Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Risk For Injury
Caricato da
Allene Paderanga0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
664 visualizzazioni5 pagineNursing care plan XUCN 2017
Titolo originale
Risk for injury
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoNursing care plan XUCN 2017
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
664 visualizzazioni5 pagineRisk For Injury
Caricato da
Allene PaderangaNursing care plan XUCN 2017
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 5
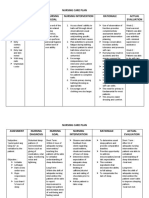
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING RATIONALE EVALUATION
IMPLEMENTATION
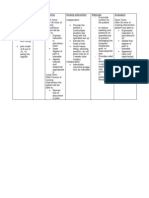
Subjective Cues: Activity Short term: Independent: Short term:
Intolerance At the end of 1 1. Determine the 1. Fatigue can limit At the end of 1 hour
Ginatabangan ko related to hour of nursing clients routine and the clients ability to of nursing
mag lakaw as generalized body intervention the over the counter perform needed intervention the
verbalized. weakness client will be able medication. activity. It can also client was able to:
secondary to to: be a medication
Objective Cues: progressive effect. a. Verbalize
disease state a. Verbalize how to how to use
-Dependent use energy 2. Placed client in a 2. a comfortable energy
mobility conservation comfortable position positon will help conservation
-Needs assistance techniques. and adjust the provide techniques
from time to time b. Identify methods position comfortable opportunities for b. Identify
-LOM: limited to reduce activity as preferred. relaxation the methods to
mobility intolerance. muscles optimally reduce
-Body weakness is c. Participate by activity
observed cooperating in the 3. Minimize 3. Quiet intolerance.
nursing environmental environment lessen c. Participate
management to activity and noise; stimuli that may by
alleviate providing clean, aggravate pain; cooperating
intolerance. quiet and calm calm environment in the
environment. help the client rest nursing
well management
Long term: to alleviate
At the end of 4 4. Instruct the client 4. Energy-saving intolerance.
hours of nursing in energy-saving techniques helps
intervention the techniques such as the client exert less Long Term:
client will be able sitting when effort in activities At the end of 4
to: bathing, sitting to that cannot be hours of nursing
brush or comb hair. tolerated
a. Demonstrate 5. instruct the client 5. Strenuous intervention the
non- to avoid strenuous activities may client was able to:
pharmacological activities consume a lot of
ways to reduce energy that may a. Demonstrate
activity trigger the inability
non-
b. Rest/Sleep and to perform activities
pharmacological
participate in ways to reduce
activities 6. Monitor hours of 6. Enough sleep for activity
appropriately. sleep at least 6-8 hours, b. Rest/Sleep and
c. Participate in the helps to conserve participate in
treatment regimen and provide activities
or activities to energy. appropriately.
correct the crisis.
d. Report the ability 7.Observe and 7. Close monitoring
to perform required document response will serve as a
activities. to activity guide for optimal
progression of
activity.
Collaborative:
1. Administer 1. Analgesic
pain mediation
medications can help
as ordered: reduce the
paracetamol clients pain.
600 mg IV
Q6 and
tramadol
5mg IV Q6
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING RATIONALE EVALUATION
IMPLEMENTATION
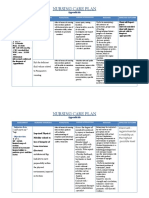
Subjective Cues: Short term: Independent: Short term:
mura kog Risk for injury At the end of 1 1.Assess general 1. This is to At the end of 1
madagma kung related to hour of nursing status of patient determine the hour of nursing
ako ra isa generalized intervention the patients condition intervention the
maglakaw as weakness client will be able that may cause client was able to:
verbalized to: injury.
a. Explain methods a. Explain methods
Objective Cues: to prevent injury 2. Thoroughly 2. The patient must to prevent injury
-Needs assistance b. Identifies factors conform patient to get used to the b. Identifies factors
in ambulation that increase risk surroundings. Put layout of the that increase risk
-Limited motion for injury call light within environment to for injury
reach and teach avoid accidents.
