Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Eet 1240
Caricato da
khicomCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Eet 1240
Caricato da
khicomCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology_EET1240ET212
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY
The City University of New York
DEPARTMENT: Electrical and Telecommunications
Engineering Technology
SUBJECT CODE EET1240/ET212
AND TITLE: Electronics
COURSE DESCRIPTION: Characteristics and applications of semiconductor elements
such as diodes, bipolar junction transistors and field effect
transistors are covered. Applications include dc power
supplies, voltage regulators, small signal amplifiers (single
and multi-stage), operational amplifiers, negative feedback,
and frequency response.
PRE -COREQUISITE: EET1222/ET242
TEXTBOOK: Electronics Devices
By Thomas L. Floyd, Eighth Edition, 2008 Prentice Hall
COURSE OBJECTIVES/ Upon completion of this course, students will be able to:
STUDENTS OUTCOMES 1. Describe characteristics of diode, transistors, and
semiconductor amplifiers (ABET criteria 3a).
2. Apply knowledge of diode, transistors, and
semiconductor amplifiers in various applications such as
clipping and clamping of signals, full-wave rectifier,
common emitter, common collector, and common base
amplifiers (ABET criteria 3b).
3. Design circuit utilizing components such as diode,
transistors, and semiconductor amplifiers (ABET Criteria-
PC.a).
4. Analyze circuit involving diode, transistors, and
semiconductor amplifiers (ABET criteria 3e, PC.a).
TOPICS: Topics include semiconductor diodes characteristics, diode
clipping and clamping circuits, zener diode regulators and
applications. Characteristics of bipolar junction transistors
and field effect transistors. Analysis and design of
semiconductor amplifiers.
CLASS HOURS: 4
CREDITS: 4
Prepared by: Professor H. Marandi
January 2013
Course Coordinator: Professor M. Kouar
Email: mkouar@citytech.cuny.edu
Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology_EET1240ET212
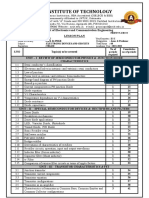
GRADING POLICY: EET 1240/ET 212
Homework and class participation 10%
Exams 60%
Final Examination 30%
Letter Grade Numerical Grade Ranges Quality
A 93-100 4.0
A- 90-92.9 3.7
B+ 87-89.9 3.3
B 83-86.9 3.0
B- 80.82.9 2.7
C+ 77-79.9 2.3
C 70-76.9 2.0
D 60-69.9 1.0
F 59.9 and below 0.0
Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology_EET1240ET212
Assessment
The following assessment techniques are
Correlated to the course objectives as
follows: In addition, each assessment
technique incorporates one or more of
the following ABET Criteria 3 outcomes
(ABET Criteria 3a, 3b, 3e, PC.a)
Course Objectives Assessment
1. Describe characteristics of diode, 1.1 Explain the characteristics of diode.
transistors, and semiconductor 1.2 Explain the characteristics of
amplifiers. transistors.
1.3 Explain the characteristics and of
amplifiers.
2. Apply knowledge of diode, transistors 2.1 Explain the operation and application
and semiconductor amplifiers in various of diode in clipping and clamping of
applications such as clipping and signals, half and full-wave rectifiers.
clamping of signals, full-wave rectifier, 2.2 Explain the operation and application
common emitter, common collector, and of transistors in various
common base amplifiers. configurations:
common emitter, common collector,
common base amplifiers.
2.3 Explain the operation and application
of operational amplifiers.
3. Design circuit utilizing components 3.1 Design voltage regulators.
such as diode, transistors, semiconductor 3.2 Design transistor amplifiers to
amplifiers. achieve desired current, voltage gain.
3.3 Design amplifier circuit to achieve
high and low frequency response.
4. Analyze circuit involving diode, 4.1 Analyze diode voltage regulators.
transistors, and semiconductor 4.2. Analyze common emitter, common
amplifiers. collector, common base amplifier
circuits
4.3 Analyze multistage amplifier
operation.
4.4 Analyze the frequency response of
amplifier.
Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology_EET1240ET212
WEEK TOPIC READING HOMEWORK
ASSIGNMENT
1. Introduction to Electronics. Semiconductor Chapter 1 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11,
Physics. The PN junction. Biasing the PN Pages 1-33 13, 15, 17, 19
junction. The diode.
2. Diode applications. Half-wave and full-wave Chapter 2 1-11
rectifiers. Power supply filters. Pages 45-65
3. Clipping and clamping circuits. The diode Chapter 2: 12, 14, 24-26
data sheet. Pages 65-78
4. Zener diode and Applications. Zener Chapter 3 6, 7, 8, 10, 12,
regulation. Pages 106-121 13
Exam I
5 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs). Chapter 4: 1, 6,7, 9, 12,
Transistors characteristics and parameters. Pages163-179 15, 18, 20, 22
Basic transistor operation.
6 Transistor as an amplifier. Transistor as a Chapter 4 24, 26, 29
switch. Pgs. 180-185
7 Transistor Bias Circuits BJT. Small signal Chapter 5 Chapter5
Analysis. Pages 216-236 2-5, 9, 10, 20,
Chapter 6 24
Pages 256-263
8 Common-Emitter Amplifiers. Chapter 6 7, 13, 18, 19
Pages 263-276
Exam II
9 Common-Collector amplifiers. Common- Chapter 6 20, 24, 27, 30,
Base amplifiers. Multistage amplifiers. Pages 276-289 32
Electrical and Telecommunications Engineering Technology_EET1240ET212
WEEK TOPIC READING HOMEWORK
ASSIGNMENT
10 General concepts of amplifiers frequency Chapter 10 2, 5, 6, 9, 10,
response. The Decibel. Low-frequency Pages 492-508 13, 16
amplifier response.
11 High-frequency amplifier response. Chapter 10 Chapter 10
Pages 517-522 19, 22
Operational amplifiers (OP AMPs). The Chapter 12 Chapter 12
differential amplifier. Pages 592-601 3, 5, 6, 10
12 Negative feedback. Op-Amp Chapter 12 14, 16, 17, 18,
configurations with negative feedback. Pages 602-608 19, 20
13 Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFETs) Chapter 8 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
Pages 368-380 7
Exam III
14 FET Biasing Chapter 8 16, 17, 20, 26,
Metal Oxide semiconductor FETs Pages 381-409 28, 34, 35, 37
(MOSFETs).
15 Final Exam
New York City College of Technology Policy on Academic Integrity
Students and all others who work with information, ideas, texts, images, music,
inventions, and other intellectual property owe their audience and sources accuracy and
honesty in using, crediting, and citing sources. As a community of intellectual and
professional workers, the college recognizes its responsibility for providing instruction in
information literacy and academic integrity, offering models of good practice, and
responding vigilantly and appropriately to infractions of academic integrity. Accordingly,
academic dishonesty is prohibited in the City University of New York and at New York
City College of Technology and is punishable by penalties, including failing grades,
suspension, and expulsion. The complete text of the College policy on the Academic
Integrity may be found in the catalog.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Electronics For Technicians and Engineers PDFDocumento618 pagineElectronics For Technicians and Engineers PDFJorge Roa50% (2)
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocumento185 pagineElectronic Devices and CircuitsArun P S100% (1)
- Electronics—From Theory Into Practice: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesDa EverandElectronics—From Theory Into Practice: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- GATE EC 10 Volume Set by RK KanodiaDocumento629 pagineGATE EC 10 Volume Set by RK KanodiaSampreeth Nambisan PeriginiNessuna valutazione finora
- m820 Sol 2011 PDFDocumento234 paginem820 Sol 2011 PDFkhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- TransistorsDocumento41 pagineTransistorsJacobNessuna valutazione finora
- 18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFDocumento125 pagine18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFsuhas kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample 7436Documento11 pagineSample 7436Ram BalajiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQsDocumento467 pagine1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQskibrom atsbha67% (3)
