Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Reported Speech
Caricato da
Karola Cosme0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
71 visualizzazioni3 pagineestilo indirecto en ingles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoestilo indirecto en ingles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
71 visualizzazioni3 pagineReported Speech
Caricato da
Karola Cosmeestilo indirecto en ingles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
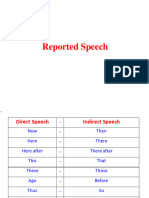
REPORTED SPEECH
Direct speech Reported speech
She says: "Im tired." She says that she is tired.
She said: "I'm visiting Paris next weekend" She said that she was visiting Paris the following weekend.
A. Reporting Statements
check whether you have to change:
1- Pronouns
She says, My dad likes roast chicken. She says that her dad likes roast chicken.
2- Tenses
Direct speech Reported speech
(no backshift) I write poems. He says that he writes poems.
(backshift) I write poems. He said that he wrote poems.
Examples of the main changes in tense:
Direct Speech Reported Speech
Simple Present Simple Past
He said: "I am happy" He said that he was happy
Present Progressive Past Progressive
He said: "I'm looking for my keys" He said that he was looking for his keys
Simple Past Past Perfect Simple
He said: "I visited New York last year" He said that he had visited New York the previous year.
Present Perfect Past Perfect
He said: " I've lived here for a long time " He said that he had lived there for a long time
Past Perfect Past Perfect
He said: "They had finished the work when I arrived" He said that they had finished the work when he had
arrived"
Past Progressive Past Perfect Progressive
He said: "I was playing football when the He said that he had been playingfootball when the
accident occurred" accident had occurred
Present Perfect Progressive Past Perfect Progressive
He said:"I have been playingfootball for two hours." He said that he had been playingfootball for two hours
Past Perfect Progressive Past Perfect Progressive
He said: "I had been reading a newspaper when the He said that he had been reading a newspaper when the
light went off" light had gone off
Future Simple (will+verb) Conditional (would+verb)
He said: "I will open the door." He said that he would open the door.
Conditional (would+verb) Conditional (would+verb)
He said: "I would buy Mercedes if I were rich" He said that he would buy Mercedes if he had been rich"
The modal verbs could, should, would, might, needn't, ought to, used to do not normally change.
Example:
He said, "She might be right." He said that she might be right.
Other modal verbs may change:
Modal Direct speech Reported speech
can "I can do it." He said he could do it.
may "May I go out?" He wanted to know if he might go out.
must "She must apply for the job." He said that she must/had to apply for the job.
will "They will call you." He told her that they would call her.
3- Place, demonstratives and time expressions.
Direct Speech Reported Speech
Time Expressions
today that day
now then
yesterday the day before
days ago days before
last week the week before
next year the following year
tomorrow the next day / the following day
Place
here there
Demonstratives
this that
these those
B. Reporting Questions
Types of questions Direct speech Reported speech
With question word (what, why, "Why" dont you speak He asked me why I didnt speak
where, how...) English? English.
Without question word (yes or no Do you speak English? He asked me whether / if I spoke
questions) English.
C. Reporting requests / commands
Direct speech Reported speech
Nancy,do the exercise. He told Nancy to do the exercise.
"Nancy, give me your pen, please." He asked Nancy to give him her pen.
Tenses are not relevant for requests simply use to / not to + verb (infinitive without "to")
For affirmative use to + infinitive (without to)
For negative requests, use not to + infinitive (without to).
Main clauses connected with and/but
If two complete main clauses are connected with and or but, put that after the conjunction.
Example:
He said,I saw her but she didn't see me. He said that he had seen her but that she hadn't seen him.
If the subject is dropped in the second main clause (the conjunction is followed by a verb), do not use that.
