Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
555 Timer
Caricato da
Sagor SahaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
555 Timer
Caricato da
Sagor SahaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Timer: A square wave generator is known as a multivibrator.
Timer circuit is called multivibrator because it produces
square pulses.
Types: 3 types
(a) Monostable (One-shot): In which one state is stable i.e. off state, but the other state is unstable (transient). A
trigger pulse causes the circuit to enter the temporary unstable state. After entering the unstable state, the
circuit will return to the stable state after a set time. The time period of unstable state is determined by an RC
network. Such a circuit is useful for creating a timing period of fixed duration (i.e. Stopwatch).
(b) Astable (Oscillator): It is not stable in either state. It continuously switches from one state to the other.
(c) Bistable (Flip flop): It is stable in either state. If you flip it on, it stays on. If you flip it off, it stays off.
Basic Operation of 555 Timer IC:
For comparators: If (+ve) i/p > (-ve) i/p then Vout=1
For comparators: If (+ve) i/p < (-ve) i/p then Vout=0
- The voltage divider consisting of three 5 k resistors provides a trigger level of 1/3 Vcc and a threshold level of 2/3
V cc .
- When the normally HIGH trigger input momentarily goes below 1/3 Vcc , the output of comparator B switches
from LOW to HIGH and sets the S-R latch (Q=1). causing the output (pin 3) to go HIGH and turning the discharge
transistor Q1 off.
Fig 1. Internal functional diagram of a 555 timer.
- When the LOW threshold input goes above 2/3 Vcc and causes the output of comparator A to switch from LOW
to HIGH. This resets the latch (Q=0), causing the output (pin 3) to go back LOW and turning the discharge
transistor on.
(Note: The trigger and threshold inputs (pins 2 and 6) are controlled by external components connected to produce
either monostable or astable action.)
Prepared by Md. Sajid Hossain
Astable Opearation:
-Initially, when the power is just turned on, the capacitor (C1) remain Uncharged and thus the trigger (pin 2) and
threshold (pin 6) is at 0 V. So, Vout (comp. A) = 0 and Vout (comp. B) = 1. Thats why Q1 is OFF.
2/3 Vcc
1/3 Vcc
Fig. Operation of the 555 timer in the astable mode.
-Now, C1 begins charging through R1 and R2, indicated in Figure.
2
When, C1 is just above Vcc then Vout= (comp A)=1 and Vout= (comp B)=0 which Resets the latch (Q=0).
3
At this state Q1 turns ON and creates a discharging path as shown in the figure.
1
-When C1 discharge it causes Vout (comp. A)=0 and when C1 discharges down to 3 Vcc then Vout (comp. B)=1. This again
Sets latch and turning off Q1 again. Another charging cycle begins and the entire process repeats.
Prepared by Md. Sajid Hossain
Monostable Mode Operation:
-Before a trigger pulse is applied, the output is LOW (Stable off-state) and the discharge transistor Q1 is ON, keeping C1
discharged as shown in Figure (a).
-At time, t0 a negative going triggering pulse applied then (+ve) i/p > (-ve) i/p for comp. B. So, Comp. B = 1 which makes
Output = High. Q1 is off and allowing C1 to charge through R1.
- At time, t1 when C1 is just above 2/3 Vcc then (+ve) i/p > (-ve) i/p for comp. A. So, Comp. A = 1.
-At the same time, (-ve) i/p of comp. B ( HIGH) > (+ve) i/p of comp. B (1/3 of Vcc). So, comp. B = 0.
Thus o/p = 0 (LOW) at t1 state. This turns on Q1 and helps C1 to discharge.