- Gate Ec RK KanodiaDocumento629 pagineGate Ec RK Kanodiavasudev jella100% (2)
- Sample 7600Documento11 pagineSample 7600Retyuin100% (1)
- Printed Circuit Board Design Techniques For EMC Compliance A Handbook For Designers, 2nd Edition PDFDocumento328 paginePrinted Circuit Board Design Techniques For EMC Compliance A Handbook For Designers, 2nd Edition PDFJoao100% (2)
- Clap Switch Report EditedDocumento47 pagineClap Switch Report EditedKeshav Krishna60% (5)
- Electronics – From Theory Into Practice: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionDa EverandElectronics – From Theory Into Practice: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Theory of Semiconductor Junction Devices: A Textbook for Electrical and Electronic EngineersDa EverandTheory of Semiconductor Junction Devices: A Textbook for Electrical and Electronic EngineersValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Radio Frequency Transistors: Principles and Practical ApplicationsDa EverandRadio Frequency Transistors: Principles and Practical ApplicationsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Eet 1240 OutlineDocumento2 pagineEet 1240 OutlinekhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Outline EDC Dr. HussainDocumento6 pagineCourse Outline EDC Dr. Hussainarkhanjee12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bme 311Documento5 pagineBme 311salem aljohiNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus BME 313Documento4 pagineSyllabus BME 313Mousum KabirNessuna valutazione finora
- Nria20 Edc Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineNria20 Edc Lesson PlanD. Ravi ShankarNessuna valutazione finora
- AEC Course MaterialDocumento144 pagineAEC Course MaterialBruce LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices and Circuit TheoryDocumento2 pagineElectronic Devices and Circuit Theoryghftyftfhfhg50% (4)
- Semester: Even Name of The Program: B.Tech in ECE Year: IIDocumento6 pagineSemester: Even Name of The Program: B.Tech in ECE Year: IINandan BallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diploma Ii Year (Electrical Engineering) : 2011-2012 SubjectsDocumento28 pagineDiploma Ii Year (Electrical Engineering) : 2011-2012 SubjectsMeenu SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics I Lab. ECE 201Documento40 pagineElectronics I Lab. ECE 201ajf3215Nessuna valutazione finora
- EDC-R10 Course TemplateDocumento6 pagineEDC-R10 Course Templatekprk414Nessuna valutazione finora
- Polytechnic 3rd Year SlaybusDocumento23 paginePolytechnic 3rd Year SlaybusSudhakar MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Microwave Devices and CircuitsDocumento6 pagineMicrowave Devices and Circuitsakhinageorge21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Model Question Bank - EDCDocumento12 pagineModel Question Bank - EDCsangeetadineshNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento75 pagineUntitledAbel MathewNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece Vii Power Electronics 10ec73 NotesDocumento264 pagineEce Vii Power Electronics 10ec73 NotesBhakti KalyankastureNessuna valutazione finora
- ALL ECE S4 2019 Scheme Syllabus Ktustudents - inDocumento86 pagineALL ECE S4 2019 Scheme Syllabus Ktustudents - inRajagiri CollegeNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 EDC Lab ManualDocumento73 pagine3 EDC Lab ManualVijayalakshmi PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Sem Basic ElectronicsDocumento4 pagine2nd Sem Basic ElectronicsshinoNessuna valutazione finora
- RP 5Documento34 pagineRP 5Masood AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics Earist BackupDocumento174 pagineBasic Electronics Earist BackupSamuelJrManatadNessuna valutazione finora
- Mini Project 002Documento54 pagineMini Project 002Sumit ShishodiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide EE225 Ver1Documento6 pagineStudy Guide EE225 Ver1aonNessuna valutazione finora
- BSDCH ZC112 Electrical Sciences Handout 2-2019Documento5 pagineBSDCH ZC112 Electrical Sciences Handout 2-2019AGRIM PANDEYNessuna valutazione finora
