Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Strain Tunable Resin and Coating Technology For Next Generation Composites
Caricato da
scribd8341Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Strain Tunable Resin and Coating Technology For Next Generation Composites
Caricato da
scribd8341Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Strain Tunable Resin and Coating Technology for Next Generation Composites
S. Lewit*
*Scott M. Lewit, President, Structural Composites, Inc.,
7705 Technology Dr., W Melbourne, FL 32904 USA, slewit@aol.com
ABSTRACT market has achieved just 3.6% of its composite material
market potential, and the construction market has achieved
Leveraging Navy SBIR efforts, Structural Composites, Inc just 4% of its composite material market potential [1].
has invented a breakthrough coating and resin technology Even with this low level of market penetration, the dollar
for composites. Our patent pending Co-Cure technology value of materials currently being used in each of these
enables shop floor alteration of coating and resin properties, markets exceeds that of the entire 2.3 billion dollar
which can facilitate a range of performance enhancements aerospace composites material market. Just achieving a
to composite fabrications. This has the potential to impact small segment of these potential emerging markets can
the entire composites market, allowing for more cost transform the global composites industry by 10 to 100 fold
effective optimized composite structures. We are working from its current size.
with industry leaders on both the technology development
and deployment. These technology partners will become Bridging the cost gap from traditional materials while
our early adopters and will have access to the technology. maintaining the performance advantage for composites is
We are looking for key industry innovators in related the game changing technology that is needed to penetrate
emerging markets such as rail car, locomotive, wind these emerging markets. In transportation, advances in
energy, building construction, shelters and recreational composites will help make all powered vehicles lighter and
vehicles. more efficient. Weight reduction will also play an
important role by helping other emerging technologies
Keywords: composites, advanced resins and coatings, achieve commercial viability.
lightweight, emerging markets, composites for
transportation. One major area of opportunity to improve composites is in
advanced low cost coating and resin technology. Todays
low cost resins and coatings limit the performance of our
1 BACKGROUND structures. The lowest cost resins are orthophthalic
polyesters; the lower cost coatings are isophthalic polyester
Composite technology has made tremendous advances over based gel coats. Both of these materials, while cost
the past two decades. After much investment, we now effective, suffer from relatively poor mechanical properties;
understand how to better optimize the design, the material in particular, low strain to failure and fracture toughness.
systems and the manufacturing process. This has resulted
in many exciting applications for composites, in particular The recreational marine industry is a very cost sensitive
applications where traditional material technology has been industry for composites. Gel coat used as an in-mold
dominant. coating is the industry standard. Gel coat is a filled resin
system that has pigments, UV stabilizers, fillers and
We all know the advantages of composites: lightweight, additives which enable it to be sprayed onto a mold and
strong, tough, formable to complex shapes, durable and cure as thin film. Layers of composites (fibers and resin)
resistant to corrosion. In order to expand into new markets are placed over the in-mold coating to create the part, in this
such as transportation, infrastructure and building case a boat hull or deck.
construction, we face less of a performance gap but more of
a price gap. Traditional approaches to composites can meet The consumer demands a high quality visual appearance
the performance requirements, however the high cost limits from the gel coat. In boats it is commonly referred to as the
the application to those markets which value the advantage. automotive finish. Gel coat can deliver this finish, however
New designs, materials and manufacturing approaches that its brittle nature, its location on high strain surfaces and the
reduce cost open new markets for composites. dominant flexural and shock loading experienced by boats
commonly cause cracking of the coating. If you have ever
The scale of these emerging markets should not be under- owned a composite boat you have seen gel coat cracking.
estimated. A Lucintel study presented at ACMAs
Composites 2012 conference provides an indication as to
the potential market size. The markets with the largest
unachieved potential for composites are transportation and
construction. The study indicates that the transportation
only has the potential to bridge the price gap but has the
potential to change composites as we know them today.
2 CO-CURE TECHNOLOGY
Leveraging Navy SBIR efforts, Structural Composites Inc
has invented a breakthrough coating and resin technology
for composites. Our patent pending Co-Cure technology
enables shop floor alteration of coating and resin properties
which will facilitate a range of performance enhancements
to composite fabrications. This significant accomplishment
has the potential to impact the entire composites market,
allowing for more cost effective optimized composite
structures.