Prepared by Md. Sajid Hossain
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Core Modules in Communications Systems: Reliability CodingDocumento2 pagineCore Modules in Communications Systems: Reliability CodingSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Irjet V7i3567 PDFDocumento6 pagineIrjet V7i3567 PDFSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
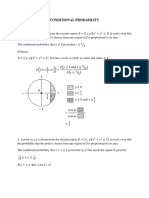
- P (D) P (+/T) P (D) P (+/T) +P (D) P (+/D) 1% 99% 1% 99%+99% 1% 99/100 99/100+99/100 1 2Documento3 pagineP (D) P (+/T) P (D) P (+/T) +P (D) P (+/D) 1% 99% 1% 99%+99% 1% 99/100 99/100+99/100 1 2Sagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Conditional Probability of Passing Three ExamsDocumento29 pagineConditional Probability of Passing Three ExamsAkhilNessuna valutazione finora
- (Program Curriculum) : PG Diploma in Data ScienceDocumento6 pagine(Program Curriculum) : PG Diploma in Data Sciencegnk68Nessuna valutazione finora
- 100 Numpy ExercisesDocumento13 pagine100 Numpy ExercisesShubham JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Clustering AnalysisDocumento102 pagineClustering AnalysisOnigh1983atdayrepdotcomNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied AI - Machine Learning Course Syllabus PDFDocumento22 pagineApplied AI - Machine Learning Course Syllabus PDFAkash Raghavendra Kathavate Dept of TENessuna valutazione finora
- JEE MAIN MathematicsDocumento301 pagineJEE MAIN MathematicsAnandhi Chidambaram100% (1)
- Power BI and Tableau Online Course GuideDocumento15 paginePower BI and Tableau Online Course GuideRahulllNessuna valutazione finora
- Laura Mitchell, Sri. Yogesh K., Vishnu Subramanian - Deep Learning With PyTorch 1.X_ Implement Deep Learning Techniques and Neural Network Architecture Variants Using Python, 2nd Edition-Packt PublishDocumento293 pagineLaura Mitchell, Sri. Yogesh K., Vishnu Subramanian - Deep Learning With PyTorch 1.X_ Implement Deep Learning Techniques and Neural Network Architecture Variants Using Python, 2nd Edition-Packt PublishSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- PM ASDS Admission Requirements 2019Documento1 paginaPM ASDS Admission Requirements 2019Sagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL INTRO - LEARN SQL DATABASE QUERY LANGUAGEDocumento127 pagineSQL INTRO - LEARN SQL DATABASE QUERY LANGUAGESagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- v α v v v v t x=v t=v y=v t− gt v gt x v t y=v x v g× x v xtanα− x vDocumento1 paginav α v v v v t x=v t=v y=v t− gt v gt x v t y=v x v g× x v xtanα− x vSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Learning Beginner to ProfessionalDocumento15 pagineMachine Learning Beginner to ProfessionalbhaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Week11 FinalDeck PDFDocumento36 pagineWeek11 FinalDeck PDFSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Samuel Kwong Resume PDFDocumento1 paginaSamuel Kwong Resume PDFSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL Basics Cheat Sheet PDFDocumento326 pagineSQL Basics Cheat Sheet PDFSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Automated Neural Image Caption Generator For Visually Impaired PeopleDocumento6 pagineAutomated Neural Image Caption Generator For Visually Impaired PeopleSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- NitishNehra ResumeDocumento1 paginaNitishNehra ResumeSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Conditional Probability of Passing Three ExamsDocumento29 pagineConditional Probability of Passing Three ExamsAkhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Science Resources PDFDocumento1 paginaData Science Resources PDFPranayNessuna valutazione finora
- 4476Documento5 pagine4476ARUN KUMAR0% (1)
- Materials Chemistry C: Journal ofDocumento11 pagineMaterials Chemistry C: Journal ofSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensors: Sensor-Based Assistive Devices For Visually-Impaired People: Current Status, Challenges, and Future DirectionsDocumento42 pagineSensors: Sensor-Based Assistive Devices For Visually-Impaired People: Current Status, Challenges, and Future DirectionsGuntoro AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Indonesia Deaf and Blind Communication System (IDBC-system) : Education and Information TechnologiesDocumento17 pagineIndonesia Deaf and Blind Communication System (IDBC-system) : Education and Information TechnologiesSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- QQQQ PDFDocumento484 pagineQQQQ PDFSagor Saha100% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning Program BrochurDocumento17 pagineArtificial Intelligence Machine Learning Program BrochursanjayNessuna valutazione finora
