>35%)
SGOT/AST (>30)
Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L) Blood Glucose (<80 or 4.44 mol/L)
Hyperinsulinemia Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L) HDL (<55 or 1.42 mmol/L)
Phosphorous (<3.0 or 0.97 mmol/L)
Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L) HDL (<55 or 1.42 mmol/L)
Hyperlipidemia Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L)
LDL (>120 or 3.1 mmol/L)
Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L)
Hyperlipoproteinemia
Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L)
BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L) or N Total protein (< 6.9 or 69 g/L)
Total Globulin (>2.8 or 28 g/L) or N albumin (<4.0 or 40 g/L)
Hypochlorhydria Phosphorous (<3.0 or 0.97 mmol/L)
Hypoglycemia- liver SGPT/ALT (>30) Blood Glucose (<80 or 4.44 mol/L)
glycogen storage Hemoglobin A1C (<4.1% or 0.041)
problem LDH (<140)
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 16 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
Blood Glucose (<80 or 4.44 mol/L)
Hypoglycemia-
Hemoglobin A1C (<4.1% or 0.041)
reactive
LDH (<140)
Increased Red blood Bilirubin (>1.2 or 20.5 mol/dL) RBCs (<3.9, <4.2)
cell destruction Indirect bilirubin (>1.0 or 17.1 mol/dL)
Total WBC (>7.5) Lymphocytes (<24%)
Neutrophils (>60%)
Infection: active
Bands (>5%)
ESR (> 10 in and > 5 in )
WBCs or N Lymphocytes (<24%)
Neutrophils (>60%)
Infection: Acute
Monocytes (recovery phase) (>7%)
bacterial
Bands (>5%)
ESR (> 10 in and > 5 in )
Total WBC (>7.5) or N Neutrophils (<40%)
Lymphocytes (>44%)
Monocytes (>7%) (recovery phase)
Infection: Acute viral
Bands (>5%)
ESR (> 10 in and > 5 in )
LDH (>200)
Infection: Chronic Serum iron (>100 or >17.91 mol/L) Total WBC count (<5.0)
viral Lymphocytes (<24%)
Inflammation- non- LDH (>200)
specific ESR (> 10 in and > 5 in )
Ferritin (>122 in and >236 in )
Basophils (>1%)
Insulin Resistance Blood Glucose (>100 or 5.55 mmol/L)
Hemoglobin A1C (>5.7% or 0.057)
Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L)
Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L)
Reticulocyte count (>1%) or N Serum iron (<50 or <8.96 mol/L)
TIBC (>350 or 62.7 mol/dL) or N serum Ferritin (<10 in and <33 in )
Internal bleeding Transferrin. HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in and <14 or 140 in )
or N HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
MCV (<89.9), MCH (<28)
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 17 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
Internal microscopic Reticulocyte count (>1%) TIBC (<250 or 44.8 mol/dL)
bleeding Transferrin
Eosinophils (>3%) or N Serum iron (<50 or <8.96 mol/L)
or N Basophils (>1%) /N HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in & <14 or 140 in )
Intestinal parasites or N Monocytes (>7%) or N HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
IgE
Stool positive for parasites or ova
Iodine deficiency T-3 (>230 or 3.53 nmol/L) T-3 uptake (<27)
T-4 (<6 or 7.2 nmol/L)
Leaky gut syndrome Uric acid (>5.9 or 351 mol/dL)
Alkaline phosphatase (>100)
Liver cell damage Globulin (>2.8 or 28 g/L)
Alkaline phosphatase (>100)
SGOT/AST (>30)
SGPT/ALT (>30)
GGTP (>30)
Liver dysfunction SGPT/ALT (>30) BUN (<10 or 3.57 mmol/L)
LDH (>200) Total protein (< 6.9 or 69 g/L)
SGOT/AST (>30) Albumin (<4.0 or 40 g/L)
Bilirubin (>1.2 or 20.5 mol/dL) Albumin/globulin ratio
Direct bilirubin (>0.2 or 3.4 mol/dL) Triglyceride (<70 or 0.79mmol/L)
Serum iron (>100 or >17.91 mol/L) Cholesterol (<150 or 3.9mmol/L)
Ferritin (>122 in and >236 in )
Monocytes (>7%)
Malabsorption BUN (<10 or 3.57 mmol/L)
GGTP (<10)
Metabolic acidosis Chloride (>106) CO2 (<25)
Anion gap (>12)
Potassium (>4.5)
Metabolic alkalosis CO2 (>30) Chloride (<100)
Calcium (<9.2 or 2.3 mmol/L)
Potassium (<4.0)
Microscopic bleeding Reticulocyte count (>1%) TIBC (<250 or 44.8 mol/dL)
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 18 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
st
Mononucleosis SGOT/AST (>30) WBCs (1 week)
