Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Reteaching 2-4
Caricato da
api-296726470Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Reteaching 2-4
Caricato da
api-296726470Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Name Class Date
Reteaching
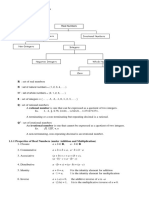
1-4 Properties of Real Numbers
Equivalent algebraic expressions are expressions that have the same value for all values
for the variable(s). For example x + x and 2x are equivalent expressions since, regardless
of what number is substituted in for x, simplifying each expression will result in the same
value. Certain properties of real numbers lead to the creation of equivalent expressions.
Commutative Properties
The commutative properties of addition and multiplication state that changing the order
of the addends does not change the sum and that changing the order of factors does not
change the product.
Addition: a + b = b + a Multiplication: a b = b a
To help you remember the commutative properties, you can think about the root
word commute. To commute means to move. If you think about commuting or
moving when you think about the commutative properties, you will remember that
the addends or factors move or change order.
Do the following equations illustrate commutative properties?
a. 3 +4=4+3 b. (5 3) 2 = 5 (3 2) c. 1 3 = 3 1
3 + 4 and 4 + 3 both simplify to 7, so the two sides of the equation in part (a) are equal.
Since both sides have the same two addends but in a different order, this equation
illustrates the Commutative Property of Addition.
The expression on each side of the equation in part (b) simplifies to 30. Both sides
contain the same 3 factors. However, this equation does not illustrate the Commutative
Property of Multiplication because the terms are in the same order on each side of the
equation.
1 3 and 3 1 do not have the same value, so the equation in part (c) is not
true. There is not a commutative property for subtraction. Nor is there a
commutative property for division.
Associative Properties
The associative properties of addition and multiplication state that changing the
grouping of addends does not change the sum and that changing the grouping of
factors does not change the product.
Addition: (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) Multiplication: (a b) c = a (b c)
Prentice Hall Algebra 1 Teaching Resources
Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
39
Name Class Date
Reteaching (continued)
1-4 Properties of Real Numbers
Do the following equations illustrate associative properties?
a. (1 + 5) + 4 = 1 + (5 + 4)
b. 4 (2 7) = 4 (7 2)
(1 + 5) + 4 and 1 + (5 + 4) both simplify to 10, so the two sides of the equation in part (a)
are equal. Since both sides have the same addends in the same order but grouped
differently, this equation illustrates the Associative Property of Addition.
The expression on each side of the equation in part (b) simplifies to 56. Both sides
contain the same 3 factors. However, the same factors that were grouped together on the
left side have been grouped together on the right side; only the order has changed. This
equation does not illustrate the Associative Property of Multiplication.
Other properties of real numbers include:
a. Identity property of addition: a+0=0 12 + 0 = 12
b. Identity property of multiplication: a1=a 32 1 = 32
c. Zero property of multiplication: a 0=0 60=0
d. Multiplicative property of negative one: 1 a = a 1 7 = 7
Exercises
What property is illustrated by each statement?
1. (m + 7.3) + 4.1 = m + (7.3 + 4.1) 2. 5p 1 = 5p
3. 12x + 4y + 0 = 12x + 4y 4. (3r)(2s) = (2s)(3r)
5. 17 + (2) = (2) + 17 6. (3) = 3
Simplify each expression. Justify each step.
