Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
LTE Radio Protocol Stack
Caricato da
zakiCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
LTE Radio Protocol Stack
Caricato da
zakiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
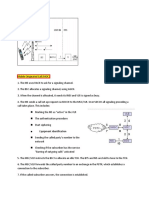
Paging Channel: Associated with the PCCH logical TM is the simplest RLC mode.
TM stands for
The Physical Broadcast Channel carries the Master
UE eNodeB S-GW P-GW
LTE Radio
Information Block (MIB). It consists of a limited number
Physical Random Access Channel: This channel is used to channel. It is mapped to dynamically allocated physical 'Transparent Mode'. The term 'Transparent' may have
PBCH of the most frequently transmitted parameters essential for
PRACH carry random access preambles used for initiation of PCH resources, and is required for broadcast over the entire cell TM many different meaning. In this case, it would mean 'the
initial access to the cell. The PBCH is designed for early
random access procedure. coverage area. It is transmitted on the Physical Downlink contents goes through this layer without any
detection by the UE, and cell-wide coverage Application
Shared Channel modification'.
Protocol Stack Paging Control Channel : A downlink channel that
transfers paging information and system information
Broadcast Channel: A downlink channel associated with
the BCCH logical channel and is used to broadcast system
Most complicated RLC type. 'AM' stands for
'Acknowledge Mode'. As it's name implies it requires
PDSCH
The Physical Downlink Shared Channel is the main
downlink data-bearing channel in LTE, used for all user
data, as well as for broadcast system information which is
Relay
GTP-U GTP-U
Relay
GTP-U GTP-U
PCCH change notifications. This channel is used for paging BCH AM ACK/NACK from the other party. It is more like TCP
when the network does not know the location cell of the
information over the entire coverage area of the cell. It has
packet in IP world, whereas RLC UM is more like UDP in
not carried on the Physical Broadcast Channel (PBCH). It
IP UDP/IP IP
a fixed transport format defined by the specifications. is also used for paging messages. UDP/IP UDP/IP UDP/IP
User Plane
UE. IP world.
Services
Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) : This control UM stands for 'Unacknowledged Mode'. 'UM' means 'it The Physical Control Format Indicator Channel is a IP Sec IP Sec IP Sec IP Sec
Prepared by channel provides system information to all mobile Downlink Shared Channel: Used for transmitting the does not require any reception response from the other downlink physical channel that carries a Control Format
Ziya Akhundov BCCH
terminals connected to the eNodeB.It allows the UE to
DL-SCH
downlink data, including both control and traffic data, and
UM
party'. 'Reception response' simply mean 'ACK' or PCFICH Indicator (CFI) which indicates the number of OFDM
retrieve cell and network configuration parameters (e.g.
PLMN code, cell identity, cell reselection parameters,
thus it is associated with both logical control and logical
traffic channels.
'NACK' from the other party. (UM mode is similar to TM
mode in that it does not require any ACK/NACK from the
symbols (i.e. normally 1, 2 or 3) used for transmission of
downlink control channel information in each sub-frame.
PDCP PDCP
etc.) required for normal operation within EUTRAN. other party).
RLC RLC L2 L2 L2 L2 L2
Physical Downlink Control Channel in LTE carries UE-
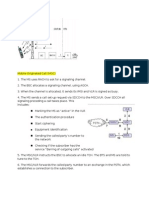
Common Control Channel: RRC signaling channel used
Both signaling radio bearers are used to transmit/receive specific scheduling assignments for DL resource
by UEs to do the initial access signaling when it is in Random Access Channel: A specific transport channel
LTE signaling messages. SRB2 is used specifically for allocation, UL grants, PRACH responses, UL power
RRC_IDLE state and wants to enter RRC_CONNECTED that is not mapped to any logical channel. It transmits PDCCH
CCCH state. The UE will send only one message (RRC RACH relatively small amounts of data for initial access or, in the SRB NAS signaling messages but if SRB2 is not at all present control commands, and common scheduling assignments MAC MAC
or established, SRB1 is used to trans/receive NAS for signaling messages (such as system information,
CONNECTION REQUEST) and case of RRC, state changes.
messages. paging, etc.).