- EE2002 Analog Electronics - OBTLDocumento8 pagineEE2002 Analog Electronics - OBTLAaron TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Course OutlineDocumento19 pagineElectronics Course OutlineOscar BoshaNessuna valutazione finora
- EngineeringDocumento5 pagineEngineeringManu ENessuna valutazione finora
- Diodes: Electronic Circuit Design 1Documento39 pagineDiodes: Electronic Circuit Design 1Nhật NamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 DiodeDocumento39 pagineChapter 2 DiodeNam zzzNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE2002 Semiconductor Devices and Circuits - Win - 17 - 18Documento2 pagineEEE2002 Semiconductor Devices and Circuits - Win - 17 - 18Srirevathi BalapattabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDocumento238 pagineEce-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesShubhesh SwainNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts of EEE (CS)Documento8 pagineConcepts of EEE (CS)Vikram RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3110016Documento3 pagine3110016Hàiđęř KhąñNessuna valutazione finora
- 3311101electronic Components & PracticeDocumento5 pagine3311101electronic Components & PracticeDarshit KotadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 DiodeDocumento39 pagineChapter 2 DiodeTrần Anh KhoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Circuits SyllabusDocumento5 pagineAnalog Circuits SyllabusVilayil jestinNessuna valutazione finora
- Edc 1ST SemesterDocumento2 pagineEdc 1ST Semestersujeetkushwaha10042002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Electronics IDocumento4 pagineApplied Electronics IGebru GurmessaNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE109: Electronics II: 1. Topic P-NDocumento2 pagineECE109: Electronics II: 1. Topic P-NMasterMM12Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - 4 CSE Odd Sem 19.08.2019.Doc.XDocumento43 pagine1 - 4 CSE Odd Sem 19.08.2019.Doc.XNagarjun ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics IDocumento4 pagineElectronics IMark NealNessuna valutazione finora
- BEEE205L - ELECTRONIC-DEVICES-AND-CIRCUITS - TH - 1.0 - 67 - Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocumento3 pagineBEEE205L - ELECTRONIC-DEVICES-AND-CIRCUITS - TH - 1.0 - 67 - Electronic Devices and CircuitsNithish kumar RajendranNessuna valutazione finora
- School of Ece and EeDocumento211 pagineSchool of Ece and EeRaviKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sedra Smith Microelectronic Circuits 8Th Edition by Adel S Sedra Author Full Download ChapterDocumento51 pagineSedra Smith Microelectronic Circuits 8Th Edition by Adel S Sedra Author Full Download Chapterandrea.johnson263100% (16)
- Lec 1 - LaptopsDocumento10 pagineLec 1 - LaptopskhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem 1: 1 2 −jπ jπ/2 −jπ/2 j5π/2 jπ/4Documento2 pagineProblem 1: 1 2 −jπ jπ/2 −jπ/2 j5π/2 jπ/4khicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng Ek 127 Worksheet 3A: Vec Input ('Enter A Vector: ')Documento2 pagineEng Ek 127 Worksheet 3A: Vec Input ('Enter A Vector: ')khicomNessuna valutazione finora
- AWS Customer AgreementDocumento19 pagineAWS Customer AgreementkhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng Ek 127 Worksheet 2ADocumento8 pagineEng Ek 127 Worksheet 2AkhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys 1442Documento4 paginePhys 1442khicomNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE Undergrad Syllabus Ec455 2015Documento2 pagineECE Undergrad Syllabus Ec455 2015khicomNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY2028 - Getting Started With SpiceDocumento3 paginePHY2028 - Getting Started With SpicekhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Variable End PointDocumento227 pagineVariable End PointkhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Descriptions of Electronic DevicesDocumento2 pagineDescriptions of Electronic DeviceskhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet Exam 2 ADocumento3 pagineFormula Sheet Exam 2 AkhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz2 A3 SolDocumento1 paginaQuiz2 A3 SolkhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter4 - Single Sideband CommunicationsDocumento26 pagineChapter4 - Single Sideband CommunicationskhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading: Hibbeler, Chapter 3.1-3.4 and Chapter 2.8-2.9 Remember ToDocumento6 pagineReading: Hibbeler, Chapter 3.1-3.4 and Chapter 2.8-2.9 Remember TokhicomNessuna valutazione finora