Figure 1: Conventional gel coat on recreational marine Current state of the art is for fabricators to purchase a fully
product. formulated resin or coating system. The co-cure
technology enables resin or coating formulation at the
Recreational boat manufacturers indicate about 50% of all fabricator site at the resin gun head/dispensing equipment,
warranty claims are centered around the gel coat. In thus the coating and resin properties can be formulated on
essence, todays composite products that use in-mold gel the fly and applied to the part. This development opens a
coat are designed around the gel coat, as this material will spectrum of opportunities for both existing and emerging
fail prior to structural failure of the fiber reinforced markets.
laminate.
The invention pertains to coatings and structural layers
A cost effective, tougher gel coat that provides a high commonly used to fabricate molded products, and in
quality cosmetic finish would be a major asset to the particular to co-cured systems having improved adhesion,
industry. It would allow thinner laminates, resulting in toughness, flexibility, and structural performance.
weight savings and cost savings. In the emerging
transportation markets (trailer, rail, bus, etc.) this can help One facet of the invention concerns gel coats comprised of
bridge the price gap and improve performance helping specially formulated co-cured urethane and vinyl ester,
drive economic viability. epoxy, or unsaturated polyester components. The gel coats
have improved toughness and flexibility compared with
Todays performance resins are epoxy, vinyl ester and conventional gel coats, they adhere well to structural layers,
polyurethane. These resins can provide far superior and they can be used in a traditional in-mold process.
performance over the low cost polyester resins. The next Laboratory testing has shown that these improved gel coats
performance step above polyester resin is vinyl ester resin, allow laminates that can withstand 25% greater allowable
at prices that can be double or more over the polyester. stress and have a superior bond, in particular for difficult
Todays advanced resins improve performance but increase applications such as continuous submergence.
the price gap.
In performance applications such as naval structures or
theme park rides, vinyl ester or expoy resins are the
standard. These applications are far less price sensitive
than the commercial transportation, civil infrastructure and
construction markets. A low cost resin that can provide the
toughness and ease of process as the current advanced
resins will help bridge the price gap for emerging markets.
Structural Composites has been at the forefront of this
effort leveraging government funding and low cost
technology from the marine industry. This has led to
several breakthroughs that are reducing the price gap and
increasing performance for composites in these emerging
markets. This paper details one aspect of the technology, Figure 2: Comparison of laminate stress cracking and
an innovative co-cure resin and coating technology that not failures in flexure for conventional gel coat and Co-Cure
coating configurations.
of the greatly reduced shelf life which have plagued
formulated hybrid resin systems.
Our goal is to develop and refine the technology and deploy
it to the composites industry with the aid of leading
industry partners. We believe the technology has broad
global application, as it can improve todays composites
and can help open doors for new emerging markets for
composites.
3 CURRENT STATE OF THE
TECHNOLOGY
Working with a major global supplier, we are currently
refining and optimizing the Co-Cure technology in
preparation for market deployment. The technology has
been applied to several prototypes in cost sensitive
emerging markets.
Figure 3: Coating adhesion test results comparison for
estuary exposure of coatings.
Another facet of the invention concerns an elastomeric
coating comprised of specifically formulated co-cured
urethane and vinyl ester, epoxy, or unsaturated polyester
components. The elastomeric coatings are flexible and
tough, they adhere well to structural layers, and unlike
conventional urethane coatings they can be used in a
traditional in-mold process. Our Co-Cure technology
combined with advanced new fibers enables a new
generation of ultra-tough composites that can better
withstand shock and impact and are more resistant to
damage.
The ability to radically alter resin properties in real-time on
the factory floor creates many exciting new opportunities
for composites. Co-Cure has tremendous potential for
producing lighter, more structurally efficient composite
structures such as wind blades, underwater turbines, boats,
aircraft, and ground transportation vehicles at more
affordable (cost neutral) pricing.
Co-Cure based on low cost unsaturated polyester resin and
moderate cost polyurethane chemistry is of particular
interest as it has the potential to bridge both the price gap
and the performance gap which prohibit broader use of
composites in many segments of transportation. Another
aspect of this market segment is the need for scalability as it
embodies a broad range of production volumes. Co-Cure
provides the ability to tune the resin cure cycle to meet the
various and diverse needs of this broad emerging market.