the rest of the communication takes place on DCCH.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is the most
commonly used protocol on the Internet. The reason for PHY PHY L1 L1 L1 L1 L1
this is because TCP offers error correction. When the TCP
The Physical Hybrid ARQ Indicator Channel is a
S1-U S5/S8 SGi
protocol is used there is a "guaranteed delivery." This is Multicast Channel: Associated with MCCH and MTCH
due largely in part to a method called "flow control." Flow Dedicated Control Channel: This control channel is used logical channels for the multicast/broadcast service. It
Data Radio Bearer: to carry user data. Data radio bearer
downlink physical channel that carries the Hybrid ARQ
(HARQ) ACK/NACK information indicating whether the Uu
TCP control determines when data needs to be re-sent, and for carrying user-specific control information, e.g. for supports Multicast/Broadcast Single Frequency Network PHICH
DCCH controlling actions including power control, handover, MCH (MBSFN) transmission, which transmits the same DRB transports the packets of an EPS bearer between a UE and eNB has correctly received a transmission on the PUSCH.
stops the flow of data until previous packets are
UE eNodeB
an eNedeB. Multiple PHICHs (for different UEs) are mapped to the
MME
successfully transferred. This works because if a packet of etc.. information on the same radio resource from multiple
same set of downlink resource elements.
data is sent, a collision may occur. When this happens, the synchronized base stations to multiple UEs.
client re-requests the packet from the server until the
whole packet is complete and is identical to its original.
Dedicated Traffic Channel: The DTCH is used for user Uplink Shared Channel: The uplink counterpart of the
Physical Multicast Channel : For transmission of multicast
and broadcast information, Format is similar to the
NAS NAS
radio bearers carrying IP traffic. The eNB connects DL-SCH. It can be associated to CCCH, DCCH, and Robust Header Compression is a standardized method to
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is anther commonly used PMCH PDSCH but it is for reception by several mobiles, Sub-
Control plane
DTCH DTCHs with their associated S1-U tunnel to the SAE GW. UL-SCH DTCH logical channels. It supports H-ARQ, dynamic link ROHC compress the IP, UDP, UDP-Lite, RTP, and TCP headers
channel spacing is 7.5 kHz and symbol length is doubled,
protocol on the Internet. However, UDP is never used to of Internet packets. Relay
DTCH can be bidirectional, uplink only or downlink only. adaption, and dynamic and semi-persistent resource
send important data such as webpages, database
information, etc; UDP is commonly used for streaming
DTCH are of course point-to-point. allocation.
Modulation QPSK, 16 QAM or 64 QAM RRC RRC S1-AP S1-AP
audio and video. Streaming media such as Windows
Media audio files (.WMA) , Real Player (.RM), and others
UDP
use UDP because it offers speed! The reason UDP is
faster than TCP is because there is no form of flow control Downlink Control Information: It carries information Physical Uplink Shared Channel: This channel is used to PDCP PDCP SCTP SCTP
Multicast Control Channel: The MCCH is associated with
related to downlink/uplink scheduling assignment, carry RRC signaling messages. Uplink RRC messages are
or error correction. The data sent over the Internet is MBMS. It allows the eNB to inform UEs that want to Integrity Protection applies only to C-Plane data (C-Plane
modulation and coding scheme, and Transmit Power PUSCH carried using PUSCH. LTE PUSCH channel contain user
affected by collisions, and errors will be present. MCCH listen to broadcast or multicast service traffic about DCI Control (TPC) command, and is sent over the Physical Integrity data means RRC/NAS message, i.e DCCH data, not
information data. The PUSCH carries both user data as
Remember that UDP is only concerned with speed. This is
the main reason why streaming media is not high quality.
availability of such services and about the associated
Downlink Control Channel (PDCCH). The DCI supports
DTCH data).
well as control signal data. RLC RLC IP IP
MBMS radio bearer (point-to-multipoint) radio bearers.
10 different formats.
H-ARQ Indicator: It carries H-ARQ acknowledgment in
Physical Uplink Control Channel: This LTE channel is
MAC MAC L2 L2
response to uplink transmissions, and is sent over the
used to carry UCI. UCI can also be transported using
HI Physical Hybrid ARQ Indicator Channel (PHICH). HI = 1 Multicast Traffic Channel: The MTCH is a point-to- Control Format Indicator: It indicates how many symbols
PUSCH channel. An LTE UE can never transmits both
for a positive acknowledgment (ACK) and HI = 0 for a multipoint traffic channel for MBMS. It carries IP traffic the DCI spans in that sub-frame. It takes values CFI = 1, Cipherin Ciphering Protection applies both C-Plane and U-Plane PUCCH
negative acknowledgment (NAK). MTCH for broadcast or multicast services driven by the MBMS CFI 2, or 3, and is sent over the Physical Control Format g Data.