Alkaline phosphatase (>100)
LDH (>200)
WBCs (2nd week)
GGTP (>30)
Lymphocytes (>44%)
Muscle- atrophy or SGOT/AST (>30) Creatinine (<0.8 or 70.7 mmol/dL)
breakdown SGPT/ALT (>30)
Oxidative stress/Free LDL (>120 or 3.1 mmol/L) Lymphocytes (<24%)
radical activity Uric acid (>5.9 or 351 mol/dL) Cholesterol (below historical average)
Total Globulin (>2.8 or 28 g/L) Albumin (<4.0 or 40 g/L)
Bilirubin (>1.2 or 20.5 mol/dL) Platelets (<150)
Ferritin (>122 in and >236 in )
Pancreatic GGTP (>30) Total WBC count
insufficiency BUN (<10 or 3.57 mmol/L)
Parasites- intestinal Eosinophils (>3%)
or N Basophils (>1%)
or N Monocytes (>7%)
Parathyroid Calcium (>10.5 or 2.5 mmol/L) Phosphorous (<3.0 or 0.97 mmol/L)
hyperfunction
Parathyroid Phosphorous (>4.0 or 1.29 mmol/L) Calcium (<9.2 or 2.3 mmol/L)
hypofunction
RBCs (>4.5 in and >4.9 in ) or N MCV (<82)
HCT (>44 or 0.44 in and >48 or 0.48 in ) or N MCH (<28
HGB (>14.5 or 145 g/L in & >15 or 150 in ) or N Serum iron (<50 or <8.96 mol/L)
Total Bilirubin (>1.2 or 20.5 mol/dL)
Polycythemia
Uric acid (>5.9 or 351 mol/dL)
Total WBC (>7.5)
Basophils (>1%)
Alk phos (>100)
Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L)
Poor fat metabolism
Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69 mmol/L)
Posterior pituitary BUN (<10 or 3.57 mmol/L)
dysfunction BUN-Creatinine ratio
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 19 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
Total Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L) Calcium in late pregnancy (<9.2 or 2.3 mmol/L)
MCV (>89.9) and MCH (>31.9) Albumin (<4.0 or 40 g/L)
Neutrophils (>60%) HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in and <14 or 140 in )
Pregnancy T-4 (>12 or 154.4 nmol/L) HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
Total WBC (>7.5) (late) T-3 uptake (<27)
Lymphocytes (<24%) (late))
Total protein (< 6.9 or 69 g/L)
BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L)
or N Creatinine (>1.1 or 97.2 mmol/dL)
Renal insufficiency
or N Uric acid (>5.9 or 351 mol/dL)
Phosphorous (>4.0 or 1.29 mmol/L
Creatinine (>1.1 or 97.2 mmol/dL)
BUN-Creatinine ratio
BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L)
Renal disease Uric acid (>5.9 or 351 mol/dL)
Phosphorous (>4.0 or 1.29 mmol/L
LDH (>200)
SGOT/AST (30)
RBCs (>4.5 in and >4.9 in )
HGB (>14.5 or 145 g/L in & >15 or 150 in )
Respiratory distress
HCT (>44 or 0.44 in and >48 or 0.48 in )
Eosinophils (>3%)
T-3 (<100 or 1.54 nmol/L)
Selenium deficiency
T-3 uptake (<27)
in all white blood cells
Suppressed bone RBCs (<3.9, <4.2)
marrow production HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in and <14 or 140 in )
Blood Glucose (>100 or 5.55 mmol/L) HDL (<55 or 1.42 mmol/L)
Syndrome Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L)
X/Metabolic Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L)
Syndrome LDL (>120 or 3.1 mmol/L)
Hemoglobin A1C (>5.7% or 0.057)
Lymphocytes (>44%)
Systemic toxicity
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 20 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
Blood Glucose (>100 or 5.55 mmol/L) CO2 (<26)
Thiamine deficiency
Anion Gap (>12)
Bilirubin (>1.2 or 20.5 mol/dL)
HGB (>14.5 or 145 g/L in and >15 or 150 in )
Thymus dysfunction
HCT (>44 or 0.44 in and >48 or 0.48 in )
RBCs (>4.5 in and >4.9 in )
Thyroid hormone T-4 (>12 or 154.4 nmol/L)
replacement T-3 uptake (>37)
T-3 (>230 or 3.53 nmol/L) Triglyceride (<70 or 0.79mmol/L)
Thyroid T-4 (>12 or 154.4 nmol/L) Cholesterol (<150 or 3.9mmol/L)
hyperfunction T-3 uptake (>37) HDL (<55 or 1.42 mmol/L)
TSH (<2.0)
Thyroid TSH (>4.4) T-3 (<100 or 1.54 nmol/L)
hypofunction- Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L) T-4 (<6 or 7.2 nmol/L)
primary Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L) T-3 uptake (<27)
Thyroid Triglycerides (>110 or 1.24 mmol/L) TSH (<2.0)
hypofunction- Cholesterol (>220 or 5.69mmol/L) T-3 uptake (<27)
secondary due to BUN (>16 or 5.71 mmol/L)
anterior pituitary
dysfunction
Potassium (>4.5)
Tissue destruction LDH (>200)