Previous work has focused on hybrid resin systems, such as
Amocos Xycon Resin (1990s), where single property
systems were formulated at the resin manufacturer and
compounded. Co-Cures ability to alter resin properties on
the factory floor, on-the-fly, literally at the resin gun head, Figure 4: Co-Cure coating as a wear surface for a prototype
is distinctive. Importantly, Co-Cure also eliminates issues produce box truck.
It is anticipated that a military version of gel coat
replacement will be available and fielded in 2014.
Production volumes scaled for this market are targeted to
begin in 2015.
Figure 5: SBIR Phase III 11M low cost lightweight shock
mitigating prototype combatant craft hull in fabrication.
In parallel with this, experimentation is underway to
develop a gel coat replacement that will meet the cosmetic
requirements for consumer goods such as boats, RVs
trailers and buses. Trials are in progress and prototype
products are being produced or in planning.
In addition to the coating technology the team is working
on a complementary low cost co-cure resin system to help
bridge the price gap for transportation, infrastructure and
construction. Our goal is to develop a high performance
resin at 30-40% lower cost than current low cost
performance resins. The significance of this invention will
be market opportunities for composites that in past studies
have not been financially viable.
We are working with industry leaders on both the
technology development and deployment. These
technology partners will become our early adopters and will
have access to the technology.
We are looking for key industry innovators in related
emerging markets, including rail car, locomotive, wind
energy, building construction, shelters and recreational
vehicles.
REFERENCES
[1] Chuck Kazmierski Program Manager, Lucintel,
"Growth Opportunities in Global Composites Industry,
2012-2017, ACMA Composites 2012, Mandalay Bay
Convention Center, Las Vegas, NV, Feb 21-23 2012.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Pt2735a BDocumento2 paginePt2735a Bscribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cored Hull BottomsDocumento13 pagineCored Hull Bottomsscribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aerospace-Composite-Products-E-Z LAM HT Data SheetDocumento1 paginaAerospace-Composite-Products-E-Z LAM HT Data Sheetscribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- PT1158Documento2 paginePT1158scribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Regenerative AgricultureDocumento11 pagineRegenerative Agriculturescribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- DowDocumento2 pagineDowscribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- FAANG Options Trader Report 2018Documento10 pagineFAANG Options Trader Report 2018scribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- TDS - Es-221Documento2 pagineTDS - Es-221scribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Siemens Basic DynamicsDocumento406 pagineSiemens Basic Dynamicsscribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sea Ray and Balsa Core Bottoms - by David Pascoe, Marine SurveyorDocumento12 pagineSea Ray and Balsa Core Bottoms - by David Pascoe, Marine Surveyorscribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cored Hull BottomsDocumento13 pagineCored Hull Bottomsscribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cornwell CatalogDocumento16 pagineCornwell Catalogscribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Franklin Tubing BrochureDocumento8 pagineFranklin Tubing Brochurescribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Franklin Tubing BrochureDocumento8 pagineFranklin Tubing Brochurescribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Testrapport ASTM E84 Class A1 - IfR XorelDocumento3 pagineTestrapport ASTM E84 Class A1 - IfR XorelAnil AoNessuna valutazione finora
- HP3D Jabil3DPrinting CaseStudy 05.17Documento4 pagineHP3D Jabil3DPrinting CaseStudy 05.17scribd8341Nessuna valutazione finora
- 16cf4 Adv of Epoxy V PolyDocumento2 pagine16cf4 Adv of Epoxy V Polyscribd8341100% (1)
- NAS1102 Series Screw SpecsDocumento1 paginaNAS1102 Series Screw Specsscribd8341100% (1)
- Design of Wind TurbinesDocumento17 pagineDesign of Wind TurbineslrdseekerNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Vol-Ii M1334Documento117 pagineVol-Ii M1334Yashapuja100% (1)
