Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
General Adult Psychiatry
Caricato da
Vanessa MarsdenCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
General Adult Psychiatry
Caricato da
Vanessa MarsdenCopyright:
Formati disponibili
.
~
PME~B
Postgraduate Medical Education and Training Board
Approved by PMETB on 30 September 2005
Specialty specific guidance in support of applications under Article 14 - General Adult Psychiatry
This document sets out the criteria that will be used to make an evaluation for applications under Article 14 (4). The document
also details guidance on the standards and evidence that is required for applicants to demonstrate how they meet each
criterion.
Good Medical Practice
The evaluation criteria are based on the General Medical Council's Good Medical Practice.
Specialists must be judgement-safe and competent in their field of specialist practice. They must be able to demonstrate the qualities
and abilities to manage a clinical unit or team, ensuring high standards of professional care and effective working relationships with
colleagues across professional disciplines. Specialists should work within contemporary guidelines within the NHS. Specialists may take
on a leadership role within teams and organisations and will have the vision and foresight to develop new ways of working and the
commitment to see projects and teams through to the end. New Specialists will need to demonstrate the personal capacity and qualities
to respond positively to feedback from colleagues and patients, to take and accept responsibility for clinical decisions, and to manage
and respond to complaints from families of patients and fellow professionals in a professional manner. They will have the potential to
teach and to support training programmes for trainees, departments and staff under their supervision
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 1 of 20 30 September 2005
1. Good Clinical care
Providing a good standard of practice and care
Specialists must take and accept responsibility for the patient's journey in all clinical contexts. They will set high standards in clinical
practice in their specialist field and will be able to demonstrate strong analytic skills and insight in the clinical decisions they make about
the treatment and care of their own patients and those of other colleagues. Specialists practise safely within their specialist field and
acknowledge when cases go beyond their expertise and when they need to refer to other Specialists for advice. Specialists ensure that
they and their colleagues work within the current legal and ethical guidelines in their field. They monitor clinical practice and evaluate and
modify where appropriate protocols in the light of evidence-based research and audit findings. Specialists will ensure clear and effective
systems of sharing information, record-keeping and report-writing in the unit
Criterion Standards Suggested evidence
1.1 Specialists will have knowledge and I Specialists in General Adult Psychiatry • Full, detailed Curriculum Vitae including
skills to undertake safe, effective and will demonstrate in their practice: dates.
independent practice in their field and • Success in the MRCPsych Examination,
accept final responsibility for clinical or other test of knowledge taken as part
The breadth and depth of knowledge and
decisions that should be appropriate and of or on completion of a specialist
skills and the ability to make safe clinical
within a legislative framework. training programme.
decisions and take responsibility for them
• Membership of a learned society.
The ability to diagnose and manage all • Re-validation/ appraisal portfolio.
mental illnesses in adults They will have • 3600 appraisal/assessment outcomes.
an understanding of the relevance of • Evidence from workplace - based
physical illness and the social, cultural, assessments
ethical and legal context in which the • References/ structured reports.
patient presents. • Multi source feedback.
• Participation in clinical Multi Disciplinary
Specifically; a successful candidate will Teams, Audit, Medical Audit
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 2of20 30 September 2005
be expected to demonstrate: • Records of data for performance review
• Evidence of the methods, frequency and
outcomes of assessment e.g. Syllabi of
examinations, assessments
documentation and outcomes.
Appropriate experience in: • Record of assessment during training,
documentation and outcomes.
The assessment and management of • Evidence that training was supervised
mental illness in working age adults by relevant psychiatric authorities e.g.
Understanding issues regarding the Certification, log books/training records,
implementation of mental health portfolio
legislation and the assessment of • Evidence of subspecialty training e.g
incapacity. psychotherapy log book
• Authenticated employment record
Working in the context of listings for each post giving details of
multiprofessional teams. type of post, workplace, size factors
such as staff, patients, facilities,
Experience and understanding of the specialties and dates.
multi-agency health and social care
• Evidence of satisfactory completion of
environment in the context of developing posts authenticated by a designated
and delivering complex care packages in representative of the hospital. Evidence
accordance with National service
of satisfactory current appraisal/re
frameworks/contemporary guidance for validation.
mental health.