ESR (> 10 in and > 5 in )
Tissue inflammation/ ESR (> 10 in and > 5 in )
destruction Potassium (>4.5)
(GI, tendon/bursa, Basophils
phlebitis, sinusitis, ALP increased with liver, bone or gastric
musculoskeletal) inflammation (>100)
Urinary tract Creatinine (>1.1 or 97.2 mmol/dL)
congestion Monocytes (>7%)
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 21 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONDITION HIGH LOW
MCH (>31.9) RBCs (<3.9, <4.2)
MCV (>89.9) HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
Vitamin B12/folate RDW (>13) HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in and <14 or 140 in )
deficiency Serum iron (>100 or >17.91 mol/L) Total WBC count (<5.0)
LDH (>200) Neutrophils (<40%)
Uric acid (<3.5 or 208 mol/dL)
MCV (>89.9) Albumin (<4.0 or 40 g/L)
Alk Phos (>100) MCH (<28)
Fibrinogen MCHC (<32)
Vitamin C need HGB (<13.5 or 135 g/L in and <14 or 140 in )
HCT (<37 or 0.37 in and <40 or 0.4 in )
RBCs (<3.9, <4.2)
Serum iron (<50 or <8.96 mol/L)
Zinc deficiency Alkaline phosphatase (<70)
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 22 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
Stained Red Cell Examination
Discussion
The stained film examination provides information on red blood cell variation and abnormalities in red blood cell size, shape,
hemoglobin content.
When would you run this test?
1. To help diagnose blood disorders: anemia, Thalassemia, and other hemoglobin disorders will have distinctive morphological
changes that can be appreciated via a stained blood cell examination
2. As a guide to therapy: if therapy is effective the abnormalities will begin to clear up.
3. Often a Complete blood count (CBC) will include a stained red cell examination if gross abnormalities are seen
Clinical implications of abnormalities
Abnormality Clinical Implication
Anisocytosis (abnormal Any severe anemia (iron deficiency, megaloblastic)
variations in size) Liver dysfunction
Microcytosis Iron deficiency and iron loading anemia
Thalassemia
Lead poisoning
Macrocytosis Megaloblastic anemia (Vitamin B12/foliate deficiency anemia)
Liver disease
Macroovalocytosis Megaloblastic anemia
Hypochromia ( Iron deficiency and iron loading anemia
concentration of Thalassemia
hemoglobin)
Lead poisoning
Nucleated red blood cells Hemolytic anemia
Leukemias
Myeloproliferative diseases
Multiple myeloma
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 23 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
Abnormality Clinical Implication
Howell-Jolly bodies Hyposplenism
Pernicious anemia
Heinz bodies Congenital hemolytic anemias
Thalassemia
Siderocytes Iron loading anemia
Hyposplenism
Hemolytic anemia
Cabots rings Pernicious anemia
Lead poisoning
Basophilic stippling Hemolytic anemia
Lead poisoning
Rouleaux Tissue hypoxia
Ph imbalances and dysbiosis
Poor protein metabolism
Liver dysfunction
Multiple myeloma
Poikilocytosis (abnormal Digestive disorders especially dysbiosis
variations in shape) Need for essential fatty acids
Increased free radical activity
Liver toxicity
Poor circulation
Any severe anemia
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 24 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
Degree of Poikilocytosis
Certain shapes are diagnostically helpful. The following are shapes seen on stained blood examination:
Abnormality Clinical Implication
Ovalocytes Iron deficiency
B12/folate imbalances
Hormonal imbalance
Sickle cells Sickle cell disease
Target cells Liver disease and bile insufficiency
Dysbiosis
Iron deficiency
Thalassemia
Shistocytes Increased toxins
Spleen dysfunction
Uremia
Burr cells Hemolytic anemias
Liver disease
Acanthocytes Liver and spleen dysfunction
Ph and overall terrain imbalance
Vitamin E deficiency
Hypercholesterolemia
Teardrop cells Lack of assimilation
Liver dysfunction
Weatherby & Associates, LLC 25 www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CHEMSCREEN and CBC RESULTS TRACKING FORM STANDARD U.S. UNITS
NAME: DATE:
