Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
THY Ibd2 5 PDF
Caricato da
vainateyagoldarTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
THY Ibd2 5 PDF
Caricato da
vainateyagoldarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
578 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 49, NO.
3, JUNE 2002
Fig. 8. Harmonic current estimation in overmodulation during six-step. All
magnitudes expressed in per unit.
Fig. 7. Estimation of current harmonics in field coordinates using a first-order
model.
field coordinates. The harmonic voltage in field coordinates is
given by
(17)
where is the angular position of the field coordinate
system with respect to the stator coordinates.
Fig. 9. Compensated synchronous PI current control with overmodulation:
signal flow graph.
A. Harmonic Current Estimation
The harmonic current can be estimated if the estimated
becomes necessary when estimating in field coordinates. How-
harmonic voltage (17) is fed to the estimator (see Fig. 7). The
ever, the overall structure of the conventional vector control is
electromagnetic system is essentially of a second order. A
retained while a simple first-order system and coordinate trans-
magnitude-frequency plot for the complex signal flow graph
form is added. The space-vector modulation code is upgraded
expressed as single-inputsingle-output (SISO) with current
to include overmodulation.
output is shown in Fig. 7. In the same graph, a first-order ap-
proximation of the system as given by the signal flow graph is
V. COMPENSATION OF CURRENT DISTORTION
shown. For the harmonic angular frequencies ( ),
the first-order approximation is sufficient to model the system. The estimated current is used to compensate the harmonics
Hence, a simple first-order model will be used to estimate the present in the measured current before it is fed to the current
harmonic current, which is given by controller (see Fig. 9). The harmonic current error due to the
overmodulation is compensated by an estimated value and the
(18) degree of compensation is given by
(19)
where and is the leakage factor. is the nor-
malized stator inductance and is the total The current controller now operates under low noise condition.
resistance as seen from the stator. During the normal region of Under such conditions, the system is not excited by the pres-
operation, the difference . Hence, the output of the ence of harmonics and, hence, the high bandwidth of the cur-
harmonic estimator is zero. During overmodulation, a finite har- rent controller can be maintained. The results of the compen-
monic error voltage vector will exist and, hence, the estimation sated current control in overmodulation is shown in Fig. 10. The
will produce a finite nonzero output. The result of the estimator problem is severe during six-step operation (see Fig. 8), and the
is shown in Fig. 8. The current estimation is carried out in field results of compensation can be seen in Figs. 11 and 12. On the
coordinates because it simplifies the model for estimation. In other hand, in the operating range below overmodulation, no
stator coordinates, we deal with complex time-varying vector harmonic voltage is introduced by the preprocessor, hence, both
quantities, hence, the estimator model has to compensate for the estimated harmonic current and the harmonic current
the phase delay introduced. This complicates the estimator error are zero. Thus, the scheme is active continuously in
structure. As a tradeoff, additional coordinate transform the complete range of operation. The scheme, therefore, makes
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Algorithm 4 Procedure Next - Gen - GA Input The Current Population Output The Next Population While SNDocumento1 paginaAlgorithm 4 Procedure Next - Gen - GA Input The Current Population Output The Next Population While SNvainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Min - Util, Ce Is Not An HUI. The TU of T T TWU (Ce) TU (T: Tid T T T T T T T T T TDocumento1 paginaMin - Util, Ce Is Not An HUI. The TU of T T TWU (Ce) TU (T: Tid T T T T T T T T T TvainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- C. Illustrated ExampleDocumento5 pagineC. Illustrated ExamplevainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1, If 0, Otherwise : Iii. The Proposed FrameworkDocumento1 pagina1, If 0, Otherwise : Iii. The Proposed FrameworkvainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- K-Itemset. Let D (T: Ux uXTDocumento1 paginaK-Itemset. Let D (T: Ux uXTvainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Proc. POWERCON 7, 1980, Pp. E3-1-E3-15.: OnclusionDocumento1 paginaProc. POWERCON 7, 1980, Pp. E3-1-E3-15.: OnclusionvainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Steady State Genetic Algorithms Can Hillclimb Faster Than Mutation-Only Evolutionary AlgorithmsDocumento14 pagineStandard Steady State Genetic Algorithms Can Hillclimb Faster Than Mutation-Only Evolutionary AlgorithmsvainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Binder2 5Documento1 paginaBinder2 5vainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.4li + Sno - 8.4li + Sno, - : A Reasonable Correlation Between The Calculated andDocumento1 pagina6.4li + Sno - 8.4li + Sno, - : A Reasonable Correlation Between The Calculated andvainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lo:an1jj: II II Lilt IIDocumento1 paginaLo:an1jj: II II Lilt IIvainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
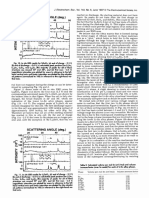
- Scattering Angle (Deg.) Scattering Angle (Deg.)Documento1 paginaScattering Angle (Deg.) Scattering Angle (Deg.)vainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- i1T5u20L.3: Scattering Angle (Deg.)Documento1 paginai1T5u20L.3: Scattering Angle (Deg.)vainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