Example:
She said,I am a nurse and work in a hospital. He said that she was a nurse and worked in a hospital.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reported SpeechDocumento4 pagineReported SpeechNoa PahlićNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech GuideDocumento5 pagineReported Speech GuideKatita VieraNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonDocumento5 pagineReported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonRishit ChandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech Short SummaryDocumento2 pagineReported Speech Short Summaryfederica fissoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocumento2 pagineDirect Speech Reported SpeechЮля КряталоваNessuna valutazione finora
- General RevisionDocumento20 pagineGeneral RevisionJESuisAhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)Documento3 pagineReported Speech (Indirect Speech)Pili Lema BlancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFDocumento4 pagineGrammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFHadjab LyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting StatementsDocumento6 pagineReported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting Statementsriaadria100% (1)
- Direct Speech Reported Speech: ST NDDocumento3 pagineDirect Speech Reported Speech: ST NDMartaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento17 pagineReported SpeechalwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech - SummaryDocumento2 pagineReported Speech - SummaryFreddy Murrugarra100% (1)
- 1 - Reported Speech - StatementsDocumento3 pagine1 - Reported Speech - StatementsJohnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Indirect Speech Lesson With ExercisesDocumento10 pagineIndirect Speech Lesson With Exercisesmohammad515Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: Material Prepared By: Javier Medina, Valeria Martinez, Carlos Monceratt, and Eduardo MoralesDocumento9 pagineReported Speech: Material Prepared By: Javier Medina, Valeria Martinez, Carlos Monceratt, and Eduardo MoralesJavier MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocumento4 pagineReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsZaniShira100% (1)
- Reported Speech Guide: How to Transform Direct Quotes Into Indirect SpeechDocumento4 pagineReported Speech Guide: How to Transform Direct Quotes Into Indirect SpeechZaniShiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual English Lesson Report: Reported Speech, Exercises, and Life Project PresentationDocumento6 pagineVirtual English Lesson Report: Reported Speech, Exercises, and Life Project PresentationYefer romañaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocumento5 pagineReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsSofia AngelovaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Reported Speech 1Documento4 pagine01 Reported Speech 1katia.khimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar - Notes of Reported SpeechDocumento7 pagineGrammar - Notes of Reported SpeechGhost GamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Example: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishDocumento4 pagineExample: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishRita QuispeNessuna valutazione finora
- Estilo Indirecto (Reported Speech) : Can Could Must Had To May MightDocumento2 pagineEstilo Indirecto (Reported Speech) : Can Could Must Had To May MightmifernandezfNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech GuideDocumento4 pagineReported Speech GuideIeva VaičikauskaitėNessuna valutazione finora
- Tense Changes When Using Reported Speech GrammarDocumento11 pagineTense Changes When Using Reported Speech GrammarDenzel Guden Bautista MolloNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect NarrationDocumento6 pagineDirect and Indirect Narrationrizwan afzalNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech For FCEDocumento4 pagineReported Speech For FCEMarinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech-1Documento34 pagineReported Speech-1sanchisanchita9Nessuna valutazione finora
- DirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Documento17 pagineDirectIndirect Speech PPT 1Puja RatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento2 pagineDirect and Indirect SpeechDanielleOkNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento19 pagineReported Speechumurita37Nessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and IndirectDocumento11 pagineDirect and IndirectAssel SmagulovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect (Or Reported) Speech. IntroductionDocumento12 pagineDirect and Indirect (Or Reported) Speech. IntroductionJavier LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- EstiloindirectoDocumento19 pagineEstiloindirectoTatiana García SolanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and IndirectDocumento11 pagineDirect and IndirectAssel SmagulovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento44 pagineDirect and Indirect SpeechJoy JRNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar - Reported SpeechDocumento6 pagineGrammar - Reported SpeechAndres santos mendoza100% (1)