PUCCH and PUSCH during the same sub-frame. If UE
has application data then UCI is carried over PUSCH. If
PHY PHY L1 L1
feature. Indicator Channel (PCFICH).
UE does not have data UCI is carried over PUCCH. Uu S1-MME
Uplink Control Information: It is for measurement
indication on the downlink transmission, scheduling
CONTROL PLANE USER PLANE USER PLANE CONTROL PLANE
request of uplink, and the H-ARQ acknowledgment of
UCI downlink transmissions. The UCI can be transmitted
either on the Physical Uplink Control Channel (PUCCH)
or the Physical Uplink Shared Channel.
Mobility Management, Session Mobility Management, Session
Management, Bearer Management, Applications Applications NAS
Management, Bearer Management,
Paging Control, Security Management NAS SM GMM IP
UDP TCP TCP UDP SM GMM MM
Paging Control, Security Management
MM
Mobility Management, Configuration Mobility Management, Configuration
Management, Connection
L3 RRC
IP IP
RRC L3 Management, Connection
Management, Paging Control, Security Management, Paging Control, Security
Management, Broadcast, RRC IP IP RRC Management, Broadcast,
Measurement Configuration,
Radio Bearers SRB0 SRB1 SRB2 DRB DRB DRB DRB SRB0 SRB1 SRB2 Radio Bearers Measurement Configuration,
Measurement Reporting, Cell Measurement Reporting, Cell
Selection/Reselection Selection/Reselection
Integrity ROHC ROHC Integrity
Sequence Number Addition, Hand
In Sequence Delivery, Duplicate Packet PDCP
Ciphering Ciphering
Detection, Integrity Validation, De-
PDCP Ciphering optional optional
Ciphering
Over Data Handling, Integrity
Protection, Ciphering, Header-
ciphering, Header-Decompression Compression
RLC Mode TM TM TM UM AM UM AM UM AM TM UM AM RLC Mode
Re-Ordering, Reassembly, ARQ (for Buffer Status Report, Segment &
AM mode) RLC RLC Concatenation, ARQ (for AM
L2 L2 mode)
Logical Channels PCCH BCCH CCCH DCCH DTCH MCCH MTCH DTCH CCCH DCCH Logical Channels
Channel Mapping, De-Multiplexing,
Channel Mapping, Multiplexing,
Handling Control Elements, HARQ,
DRX MAC MAC Handling Control Elements, HARQ,
Random Access Procedure, Logical
Channel Priority, Sending BSR
Transport Channels PCH BCH DL-SCH CFI DCI HI MCH UL-SCH UCI RACH Transport Channels
HARQ,CRC, Coding, De-Scrambling,
PHY PHY HARQ,CRC, Coding, Scrambling,
De-Modulation, Measurement, L1 L1 Modulation, Measurement,
Resource Element De-Mapping, MIMO Resource Element Mapping, MIMO
Physical Channels PBCH PDSCH PCFICH PDCCH PHICH PMCH PUSCH PUCCH PRACH Physical Channels
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Netmanias.2013.08.20-LTE Identification I-UE and ME Identifiers (En) PDFDocumento15 pagineNetmanias.2013.08.20-LTE Identification I-UE and ME Identifiers (En) PDFFiras Ibrahim Al-HamdanyNessuna valutazione finora
- CSFB Guideline and Related FeaturesDocumento12 pagineCSFB Guideline and Related FeaturesSedjali Ali-MustaphaNessuna valutazione finora
- Netmanias.2013.02.15 LTE Protocol Stack UE Side (E)Documento1 paginaNetmanias.2013.02.15 LTE Protocol Stack UE Side (E)Mahendra Nath ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lte Enodeb EmulatorDocumento2 pagineLte Enodeb EmulatorSaurabh SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- S1AP View of LTE Attach & EPS Bearer Setup (2018-0326)Documento97 pagineS1AP View of LTE Attach & EPS Bearer Setup (2018-0326)paulyenNessuna valutazione finora
- NG Dcca IfdDocumento69 pagineNG Dcca IfdBluesinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Handover AnalysisDocumento29 pagineAdvanced Handover AnalysisPham Xuan ThongNessuna valutazione finora
- CSFB (Circuit Switch Fall Back) Explanation & Optimization - Our Technology PlanetDocumento6 pagineCSFB (Circuit Switch Fall Back) Explanation & Optimization - Our Technology PlanetMd Sazidur RahamanNessuna valutazione finora
- VOLTE MobilityDocumento27 pagineVOLTE MobilityHoudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Intra Lte MobiltyDocumento5 pagineIntra Lte MobiltyechakhaouiNessuna valutazione finora
- NPT 2g Parameters Ericsson r07b 07072011Documento79 pagineNPT 2g Parameters Ericsson r07b 07072011bernNessuna valutazione finora