TEST REF. RANGE RESULT OPTIMAL / NOTES
Glucose 65 115 80 100
HgB A1C <7% 4.1 5.7%
BUN 5 25 10 16
Creatinine 0.6 1.5 0.8 1.1
Sodium 135 147 135 142
Potassium 3.5 5.3 4.0 4.5
Chloride 96 109 100 106
CO2 22 32 25 30
Anion Gap 6 16 7 12
2.2 7.7 3.5 5.9 male
Uric Acid
3.0 5.5 female
Total Protein 6.0 8.5 6.9 7.4
Albumin 3.5 5.5 4.0 5.0
Calcium 8.5 10.8 9.2 10.0
Phosphorous 2.5 4.5 3.0 4.0
Alk Phos 25 140 70 100
SGOT(AST) 0 40 10 30
SGPT(ALT) 0 45 10 30
LDH 1 240 140 200
total Bilirubin0.1 1.2 0.1 1.2 (>2.6)
direct 0 0.2 0 0.2 (>0.8)
indirect 0.1 1.0 0.1 1.0 (>1.8)
GGTP 1 70 10 30
Globulin 2.0 3.9 2.4 2.8
A/G ratio 1.0 2.4 1.4 2.1
BUN/Creat. 7 18 10 16
Total iron 30 170 50 100
Cholesterol 130 200 150 220
Triglycerides 30 150 70 110
LDL 60 130 <120
HDL 40 90 >55
Chol/HDL Ratio <4
33 - 236 33 236 male
Ferritin
10 - 122 10 122 female
TIBC 250 350 250 350
TSH 0.35 5.50 2.0 4.4
Free T-3 2.3 4.2 2.3 4.2
T-3 60 181 100 165
Free T-4 0.70 2.4 0.70 1.53
T-4 thyroxine 4.5 13.2 6 12
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
WBC 3.7 10.5 5.0 7.5
4.1 5.6 4.2 4.9 male
RBC
3.8 5.1 3.9 4.5 fem
Reticulocyte 0.5 1 0.5 1
12.5 17.0 14 15 male
Hemoglobin
11.5 15.0 13.5 14.5 fem
36 50% 40 48 male
Hematocrit
34 44 37 4 4 female
MCV 80 98 82 89.9
MCH 27 34 28 31.9
MCHC 32 36 32 35
Platelets 155 385 150 385 x 1000
RDW 11.7 15.0 <13
Neutrophils 40 74% 40 60%
Lymphs 14 46% 24 44%
Monocytes 4 13% 0 7%
Eosinophils 0 7% 0 3%
Basophils 0 3% 0 1%
Weatherby & Associates, LLC www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CONVERSION CHART FOR CONVERTING STANDARD US UNITS INTO STANDARD
INTERNATIONAL UNITS
CONVERSION FACTOR
TEST US UNITS Multiply S.I. UNITS
Divide
Glucose mg/dL 0.05551 mmol/L
HgB A1C % 0.01
BUN mg/dL 0.357 mmol/L
Creatinine mg/dL 88.4 mol/dL
Sodium mEq/L 1 mmol/L
Potassium mEq/L 1 mmol/L
Chloride mEq/L 1 mmol/L
CO2 mEq/L 1 mmol/L
Anion Gap mEq/L 1 mmol/L
Uric Acid mg/dL 59.48 mol/dL
Total Protein g/dL 10 g/L
Albumin g/dL 10 g/L
Calcium mg/dL 0.250 mmol/L
Phosphorous mg/dL 0.3229 mmol/L
Alk Phos U/L 1 U/L
SGOT(AST) U/L 1 U/L
SGPT(ALT) U/L 1 U/L
LDH U/L 1 U/L
Bilirubin values mg/dL 17.1 mol/dL
GGTP U/L 1 U/L
Globulin g/dL 10 g/L
A/G ratio Ratio 1 Ratio
BUN/Creat. Ratio 1 Ratio
Total iron mg/dL 0.1791 mol/dL
Cholesterol mg/dL 0.02586 mmol/L
Triglycerides mg/dL 0.01129 mmol/L
LDL mg/dL 0.02586 mmol/L
HDL mg/dL 0.02586 mmol/L
Chol/HDL Ratio 1 Ratio
Ferritin ng/mL 1 g/L
TIBC g/dL 0.1791 mol/dL
TSH IU/mL 1 mIU/L
T-3 uptake % 0.01 %
T-3 ng/dL 0.01536 nmol/L
Free T-3 pg/dl 0.01536 pmol/L
T-4 thyroxine g/dL 12.87 nmol/L
Free T-4 ng/dl 12.87 pmol/L
FTI/ T-7 1
3 3 9
WBC x 10 /mm 1 10 /L
6 3 `12
RBC x 10 /mm 1 10 /L
Hemoglobin g/dL 10 g/L
Hematocrit % 0.01 1
3
MCV Microns 1 fL
MCH pg 1 pg
MCHC g/dL 1 1
3 3 9
Platelets x 10 /mm 1 10 /L
RDW Calculated 1 Calculated
Neutrophils % 1 %
Lymphs % 1 %
Monocytes % 1 %
Eosinophils % 1 %
Basophils % 1 %
Weatherby & Associates, LLC www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
CHEMSCREEN and CBC RESULTS TRACKING FORM STANDARD INTERNATIONAL UNITS
NAME: DATE:
TEST REF. RANGE RESULT OPTIMAL / NOTES
Glucose 3.61 6.38 4.44 5.55
HgB A1C <0.07 0.041 0.057
BUN 1.79 8.93 3.57 5.71
Creatinine 53.0 132.6 70.7 97.2
Sodium 135 147 135 142
Potassium 3.5 5.3 4.0 4.5
Chloride 96 109 100 106
CO2 22 32 25 30
Anion Gap 6 16 7 12
131 458 208 351 male
Uric Acid
178 327 female
Total Protein 60 85 69 74
Albumin 35 55 40 50
Calcium 2.13 2.70 2.30 2.50
Phosphorous 0.81 1.45 0.97 1.29
Alk Phos 25 140 70 100
SGOT(AST) 0 40 10 30
SGPT(ALT) 0 45 10 30
LDH 1 240 140 200
total Bilirubin1.7 20.5 1.7 20.5 (>44.5)
direct 0 3.4 0 3.4 (>13.7)
indirect 1.7 17.1 1.7 17.1 (>30.8)
GGTP 1 70 10 30
Globulin 20 39 24 28
A/G ratio 1.1 2.5 1.5 2.0
BUN/Creat. 7 14 13 17
Total iron 5.37 30.45 8.96 17.91
Cholesterol 3.36 5.20 3.9 5.69
Triglycerides 0.34 1.7 0.79 1.24
LDL 1.55 3.36 <3.1
HDL 1.03 2.32 >1.42
Chol/HDL Ratio <4
33 - 236 33 236 male
Ferritin
10 - 122 10 122 female
TIBC 44.8 62.7 44.8 62.7
TSH 0.35 5.50 2.0 4.4
Free T-3 3.59 6.56 3.59 6.56