• Evidence of relevant recent Continuing
Professional Development (CPO
An understanding and demonstrable
certificates, or equivalent overseas
advocacy of the medical and social rights
documentation required).
patients.
• Structured Reports
Taking responsibility for effective
consultation including a detailed mental
It is anticipated that successful
state, cognitive and physical examination
candidates would have at least five years
and psychosocial assessment of the
patient. of general psychiatric training or
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 3 of 20 30 September 2005
Formulating a management plan, experience of which a minimum of two
acknowledging the relevance of age years at a senior level (higher specialist
related issues, catering for physical, training or equivalent)
psychiatric and social aspects of
presentation. This experience should include working
in the context of multi-disciplinary teams
Providing clinical leadership in the in community, out-patient and inpatient
management of complex cases involving settings, catering for acute and non
multiple agencies, in accordance with the acute referrals.
national service
frameworks/contemporary guidance for • Section 12 MHA approval or
mental health. equivalent
• Evidence of supervised training in
Building therapeutic and supportive psychotherapy, either completion
relationships with both patients and of postgraduate course or series
carers. of supervised cases.
Working in long term support of both • Registration to practice as a
mentally and physically frail people in specialist
• Appraisal/revalidation
community and institutional settings. documentation
• Other evidence of
The prescribing and delivery of drug formative/summative assessment
treatments, electroconvulsive therapy and • Demonstrating satisfactory
psychosocial interventions in the context performance at the level outlined
of individual patients with complex mental in the standards
and physical illness. • Multi-source feedback confirming
satisfactory performance in the
areas and at the level outlined in
the standards.
• Evidence from\ case placed
discussions across a range of
complex cases as demonstration
of clinical decision making skills.
• Other work olace based
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 4 of 20 30 September 2005
assessments such as directly
observed interactions or
procedures
1.2 Have the self-awareness to 1 Specialists in General Adult psychiatry • Appraisal/revalidation documentation
acknowledge where the limits of will demonstrate in their practice: • Other evidence of formative or
competence lie and when it is summative assessment
appropriate to refer to other senior An understanding of the limitations of demonstrating satisfactory
colleagues for advice their competence. in clinical practice and performance at the level outlined in
their relationship with patients and know the standards
where and when to ask for help, support • Multi-source feedback confirming
or supervision. satisfactory performance in the areas
and at the level outlined in the
The self-knowledge, confidence and standards.
personal high standards to acknowledge • Structured reports from the
where an assessment may not be supervisors and colleagues
comprehensive and to recognise that they (nominated referees)
need to return to the patient, carers and • Reflective entries in portfolio around
multiprofessional team for further specific learning incidents.
information.
An awareness of the ways in which their
personal experiences, values and
attitudes might affect their professional
practice and know when to refer to a case
to another doctor
The principle that all decisions should be
made in the best interests of the
patient in their care.
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 50f20 30 September 2005
1.3 Have the potential (or ability) to take Specialists in General Adult Psychiatry • Success in MRCPsych or other tests
responsibility for clinical governance will demonstrate in their practice: of knowledge skills and attributes
activities, risk management and audit in • Appraisal/revalidation documentation
order to improve the quality of service Knowledge about policy and practice • Evidence of other formative or
provision relevant to clinical governance summative assessments
demonstrating satisfactory
Participation in and responsibility for performance at the level outlined in
clinical governance activities and the standards.
encourage and support colleagues in • Multi-source feedback confirming
their participation. satisfactory performance in the areas
and at the level outlined in the
An awareness of local processes for standards.
dealing with and learning from clinical • Structured reports from supervisors
errors and to be able to work within them and colleagues (nominated referees)
• Reflective entries in portfolio
Experience in the assessment and
• Description of clinical governance
management of patients considered to be
experience, responsibilities and
at high risk of self harm, suicide or risk to outcomes
others.
• Details of clinical audit activity
• Evidence of post incident reviews
pertaining to serious untoward
incident reporting.
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 60f20 30 September 2005
2. Relationships with patients
Specialists will demonstrate the capacity to build trust and to develop and maintain effective relationships with patients and their families.
They will be good listeners and show respect and understanding for patients' perspectives on their illnesses or conditions. They must
demonstrate a commitment to the principles and practice of consent and confidentiality.