7. (12 + 8x) + 13 8. (5 m) 7
9. (7 7) + 12
Prentice Hall Algebra 1 Teaching Resources
Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
40
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Algebraic Expressions For ClassDocumento25 pagineAlgebraic Expressions For ClassRonald Abrasaldo SatoNessuna valutazione finora
- LET Reviewer MathDocumento10 pagineLET Reviewer MathRoute87 Internet CafeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Distributive Property NotesDocumento8 pagineThe Distributive Property Notesapi-310102170Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan MathematicsDocumento5 pagineLesson Plan MathematicsEstepanie Gopet100% (1)
- Algebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsDa EverandAlgebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsNessuna valutazione finora
- WEEK 8.3. Lesson Plan Properties of EqualityDocumento6 pagineWEEK 8.3. Lesson Plan Properties of EqualityEdelyn Paulinio100% (1)
- 1 5 Properties of Real NumbersDocumento14 pagine1 5 Properties of Real Numbersapi-233527181100% (1)
- TG - Math 7 - Q3 PDFDocumento37 pagineTG - Math 7 - Q3 PDFDoris Rosario Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro to Conic Sections and CirclesDocumento7 pagineIntro to Conic Sections and Circlesha hakdogNessuna valutazione finora
- G7mathq2w9 SLMDocumento15 pagineG7mathq2w9 SLMDana Hamdani100% (2)
- Properties On Operation of IntegersDocumento31 pagineProperties On Operation of IntegersElla mei OralloNessuna valutazione finora
- Equalities and Inequalities in One Variable: Lesson 5.1 Properties of Real NumbersDocumento58 pagineEqualities and Inequalities in One Variable: Lesson 5.1 Properties of Real NumbersJoyvy KidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Lesson Plan for Solving Linear Equations AlgebraicallyDocumento4 pagineSample Lesson Plan for Solving Linear Equations AlgebraicallyHassan GandamraNessuna valutazione finora
- M7 Q1L4.1 Properties of IntegersDocumento4 pagineM7 Q1L4.1 Properties of IntegersCaitlin Joy MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics: Quarter III-Week 1 Learning Activity Sheets (LAS)Documento8 pagineMathematics: Quarter III-Week 1 Learning Activity Sheets (LAS)Florame Algarme MelanoNessuna valutazione finora
- 08.29.2017 Daily Lesson Properities of Ratioanl NumbersDocumento33 pagine08.29.2017 Daily Lesson Properities of Ratioanl NumbersChristeus Von SujeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Linear Equations Algebraically in 40 CharactersDocumento5 pagineSolving Linear Equations Algebraically in 40 CharactersHassan GandamraNessuna valutazione finora
- L2 - Mathematical Language & SymbolsDocumento8 pagineL2 - Mathematical Language & Symbolsdevora aveNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Point On Properties2Documento11 paginePower Point On Properties2Jezreel Jezz David BaculnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 TG Math 3rd Quarter PDFDocumento37 pagineGrade 7 TG Math 3rd Quarter PDFSedie Z. Saavedra - SelmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Midsem Reviewer S6, 2023-2024Documento13 pagineMath Midsem Reviewer S6, 2023-2024alte2028Nessuna valutazione finora
- MATHEMATICS 7 2ND Quarter LAS Week 8 Solving Linear Equations and InequalitiesDocumento10 pagineMATHEMATICS 7 2ND Quarter LAS Week 8 Solving Linear Equations and InequalitiesNimfa MalizaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.1 Associative Property PDFDocumento3 pagine6.1 Associative Property PDFJamel CrawfordNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 1: Property Real Numbers: Identify The Property Illustrated in Each Sentence. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10Documento5 pagineActivity 1: Property Real Numbers: Identify The Property Illustrated in Each Sentence. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10Juhainah C. Guro LptNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Equation Inequality in One VariableDocumento44 pagineLinear Equation Inequality in One VariablePrecious Aaricca MambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math VII Learners Materials q3Documento31 pagineMath VII Learners Materials q3Abdullah MundasNessuna valutazione finora
- CH# 2 Solving Linear Equation's and Inequalities: by Mohammad Sabaoon MSC Mathematics (U.O.P)Documento45 pagineCH# 2 Solving Linear Equation's and Inequalities: by Mohammad Sabaoon MSC Mathematics (U.O.P)Samsoor SamirNessuna valutazione finora
- 8th Grade Summer Math PacketDocumento12 pagine8th Grade Summer Math Packetemreturkoglu729Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 9 Properties of The Operation On Rational Numbers - JalidronDocumento39 pagineLesson 9 Properties of The Operation On Rational Numbers - JalidronjohnalcuinNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics: and Vice Versa - M8AL-If-1Documento8 pagineMathematics: and Vice Versa - M8AL-If-1Israel MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebraic Properties ExplainedDocumento26 pagineAlgebraic Properties ExplainedIroh IrohNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Quarter 3 PDFDocumento32 pagineMathematics Quarter 3 PDFJustine Cole CariñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Four Properties of AdditionDocumento5 pagineFour Properties of AdditionDean Ariola-SanNessuna valutazione finora