T-3 1.23 3.53 1.54 3.53
Free T4 9.1 31.0 9.1 19.7
T-4 thyroxine 61.8 169.9 77.2 154.4
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
WBC 3.7 10.5 5.0 7.5
RBC 4.1 5.6 4.2 4.9 male
3.8 5.1 3.9 4.5 fem
Reticulocyte 0.5 1 0.5 1
Hemoglobin 125 170 140 150 male
115 150 135 145 fem
Hematocrit 0.36 0.50 0.40 0.48 male
0.34 0.44 0.37 0.44 fem
MCV 80 98 82 89.9
MCH 27 34 28 31.9
MCHC 32 36 32 35
Platelets 155 385 150 385 x 1000
RDW 11.7 15.0 <13
Neutrophils 40 74% 40 60%
Lymphs 14 46% 24 44%
Monocytes 4 13% 0 7%
Eosinophils 0 7% 0 3%
Basophils 0 3% 0 1%
Weatherby & Associates, LLC www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.com
Weatherby & Associates, LLC www.BloodChemistryAnalysis.c
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- FBCA Biomarkers and ConditionsDocumento8 pagineFBCA Biomarkers and Conditionsmet50% (2)
- Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis: Clinical Laboratory Testing From A Functional Perspective - DR Dicken WeatherbyDocumento5 pagineBlood Chemistry and CBC Analysis: Clinical Laboratory Testing From A Functional Perspective - DR Dicken Weatherbymywimyxe0% (14)
- Functional Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - The Foundational HierarchyDocumento2 pagineFunctional Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - The Foundational HierarchymetNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomarker Ranges Functional Vs StandardDocumento3 pagineBiomarker Ranges Functional Vs Standardswetor100% (1)
- Textbook of Clinical Nutrition and Functional Medicine, vol. 2: Protocols for Common Inflammatory DisordersDa EverandTextbook of Clinical Nutrition and Functional Medicine, vol. 2: Protocols for Common Inflammatory DisordersValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Functional Medicine Approach To Diagnosis and Treatment of Thyroid DysfunctionDocumento77 pagineFunctional Medicine Approach To Diagnosis and Treatment of Thyroid DysfunctionDaniel Barber100% (4)
- 10 Important Blood Tests PART-1 PDFDocumento22 pagine10 Important Blood Tests PART-1 PDFDimple100% (3)
- Textbook of Clinical Nutrition and Functional Medicine, vol. 1: Essential Knowledge for Safe Action and Effective TreatmentDa EverandTextbook of Clinical Nutrition and Functional Medicine, vol. 1: Essential Knowledge for Safe Action and Effective TreatmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Kalish GI ProtocolsDocumento5 pagineKalish GI Protocolsgoosenl100% (1)
- Healthy Hormone Book by Dan KalishDocumento136 pagineHealthy Hormone Book by Dan KalishAashish Singh100% (3)
- Functional Medicine ProtocolDocumento27 pagineFunctional Medicine Protocolmuhjaer100% (5)
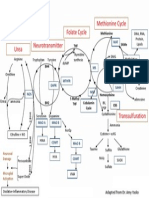
- Methylation DiagramDocumento1 paginaMethylation Diagrampkdo2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Insider's Guide 67Documento13 pagineInsider's Guide 67Lamin100% (1)
- Insider'S Guide Special Topic: The FDM Approach To Auto-Immune ConditionsDocumento56 pagineInsider'S Guide Special Topic: The FDM Approach To Auto-Immune Conditionssam100% (1)
- EFA PathwayDocumento1 paginaEFA Pathwaypkdo2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Signs and Symptoms Analysis From A Functional Perspective - Dr. Dicken WeatherbyDocumento5 pagineSigns and Symptoms Analysis From A Functional Perspective - Dr. Dicken Weatherbyjehobami0% (6)
- Nutrigenomics GuidebookDocumento166 pagineNutrigenomics GuidebookBravedarlin100% (6)
- Hypohomocysteinemia MM WhitePaperDocumento5 pagineHypohomocysteinemia MM WhitePaperMetametrix100% (1)
- Insider's Guide 37Documento18 pagineInsider's Guide 37whiteyasminNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - The Foundational HierarchyDocumento2 pagineFunctional Blood Chemistry and CBC Analysis - The Foundational Hierarchymet100% (1)
- Clinical Nutrition - A Functional PerspectiveDocumento324 pagineClinical Nutrition - A Functional PerspectivelenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Suggested Biomarkers ODX ApplicationDocumento3 pagineSuggested Biomarkers ODX ApplicationmetNessuna valutazione finora