Criterion Standards Suggested evidence
2.1 Specialists will need to develop Specialists in General Adult I. Success in the MRCPsych or other test of
trusting relationships with patients, psychiatry will demonstrate: knowledge skills and attributes
carers and colleagues in all • Evidence of Psychotherapeutic training;
disciplines. Recognise and respect An understanding of the importance of either appropriate postgraduate
patients' diversity, including cultural sociological cultural and religious beliefs qualification or evidence of supervised
and religious beliefs and practices. in the health and social care context. training.
• Appraisals/revalidation
Emphasise through example the, • Other evidence of formative or summative
importance of the person's autonomy assessment demonstrating satisfactory
and dignity, the rights of the individual performance in appropriate areas and to
and the relevance of involvement of the the appropriate standard as described in
family and carers within the context of the document.
assessment and management.
• Evidence from direct observation of
patient and family consultations
An understanding of the relevance of I •
Examples of written communications in
advance directives. portfolio
An understanding and knowledge of •
Patient feedback data, formal and
informal
legislation regarding protecting the rights
Evidence from specific cases
of working age adults including the court ,.
Reflective entries in appraisal/revalidation
of protection. •
portfolio.
Effective and active listenina skills in
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 7 of 20 30 September 2005
consultations with individuals and their
carers, respecting their views and
responding appropriately.
The ability to develop a therapeutic
relationship and undertake appropriate
psychotherapeutic interventions with
patients, irrespective of age, physical or
mental health.
A commitment to ensure that spoken and
written communication with lay people
are written in non technical English
designed to be understood by the
recipient.
Awareness that treatment and care
accommodates the cultural and religious
beliefs of the individual and relevant
carers.
Genuiness, empathy, courtesy and
acceptance in terms of relationships with
patients as expressed through
knowledge, skills and experience in
clinical practice and in their ability to
work independently.
2.2 Specialists will follow the principles Specialists in General Adult I • Success in the MRCPsych or other test
and legal aspects of consent and Psychiatry will demonstrate in their of knowledge skills and attributes
confidentiality. Working knowledge of practice: I • Evidence of Psychotherapeutic
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 8 of 20 30 September 2005
the relevant legislative framework. training; either appropriate
Knowledge of key legal and ethical postgraduate qualification or evidence
guidelines to support their work of supervised training.
especially relating to consent to • Appraisals/revalidation
treatment and the right to refuse • Other evidence of formative or
treatment by patients. summative assessment demonstrating
satisfactory performance in appropriate
An understanding of the rules relating to areas and to the appropriate standard
confidentiality in the context of the mult as described in the document.
disciplinary team, carers and other staff • Evidence from direct observation of
involved in the individual's care. patient and family consultations
Recognition of when the need to protect
• Examples of written communications in
portfolio
a vulnerable person outweighs the need
to preserve confidentiality.
• Patient feedback data, formal and
informal
• Evidence from specific cases
• Reflective entries in
appraisal/revalidation portfolio.
Recognition of when and why to share
information about an individual patient
and how to ask for consent to share this
information and communicate concerns
clearly.
2.3 Specialists will be able to manage Specialists in General adult I • appraisals/revalidation documentation
difficult and complex situations with psychiatry will demonstrate in their • other evidence of formative or summative
patients and their families, to advise practice: assessment demonstrating satisfactory
them appropriately and to manage performance at the level outlined in the
complaints effectively Effective skills in working with patient, standards
carers and extended networks in I • multi-source feedback confirming
planning and managing treatments, satisfactory performance in the areas and
maximising the autonomy and self at the level outlined in the standards
management skills of the individual. • structured reports from supervisors and
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 9 of 20 30 September 2005
The ability to work effectively with people colleagues (nominated referees)
who may have different perspectives and • evidence from case based discussion in
understanding of mental illness the areas and at the level outlined in the
standards
A keen awareness of their own personal, • evidence from direct observation of patient
emotional reactions and the impact that and family consultations
these might have on patients, carers and I • evidence from specific cases
colleagues. (anonymised)
• reflective entries in appraisal/revalidation
portfolio
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 10 of 20 30 September 2005
3. Maintaining Good Medical Practice
Keeping up to date
Specialists set high standards in their clinical care and ensure that they remain fully competent to practise through their commitment to
continuing professional development and the process of revalidation. They foster the skills and abilities of colleagues and encourage
their professional development by identifying and ensuring their participation in further training and research opportunities. Specialists
are reflective practitioners and strive to improve standards in all aspects of their work. They demonstrate the ability to seek and respond
constructively to feedback.