how to call for Items that are too
Long term: assistance; respond far from the patient Long Term:
At the end of 4 to call light may cause hazard. At the end of 4
hours of nursing immediately. hours of nursing
intervention the intervention the
client will be able 3. Avoid use of 3. If patients are client was able to:
to: restraints. restrained, they
can sustain a. Remains free of
a. Remains free of injuries, including injuries
injuries strangulation, b. Relates intent to
b. Relates intent to asphyxiation, or practice selected
practice selected head injury leading prevention
prevention with their heads to measures.
measures. get out of the bed. c. Increase
c. Increase activities if feasible
activities if feasible 4. Ask family or 4. This is to prevent
significant others to the patient from
be with the patient accidentally falling.
to prevent him or
her from
accidentally falling.
5. Place in an 5. Such
injury-prone room placements allows
that is near the regular observation
nurses station. of the patient.
Collaborative:
1. Coordinate with 1.Gait training in
physical therapist physical therapy
for strengthening has been proven to
exercises and gait effectively prevent
training to increase falls.
mobility. Contact
occupational
therapist for
assistance with
helping patients
perform with ADLs.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- NCP For Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento2 pagineNCP For Impaired Physical MobilityPrincess Averin Navarro50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan BalnkDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan BalnkKateLayaogNessuna valutazione finora
- Casilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Documento3 pagineCasilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Ynalie Casilan100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento5 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationArian May MarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento4 pagineAcute Pain NCPBea Dela Cena100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocumento3 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveAngelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 pagineActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Altered ComfortDocumento2 pagineNCP Altered ComfortMadz Tajal0% (1)
- Ate Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Documento2 pagineAte Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Kimsha ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdar NCPDocumento3 pagineFdar NCPjasper pachingelNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 pagineActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento2 pagineAcute Pain NCPCaren AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageDocumento2 pagineNCP Disturbed Body ImageDoneva Lyn MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocumento1 paginaNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalDocumento2 pagineAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalI Am SmilingNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation: VIII. Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 paginaAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation: VIII. Nursing Care PlanKriz_sakuradreamNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Modified Radical MastectomyDocumento5 pagineNCP Modified Radical MastectomyIvan Jules P. PALMARESNessuna valutazione finora
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Documento4 pagineFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 pagineNursing Care PlanJoseph Nawen Sindiong100% (1)
- Degenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINDocumento4 pagineDegenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINHermin TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocumento1 paginaNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 pagineImpaired Skin IntegrityBesael BaccolNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Areas of AssessmentDocumento10 pagine13 Areas of AssessmentNicole Anne TungolNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 pagineNCP Activity Intolerancea22hous0% (1)
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Documento4 pagineAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP LeptospirosisDocumento6 pagineNCP LeptospirosisJean Marie DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento2 pagineNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- NCP Sleep DisturbanceDocumento1 paginaNCP Sleep DisturbanceKrystel Cate DelaCruz DamianNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP 2Documento2 pagineNCP 2ampalNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Sleeping PatternDocumento5 pagineDisturbed Sleeping PatternEllenare RacionNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For InjuryDocumento1 paginaRisk For Injuryandycamille7Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Alteration in ComfortDocumento2 pagineNCP - Alteration in ComfortPatricia CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceDocumento4 pagineNCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceBAGUIO CATSNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 pagineNCP Activity IntoleranceWyen CabatbatNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageDocumento5 pagineNCP Disturbed Body ImageEricka MunsayacNessuna valutazione finora