- A Functional Medicine Approach To Hypertension Fitzgerald 08-2011Documento3 pagineA Functional Medicine Approach To Hypertension Fitzgerald 08-2011Kara Fitzgerald100% (1)
- Functional Medicine in Primary Care: Together, We Will Get You BetterDa EverandFunctional Medicine in Primary Care: Together, We Will Get You BetterNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Medicine OverviewDocumento28 pagineFunctional Medicine Overviewmdesdoc50% (4)
- Int&Fun&Med&Nut&the&1 STDocumento1.088 pagineInt&Fun&Med&Nut&the&1 STагата кристи100% (14)
- AFMCP Presentation Applying FXN Med in Clinical PracticeDocumento3 pagineAFMCP Presentation Applying FXN Med in Clinical PracticeKCSNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To Nutrigenomic TestingDocumento34 pagineGuide To Nutrigenomic Testinggiannidiet100% (1)
- Thyroid FactorsDocumento1 paginaThyroid Factorspkdo2003100% (2)
- Fmu Trainging ModuleDocumento23 pagineFmu Trainging ModulesamNessuna valutazione finora
- Thiamine Deficiency Disease, Dysautonomia, and High Calorie MalnutritionDa EverandThiamine Deficiency Disease, Dysautonomia, and High Calorie MalnutritionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- Comprehensive Methylation Panel With Methylation Pathway AnalysisDocumento22 pagineComprehensive Methylation Panel With Methylation Pathway AnalysisMiguel Kennedy100% (2)
- ION Guide 2006Documento16 pagineION Guide 2006Metametrix100% (2)
- Urinary Organic Acids DR BralleyDocumento5 pagineUrinary Organic Acids DR BralleyMetametrixNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acids Interpretive GuideDocumento6 pagineAmino Acids Interpretive GuideMetametrix100% (3)
- Insider Guide 11Documento144 pagineInsider Guide 11sam100% (3)
- Nutrition and Functional Foods in Boosting Digestion, Metabolism and Immune HealthDa EverandNutrition and Functional Foods in Boosting Digestion, Metabolism and Immune HealthNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Nutrition ProtocolDocumento3 pagineFunctional Nutrition ProtocolCesar GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ifm Proceedings LowDocumento79 pagineIfm Proceedings LowNatalliya KlyusNessuna valutazione finora
- IFNA Blood Chem Dicken Weatherby 3 Slides Per PageDocumento25 pagineIFNA Blood Chem Dicken Weatherby 3 Slides Per PageBrendonNessuna valutazione finora
- Methylation Nutrigenomics - HeartFixerDocumento50 pagineMethylation Nutrigenomics - HeartFixerJennifer Welsh100% (2)
- Functional Medicine DiabetesDocumento51 pagineFunctional Medicine Diabetesvalentineseftiana100% (1)
- Microbiome Medicine How Bacteria Can Cure UsDocumento31 pagineMicrobiome Medicine How Bacteria Can Cure UsKsenija Medic100% (1)
- The Disease Delusion: Conquering the Causes of Chronic Illness for a Healthier, Longer, and Happier LifeDa EverandThe Disease Delusion: Conquering the Causes of Chronic Illness for a Healthier, Longer, and Happier LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Hair Meneral AnalysisDocumento22 pagineHair Meneral AnalysisWes D Gordon100% (1)
- Functional MedicineDocumento7 pagineFunctional MedicineAngela Pagliuso100% (1)
- Complementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 9: GynecologyDa EverandComplementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 9: GynecologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Feel Good Biochemistry: IntroductionDocumento5 pagineFeel Good Biochemistry: IntroductionDr. Amy Yasko100% (3)
- Practical Nutrigenomics: a guide to setting up your personalised nutrition serviceDa EverandPractical Nutrigenomics: a guide to setting up your personalised nutrition serviceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- Nutrigenetics: Applying the Science of Personal NutritionDa EverandNutrigenetics: Applying the Science of Personal NutritionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Healing Nutrients Within: Facts, Findings, and New Research on Amino AcidsDa EverandThe Healing Nutrients Within: Facts, Findings, and New Research on Amino AcidsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Food & Genes: Term Paper By: Phurpa D. ThungonDocumento15 pagineFood & Genes: Term Paper By: Phurpa D. ThungonMehul BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- The Methylation Miracle: Unleashing Your Body's Natural Source of SAM-eDa EverandThe Methylation Miracle: Unleashing Your Body's Natural Source of SAM-eNessuna valutazione finora