- Netmanias.2013.12.26-EMM Procedure 1. Initial Attach - Part 1 (En) PDFDocumento14 pagineNetmanias.2013.12.26-EMM Procedure 1. Initial Attach - Part 1 (En) PDFuttamNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Call Flow in LTE - LTE Attach ProcedureDocumento3 pagineBasic Call Flow in LTE - LTE Attach ProcedureTalent & Tech Global InfotechNessuna valutazione finora
- Lte Tracking Area Update PDFDocumento3 pagineLte Tracking Area Update PDFAnonymous SuO1HHNessuna valutazione finora
- Enodeb Protocol Conformance Tester: Test Bed StructureDocumento4 pagineEnodeb Protocol Conformance Tester: Test Bed StructureRamachandra BhyravavajhalaNessuna valutazione finora
- S1AP Message Sequence ChartDocumento6 pagineS1AP Message Sequence ChartyassminbgNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Training Course - RAN17 1 Ultrafast CS Call Setup V1 03Documento33 pagine10 Training Course - RAN17 1 Ultrafast CS Call Setup V1 03shoaib.hadi7355Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 LTE Air Interface ProtocolsDocumento56 pagine3 LTE Air Interface ProtocolsCristopher TimarioNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE LBS White Paper 2012Documento16 pagineLTE LBS White Paper 2012Sandeep KadamNessuna valutazione finora
- 22 Attach FlowfffDocumento48 pagine22 Attach FlowfffDharamveer SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Feature Parameter Description: S1-Flex eRAN3.0Documento28 pagineFeature Parameter Description: S1-Flex eRAN3.0Sergio BuonomoNessuna valutazione finora
- TekelecDSR Presentation GSIFDocumento24 pagineTekelecDSR Presentation GSIFAntonio Albo MarotoNessuna valutazione finora
- 5G PPP 5G Architecture WP July 2016Documento61 pagine5G PPP 5G Architecture WP July 2016Juan Pablo MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- XCAL - DRT LTE Scanner Quick GuideDocumento13 pagineXCAL - DRT LTE Scanner Quick GuideHeymonth ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei CloudEngine 6810 Series Data Center SwitchesDocumento11 pagineHuawei CloudEngine 6810 Series Data Center Switchesolam bator100% (1)
- Lte TimerDocumento9 pagineLte TimerMohammed Babar AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Note: Best Practices For Volte TroubleshootingDocumento9 pagineApplication Note: Best Practices For Volte Troubleshootingdamru935Nessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Technology, Architecture & Air InterfaceDocumento101 pagineLTE Technology, Architecture & Air InterfaceSherinPmNessuna valutazione finora
- 2) LTE Air InterfaceDocumento76 pagine2) LTE Air Interfacegh_jazani100% (1)
- Traffica BrochureDocumento4 pagineTraffica Brochuretimk4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Content: GSM / WCDMA / LTE InterworkingDocumento68 pagineContent: GSM / WCDMA / LTE InterworkingPuujeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 27 Upc Cups Overview GuideDocumento20 pagine21 27 Upc Cups Overview GuideDjamel HAINENessuna valutazione finora
- X2 Interface - LTEDocumento41 pagineX2 Interface - LTEa2zzman100% (1)
- RNC Ps Call Drop Rate Increase After MigrationDocumento7 pagineRNC Ps Call Drop Rate Increase After MigrationIamhere IamhereNessuna valutazione finora
- Lte2 s1 FlexDocumento24 pagineLte2 s1 FlexTuan Dao0% (1)
- Location Updatev3Documento9 pagineLocation Updatev3Bisi AdebamboNessuna valutazione finora
- Protocol BroucherDocumento11 pagineProtocol Brouchermanojsingh474Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lte System ArchitectureDocumento27 pagineLte System ArchitectureVladut PirvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Aware Traffic SteeringDocumento16 pagineBusiness Aware Traffic SteeringYounesNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Q&As VOL-1Documento78 pagineLTE Q&As VOL-1Prabhat KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To TD-LTE Handover Problem AnalysisDocumento58 pagineGuide To TD-LTE Handover Problem Analysisfahadmalik89Nessuna valutazione finora
- eRAN13.0 LTE VoLTE Solution User Guide-V1.2Documento138 pagineeRAN13.0 LTE VoLTE Solution User Guide-V1.2paul paulioNessuna valutazione finora