Criterion Standards Suggested evidence
3.1 Specialists will take responsibility Specialists in General Adult • Success in MRCPsych or other test of
for and keep up-to-date in their own Psychiatry will demonstrate in their knowledge skills and attributes
relevant professional and self practice: • Appraisals/revalidation documentation
development, and facilitate that of • Other evidence of formative or summative
others That they are up to date in their practice assessment demonstrating satisfactory
and promote evidence based medicine performance at the level outlined in the
where possible. standards
• Multi-source feedback confirming satisfactory
An understanding of the basic concepts performance in the areas and at the level
of research and ability to evaluate outlined in the standards
research effectively. • Structured reports from supervisors and
colleagues (nominated referees)
A reflective approach to their practice, • Personal learning/development plan
with an awareness of their level of
• Study leave record and other evidence of
expertise and limitations and their continuing development
development needs.
• Evidence of progression from formative
assessments
A willingness to learn from others and a
• Participation in teaching and lecturing
commitment to continuing professional
development, which would involve not • Participation in departmental audit
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 11 of 20 30 September 2005
only seeking appropriate training • Reflective entries in portfolio on evidence of
opportunities but also respond to learning from formal training, attendance at
complaints and enquiries as useful courses or from clinical practice
learning opportunities.
A willingness to accept mentoring as a
positive contribution to their own
professional development.
3.2 Specialists will acknowledge that Specialists in General Adult • Appraisals/revalidation
the balance and quality of their Psychiatry will demonstrate in their • Other evidence of formative or summative
skills and expertise will change as practice: assessment demonstrating satisfactory
their careers progress and they performance in appropriate areas and to the
specialise in certain areas of clinical The ability to apply affectively to their appropriate standard as described in the
practice practice the knowledge and document.
understanding acquired in their career • Multi-source feedback confirming satisfactory
and the use of skills and strategies to performance in the areas and at the level
respond effectively to challenges of outlined in the standards
increased responsibility • Structured reports from supervisors and
colleagues (nominated references)
Effective skills in organisation, • Reflective entries in appraisal/revalidation
prioritisation and delegation and be able portfolio.
to help others develop these
Effective professional networks that
they have developed to support clinical
practice and research activities.
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 12 of 20 30 September 2005
4. Teaching and Training, appraising and assessing
Making assessments and providing references
Specialists are usually expected to teach and train students, trainees and colleagues and to appraise colleagues and assess their work.
They will need to demonstrate effective communication skills in all of these activities, in the presentation and discussion of topics and in
their personal interactions. Specialists will be able to demonstrate an understanding of and a commitment to the principles and practice
of effective teaching and learning in clinical contexts. They must be able to take responsibility for the supervision of trainees and ensure
that effective arrangements are in place. They must demonstrate the ability to be open, honest and objective in appraisals and in written
references for colleagues.
Criterion Standards Suggested evidence
4.1 Specialists will be able to I Specialists in General Adult. appraisals/revalidation documentation
demonstrate the potential to teach Psychiatry will demonstrate in their • other evidence of formative or summative
and train effectively at all levels of practice: assessment demonstrating satisfactory
undergraduate and postgraduate performance at the level outlined in the
education where required A range of effective teaching and standards
learning skills on topics within their I • multi-source feedback confirming
specialty, in related clinical and satisfactory performance in the areas and at
research areas and in a variety of the level outlined in the standards
contexts. • structured reports from supervisors and
colleagues (nominated referees)evidence of
Responsibility for the training, super attending a suitable training course
vision and assessment of • reflective entries in appraisal/revalidation
undergraduates and trainees and other portfolio
professionals such as nurses, therapists
and social workers
The ability to assess accurately the
levels of support and supervision that
are reauired bv different members of the
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 13 of 20 30 September 2005
team they supervise.