- Diet-Microbe Interactions in the Gut: Effects on Human Health and DiseaseDa EverandDiet-Microbe Interactions in the Gut: Effects on Human Health and DiseaseKieran TuohyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Nutritional Pathophysiology of Obesity and its Comorbidities: A Case-Study ApproachDa EverandNutritional Pathophysiology of Obesity and its Comorbidities: A Case-Study ApproachNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gut-Brain Axis: Dietary, Probiotic, and Prebiotic Interventions on the MicrobiotaDa EverandThe Gut-Brain Axis: Dietary, Probiotic, and Prebiotic Interventions on the MicrobiotaNiall HylandValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- How Alchemy Benefits HerbalismDocumento8 pagineHow Alchemy Benefits HerbalismjamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- Herbs in Magic and AlchemyDocumento150 pagineHerbs in Magic and AlchemyNorischeNessuna valutazione finora
- Thomas Cattoi, June McDaniel (Eds.) - Perceiving The Divine Through The Human Body - Mystical Sensuality-Palgrave Macmillan US (2011)Documento255 pagineThomas Cattoi, June McDaniel (Eds.) - Perceiving The Divine Through The Human Body - Mystical Sensuality-Palgrave Macmillan US (2011)jamesilluminare100% (5)
- Salt Volatilisation ExperimentDocumento7 pagineSalt Volatilisation ExperimentjamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of Science Society, The University of Chicago Press IsisDocumento9 pagineThe History of Science Society, The University of Chicago Press IsisjamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- The Beginnings of Alchemy ArticleDocumento26 pagineThe Beginnings of Alchemy ArticlejamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- Chinese Alchemy ArticleDocumento12 pagineChinese Alchemy ArticlejamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- Famous Men of Rome - John H. HaarenDocumento271 pagineFamous Men of Rome - John H. HaarenjamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- Homeric Speech and The Origins of Rhetoric - Rachel Ahern KnudsenDocumento243 pagineHomeric Speech and The Origins of Rhetoric - Rachel Ahern Knudsenjamesilluminare100% (1)
- The Mysterious Island - Jules VerneDocumento526 pagineThe Mysterious Island - Jules VernejamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- Masters of Magical Powers The Nath Yogis PDFDocumento155 pagineMasters of Magical Powers The Nath Yogis PDFjamesilluminare100% (1)
- Sir Gawain and The Green Knight - Rev. Ernest J. B. KirtlanDocumento240 pagineSir Gawain and The Green Knight - Rev. Ernest J. B. KirtlanjamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- Tantric Vinyāsa Outline (2014)Documento8 pagineTantric Vinyāsa Outline (2014)jamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- The Stages of Samadhi According To The Ashtanga Yoga TraditionDocumento8 pagineThe Stages of Samadhi According To The Ashtanga Yoga Traditionjamesilluminare100% (1)
- The Japan Fad in Global Youth Culture and Millennial CapitalismDocumento12 pagineThe Japan Fad in Global Youth Culture and Millennial Capitalismjamesilluminare100% (1)
- The Keyline PlanDocumento101 pagineThe Keyline Planjamesilluminare100% (1)