- English Grammar - SpeechDocumento7 pagineEnglish Grammar - SpeechAisy AstarinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento34 pagineDirect and Indirect SpeechJimin MochiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech: Tense Changes and Other TransformationsDocumento13 pagineReported Speech: Tense Changes and Other Transformationsjoshe003Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Year EnglishDocumento6 pagine1 Year EnglishkberrabahNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech NotesDocumento5 pagineReported Speech NotesChipo MulundikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento6 pagineReported SpeechRizal rindawunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rodich Steven Class - 14-Reported - SpeechDocumento19 pagineRodich Steven Class - 14-Reported - Speechsteven rodichNessuna valutazione finora
- Tense Changes When Using Reported SpeechDocumento4 pagineTense Changes When Using Reported SpeechDanielMedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento34 pagineReported SpeechRubicel Cordova0% (1)
- Reporter SDDocumento6 pagineReporter SDKarlita NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento6 pagineDirect and Indirect SpeechHasib QureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- (GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)Documento15 pagine(GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)NamNessuna valutazione finora
- Penjelasan Tentang Direct and Indirect Speech TerlengkapDocumento11 paginePenjelasan Tentang Direct and Indirect Speech TerlengkapHasby HasbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Indirect Speech, Also Known As Reported Speech or Indirect Discourse, Is A Means ofDocumento6 pagineIndirect Speech, Also Known As Reported Speech or Indirect Discourse, Is A Means ofMikael RanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported-Speech TheoryDocumento11 pagineReported-Speech Theorykasandra_style3751Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento10 pagineReported SpeechMilica DujakovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento5 pagineDirect and Indirect SpeechGunjan GargNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento32 pagineUntitledAsad RzayevNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi Reporteed SpeechDocumento15 pagineMateri Reporteed Speechdava alfisysyahriNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct Speech and Indirect SpeechDocumento4 pagineDirect Speech and Indirect SpeechAndreea PatrauteanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct and IndirectDocumento21 pagineDirect and Indirectgeetaryan01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech (Recovered)Documento10 pagineReported Speech (Recovered)Le BlancNessuna valutazione finora
- Continents Cut PasteDocumento1 paginaContinents Cut PasteinstcrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Tiger Tales Lesson 1Documento1 paginaTiger Tales Lesson 1faustin powerNessuna valutazione finora
- T T 28988 All About Me Activity Sheet Ver 2Documento1 paginaT T 28988 All About Me Activity Sheet Ver 2Karola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- AU T 1666 Classroom Recycling Bin Posters Labels PDFDocumento4 pagineAU T 1666 Classroom Recycling Bin Posters Labels PDFMum AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Put These Sentences Into Interrogative SentencesDocumento1 paginaPut These Sentences Into Interrogative SentencesKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- T T 28988 All About Me Activity Sheet - Ver - 2 PDFDocumento1 paginaT T 28988 All About Me Activity Sheet - Ver - 2 PDFKarola Cosme100% (1)
- BodypartsDocumento1 paginaBodypartsKarola Cosme100% (1)
- Minibeasts Worksheet Beep 4Documento2 pagineMinibeasts Worksheet Beep 4Laura fbNessuna valutazione finora
- Big and Small Fun Activities Games 46424Documento1 paginaBig and Small Fun Activities Games 46424Karola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Day and Night Sorting Activity Image CardsDocumento2 pagineDay and Night Sorting Activity Image CardsKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Put These Sentences Into Interrogative SentencesDocumento1 paginaPut These Sentences Into Interrogative SentencesKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1º Grammar Consolidation Unit 8Documento2 pagine1º Grammar Consolidation Unit 8Karola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported SpeechDocumento3 pagineReported SpeechKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Special Tradition in My CountryDocumento1 paginaA Special Tradition in My CountryKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- First Second Third3 PDFDocumento1 paginaFirst Second Third3 PDFKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal RecordsDocumento1 paginaAnimal RecordsKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Unit 5Documento1 paginaHomework Unit 5Karola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- School Supply Art ActivityDocumento2 pagineSchool Supply Art ActivityKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Always Try To Answer These QuestionsDocumento1 paginaAlways Try To Answer These QuestionsSonia Daniela Ayuso Frutos100% (1)
