Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tropical Cyclone
Caricato da
Vince CastorTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tropical Cyclone
Caricato da
Vince CastorCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tropical cyclone, also called typhoon or hurricane, an intense circular storm that originates over warm tropical oceans
and
is characterized by low atmospheric pressure, high winds, and heavy rain.
The term typhoon is used only in the northwestern part of the Pacific Ocean.
In the northeastern part of the Pacific Ocean and in the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean, the equivalent term is hurricane.
Cyclone is the term used in the south Pacific or Indian Ocean.
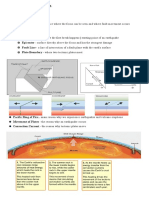
Coriolis Force
The invisible force that appears to deflect the wind is the Coriolis force. The Coriolis force applies to movement on rotating
objects. It is determined by the mass of the object and the object's rate of rotation. The Coriolis force is perpendicular to the
object's axis. The Earth spins on its axis from west to east. The Coriolis force, therefore, acts in a north-south direction. The
Coriolis force is zero at the Equator
Storms that form north of the equator spin counterclockwise. Storms south of the equator spin clockwise. This difference is
because of Earth's rotation on its axis.
Weather is what conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time, and climate is how the atmosphere "behaves"
over relatively long periods of time
Tropical depression, tropical storm, typhoon, and supertyphoon are categories of tropical cyclones. In simple terms, a tropical
cyclone is a system of thunderstorms that are moving around a center. As the winds intensify or weaken, the category is
upgraded or downgraded accordingly.
Tropical Cyclone Categories Maximum Wind Speed
Category kilometers per hour (kph)
Tropical Depression 64
Tropical Storm 118
Typhoon 200
Supertyphoon greater than 200
The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration, PAGASA, is a Philippine national
institution dedicated to provide flood and typhoon warnings, public weather forecasts and advisories, meteorological,
astronomical, climatological, and other specialized information and services primarily for the protection of life and property
and in support of economic, productivity and sustainable development.
PAGASA monitors tropical cyclone activity and issues warnings within its area of responsibility. This area is bound by an
imaginary line drawn along the following coordinates:
25N 120E, 25N 135E, 5N 135E, 5N 115E, 15N 115E, 21N 120E and back to the beginning. (Philippine Area of
Responsibility)
A comet is an icy body that releases gas or dust. They are often compared to dirty snowballs, though recent research has led
some scientists to call them snowy dirtballs. Comets contain dust, ice, carbon dioxide, ammonia, methane and more.
Comets orbit the sun, but most are believed to inhabit in an area known as the Oort Cloud, far beyond the orbit of Pluto.
Short-period comets (those which take less than 200 years to complete an orbit around the Sun) originate from the Kuiper
Belt. Danish astronomer Jan Oort proposed that comets reside in a huge cloud at the outer reaches of the solar system, far
beyond the orbit of Pluto. This has come to be known as the Oort Cloud.
Asteroids
a small rocky body orbiting the sun. Large numbers of these, ranging in size from nearly 600 miles (1,000 km) across (Ceres)
to dust particles, are found (as the asteroid belt ) especially between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, though some have more
eccentric orbits, and a few pass close to the earth or enter the atmosphere as meteors.
Meteoroid, meteor, meteorites
Meteoroids are the smallest members of the solar system, ranging in size from large fragments of asteroids or comets, to
extremely small micrometeoroids.
Whenever a meteoroid plows into the Earths atmosphere, it will create a brief flash of moving light in the sky, called a
meteor.