- An Interactive Wearable Assistive Device For Individuals Who AreDocumento10 pagineAn Interactive Wearable Assistive Device For Individuals Who AreSagor SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Upgrad + PGD+ML+BrochureDocumento8 pagineUpgrad + PGD+ML+BrochureRayvonNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- VRV A 12 PDFDocumento1 paginaVRV A 12 PDFMoe Thiri ZunNessuna valutazione finora
- 11+ Entrance Examination: Specimen PaperDocumento8 pagine11+ Entrance Examination: Specimen PaperNayem Hossain HemuNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Automation Iot Bca Up (2ND SEMINAR PPT) RTDocumento30 pagineHome Automation Iot Bca Up (2ND SEMINAR PPT) RTTejaswiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Bilstein SZ SL Sls 2010Documento16 pagineBilstein SZ SL Sls 2010Wimin HungNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 Yr 9 Linear Relations Test A SolutionsDocumento13 pagine2017 Yr 9 Linear Relations Test A SolutionsSam JeffreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Color Order SystemsDocumento30 pagineColor Order SystemsBeyene DumechaNessuna valutazione finora
- Goniophotometer T1: OxytechDocumento6 pagineGoniophotometer T1: OxytechGustavo CeccopieriNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual 1Documento37 pagineManual 1Şahin GüngörNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGG1330 2N Computer Programming I (20-21 Semester 2) Assignment 1Documento5 pagineENGG1330 2N Computer Programming I (20-21 Semester 2) Assignment 1Fizza JafferyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem 2Documento128 pagineSem 2Agustin A.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial CorelDRAW-X8Documento10 pagineTutorial CorelDRAW-X8Ajay BhargavaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Professional DesktopDocumento318 pagineThe Professional Desktopalintuta2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Differential Equations For Finding Their SolutionsDocumento2 pagineClassification of Differential Equations For Finding Their SolutionsakhileshNessuna valutazione finora
- Ema 312 Unit 4Documento22 pagineEma 312 Unit 4Ahbyna AmorNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm D5501Documento3 pagineAstm D5501mhmdgalalNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key Grade 6 - 2023Documento7 pagineAnswer Key Grade 6 - 2023ALKHANSAA ELOBEIDYNessuna valutazione finora
- M.E. Comm. SystemsDocumento105 pagineM.E. Comm. SystemsShobana SNessuna valutazione finora
- ASP Flashcards - QuizletDocumento36 pagineASP Flashcards - QuizletRehman MuzaffarNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle Data Integration - An Overview With Emphasis in DW AppDocumento34 pagineOracle Data Integration - An Overview With Emphasis in DW Appkinan_kazuki104Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kalayaan Elementary SchoolDocumento3 pagineKalayaan Elementary SchoolEmmanuel MejiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stereochemistry Practce PDFDocumento6 pagineStereochemistry Practce PDFFerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Blast Nozzle Catalog: Bringing Ceramic Technology To Industry Boride P Roduct SDocumento46 pagineAbrasive Blast Nozzle Catalog: Bringing Ceramic Technology To Industry Boride P Roduct SSamsu SamsNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 5 Mathematics Sample Paper Set NDocumento4 pagineCBSE Class 5 Mathematics Sample Paper Set NRamanjeet KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- MSYS-1 0 11-ChangesDocumento3 pagineMSYS-1 0 11-ChangesCyril BerthelotNessuna valutazione finora
- Rso PDFDocumento120 pagineRso PDFjohn shepardNessuna valutazione finora
- Tradesman Electronics PDFDocumento13 pagineTradesman Electronics PDFsandeepxrNessuna valutazione finora
- XS Power Batteries D Series InstructionsDocumento2 pagineXS Power Batteries D Series InstructionsAutopiezas PanaNessuna valutazione finora
- SDH TechnologyDocumento26 pagineSDH TechnologyJayesh SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- WebControls - TabStripDocumento38 pagineWebControls - TabStripProkopis PrNessuna valutazione finora
- Great Lakes PGDM Interview Access DetailsDocumento1 paginaGreat Lakes PGDM Interview Access DetailsJaswanth konkepudiNessuna valutazione finora