4.2 Specialists will demonstrate skills Specialists in General Adult • appraisals/revalidation documentation
and strategies in the process of Psychiatry will demonstrate in their • other evidence of formative or summative
feedback to colleagues and trainees, practice: assessment demonstrating satisfactory
ensuring positive and constructive performance at the level outlined in the
outcomes standards
• multi-source feedback confirming
An understanding of the importance of a satisfactory performance in the areas and at
positive and constructive approach to the level outlined in the standards
mentoring, giving support, guidance and • structured reports from supervisors and
feedback to trainees under their colleagues (nominated referees)
supervision. • evidence of attending a suitable training
course
The ability to identify learning needs in a • reflective entries in appraisal/revalidation
wide range of professions and build on portfolio
this in their teaching.
A reflective approach about their
experiences in order to ensure positive
experiences for trainees now under their
supervision.
4.3 Specialists will be capable of judging Specialists in General Adult • appraisals/revalidation documentation
competence and professional Psychiatry will demonstrate in their • other evidence of formative or summative
attributes in others practice: assessment demonstrating satisfactory
performance at the level outlined in the
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 14 of 20 30 September 2005
Honesty and integrity when contributing standards
to peer reviews of colleagues teaching • multi-source feedback confirming
or research satisfactory performance in the areas and at
the level outlined in the standards
Recognition of their own preferences • structured reports from supervisors and
and an acceptance of different colleagues (nominated referees)
approaches of colleagues • anonymised examples in
appraisal/revalidation portfolio
The ability to recognise and support • reflective entries in appraisal/revalidation
colleagues who may be under pressure portfolio
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 15 of 20 30 September 2005
5. Working with colleagues
Working in teams and within organisations
Specialists work as members of a number of teams and within organisations. They must be able to demonstrate an understanding of the
roles of others and a respect for the knowledge, skills and experience they bring to a team and to an organisation. They will need to
demonstrate strong interpersonal skills and an open and non-discriminatory approach to professional working relationships with
colleagues.
Criterion Standards Suggested evidence
5.1 Strive for continuing improvement in all Specialists in General Adult • Appraisal/revalidation documentation
aspects of their work and that of Psychiatry will demonstrate in their • Evidence of other formative or summative
colleagues while mindful of priorities practice: assessments demonstrating satisfactory
and high standards performance at the level outlined in the
Knowledge of how to find, review and standards.
maintain relevant knowledge in their • Multi-source feedback confirming
specialty in order to maintain their satisfactory performance in the areas and
practice at the level outlined in the standards.
• Structured reports from supervisors and
the ability to work with colleagues from colleagues (nominated referees)
a range of partner organizations both • Evidence of case based discussions in the
statutory and non-statutory including for areas and levels outlined in the standards
example social services, probation • Reflective entries in the portfolio
services, NSF, MIND, Alzheimer's
Association.
The ability to evaluate their own
performance critically and a willingness
to be open about sharing and reviewing
their practice with others
5.2 Have effective interpersonal skills I Specialists in General Adult I • Appraisal/revalidation documentation
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 16 of 20 30 September 2005
which enable them to bring out the Psychiatry will demonstrate in their • Evidence of other formative or summative
best in colleagues, to resolve conflicts practice: assessments demonstrating satisfactory
when they arise and to develop and performance at the level outlined in the
maintain productive working A commitment to ensure open and non standards.
relationships within the team. discriminatory professional working • Multi-source feedback confirming
relationships with colleagues and be satisfactory performance in the areas and
aware of the need to prevent bullying at the level outlined in the standards.
and harassment and demonstrate • Structured reports from supervisors and
effective administrative skills including colleagues (nominated referees)
ways to maximise support services.
5.3 Support teams that bring together Specialists in General Adult • Appraisal/revalidation documentation
different professionals and disciplines Psychiatry will demonstrate: • Evidence of other formative or summative
and other agencies, to provide high assessments demonstrating satisfactory
quality health care The ability to work effectively in multi performance at the level outlined in the
agency teams, for example, with social standards.
workers and teachers, and have • Multi-source feedback confirming
developed an awareness of their own satisfactory performance in the areas and
role within the team and the skills and at the level outlined in the standards.
expertise of others. • Structured reports from supervisors and
colleagues (nominated referees)
The ability to take on differing and • Evidence based from case-based
complementary roles within the different discussions in the areas and at the levels
communities of practice within which in the standards.
they work, in hospitals, in the
community and with social services and
voluntary agencies.