If remnants of the parent meteoroid survive the trip through the atmosphere to reach the ground, then these remnants are
called meteorites.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Tropical Cyclone & CometsDocumento1 paginaTropical Cyclone & CometsVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine TyphoonDocumento21 paginePhilippine TyphoonBethlehem CuradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 8 Reviewer Second QuarterDocumento4 pagineScience 8 Reviewer Second QuarterAnacondei RomanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science-Reviewer TyphoonsDocumento10 pagineScience-Reviewer TyphoonsLaxiava VaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocumento13 pagineEarthquakes and FaultsDesiree MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Typhoons in The Philippines PDFDocumento65 pagineTyphoons in The Philippines PDFThirdy EstolanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Science ReviewerDocumento6 pagineScience RevieweralehklourzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Studies CloudDocumento4 pagineSocial Studies CloudHakeem And Hadrian XDSNessuna valutazione finora
- Met o 218 Midterm HatulanDocumento12 pagineMet o 218 Midterm HatulanNick HatulanNessuna valutazione finora
- CiclonesDocumento4 pagineCiclonesAnthony RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- CyclonesDocumento8 pagineCyclonesbaljitNessuna valutazione finora
- DsfewsDocumento34 pagineDsfewsbob smithNessuna valutazione finora
- Science NotesDocumento6 pagineScience Noteskyo- sanNessuna valutazione finora
- TyphoonsDocumento45 pagineTyphoonsChristian James EdadesNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 8-Quarter 2-Lesson 5Documento28 pagineScience 8-Quarter 2-Lesson 5Ms. Rhonabelle Llerin PagudNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Notes in Grade 8Documento3 pagineSummary Notes in Grade 8Jhen BonNessuna valutazione finora
- G8 - Earthquake, Tropical Cyclones, Comets, Asteroids, and Meteoroids LectureDocumento4 pagineG8 - Earthquake, Tropical Cyclones, Comets, Asteroids, and Meteoroids LectureChelleNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Tropical Revolving StormsDocumento20 pagine05 Tropical Revolving StormsJiby John JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Met ReviewerDocumento8 pagineMet ReviewerRoxanne Laranio ManawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Cot 3 PPT Science 5Documento17 pagineCot 3 PPT Science 5GOLDIE TRONGCONessuna valutazione finora
- Science Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and TechnologyDocumento16 pagineScience Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and Technologydenise blaireNessuna valutazione finora
- 06-07 Tropical CycloneDocumento103 pagine06-07 Tropical Cycloneac3.evfrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather and Climate-2ndDocumento78 pagineWeather and Climate-2ndDwayne Lyndon GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- VolcanoDocumento10 pagineVolcanoDanGrutasNessuna valutazione finora
- Science NotesDocumento3 pagineScience NotesYaya GayatgayNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 8 ReviewerDocumento2 pagineScience 8 ReviewerRuru pyNessuna valutazione finora
- DURING READING Reading Text Cyclone.. Download and Print. Long Back To BackDocumento1 paginaDURING READING Reading Text Cyclone.. Download and Print. Long Back To BackMarjulyn RafalloNessuna valutazione finora
- IN Earth Science (Cyclone)Documento9 pagineIN Earth Science (Cyclone)Otsenre Cari Otiralab100% (1)
- 1 TyphoonDocumento33 pagine1 TyphoonCamlon KhajarNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 8 - Understanding Typhoon PDFDocumento33 pagineGrade 8 - Understanding Typhoon PDFSam Agustine Rosil0% (1)
- Science DictionaryDocumento24 pagineScience DictionaryHey BitchNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and TechnologyDocumento17 pagineScience Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and Technologydenise blaireNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrometrological HazardsDocumento23 pagineHydrometrological HazardsIril IanNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Weather Pattern - Content PaperDocumento5 pagineGlobal Weather Pattern - Content PaperBhabz KeeNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Cyclones?Documento42 pagineWhat Are Cyclones?Managsha ChibhishaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.determine The Classification of Tropical Cyclones Including Its Origin, Tracks, Movement, Development and The StatisticsDocumento6 pagine1.determine The Classification of Tropical Cyclones Including Its Origin, Tracks, Movement, Development and The StatisticsJohn Carlo De LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4Documento15 pagineUnit 4Imran Ul haq (Ammar choudhary)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Questions and Answers about: Planet EarthDa EverandQuestions and Answers about: Planet EarthValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Science 2nd Periodical Test ReviewerDocumento4 pagineScience 2nd Periodical Test ReviewerscribdpamoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 8 2023 2024 Module TyphoonDocumento5 pagineScience 8 2023 2024 Module Typhoonalex.guirigay100% (1)
- Q2 G8 Science Exam ReviewerDocumento3 pagineQ2 G8 Science Exam ReviewerEJAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind System in The WorldDocumento4 pagineWind System in The WorldFarrel LeroyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tropical Revolving Storms or Tropical Cy PDFDocumento16 pagineTropical Revolving Storms or Tropical Cy PDFNitin KafleNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Reviewer Q2Documento10 pagineScience Reviewer Q2vincentdelosantos17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2Q SCI 8 2Documento20 pagineModule 2Q SCI 8 2PeterClomaJr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amphan Cyclone-EnglishDocumento5 pagineAmphan Cyclone-EnglishshahsankNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyclone 19Documento8 pagineCyclone 19Azad SamiNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Tropical CyclonesDocumento14 pagine21 Tropical CyclonesLuisa LouisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 DRRRDocumento37 pagineChapter 7 DRRRMark Angelo AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes, Impacts & Associated Secondary HazardsDocumento32 pagineCauses, Impacts & Associated Secondary HazardsSajid Mahmood FarooqiNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding The TyphoonsDocumento27 pagineUnderstanding The TyphoonsDICES MNK Wesley L. ArconNessuna valutazione finora