- UNIT 2 Beep 3Documento1 paginaUNIT 2 Beep 3Karola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- AlAcCrds FinalDocumento80 pagineAlAcCrds FinalKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Unit 2 JaguarDocumento1 paginaHomework Unit 2 JaguarKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Teoría Inglés 1º ESODocumento16 pagineTeoría Inglés 1º ESOtealmar83% (29)
- Fastest AnimalsDocumento1 paginaFastest AnimalsKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- EJERCICIOS Finales Del Tema 1Documento2 pagineEJERCICIOS Finales Del Tema 1Karola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Islcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Elementary School Writing Adjectives Worksh Comparative2 7 299264df90f8cd83959 59857599Documento2 pagineIslcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Elementary School Writing Adjectives Worksh Comparative2 7 299264df90f8cd83959 59857599download fileNessuna valutazione finora
- Packing A SuitcaseDocumento1 paginaPacking A SuitcaseKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Kitchen Words CardsDocumento5 pagineKitchen Words CardsKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- School Supply Art ActivityDocumento2 pagineSchool Supply Art ActivityKarola CosmeNessuna valutazione finora
- English Id 1 Student's Book and WB PDFDocumento119 pagineEnglish Id 1 Student's Book and WB PDFPriscila Souza71% (42)
- Comes Before Adjectives and Adverbs. - This Coffee Is - (Adj.) - He Worked The Exam. (Adverb)Documento43 pagineComes Before Adjectives and Adverbs. - This Coffee Is - (Adj.) - He Worked The Exam. (Adverb)Victoria PanaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Linguistics Ambiguity Deep StructureDocumento10 pagineLinguistics Ambiguity Deep StructureTerrenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6 Subject Verb Agreement GwynDocumento24 pagineLecture 6 Subject Verb Agreement Gwynロクサス Roxas Yap100% (1)
- A1 Exam English Unlimited 5-7Documento2 pagineA1 Exam English Unlimited 5-7Coco LanguagesNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheets For Sem1Documento9 pagineWorksheets For Sem1Shery MujosNessuna valutazione finora
- Work Book-English-Grade 11&12 PDFDocumento41 pagineWork Book-English-Grade 11&12 PDFfraol100% (4)
- The Simple Present TenseDocumento15 pagineThe Simple Present TenseDewa OngNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar Workbook: Grade 11Documento141 pagineGrammar Workbook: Grade 11W MSNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Syllabus English IIDocumento12 pagineCourse Syllabus English IIANDRESNessuna valutazione finora
- English 10 Worksheet Quarter 4 Week 5 8Documento4 pagineEnglish 10 Worksheet Quarter 4 Week 5 8Ren AkiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Hausa LanguageDocumento2 pagineHausa Languageoluwatobilobaayomide098Nessuna valutazione finora
- Present Simple vs Present ContinuousDocumento15 paginePresent Simple vs Present ContinuousDaiva SnipaitieneNessuna valutazione finora
- ConditionalsDocumento17 pagineConditionalsNaveen YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- The PassiveDocumento38 pagineThe PassiveTweetyandBeastNessuna valutazione finora
- EnglishDocumento145 pagineEnglishmvianoliNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Grammar Exercises (Unit 9, Page 100) : We All Hope There Will Soon Be (The Peace / Peace) in The WorldDocumento4 pagineExtra Grammar Exercises (Unit 9, Page 100) : We All Hope There Will Soon Be (The Peace / Peace) in The WorldjasirNessuna valutazione finora
- 30 20-23-10HANDOUT The Syntax of Romanian DemonstrativesDocumento26 pagine30 20-23-10HANDOUT The Syntax of Romanian DemonstrativesCristina TomaNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing Session - Unit 1,2 and 3 - Group - 216Documento12 pagineWriting Session - Unit 1,2 and 3 - Group - 216Miller Rincon SastoqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Teste 5º Ano InglesDocumento3 pagineTeste 5º Ano InglesclaudiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Definition of GrammarDocumento14 pagineDefinition of Grammarpresident crj100% (1)
- Construction ShiftDocumento28 pagineConstruction ShiftShebece Patt100% (1)
- ExercisesDocumento3 pagineExercisesDel MonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.Concord-RULES OF ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND USAGE PDFDocumento18 pagine8.Concord-RULES OF ENGLISH GRAMMAR AND USAGE PDFfhgsdas73% (41)
- Lesson Plan 4-2Documento3 pagineLesson Plan 4-2api-252662730Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kachin Today English - Kachin Dictionary & ThesaurusDocumento2 pagineKachin Today English - Kachin Dictionary & ThesaurusN-gun Ja WaNessuna valutazione finora
- For CC WaaaaaaaaaaawDocumento21 pagineFor CC WaaaaaaaaaaawMoha Zahmonino100% (1)
- EL120: English Phonetics and Linguistics: All BranchesDocumento5 pagineEL120: English Phonetics and Linguistics: All BranchesAli Al KhamisNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1. Numbers and Operations With NumbersDocumento10 pagine1.1. Numbers and Operations With NumbersCuentasSCB89Nessuna valutazione finora
- (Merrill Y. Van Wagoner) Spoken Arabic Saudi (Bookos - Org) TextDocumento157 pagine(Merrill Y. Van Wagoner) Spoken Arabic Saudi (Bookos - Org) TextShafiullah KhanNessuna valutazione finora