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 17 of 20 30 September 2005
6. Probity and Health
Protecting patients and the profession
Specialists are honest and trustworthy, recognising the privileges and responsibilities of their position. They ensure the standards of
Good Medical Practice as set out by the General Medical Council and other relevant Colleges/Faculties or professional bodies are met.
Criterion Standards Suggested evidence
6.1 Always act in their personal and Specialists in General Adult • Appraisal/revalidation documentation
professional lives to maintain public Psychiatry will demonstrate in their
• Evidence of other formative or summative
trust in the profession. practice: assessments demonstrating satisfactory
performance at the level outlined in the
An understanding of national and local standards.
regulatory bodies involved in standards • Multi-source feedback confirming satisfactory
of professional and personal behaviour, performance in the areas and at the level
clinical practice and in education, outlined in the standards.
training and assessment. • Structured reports from supervisors and
colleagues (nominated referees)
Probity in their personal and • Current evidence of good standing and the
professional life relevant regulatory body
• Probity statement
• Health statement
6.2 Act quickly and effectively if they Specialists in General Adult • Appraisal/revalidation documentation
have a reason to believe that their Psychiatry will demonstrate in their • Evidence of other formative or summative
own or a colleagues conduct, practice: assessments demonstrating satisfactory
performance or health may put a performance at the level outlined in the
patient at risk Be honest and know the procedures to standards.
follow where there is a concern about • Multi-source feedback confirmina satisfactory
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 18 of 20 30 September 2005
the professional practice of a colleague performance in the areas and at the level
which might be putting the health of outlined in the standards.
patients at risk. • Structured reports from supervisors and
colleagues (nominated referees)
Responsibility for their own health in so
far as it might affect the welfare of
patients' safety.
6.3 Undertake duties such as writing Specialists in General Adult • Appraisals/revalidation documentation
reports, giving evidence and Psychiatry will demonstrate in their • Other evidence of formative or summative
completing and signing documents practice: assessment demonstrating satisfactory
in a timely honest and conscientious
I performance at the level of the outlined
with due respect for patients' Know how to write reports concerning standards.
confidentiality. capacity assessment for social services • Multi-source feedback confirming satisfactory
and the courts. performance in the areas and at the level
outlined in the standards.
Making accurate and comprehensive • Structured reports from supervisors and
reports that will subsequently withstand colleagues (nominated referees)
scrutiny in a court of law or Mental • Examples of written communications in
Health Act Appeal Tribunal portfolio
• Evidence from case based discussion in the
Effective skills in written areas and at the level outlined in the
communications for a range of standards.
audiences, for patients and their
families, colleagues and other
professional organisations.
The ability to prepare a court report as
a professional witness and develop the
skills to present such material in court.
6.4 Through leadership encourage the Specialists in General Adult • Multi-source feedback confirming satisfactory
development and practice of these Psychiatry will demonstrate in their performance in the areas and at the level
qualities in their colleagues practice: outlined in the standards.
