Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Asignment Chapter-1 PDF
Caricato da
Susanta Kumar RoutTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Asignment Chapter-1 PDF
Caricato da
Susanta Kumar RoutCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Operational Amplifier Fundamentals (Chapter-1)
All the symbols used in the questions represent conventional meaning as per prescribed text book.
(i.e. Design with Operational Amplifiers and Analog Integrated Circuits, by S. FRANCO)
1. In the design of function generators the need arises to offset as well as amplify a given
voltage to obtain a voltage of the type , where is the desired
amount of offset. An offsetting amplifier can be implemented with a summing
amplifier in which one of the inputs is and the other is either or , the
regulated supply voltages used to power the op amp. Using standard 5% resistances,
design a circuit such that
2. Using just one op amp powered from 12-V regulated supplies, design a circuit to
yield (a) ; (b) .
3. Design a circuit such that and . Here and
represents the input voltage applied at the inverting and non-inverting terminal of an
op amp. Similarly and are known as the internal resistance developed
corresponding terminal. The output voltage is defined as .
4. (a) Design a noninverting amplifier whose gain is variable over the range
by using a potentiometer.
(b) Repeat the steps of (a) to get a variable gain for . (Hint:
You need an input voltage divider to achieve )
5. (a) Design an inverting amplifier whose gain is variable over the range
by means of a pot.
(b) Repeat the steps of (a) to get a variable gain for . (Hint:
To prevent A reaching zero, you must use a suitable resistor in series with the pot)
6. (a) Using standard 5% resistances in the kilo-ohm range, design a circuit to yield
(b) If and , find for .
7. Using standard 5% resistances, design a circuit to yield
.
8. Using standard 5% resistances, design a circuit to provide (a)
(b) , where is variable over the range by means
of a pot. (Hint: Connect the pot between the 15 V supplies and use the wiper
voltage as one of the inputs to your circuit.)
9. Design a four-input op amp amplifier such that it yields an output
. Use minimum number of resistors during the design process.
Operational Amplifier Fundamentals (Chapter-1)
10. Design a two-input, two-output circuit that yields the sum and the difference of its
inputs: and . Try minimizing the component count
during the design.
11. In the traditional op amp differentiator circuit the values of different parameters are:
and . The input signal is a periodic time varying signal
alternating between 0 V and 2 V with a frequency of 100 Hz. Sketch and label
and if input is a (a) sine wave (b) triangular wave.
12. In the op amp integrator circuit, and . Sketch and label
and if
(a) and
(b) [ ] and
where is the unit step function.
13. Design an amplifier having closed loop gain A of 102 V/V with accuracy of 0.1% i.e.
. All you have available are amplifier stages with
each. Your amplifier can be implemented using a cascade of basic
stages, each employing suitable negative feedback circuit. What is the minimum
number of stages required? What is the of each stage?
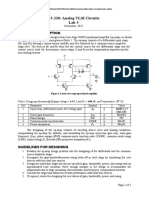
14. Find the ideal closed loop gain Aideal for the circuit given in Figure 1. Here all
resistances are considered equal.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lab 3 Spring 2020 LTSpice Edition-1Documento6 pagineLab 3 Spring 2020 LTSpice Edition-1dadNessuna valutazione finora
- Sol ELCT 371 Homework2 Sp14Documento5 pagineSol ELCT 371 Homework2 Sp14DrÖzkan Ahmed Atar100% (1)
- Full Wave Bridge Peak RectifierDocumento4 pagineFull Wave Bridge Peak RectifierMuhammad TehreemNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Objective QuestionsDocumento5 pagineUnit 4 Objective QuestionsRaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Cairo University Electronics Course Chapter on Operational AmplifiersDocumento16 pagineCairo University Electronics Course Chapter on Operational AmplifiersMerna AtefNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements of Electronics Engineering Question Bank Unit - 1Documento5 pagineElements of Electronics Engineering Question Bank Unit - 1rahul vadhyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 9Documento5 pagineLab 9gratz_redobleNessuna valutazione finora
- OpAmp DesignDocumento3 pagineOpAmp DesignSOHAN DEBNATHNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and analyze a non-inverting op-amp circuit with gain of 10Documento7 pagineDesign and analyze a non-inverting op-amp circuit with gain of 10Mandeep KaloniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Title: Op-Amp As Basic Comparator. ObjectivesDocumento3 pagineTitle: Op-Amp As Basic Comparator. ObjectivesJaideep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Purpose: Lab 4 BJT AmplifiersDocumento3 paginePurpose: Lab 4 BJT AmplifiersEstéfano GómezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 9 Operational Amplifier Applications I: PurposeDocumento4 pagineLab 9 Operational Amplifier Applications I: PurposenotarajordanNessuna valutazione finora
- Updated Electronics Module 1 Question BankDocumento3 pagineUpdated Electronics Module 1 Question Bankblehbo100% (1)
- Op-Amps: Experiment Guide: Part 1: Noninverting Amplifier (A) DC MeasurementsDocumento4 pagineOp-Amps: Experiment Guide: Part 1: Noninverting Amplifier (A) DC MeasurementsRohini PalanisamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Op Amp Circuits GuideDocumento11 pagineOp Amp Circuits Guidelibrian_30005821Nessuna valutazione finora
- Silicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationDocumento21 pagineSilicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationMangaiyarkarasi VengatachalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Sinusoidal AmplifierDocumento25 pagineSinusoidal AmplifierVandhana PramodhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lic QBDocumento17 pagineLic QBsujaganesan2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- LM358 Op AmpDocumento7 pagineLM358 Op AmpRuang OtomasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Term Paper: "Analog Circuits and Linear Ic'S"Documento17 pagineTerm Paper: "Analog Circuits and Linear Ic'S"Deep Chand SinglaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Op-Amps Student TutorialDocumento12 pagine01 Op-Amps Student TutorialniomariNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 4 More Applications of The Op-Amp: Objective: Parts ListDocumento3 pagineExperiment 4 More Applications of The Op-Amp: Objective: Parts Listahmed shahNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Op-Amp CircuitsDocumento12 pagineBasic Op-Amp CircuitsRoxana100% (1)
- Linear Integrated CircuitsDocumento15 pagineLinear Integrated CircuitsAISWARYA MNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 - Differential AmplifiersDocumento36 pagine8 - Differential AmplifiersSainyNessuna valutazione finora
- Weign Bridge OscillatorDocumento4 pagineWeign Bridge Oscillatormanojkumar9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiDocumento28 pagineLaboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiAtul SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Op-amp ac amplifiers and signal processing circuitsDocumento14 pagineOp-amp ac amplifiers and signal processing circuitssan86jay36Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Brief and GuidanceDocumento3 pagineAssignment Brief and GuidancekamranNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Integrated Circuits Question BankDocumento3 pagineLinear Integrated Circuits Question BankBhonandh Sai Kandru100% (1)
- EEEB113 Circuit Analysis I: Operational AmplifiersDocumento39 pagineEEEB113 Circuit Analysis I: Operational AmplifiersMuhd RzwanNessuna valutazione finora
- OperationalAmplifiersAndLinearICs 3EDocumento6 pagineOperationalAmplifiersAndLinearICs 3ELakshita SejraNessuna valutazione finora
- All-in-One Op-Amp Laboratory Kit GuideDocumento44 pagineAll-in-One Op-Amp Laboratory Kit GuideQodor MubarakNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsDocumento13 pagineInverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsBereket TsegayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt. No. 2 - Basic Operational Amplifier Circuit PDFDocumento2 pagineExpt. No. 2 - Basic Operational Amplifier Circuit PDFPradeep DiwakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt 05 - Integrated CE AmplifierDocumento2 pagineExpt 05 - Integrated CE AmplifierSidharth SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- AIC LAB Manual - Cycle 1Documento30 pagineAIC LAB Manual - Cycle 1Dinesh GaikotiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab 3 - Operational AmplifierDocumento90 pagineBab 3 - Operational AmplifierAryu MitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise On Analog Circuits: PHYS 331: Junior Physics Laboratory IDocumento6 pagineExercise On Analog Circuits: PHYS 331: Junior Physics Laboratory Iviso167Nessuna valutazione finora
- AC Characteristics of Operational AmplifiersDocumento8 pagineAC Characteristics of Operational Amplifiersmahesh babuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1-Bjt AmplifierDocumento8 pagineLab 1-Bjt Amplifierhasnain3257100% (1)
- ch5-2 1Documento63 paginech5-2 1avishek aviNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear IC Circuits & Op-Amp Applications ExplainedDocumento2 pagineLinear IC Circuits & Op-Amp Applications Explainedspock773Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bubba OscillatorDocumento7 pagineBubba OscillatorUmairRashidNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 101 - Assignment - 4Documento3 pagineEE 101 - Assignment - 4Harsh ChandakNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec6 - DC MachinesDocumento17 pagineLec6 - DC MachinesjunryNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1 Operational AmplifiersDocumento12 pagineLab 1 Operational AmplifiersChris BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- CBCC Amp 2Documento5 pagineCBCC Amp 2sru_1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adic LabDocumento43 pagineAdic LabSamuel Gill ChristinNessuna valutazione finora
- OpAmp Golden RulesDocumento8 pagineOpAmp Golden RulesChai Min HiungNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics Engineering Chapter 4Documento16 pagineBasic Electronics Engineering Chapter 4HabHabNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices and Circuits (EME-306) Lab 1: ObjectiveDocumento7 pagineElectronic Devices and Circuits (EME-306) Lab 1: ObjectiveAhmed SayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 6Documento10 pagineLab 6willstamp2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2Documento11 pagineWein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2krishna goggiNessuna valutazione finora