- Tropical Cyclones or TrsDocumento135 pagineTropical Cyclones or TrsRigel Nath100% (1)
- P EcoDocumento13 pagineP EcoCllyan ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Aisyah StormDocumento3 pagineAisyah StormdejamsNessuna valutazione finora
- ScienceDocumento22 pagineScienceJanakiraman BalachandranNessuna valutazione finora
- CycloneDocumento5 pagineCycloneAlok MajumdarNessuna valutazione finora
- All Types of Wind SarsijDocumento16 pagineAll Types of Wind SarsijSarsij NayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of DepressionDocumento5 pagineStructure of DepressionSelwyn GuiruelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate-Tectonic-TheoryDocumento15 paginePlate-Tectonic-TheoryVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- DiscoDocumento4 pagineDiscoVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine Pop and JazzDocumento13 paginePhilippine Pop and JazzVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- Gorgon's HeadDocumento11 pagineGorgon's HeadVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth's MechanismDocumento20 pagineEarth's MechanismVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyberlink Powerdirector 12: Media Room, FX Room, Transition RoomDocumento4 pagineCyberlink Powerdirector 12: Media Room, FX Room, Transition RoomVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- Buko Pie RecipeDocumento1 paginaBuko Pie RecipeVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- IndonesiaDocumento6 pagineIndonesiaVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5 ThailandDocumento21 pagineGroup 5 ThailandVince CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 4 Disaster MGMT PDFDocumento13 pagineMod 4 Disaster MGMT PDFConanNessuna valutazione finora
- TITANICDocumento2 pagineTITANICNicoMatelesiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Three Level Framework For Multi Risk AssessmentDocumento17 pagineA Three Level Framework For Multi Risk AssessmentSanda RoșcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Disasters Word Search PuzzleDocumento1 paginaNatural Disasters Word Search PuzzlegabbydavilaNessuna valutazione finora
- MELC 2 - Day 6Documento36 pagineMELC 2 - Day 6JUSTINE C. DE VILLANessuna valutazione finora
- Disaster Management Using IoT - Docx 1Documento4 pagineDisaster Management Using IoT - Docx 1balaNessuna valutazione finora
- City of Timmins-Minimum Maintenance Standard-Power Point Presentation PDFDocumento16 pagineCity of Timmins-Minimum Maintenance Standard-Power Point Presentation PDFTDPNEWSNessuna valutazione finora
- DISASTER Management and ResponseDocumento11 pagineDISASTER Management and Responseleojay24Nessuna valutazione finora
- MRADocumento1 paginaMRAChristine RucklinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab10CoastalErosion 1Documento1 paginaLab10CoastalErosion 1ramizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Titanic SummaryDocumento3 pagineTitanic SummaryIrene Zabiela CobasNessuna valutazione finora
- BDRRM Polo Action PlanDocumento3 pagineBDRRM Polo Action Planmicah bitantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnitude and IntensityDocumento45 pagineMagnitude and IntensityJefrey PaglinawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Resistensi PinjalDocumento13 pagineJurnal Resistensi Pinjalpuskesmas pontangNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Message/ Plan ICS 208: From (Date and Time) : To (Date and Time)Documento2 pagineSafety Message/ Plan ICS 208: From (Date and Time) : To (Date and Time)PELIGRO RAMIENessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus in Disaster Risk ReductionDocumento3 pagineSyllabus in Disaster Risk ReductionAlbert RoseteNessuna valutazione finora
- Typhoon PAENG ReportDocumento2 pagineTyphoon PAENG Reportkuro hiakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Cassandra in OresteiaDocumento34 pagineRole of Cassandra in OresteiaTrivia Tatia MoonsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Spotters Field GuideDocumento30 pagineAdvanced Spotters Field Guidesrtmedic100% (1)
- TcasDocumento15 pagineTcasKakumkum Blanco100% (1)
- Momin Ka Hathyaar in English (Only D'Ua)Documento61 pagineMomin Ka Hathyaar in English (Only D'Ua)Fahad Mahdi100% (1)
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction (DRRR)Documento2 pagineDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction (DRRR)Junrick VacalNessuna valutazione finora
- Hitachi Solution Profile 3dc Disaster RecoveryDocumento6 pagineHitachi Solution Profile 3dc Disaster RecoveryarvindNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhopal Gas Tragedy Case StudyDocumento10 pagineBhopal Gas Tragedy Case StudyAbhijith MadabhushiNessuna valutazione finora
- Super Typhoon HaiyanDocumento25 pagineSuper Typhoon Haiyanapi-239410749Nessuna valutazione finora
- DRR 12 1st Long TestDocumento3 pagineDRR 12 1st Long TestRoy CanoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bauer Review - 42 - en PDFDocumento44 pagineBauer Review - 42 - en PDFDudee Daryan100% (1)
- Audio Script and Sample of Exercise Natural DisastersDocumento3 pagineAudio Script and Sample of Exercise Natural DisastersLulu Supergirl50% (2)
- Concepts of Security Threats, Challenges, Vulnerabilities and RisksDocumento47 pagineConcepts of Security Threats, Challenges, Vulnerabilities and RisksMarina-Larisa SperleaNessuna valutazione finora
- Focus5 2E Grammar Quiz Unit8.3 GroupB 1kolDocumento2 pagineFocus5 2E Grammar Quiz Unit8.3 GroupB 1kolRadosław AlbińskiNessuna valutazione finora