- ImmobilityDocumento1 paginaImmobilitymicopoliNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaDocumento3 pagineAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Physical MobilityJohn Michael FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute PainDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan: Acute PainEvet VaxbmNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP 2Documento2 pagineNCP 2Neil Abraham Mendoza Lalap100% (2)
- NCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyDocumento3 pagineNCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyKyle Stephen TancioNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 pagineNCP - Activity Intolerancejanelee2824Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired SkinDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCP For Acute PainDocumento2 pagineNCP For Acute PainEmman RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- R.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Documento2 pagineR.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Karen Joy ItoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineDrug StudyKarla Karina Dela Cruz100% (1)
- NCP Bed MobilityDocumento1 paginaNCP Bed MobilityDiana Laura Lei100% (2)
- NCP-Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento3 pagineNCP-Impaired Physical MobilityRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Acute PainDocumento2 pagineTuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Acute PainSALMA M. TUANONessuna valutazione finora
- NCP PainDocumento1 paginaNCP Painsitz04Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ncp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDDocumento4 pagineNcp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDJordz PlaciNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP sLEEP DEPRIVATIONDocumento4 pagineNCP sLEEP DEPRIVATIONArianna MabungaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento3 pagineNCPeun kyung shinNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento1 paginaAcute Pain NCPJed AvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocumento3 pagineDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJoenna GaloloNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento5 pagineNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Actual EvaluationFebee GeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre NCP FatigueDocumento2 paginePre NCP Fatigueirisjabines67% (3)
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocumento3 pagineSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalNicholas TagleNessuna valutazione finora
- GRPD SomaticNCP-1Documento2 pagineGRPD SomaticNCP-1Macmac GalabacNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric DosageDocumento2 paginePediatric DosageAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Topnotch Pediatrics SuperExam PDFDocumento97 pagine11 Topnotch Pediatrics SuperExam PDFDre Valdez100% (4)
- Attitude Evaluation 1Documento1 paginaAttitude Evaluation 1Allene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedia Case ProtocolDocumento5 paginePedia Case ProtocolAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- FAM MED COVID 19 by SC Rana RojoDocumento112 pagineFAM MED COVID 19 by SC Rana RojoAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.07 (OB-CK) Second Stage of LaborDocumento9 pagine1.07 (OB-CK) Second Stage of LaborAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tickler 1 PDFDocumento8 pagineTickler 1 PDFApril Rae Obregon GarcesNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Reconstructive and Aesthetic Plastic SurgeryDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To Reconstructive and Aesthetic Plastic SurgeryAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.43 (FCM) Logic ModelsDocumento6 pagine2.43 (FCM) Logic ModelsAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast SchwartzDocumento72 pagineBreast SchwartzAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.63 Gyne Abnormal Uterine Bleeding 1Documento6 pagine1.63 Gyne Abnormal Uterine Bleeding 1Allene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The Ear: OutlineDocumento12 pagineAnatomy of The Ear: OutlineAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.27 (FCM) Strategies For COVID-19Documento9 pagine2.27 (FCM) Strategies For COVID-19Allene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- PDR Respiratory System Thorax LungsDocumento4 paginePDR Respiratory System Thorax LungsAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug InfographicsDocumento8 pagineDrug InfographicsAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Galing Pook Awards Research ResultsDocumento5 pagineThe Galing Pook Awards Research ResultsAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- PDR HISTORY TAKING PEDIA HX ClinicsDocumento11 paginePDR HISTORY TAKING PEDIA HX ClinicsAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug ScriptDocumento1 paginaDrug ScriptAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- CestodesDocumento3 pagineCestodesAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trematode SDocumento2 