- HW - Day 1Documento8 pagineHW - Day 1Kian LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Equation .Lec1Documento49 pagineLinear Equation .Lec1Njood AdelNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 7Documento27 pagineMath 7Billy Joe DG DajacNessuna valutazione finora
- 2Q 6 Properties of IntegersDocumento99 pagine2Q 6 Properties of IntegersRaymond De VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra 1.notesDocumento256 pagineAlgebra 1.notesabcbcs333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Year 9 MATHEMATICSDocumento153 pagineYear 9 MATHEMATICSCindy InternetNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Course 8 Matrices and VectorsDocumento23 pagineTraining Course 8 Matrices and VectorsRichardoBrandonNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced GeometryDocumento7 pagineAdvanced GeometryGenelle Mae MadrigalNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Real NumbersDocumento102 pagineProperties of Real NumbersLuke WekesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Week 10 With Template1Documento5 pagineMath Week 10 With Template1Ken De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Quarter 3 - Grade 8 - Week 2Documento26 pagineQuarter 3 - Grade 8 - Week 2Carmina CunananNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of EqualityDocumento2 pagineProperties of EqualityAlleyssa SahayNessuna valutazione finora
- Relation, Function and LogicDocumento47 pagineRelation, Function and LogicAllen Kurt RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2Documento7 pagineLesson 2Saalivaahanan BaskaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of A Real Number 1Documento10 pagineProperties of A Real Number 1Hastyn Shane BorinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Handouts On AlgebraDocumento8 pagineHandouts On AlgebraGerman AbihayNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra Advanced (Coret)Documento23 pagineAlgebra Advanced (Coret)Reinaldo SalimNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Column ProofsDocumento3 pagineTwo Column Proofsapi-488689204Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 08a Linear Equations in One VariableDocumento28 pagineLecture 08a Linear Equations in One VariableOnofre Algara JrNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Equations and InequalitiesDocumento6 pagineLinear Equations and Inequalitiesaxzhelle borenNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics7 Quarter2 Week8Documento6 pagineMathematics7 Quarter2 Week8Sage SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Function and Linear InequalityDocumento18 pagineLinear Function and Linear InequalitymayooNessuna valutazione finora
- Heep208 PDFDocumento36 pagineHeep208 PDFSathish VanaparlaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Sem w2 Gen MathDocumento13 pagine1st Sem w2 Gen MathSitti Rohima MarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Unit 1A PreCalc ConceptsDocumento9 pagineModule 1 Unit 1A PreCalc Conceptskorleon gNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Mathematics Part 10Documento6 pagineBusiness Mathematics Part 10Aisha GadkariNessuna valutazione finora
- Textbook 2 4Documento8 pagineTextbook 2 4api-293865618Nessuna valutazione finora
- Commutative, Distributive, and Associative Properties Commutative PropertyDocumento4 pagineCommutative, Distributive, and Associative Properties Commutative PropertyErnesto Mike Cristobal Deniega IIINessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 3-7Documento2 pagineReteaching 3-7api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 2-7Documento2 paginePractice K 2-7api-2967264700% (1)
- Practice K 3-7Documento2 paginePractice K 3-7api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 2-7Documento2 pagineReteaching 2-7api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 3-6Documento2 paginePractice K 3-6api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 3-3Documento2 paginePractice K 3-3api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 3-5Documento3 pagineReteaching 3-5api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 3-5Documento2 paginePractice K 3-5api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 3-3Documento2 pagineReteaching 3-3api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 3-6Documento2 pagineReteaching 3-6api-296726470100% (1)
- Practice K 3-4Documento2 paginePractice K 3-4api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 3-4Documento2 pagineReteaching 3-4api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 3-2Documento2 pagineReteaching 3-2api-2967264700% (1)