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 19 of 20 30 September 2005
• Structured reports from supervisors and
The high standards expected of them colleagues (nominated referees)
by patients and carers, providing a role • Examples of written communications in
model for other professionals in portfolio
promoting the mental health of older • Other evidence of formative or summative
people. assessment demonstrating satisfactory
performance at the level of the outlined
standards
PMETB General Adult Psychiatry SSG Page 20 of 20 30 September 2005
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Inner Child WorkDocumento31 pagineInner Child WorkPradita Lanuansha Putri Irianto100% (5)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Intensive Behavioral Therapy For Autism Spectrum Disorders: Coverage RationaleDocumento14 pagineIntensive Behavioral Therapy For Autism Spectrum Disorders: Coverage Rationalediana100% (1)
- Clinical Topics in PsychotherapyDocumento388 pagineClinical Topics in Psychotherapyfllorinv7100% (1)
- The Role of A Pastor As A CounselorDocumento5 pagineThe Role of A Pastor As A Counselorkhetsiwe gule100% (2)
- What Is Integral Somatic PsychologyDocumento17 pagineWhat Is Integral Somatic PsychologyInglês The Right WayNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Counseling and PsychotherapyDocumento14 pagineBasics of Counseling and Psychotherapyirish x100% (2)
- Scope and Principles of CounselingDocumento22 pagineScope and Principles of CounselingAirabel Jamisola100% (3)
- Patient Counseling PresentationDocumento30 paginePatient Counseling PresentationBaguma Michael100% (1)
- Psych EEDocumento6 paginePsych EESindhuja RamanNessuna valutazione finora
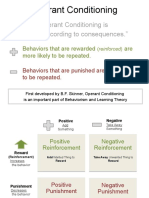
- Operant Conditioning Is "Learning According To Consequences."Documento14 pagineOperant Conditioning Is "Learning According To Consequences."Maria Elizabeth SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Self Care AssessmentDocumento3 pagineSelf Care AssessmentChet Jerry AckNessuna valutazione finora
- House2008 - The Dance of Psychotherapy and Politics PDFDocumento12 pagineHouse2008 - The Dance of Psychotherapy and Politics PDFBakos BenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Trance: Ns. Mohamad Nur, S.Kep.,M.Si (Ked)Documento38 pagineTrance: Ns. Mohamad Nur, S.Kep.,M.Si (Ked)Asiatul JannahNessuna valutazione finora
- Pennys CV Webpage VersionDocumento4 paginePennys CV Webpage Versionapi-251536652Nessuna valutazione finora
- Potential Therapeutic Effects of PsilocybinDocumento7 paginePotential Therapeutic Effects of Psilocybindaniel_jose_skateNessuna valutazione finora
- An Occupational Therapy Perspective of A School-Based Suicide PreDocumento100 pagineAn Occupational Therapy Perspective of A School-Based Suicide PreMarcelo Jorge EuredjianNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the Evolution of Psychology from Ancient to Modern TimesDocumento9 pagineUnderstanding the Evolution of Psychology from Ancient to Modern TimesRamiz OruceliyevNessuna valutazione finora
- Download Becoming A Helper 8Th Edition Marianne Schneider Corey full chapterDocumento67 pagineDownload Becoming A Helper 8Th Edition Marianne Schneider Corey full chapterannie.coombs631100% (5)
- Ishiyama 1995 Use of Validationgram in Counselling - Exploring Sources of Self-Validation and Impact of Personal TransitionDocumento13 pagineIshiyama 1995 Use of Validationgram in Counselling - Exploring Sources of Self-Validation and Impact of Personal Transitionhoorie100% (1)
- Fandagani Module 9Documento3 pagineFandagani Module 9Ron GaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychoeducation For Severe Mental Illnesses Theory and Practice, Final Seminar PrintDocumento22 paginePsychoeducation For Severe Mental Illnesses Theory and Practice, Final Seminar PrintAnnPSWNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 1Documento35 pagineCH 1ravibunga4489Nessuna valutazione finora
- On The Fear of Death As The Primary Anxiety How and Why Klein Differs From FreudDocumento16 pagineOn The Fear of Death As The Primary Anxiety How and Why Klein Differs From FreudRekhtman DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Holistic Nursing Care: Theories and Perspectives: February 2013Documento6 pagineHolistic Nursing Care: Theories and Perspectives: February 2013Aulia Al JamalulaiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4-6Documento37 pagineLesson 4-6Vea Patricia AngeloNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010SAJPPretoriusPfeifer PDFDocumento13 pagine2010SAJPPretoriusPfeifer PDFPhilip John PajaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effectiveness of 6 Versus 12-Months of DBTDocumento16 pagineThe Effectiveness of 6 Versus 12-Months of DBTPechopalomo 90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Uncovering the Past Through Present TransferenceDocumento35 pagineUncovering the Past Through Present TransferenceGenaro SánchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson - Plan - 3rd Grade Unit 1 Week1Documento2 pagineLesson - Plan - 3rd Grade Unit 1 Week1api-27344754100% (1)
- Ahmed Elnahhas Thesis - Modulation of Muscle Tightness by Manual Stretching in Children With Spastic Cerebral Palsy (A Systematic Review)Documento76 pagineAhmed Elnahhas Thesis - Modulation of Muscle Tightness by Manual Stretching in Children With Spastic Cerebral Palsy (A Systematic Review)aelnahhas84Nessuna valutazione finora