pagineTrematode SAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- CestodesDocumento3 pagineCestodesAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug ScriptDocumento1 paginaDrug ScriptAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento3 pagine1Allene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- French Toast Baked Omelette Breakfast Tacos Belgian Waffles Egg CasseroleDocumento7 pagineFrench Toast Baked Omelette Breakfast Tacos Belgian Waffles Egg CasseroleAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shalai Catering ServicesDocumento4 pagineShalai Catering ServicesAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trematode SDocumento2 pagineTrematode SAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Repro HistoDocumento26 pagineFemale Repro HistoAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary Endocrine Axis and Posterior Pituitary HormonesDocumento11 pagineHypothalamic-Pituitary Endocrine Axis and Posterior Pituitary HormonesAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebrum, Ventricular SystemDocumento3 pagineCerebrum, Ventricular SystemAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport of Sodium and ChlorideDocumento12 pagineTransport of Sodium and ChlorideAllene PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- z482 E3b en (3a2)Documento2 paginez482 E3b en (3a2)Gerencia General ServicesNessuna valutazione finora
- Tank Gauging TankvisionDocumento31 pagineTank Gauging Tankvisionkhangduongda3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Engineering Topics V4Documento409 pagineCivil Engineering Topics V4Ioannis MitsisNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogue: Packer SystemDocumento56 pagineCatalogue: Packer SystemChinmoyee Sharma100% (1)
- Into The Unknown 21 Doc PDFDocumento9 pagineInto The Unknown 21 Doc PDFFernando AlbuquerqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Web+Presentation+12+July+2016 EA+-+Eric+LumeDocumento57 pagineWeb+Presentation+12+July+2016 EA+-+Eric+LumetranthabinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bluforest, Inc. (OTC: BLUF) InvestigationDocumento5 pagineBluforest, Inc. (OTC: BLUF) Investigationfraudinstitute100% (1)
- M1-Safety StandardsDocumento9 pagineM1-Safety StandardscarlNessuna valutazione finora
- PDFDocumento8 paginePDFDocNessuna valutazione finora
- RE2S PE LPG CNG SPC Part 1Documento32 pagineRE2S PE LPG CNG SPC Part 1Inversiones RinocellNessuna valutazione finora
- ONGC Buyout GOI's Entire 51.11% Stake in HPCLDocumento4 pagineONGC Buyout GOI's Entire 51.11% Stake in HPCLArpan AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- +chapter 6 Binomial CoefficientsDocumento34 pagine+chapter 6 Binomial CoefficientsArash RastiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sotero 05activity EnvironmetnDocumento3 pagineSotero 05activity Environmetnbernadette soteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Macleod - 1974 - Lucian's Knowledge of TheophrastusDocumento2 pagineMacleod - 1974 - Lucian's Knowledge of TheophrastusSIMONE BLAIRNessuna valutazione finora
- Caption Sheet 4-Kailynn BDocumento4 pagineCaption Sheet 4-Kailynn Bapi-549116310Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 28: Outline: Hour 1: Displacement Current Maxwell's Equations Hour 2: Electromagnetic WavesDocumento33 pagineClass 28: Outline: Hour 1: Displacement Current Maxwell's Equations Hour 2: Electromagnetic Wavesakirank1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 FinalizedDocumento11 pagineChapter 3 Finalizedpeter vanderNessuna valutazione finora
- ELC609F12 Lec0 IntroductionDocumento16 pagineELC609F12 Lec0 IntroductionMohammed El-AdawyNessuna valutazione finora
- AnamnezaDocumento3 pagineAnamnezaTeodora StevanovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Karan AsDocumento3 pagineKaran AsHariNessuna valutazione finora
- Solomon On Sex - Avoiding Marital Disaster: February 12, 2012Documento14 pagineSolomon On Sex - Avoiding Marital Disaster: February 12, 2012baimareanNessuna valutazione finora
- BLANCHARD-The Debate Over Laissez Faire, 1880-1914Documento304 pagineBLANCHARD-The Debate Over Laissez Faire, 1880-1914fantasmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Toptica AP 1012 Laser Locking 2009 05Documento8 pagineToptica AP 1012 Laser Locking 2009 05Tushar GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ac 521 007Documento10 pagineAc 521 007JacquesNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before UseDocumento9 pagineSmart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before Useeliaszarmi100% (3)
- Additive Manufacturing Objective QuestionsDocumento7 pagineAdditive Manufacturing Objective Questionsmohammad shaqib100% (4)
- Tempera 2018 AbstractsDocumento45 pagineTempera 2018 AbstractsGerard Emmanuel KamdemNessuna valutazione finora
- Cateora2ce IM Ch012Documento9 pagineCateora2ce IM Ch012Priya ShiniNessuna valutazione finora
- An Appraisal of The Literature On Centric Relation. Part II: ReviewDocumento11 pagineAn Appraisal of The Literature On Centric Relation. Part II: ReviewManjulika TysgiNessuna valutazione finora
- Output Process Input: Conceptual FrameworkDocumento4 pagineOutput Process Input: Conceptual FrameworkCHRISTINE DIZON SALVADORNessuna valutazione finora