- Dow Epoxy ResinDocumento5 pagineDow Epoxy ResinSrinivasan ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cera DampproofDocumento2 pagineCera DampproofAnwar HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer-Plastics Additives PDFDocumento643 paginePolymer-Plastics Additives PDFwardolier67% (3)
- Masterflow 410 PCDocumento3 pagineMasterflow 410 PCFrancois-Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Discussion of HVAC Coil CoatingsDocumento4 pagineA Discussion of HVAC Coil Coatingsfawmer61Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carbothane 134 Za (April 2013 Replaces November 2012)Documento2 pagineCarbothane 134 Za (April 2013 Replaces November 2012)emilliomudNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 5 MountingDocumento6 pagineExperiment 5 MountingMohanadAlrofuNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation and Rigging Procedures: Advanced Technology Performance and Environmental Improvement Systems For YourDocumento33 pagineInstallation and Rigging Procedures: Advanced Technology Performance and Environmental Improvement Systems For YourRene QueirozNessuna valutazione finora
- Grouting Soultions BrochureDocumento4 pagineGrouting Soultions BrochureafrdhkNessuna valutazione finora
- Diversified Wood Cat 2017Documento59 pagineDiversified Wood Cat 2017codeethylNessuna valutazione finora
- 23) CDS Pouring Concrete UWDocumento2 pagine23) CDS Pouring Concrete UWho wa chowNessuna valutazione finora
- D 6412 - D 6412m - 99 Rdy0mtivrdy0mtjnDocumento4 pagineD 6412 - D 6412m - 99 Rdy0mtivrdy0mtjnMarceloNessuna valutazione finora
- Distributed By:: Beyond Expectation & Beyond LimitationDocumento27 pagineDistributed By:: Beyond Expectation & Beyond LimitationFran PesqueraNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Stability of Shape Memory Polymers, Polymer Blends, and CompositesDocumento31 pagineThermal Stability of Shape Memory Polymers, Polymer Blends, and CompositesVeeturiVarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Line Oil GasDocumento16 pagineProduct Line Oil GasFabian Hernandez VeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ms Painting Shaybah Rev 00Documento14 pagineMs Painting Shaybah Rev 00Haroonamjan MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- SIGMALINE™ 2500: Product Data SheetDocumento5 pagineSIGMALINE™ 2500: Product Data SheetEduardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quickmast 341Documento2 pagineQuickmast 341rakeshNessuna valutazione finora
- HPSR Road Pmgsy16Documento62 pagineHPSR Road Pmgsy16rajinder kutaal100% (2)
- Food and Beverage Can Coatings A Review On Chemicalanalysis, Migration, and Risk AssessmentDocumento54 pagineFood and Beverage Can Coatings A Review On Chemicalanalysis, Migration, and Risk AssessmentAna Julia Mayumi PupinNessuna valutazione finora
- Hexcel's Composite Materials, ProcessesDocumento12 pagineHexcel's Composite Materials, Processessathiskumar411Nessuna valutazione finora
- Strengthening of Reinforced Concrete Beams by Using Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites - A ReviewDocumento12 pagineStrengthening of Reinforced Concrete Beams by Using Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites - A ReviewJenkin CacapitNessuna valutazione finora
- Epilux - HB - MIO - Coating-Grey PDFDocumento2 pagineEpilux - HB - MIO - Coating-Grey PDFRanjan Kumar SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynasolve™ 185: Cleaning Applications: Product Usage GuidelinesDocumento2 pagineDynasolve™ 185: Cleaning Applications: Product Usage Guidelinesmario230991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diab Foam MaterialsDocumento16 pagineDiab Foam MaterialsOğuzhan M. BostancıNessuna valutazione finora
- Bolted FRP Flange Joints For Pipelines A Review of Current Practice and Future ChallengesDocumento34 pagineBolted FRP Flange Joints For Pipelines A Review of Current Practice and Future ChallengesiJordanScribdNessuna valutazione finora
- AGI EnclosuresDocumento5 pagineAGI EnclosuressalamrefighNessuna valutazione finora
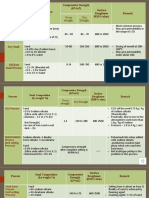
- Compressive Strength (kN/m2) Surface Roughness (RMS Value) RemarkDocumento5 pagineCompressive Strength (kN/m2) Surface Roughness (RMS Value) RemarksumeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1555609Documento2 pagineTechnical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1555609MansoorNessuna valutazione finora