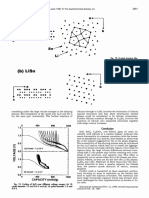
- S - 5 S - SS - : (A) Li2Sn5Documento1 paginaS - 5 S - SS - : (A) Li2Sn5vainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fig. 5. Double-Sided Switching Pattern in A Cycle Period: Casadei Et Al.: Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies 375Documento1 paginaFig. 5. Double-Sided Switching Pattern in A Cycle Period: Casadei Et Al.: Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies 375vainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fig. 2. Double-Sided Switching Pattern in A Cycle PeriodDocumento1 paginaFig. 2. Double-Sided Switching Pattern in A Cycle PeriodvainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Casadei Et Al.: Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies 373: A. SVM TechniqueDocumento1 paginaCasadei Et Al.: Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies 373: A. SVM TechniquevainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fig. 1. Basic Scheme of Matrix Converters.: Casadei Et Al.: Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies 371Documento1 paginaFig. 1. Basic Scheme of Matrix Converters.: Casadei Et Al.: Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies 371vainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies: A New General Approach Based On Space-Vector Representation of The Switch StateDocumento1 paginaMatrix Converter Modulation Strategies: A New General Approach Based On Space-Vector Representation of The Switch StatevainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Binder1 40Documento1 paginaBinder1 40vainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Matrix Converter Modulation Strategies: A New General Approach Based On Space-Vector Representation of The Switch StateDocumento1 paginaMatrix Converter Modulation Strategies: A New General Approach Based On Space-Vector Representation of The Switch StatevainateyagoldarNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Chapter - 17 Advent of Modern Physics PDFDocumento8 pagineChapter - 17 Advent of Modern Physics PDFsingoj.bhargava charyNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Drilling Fluids NewDocumento74 pagineIntro To Drilling Fluids NewSaul Pimentel100% (2)
- HT3 - Unsteady State Heat Transfer - F.PPTX (Lipika Mam)Documento13 pagineHT3 - Unsteady State Heat Transfer - F.PPTX (Lipika Mam)Clash With KAINessuna valutazione finora
- ENERGY CHANGEs IN CHEMICAL REACTIONsDocumento20 pagineENERGY CHANGEs IN CHEMICAL REACTIONsKristan RialaNessuna valutazione finora
- Merida FullProf A PDFDocumento24 pagineMerida FullProf A PDFAhmad AwadallahNessuna valutazione finora
- Dosya 6Documento10 pagineDosya 6Mehmet ÇobanNessuna valutazione finora
- E Electric Circuit PDFDocumento44 pagineE Electric Circuit PDFPam G.Nessuna valutazione finora
- ESafetyRegulations enDocumento179 pagineESafetyRegulations enmurugan2002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Process Control and Instrumentation: B. Tech. Seventh Semester (Chemical Engineering) (C.B.S.)Documento2 pagineProcess Control and Instrumentation: B. Tech. Seventh Semester (Chemical Engineering) (C.B.S.)artiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11. A Sling Psychrometer and Relative Humidity: A Structured-Inquiry ActivityDocumento4 pagineChapter 11. A Sling Psychrometer and Relative Humidity: A Structured-Inquiry Activityks aksNessuna valutazione finora
- Susol MCCB ManualDocumento140 pagineSusol MCCB ManualFakhr-e-AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- ASHRAE Self Contamination CalculationDocumento4 pagineASHRAE Self Contamination Calculationsiddique27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Biophotonics PDFDocumento2 pagineIntroduction To Biophotonics PDFDebashish PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Task 3 - Will ColeyDocumento20 pagineTask 3 - Will ColeyJose Daniel Ochoa MoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmission-Line FiltersDocumento6 pagineTransmission-Line FiltersgongsengNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas 1 Advanced CrystallographyDocumento7 pagineTugas 1 Advanced CrystallographyMuhammad Hisyam FMIPANessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report Phy 3Documento4 pagineLab Report Phy 3Eri SkcNessuna valutazione finora
- Reynolds Transport TheoremDocumento2 pagineReynolds Transport TheoremNati FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Mech Eng HeDocumento12 pagineMech Eng HeAtanasio PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Operation and Maintenance of A Substation-Libre PDFDocumento60 pagineOperation and Maintenance of A Substation-Libre PDFShareef KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Analysis 1011Documento129 paginePlastic Analysis 1011F Azam Khan Ayon100% (1)
- CMG 100 New SyllabusDocumento3 pagineCMG 100 New SyllabusSakib NehalNessuna valutazione finora
- SENIOR TWO PhysicsDocumento7 pagineSENIOR TWO PhysicsNdawula Isaac100% (1)
- Eddy Current Losses TurowskiDocumento6 pagineEddy Current Losses TurowskiHafsa IkramNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Tool Structures PDFDocumento10 pagineMachine Tool Structures PDFMohan Nanjan S50% (2)
- ArchimedesDocumento5 pagineArchimedesvision100% (2)
- Skema Kertas 2 KimiaDocumento9 pagineSkema Kertas 2 KimiaariesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report Cell Phone EnergyDocumento7 pagineLab Report Cell Phone EnergysmurfyblueberryNessuna valutazione finora
- UPMT 2015 BrochureDocumento49 pagineUPMT 2015 BrochureMota ChashmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Assessed Homework MsDocumento3 pagine1.1 Assessed Homework MsDril LiaNessuna valutazione finora