- EcE-22011 CH-6 1st Lecture EditDocumento32 pagineEcE-22011 CH-6 1st Lecture Editsoethurein227Nessuna valutazione finora
- ADE LAB UPDATED Manual-Draft 22 SCHEME - 23-24Documento87 pagineADE LAB UPDATED Manual-Draft 22 SCHEME - 23-24Harish G CNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Exercises 3aDocumento9 pagineLaboratory Exercises 3aIan VillarojoNessuna valutazione finora
- Exit PreparationDocumento92 pagineExit PreparationERMIAS AmanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- 106 Sample ChapterDocumento30 pagine106 Sample ChapterMARYAM ACHIKNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 11Documento16 pagineLecture 11Nooruddin SheikNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 2 BJT AmplifiersDocumento71 pagineChapter - 2 BJT AmplifiersNguyễn Phước Định TườngNessuna valutazione finora
- Fail Kursus DEB1133 Fundemental of Electronic $ Circuit TheoryDocumento268 pagineFail Kursus DEB1133 Fundemental of Electronic $ Circuit TheoryAiman AmnNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Bxe-Unit2Documento20 pagineMock Bxe-Unit2kadaNessuna valutazione finora
- EC8361 - ADCLab Manual PDFDocumento105 pagineEC8361 - ADCLab Manual PDFeshwari2000100% (1)
- Syllabus For Kvs TGT We ExamDocumento9 pagineSyllabus For Kvs TGT We ExamsaralabitmNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Emitter AmplifierDocumento4 pagineCommon Emitter AmplifierRania KhaderNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics - K-Wiki - Chapter 2 - BJTDocumento74 pagineAnalog Electronics - K-Wiki - Chapter 2 - BJTmadivala nagarajaNessuna valutazione finora
- BSCS 2016-20, 2017-21, 2018-22Documento167 pagineBSCS 2016-20, 2017-21, 2018-22Hoorain CHNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 RC Phase ShiftDocumento6 pagine6 RC Phase ShiftengineerluvNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Circuit Design Lab ManualsDocumento71 pagineElectronics Circuit Design Lab ManualsTalha WaqarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4Documento35 pagineUnit 4Venkat ChadalavadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment4 Frequency Response2122016Documento10 pagineExperiment4 Frequency Response2122016Babasrinivas GuduruNessuna valutazione finora
- Unisonic Technologies Co., LTD: Voltage Mode PWM Control CircuitDocumento7 pagineUnisonic Technologies Co., LTD: Voltage Mode PWM Control CircuitEnica LiviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt1 CE AmplifierDocumento5 pagineExpt1 CE AmplifierkeshavNessuna valutazione finora
- Eet - Student Text PDFDocumento135 pagineEet - Student Text PDFvinodNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic DevicesDocumento28 pagineElectronic Devicessetsindia3735Nessuna valutazione finora
- Switchless Bi-Directional AmplifierDocumento4 pagineSwitchless Bi-Directional AmplifierHam Radio HSMMNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Phone DetectorDocumento11 pagineMobile Phone DetectorrockyNessuna valutazione finora
- Diodes and TransistorsDocumento46 pagineDiodes and Transistorsjudysabbagh23Nessuna valutazione finora
- ENGN 2218 - HLab 1Documento10 pagineENGN 2218 - HLab 1varshav_4Nessuna valutazione finora
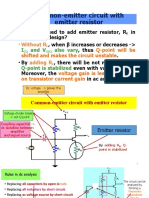
- Common-Emitter Circuit With Emitter Resistor: Without RDocumento16 pagineCommon-Emitter Circuit With Emitter Resistor: Without RMuthukrishnan Vijayan VijayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: (Autonomous)Documento4 pagineInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: (Autonomous)VigneshNessuna valutazione finora
- 2SA1235A 2SA1602A 2SA1993: Small-Signal TransistorDocumento5 pagine2SA1235A 2SA1602A 2SA1993: Small-Signal Transistorjavier venturaNessuna valutazione finora