- 9YZ054810005RKZZA Vol1 9471 Wireless Mobility Manager WMM Alarm Dictionary, WM7.0.0Documento376 pagine9YZ054810005RKZZA Vol1 9471 Wireless Mobility Manager WMM Alarm Dictionary, WM7.0.0SuswanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultra Flash CSFB 10dec2020Documento15 pagineUltra Flash CSFB 10dec2020hamadashraf301Nessuna valutazione finora
- LTE FundamentalsDocumento16 pagineLTE FundamentalsPavan Kumar Reddy ChillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Principles and O&M of The IGWB (ATCA)Documento71 pagineWorking Principles and O&M of The IGWB (ATCA)kienna100% (1)
- LTE X2 Handover MessagingDocumento13 pagineLTE X2 Handover Messagingfahmi1987Nessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Mobility Optimization-1Documento13 pagineLTE Mobility Optimization-1kamal waniNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 - Ra4133 - rl20 - Lte Rab and Nas Counters - E01Documento35 pagine06 - Ra4133 - rl20 - Lte Rab and Nas Counters - E01Teguh YuliantoNessuna valutazione finora
- IMS Basic Concepts and Network Structure-20091029-A-1.0Documento106 pagineIMS Basic Concepts and Network Structure-20091029-A-1.0Ahmed Gad100% (1)
- LTE Radio Interface Section 1Documento82 pagineLTE Radio Interface Section 1Nikan AminiNessuna valutazione finora
- Attach Call FlowDocumento8 pagineAttach Call Flowgyansingh25Nessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Basic Principle: Security LevelDocumento17 pagineLTE Basic Principle: Security LevelroniNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Basic Principle: C&Wi 售前网络规划部 C&Wi Pre-sale RNP DeptDocumento61 pagineLTE Basic Principle: C&Wi 售前网络规划部 C&Wi Pre-sale RNP DeptSwandito HaryoyudantoNessuna valutazione finora
- GSMLTE InteroperabilityDocumento34 pagineGSMLTE InteroperabilityambroserfNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Troubleshooting - PS - PDP Context Activation v0.1Documento12 paginePerformance Troubleshooting - PS - PDP Context Activation v0.1deepakNessuna valutazione finora
- Interworking 4G-3G SampleDocumento31 pagineInterworking 4G-3G SampleChee Leong100% (1)
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkDa EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- MOCDocumento3 pagineMOCzakiNessuna valutazione finora
- An Algorithm of DL Cell Throughput Based On MCS Level in LTE NetworkDocumento5 pagineAn Algorithm of DL Cell Throughput Based On MCS Level in LTE NetworkzakiNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Bsic and Its Use in GSM - TeletopixDocumento2 pagineWhat Is Bsic and Its Use in GSM - TeletopixzakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Moc MTCDocumento3 pagineMoc MTCRaju_RNO EnggNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Log-Normal Fading, Link BudgetsDocumento4 pagineLog-Normal Fading, Link BudgetszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- OFDM and Cyclic Pre X - A Hands-On Demonstration Using MatlabDocumento4 pagineOFDM and Cyclic Pre X - A Hands-On Demonstration Using MatlabzakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Long Term Evolution Simulator - A SurveyDocumento5 pagineLong Term Evolution Simulator - A SurveyzakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Peak Capacity Explained: How To Calculate It?Documento11 pagineLTE Peak Capacity Explained: How To Calculate It?zakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ofdma vs. Sc-Fdma PerformanceDocumento9 pagineOfdma vs. Sc-Fdma PerformancezakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ofdma vs. Sc-Fdma PerformanceDocumento9 pagineOfdma vs. Sc-Fdma PerformancezakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Long Term Evolution Simulator - A SurveyDocumento5 pagineLong Term Evolution Simulator - A SurveyzakiNessuna valutazione finora