- Reteaching 3-1Documento2 pagineReteaching 3-1api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 3-1Documento2 paginePractice K 3-1api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 3-2Documento2 paginePractice K 3-2api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 2-3Documento2 pagineReteaching 2-3api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 2-6Documento2 paginePractice K 2-6api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 2-4Documento2 paginePractice K 2-4api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 2-5Documento2 pagineReteaching 2-5api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 2-6Documento2 pagineReteaching 2-6api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 2-1Documento2 paginePractice K 2-1api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 2-1Documento2 pagineReteaching 2-1api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 2-5Documento2 paginePractice K 2-5api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reteaching 2-2Documento2 pagineReteaching 2-2api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 2-2Documento2 paginePractice K 2-2api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice K 2-3Documento2 paginePractice K 2-3api-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Deer Population RubricDocumento1 paginaDeer Population Rubricapi-296726470Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 Base API County List of Schools - SANTA CLARA CountyDocumento15 pagine2012 Base API County List of Schools - SANTA CLARA CountySteve Mun GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- MMMMDocumento9 pagineMMMMEce LptNessuna valutazione finora
- PTA Narrative and OfficersDocumento2 paginePTA Narrative and OfficersJennelyn CalilanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluman 5th - Chapter 3 HW SolnDocumento12 pagineBluman 5th - Chapter 3 HW SolnDriton Krasniqi50% (2)
- Walter ResumeDocumento3 pagineWalter Resumeapi-285973207Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 2Documento4 pagineLesson Plan in Mathematics 2Lady Jane CainongNessuna valutazione finora
- Mike Opake Memorial RemarksDocumento4 pagineMike Opake Memorial Remarksapi-274543738Nessuna valutazione finora
- FP1 A-Level Formula SheetDocumento7 pagineFP1 A-Level Formula SheetF JNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional ResumeDocumento4 pagineProfessional Resumeapi-315742102Nessuna valutazione finora
- Iquanta Quant Formulae EbookDocumento59 pagineIquanta Quant Formulae EbookonhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Higher Math 1st Paper 2024Documento9 pagineHigher Math 1st Paper 2024itisjitu01Nessuna valutazione finora
- June 2016 Mark Scheme 11 PDFDocumento2 pagineJune 2016 Mark Scheme 11 PDFjohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Quiz on Fractions, Ratios, Percentages and ProportionsDocumento19 pagineMath Quiz on Fractions, Ratios, Percentages and ProportionsImeelyn ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Consolidated Result: Science Investigatory Project (Sip) - Team Category Elementary SchoolDocumento12 pagineConsolidated Result: Science Investigatory Project (Sip) - Team Category Elementary SchoolLester Gene Villegas ArevaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Test in Mathematics 5Documento6 pagineDiagnostic Test in Mathematics 5Queen Ve Nus100% (1)
- Integration 2Documento9 pagineIntegration 2Dominic SavioNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths InterviewDocumento6 pagineMaths InterviewKeamogetse BoitshwareloNessuna valutazione finora
- DM-CID-LRMS No. 269, S. 2019 (Feedback On Contextualized Bigbooks)Documento2 pagineDM-CID-LRMS No. 269, S. 2019 (Feedback On Contextualized Bigbooks)Rayan CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- C2 Algebra - Remainder and Factor TheoremDocumento37 pagineC2 Algebra - Remainder and Factor TheoremDermot ChuckNessuna valutazione finora
- Registration Form Scilympics16Documento17 pagineRegistration Form Scilympics16Emel AmboNessuna valutazione finora
- Euclidean Geometry: Elements Elements ElementsDocumento1 paginaEuclidean Geometry: Elements Elements ElementsPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce2204 Surveying IDocumento23 pagineCe2204 Surveying ISiva VadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Newsletter Vol 1Documento3 pagineNewsletter Vol 1Yakamia Primary SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Kumar Online Class: CBSE Maths Lines and Angles Assertion & Reasoning QuestionsDocumento15 pagineKumar Online Class: CBSE Maths Lines and Angles Assertion & Reasoning QuestionsHarshvardhan S. KantimahanthiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 AMC 8 ProblemsDocumento8 pagine2015 AMC 8 Problemsalex jobogNessuna valutazione finora
- Application For Original Degree-2013Documento6 pagineApplication For Original Degree-2013SIVA KRISHNA PRASAD ARJA0% (1)
- Y6 White Rose Problems Mon ThursDocumento18 pagineY6 White Rose Problems Mon ThursKki YuNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluating Integrals by Contour Integration: Finding ResiduesDocumento4 pagineEvaluating Integrals by Contour Integration: Finding ResiduesTrinh NgọcNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordinate Geometry SolutionsDocumento20 pagineCoordinate Geometry SolutionsWeird DemonNessuna valutazione finora