- Review - The Influence of Manga On JapanDocumento3 pagineReview - The Influence of Manga On JapanjamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- The Paradox of Declining Female HappinessDocumento45 pagineThe Paradox of Declining Female HappinessjamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- The Werewolf in The Crested Kimono - The Wolf-Human Dynamic in Anime and MangaDocumento17 pagineThe Werewolf in The Crested Kimono - The Wolf-Human Dynamic in Anime and MangajamesilluminareNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Ascites in Children Lane2015Documento13 pagineManagement of Ascites in Children Lane2015Henry BarberenaNessuna valutazione finora
- MARYJOYDELANDocumento1 paginaMARYJOYDELANMary Joy Rosales DelanNessuna valutazione finora
- HANDOUT MTP022 Fatty LiverDocumento21 pagineHANDOUT MTP022 Fatty LiverShyama SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Organs of Human BodyDocumento6 pagineInternal Organs of Human BodyVimalaChristinalNessuna valutazione finora
- Peritoneum 1Documento47 paginePeritoneum 1Mohd FardeenNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM116 - Metabolic - Endocrine DisordersDocumento24 pagineNCM116 - Metabolic - Endocrine DisordersDan Hizon100% (1)
- Surgtest GI Surgery NEET SS 2022 RecallDocumento58 pagineSurgtest GI Surgery NEET SS 2022 RecallRajhan 410Nessuna valutazione finora
- Encephalopathy HepaticumDocumento2 pagineEncephalopathy Hepaticumtitis dwi tantiNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 Anesthesia For Biliary AtresiaDocumento19 pagine19 Anesthesia For Biliary AtresiaDwiki Surya PrayogaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatobiliary Imaging by Multidetector Computed Tomography (MDCT)Documento2 pagineHepatobiliary Imaging by Multidetector Computed Tomography (MDCT)Patwin ZadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Mam ChanDocumento3 pagineExam Mam ChanEustass KiddNessuna valutazione finora
- Biliary StrictureDocumento27 pagineBiliary StrictureMohammad Nazar100% (2)
- DC-40 With Full HD Specification 181004Documento17 pagineDC-40 With Full HD Specification 181004Mîss PàrīsNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcoholic Hepatitis: Ekaterine Labadze MDDocumento18 pagineAlcoholic Hepatitis: Ekaterine Labadze MDsushant jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Common Bile Duct ExplorationDocumento51 pagineOpen Common Bile Duct Explorationmathisync100% (4)
- Liver Transplantation: Diseases Suitable For TransplantationDocumento2 pagineLiver Transplantation: Diseases Suitable For TransplantationgeorgedejeuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Transaminitis 07Documento39 pagineChronic Transaminitis 07Jessica GarletsNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive Care Package AdvancedDocumento22 pagineDigestive Care Package AdvancedWwNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Diagnosis of JaundiceDocumento4 pagineDifferential Diagnosis of JaundiceVirag PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal Trauma - 0Documento129 pagineAbdominal Trauma - 0Tan DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatic Portal CirculationDocumento4 pagineHepatic Portal CirculationFaye Mie VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Goljan Audio Transcripts PDFDocumento401 pagineGoljan Audio Transcripts PDFDavid FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Xingjian Liv-2: Moving BetweenDocumento3 pagineXingjian Liv-2: Moving Betweenray72roNessuna valutazione finora
- Edan Acclarix AX3 Series DatasheetDocumento22 pagineEdan Acclarix AX3 Series DatasheetCasique OldemarNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive Anatomy LabDocumento124 pagineDigestive Anatomy LabMary Beth DawsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Gallstone DiseaseDocumento104 pagineGallstone DiseaseTan DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug-Induced Liver Disease.Documento16 pagineDrug-Induced Liver Disease.Dr. Ammar Khalil100% (1)
- Anatomy 7 Digestive SystemDocumento181 pagineAnatomy 7 Digestive SystemJeanette LynnNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition 3Documento2 pagineNutrition 3azszahNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Liver CirrhosisDocumento15 pagineBiology Liver CirrhosisjohanstinNessuna valutazione finora