- OFDM and Cyclic Pre X - A Hands-On Demonstration Using MatlabDocumento4 pagineOFDM and Cyclic Pre X - A Hands-On Demonstration Using MatlabzakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelsDocumento10 pagineLTE Coverage Network Planning and Comparison With Different Propagation ModelszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE and The Number of Simultaneously Connected UsersDocumento3 pagineLTE and The Number of Simultaneously Connected UserszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ofdma vs. Sc-Fdma PerformanceDocumento9 pagineOfdma vs. Sc-Fdma PerformancezakiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE and The Number of Simultaneously Connected UsersDocumento3 pagineLTE and The Number of Simultaneously Connected UserszakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Receiver Sensitivity / NoiseDocumento9 pagineReceiver Sensitivity / NoiseThiyagu MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Receiver Sensitivity / NoiseDocumento9 pagineReceiver Sensitivity / NoiseThiyagu MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Receiver Sensitivity / NoiseDocumento9 pagineReceiver Sensitivity / NoiseThiyagu MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshoot Switch Port and Interface ProblemsDocumento45 pagineTroubleshoot Switch Port and Interface ProblemsRichard BravoNessuna valutazione finora
- Why IP RAN Is Better Than MPLS-TPDocumento5 pagineWhy IP RAN Is Better Than MPLS-TPgo4adilNessuna valutazione finora
- BRKIPM 2001 NSF NSRDocumento94 pagineBRKIPM 2001 NSF NSRkds850Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 VlanDocumento14 pagine2.2 VlanSaurav SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- AMR WB Speech and HSPA PS Interactive RAB CombinationDocumento6 pagineAMR WB Speech and HSPA PS Interactive RAB Combinationpote100% (1)
- 5G IntroductionDocumento27 pagine5G IntroductionJoaquim PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- 3GPP TS 23.016Documento31 pagine3GPP TS 23.016santanameroNessuna valutazione finora
- CEH Port NumbersDocumento37 pagineCEH Port Numberskumusha123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Section 1 GSM Qos Monitoring: Do Not Delete This Graphic Elements in HereDocumento481 pagineSection 1 GSM Qos Monitoring: Do Not Delete This Graphic Elements in Hereemm11111111Nessuna valutazione finora
- DCC MicroprojectDocumento15 pagineDCC Microprojectmangatkumar760Nessuna valutazione finora
- STP Interview QuestionDocumento11 pagineSTP Interview QuestionAzizuddin AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- CPT250 AllTutsDocumento32 pagineCPT250 AllTutsseggy7Nessuna valutazione finora
- BR XGeniusDocumento4 pagineBR XGeniusSwapnil NageNessuna valutazione finora
- CNDocumento5 pagineCNMudit JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Jet Air, Jet Air Duo: PTMP Base StationDocumento6 pagineJet Air, Jet Air Duo: PTMP Base StationAmos GoldmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No 1Documento2 pagineAssignment No 1hamza syedNessuna valutazione finora
- Developers in ChennaiDocumento3 pagineDevelopers in ChennaiyescheenuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nokia ReportsDocumento2 pagineNokia Reportsnarendraiit2003100% (3)
- RFC 3551Documento6 pagineRFC 3551jupivipaNessuna valutazione finora
- MEF-CECP Boot Camp Survival Guide-2018Documento22 pagineMEF-CECP Boot Camp Survival Guide-2018joshua.lin.2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- BMIT2164 T3 Inter-Vlan RoutingDocumento3 pagineBMIT2164 T3 Inter-Vlan RoutingyuenNessuna valutazione finora
- Bharti Airtel'S GSM Technology: A Presentation OnDocumento21 pagineBharti Airtel'S GSM Technology: A Presentation OnVineet VidyarthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento74 pagineChapter 3Berhane KifleNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of CdmaDocumento4 pagineEvolution of CdmamonumunduriNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Transport Networks TrainingDocumento7 pagineOptical Transport Networks TrainingEhsan RohaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PortSecurity JuniperDocumento34 paginePortSecurity JunipergicochavezNessuna valutazione finora
- TOI High Availability v4Documento286 pagineTOI High Availability v4Amad LamineNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Configuration Nexus 5000 and Nexus 2000 With FEXDocumento11 pagineSample Configuration Nexus 5000 and Nexus 2000 With FEXgochorneaNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei S5300 DatasheetDocumento16 pagineHuawei S5300 DatasheetJenny MuñozNessuna valutazione finora
- 3Gpp Ts 24.501Documento1.141 pagine3Gpp Ts 24.501Darketel DarketelNessuna valutazione finora