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: June 2016 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsDocumento4 pagineBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: June 2016 Semester End Make Up Examinationskoushik bhatNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Supply Design for EE 310Documento11 paginePower Supply Design for EE 310Praharsh VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Viva Questions For "Analog Electronics"Documento24 pagineModel Viva Questions For "Analog Electronics"profmns100% (1)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignDa EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorDa Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- SLR WorkshopDocumento1 paginaSLR WorkshopSusanta Kumar RoutNessuna valutazione finora
- Resistors and Capacitors in HW LabDocumento1 paginaResistors and Capacitors in HW LabSusanta Kumar RoutNessuna valutazione finora
- MeasurementsandControlSystemLab EE0311Documento70 pagineMeasurementsandControlSystemLab EE0311Arijeet MondalNessuna valutazione finora
- IKU Electrical Measurement Lab Experiment 1 Errors and StatisticsDocumento70 pagineIKU Electrical Measurement Lab Experiment 1 Errors and StatisticsSusanta Kumar Rout100% (1)
- Tutorial - 1: Questions On Electronic Devices and Circuits With SolutionsDocumento1 paginaTutorial - 1: Questions On Electronic Devices and Circuits With SolutionsSusanta Kumar RoutNessuna valutazione finora
- GateDocumento5 pagineGateSusanta Kumar RoutNessuna valutazione finora
- GateDocumento5 pagineGateSusanta Kumar RoutNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 4 Power ElectronicsDocumento16 pagineTutorial 4 Power ElectronicsFerhat Gürer100% (1)
- Const. K HP FilterDocumento14 pagineConst. K HP FilterRavi KantNessuna valutazione finora
- Preview of "X-4046 VCO"Documento7 paginePreview of "X-4046 VCO"Stephen ScuttNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuous-Time Common-Mode Feedback For High-Speed Switched-Capacitor Networks. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40 (8), 1610-1617Documento9 pagineContinuous-Time Common-Mode Feedback For High-Speed Switched-Capacitor Networks. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40 (8), 1610-1617LaurMateiNessuna valutazione finora
- TL431 Programmable Precision References: Features TO-92 Pin Arrangement DIP-8Documento9 pagineTL431 Programmable Precision References: Features TO-92 Pin Arrangement DIP-8Arturo GilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Resources Hobby ProjectsDocumento3 pagineElectronic Resources Hobby ProjectsĐường Khánh Sơn100% (2)
- Registers and Counters Design in VerilogDocumento65 pagineRegisters and Counters Design in VerilogPurushothama ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Op To CouplerDocumento5 pagineOp To CouplersamponNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-5 Goals Chapter 4 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationDocumento9 pagineChapter-5 Goals Chapter 4 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8-Differential and Multistage AmplifiersDocumento85 pagineChapter 8-Differential and Multistage Amplifiersf94106070Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lica LabDocumento56 pagineLica LabShivakumar goudNessuna valutazione finora
- GaN Sequencing CircuitDocumento5 pagineGaN Sequencing Circuitbharathi83Nessuna valutazione finora
- NTE1830 & NTE1831 Integrated Circuit Dual Audio Power Amplifier, 5.8W (19W BTL)Documento3 pagineNTE1830 & NTE1831 Integrated Circuit Dual Audio Power Amplifier, 5.8W (19W BTL)alex smuck kamusNessuna valutazione finora
- Reverse Polarity Circuit ExampleDocumento2 pagineReverse Polarity Circuit ExampleClifford LambertNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistemet Elektronike - Ciftimi NegativDocumento5 pagineSistemet Elektronike - Ciftimi NegativINGNessuna valutazione finora
- DIB - Week 12 - FilterDocumento46 pagineDIB - Week 12 - FilterIbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Technological Studies: Applied Electronics (AH) Sequential Logic DevicesDocumento116 pagineTechnological Studies: Applied Electronics (AH) Sequential Logic DevicesPham PunNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5 - Combinational Logic-Adders and SubtractorsDocumento11 pagineLab 5 - Combinational Logic-Adders and SubtractorsAngelicaNessuna valutazione finora
- AIC Practical FileDocumento50 pagineAIC Practical FileSAKSHI ANessuna valutazione finora
- Using Overture Design GuideDocumento5 pagineUsing Overture Design Guideeleceng1979Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5 BPF, BRF1Documento7 pagine5 BPF, BRF1anandhmc100% (1)
- Using The ADC0808/ ADC0809 8-Bit MP Compatible A/D Converters With 8-Channel Analog MultiplexerDocumento16 pagineUsing The ADC0808/ ADC0809 8-Bit MP Compatible A/D Converters With 8-Channel Analog MultiplexerSantiago SerranoNessuna valutazione finora
- SchematicDocumento1 paginaSchematicHồ Minh HớiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 9 Common Emitter Amplifier: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocumento7 pagineLab 9 Common Emitter Amplifier: Department of Electrical EngineeringKainat KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- TOP22XDocumento20 pagineTOP22XNal FivefivetwooneNessuna valutazione finora
- Operational Amplifier Circuit AnalysisDocumento84 pagineOperational Amplifier Circuit Analysisvivekroy2991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fairchild Analog CRDocumento12 pagineFairchild Analog CRjosetantonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Module Descriptor For Digital ElectronicsDocumento4 pagineModule Descriptor For Digital ElectronicsTashi DendupNessuna valutazione finora
- 74HC4050Documento8 pagine74HC4050Thai Khang VanNessuna valutazione finora
- QuestionDocumento80 pagineQuestionRodalie Vale CruzNessuna valutazione finora