Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Icd10 Congestive Heart Failure
Caricato da
rizkaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Icd10 Congestive Heart Failure
Caricato da
rizkaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE (CHF)
Providers guide to diagnose and code CHF
Congestive Heart Failure is a chronic complex clinical syndrome which prevents filling or emptying of blood from the heart. CHF is
caused by either a structural (valvular or congenital) and/or a dysfunctional (myocardial infarction) anomaly. The most frequently
observed clinical manifestations include shortness of breath, edema and weight gain. Of those that are diagnosed about half of the
patients will die within five years from their initial date of diagnosis.
The hearts function is measured based upon a percentage, The diagnosis of CHF is progressive, which requires chronic
also known as the ejection fraction (EF). The EF is defined as disease management. The stages of disease progression are
the fraction of blood that is pumped out of the heart with each as follows:
heartbeat from the left side of the heart. The EF plays a primary
Stage A At high risk for CHF but without structural heart
role in the diagnosis of CHF. A normal EF is classified as above
disease or symptoms of CHF
50%. Imaging studies such as an echocardiogram, cardiac MRI
Stage B Structural heart disease but without signs or
or a nuclear cardiac scan can estimate the EF.
symptoms of CHF
Stage C Structural heart disease with prior or current
Type of heart failure EF Etiology symptoms of CHF
Stage D Refractory CHF requiring specialized
Diastolic (HFpEF) Normal EF Hypertension
interventions.
stiff heart
The therapeutic options for CHF include medication and
Systolic (HFrEF) < 50% Related to ischemic disease device interventions. Medications such as beta blockers,
flaccid heart such as coronary disease; Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-i), Angiotensin
or non-ischemic disease receptor blockers (ARBs), diuretics are used in both diastolic
such as myocarditis and systolic heart failure patients. Device interventions such
as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) and implantable
Left sided Variable Variable cardiac defibrillators (ICD) are used to either improve CHF
Right sided (a result of Typically Sleep apnea, Hypertension symptoms or prevent sudden cardiac death.
pulmonary hypertension), also normal EF
From a wellness standpoint, patients with CHF should be
known as Cor Pulmonale re-evaluated every 30 to 90 days. At every visit, the patient
should be:
Generally, the evaluation of CHF includes:
Educated to weigh daily; data to be recorded and shared
History intake paying particular attention to the risk factors Encouraged to exercise daily
of the disease Told to adhere to a salt restricted diet of no more than three
Physical examination grams of salt daily
Objective data such as: chest film, echocardiogram, cardiac Informed to ingest no more than three liters of fluid
MRI and lab work namely a Brain Naturetic Peptide (BNP). Educated that the use of non-steroidal medications
(NSAIDs) can lead to fluid retention and should be avoided
The severity of CHF is classified through clinical symptoms Encouraged to obtain preventive vaccines.
along with the New York Heart Association (NYHA)
classification system: Documentation and coding tips
Provide clear and concise documentation
Class I Symptoms of CHF only at activity levels that would Describe the type of CHF as systolic and/or diastolic
limit normal individuals Anatomically relate the CHF as left or right side
Class II Symptoms of CHF with ordinary exertion Note the stability of the CHF presentation as being acute
Class III Symptoms of CHF with less than ordinary exertion or chronic
Class IV Symptoms of CHF at rest. If known, link CHF to other associated conditions, i.e.
Hypertension (HTN) & Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
When making a diagnosis, also provide a treatment plan
Remember that CHF is a targeted, monitored outcome for
HFpEF = CHF with preserved EF the Hospital Readmission Reduction Program as part of the
Affordable Care Act
HFrEF = CHF with reduced EF For CHF there was no change in the code specificity from
GDMT = Guideline determined medical therapy I9 to I10
Consider with every clinical encounter:
HRQOL = Health related quality of life Verify patient name and date of birth
MCS = Mechanical circulatory support Include date of service
Include provider name, credentials and signature
AF = Atrial fibrillation A (-) dash is used instead of (x), which indicates the need for
additional code characters
Non-specific codes will be rejected in claims
There is no need to code hypertension as malignant, benign,
or unspecified
Use additional codes to identify stage of CKD.
Heart disease must be linked to HTN by use of linkage terms
such as: CHF secondary to HTN
All Cigna products and services are provided exclusively by or through operating subsidiaries
of Cigna Corporation. The Cigna name, logos, and other Cigna marks are owned by Cigna
Intellectual Property, Inc. 2015 Cigna INT_14_30779 06282015
A summary treatment guide for the clinician reprinted with permission for non-commercial use*
At risk for heart failure Heart failure
Stage A Stage B Stage C Stage D
At high risk for HF but without Structural heart disease but Structural heart disease with prior or current symptoms of HF Refractory HF
structural heart disease without signs or symptoms of HF
Patients with: Patients with:
or symptoms of HF Patients with: Known structural heart disease and Marked HF symptoms at rest
Patients with: Previous MI HF signs and symptoms Recurrent hospitalizations
HTN LV remodeling including despite GDMT
Atherosclerotic disease LVH and low EF
DM Asymptomatic
Obesity valvular disease
Metabolic syndrome
Or Patients
Structural heart
Using cardiotoxins disease Development of Refractory symptoms of HF
With family history of symptoms of HF at rest, despite GDMT
cardiomyopathy
HFpEF HFrEF
Therapy Therapy Therapy Therapy Therapy
Goals Goals Goals Goals Goals
Heart healthy lifestyle Prevent HF symptoms Control symptoms Control symptoms Patient education Control symptoms
Prevent vascular, Prevent further cardiac Improve HRQOL Prevent hospitalization Prevent mortality Improve HRQOL
coronary disease remodeling Prevent hospitalization Drugs for routine use Reduce hospital readmissions
Prevent LV structural Drugs Prevent mortality Diuretics for fluid retention Establish patients
abnormalities Strategies Aldosterone antagonists end-of life goals
ACEI or ARB as appropriate
Drugs Beta blockers as appropriate Identification of ACEI or ARB Beta blockers Options
ACEI or ARB in appropriate In selected comorbidities Drugs for use in Advanced care measures
patients for vascular patients Treatment selected patients Heart transplant
disease or DM Hydralazine/isosorbide dinitrate Chronic inotropes
ICD Diuresis to relieve
Statins as appropriate ACEI and ARB Digitalis Temporary or permanent MCS
Revascularization or valvular symptoms of congestion
surgery as appropriate Follow guideline driven In selected patients Experimental surgery or drugs
indications for comorbidities, CRT ICD Palliative care and hospice
e.g., HTN, AF, CAD, DM Revascularization or valvular ICD deactivation
surgery as appropriate
ICD
10-CM ICD-10-CM description Definition/tips
codes
I50.1 Left ventricular failure
I50.2 Systolic (congestive) heart failure
(-) Add 5th character:
I50.3 Diastolic (congestive) heart failure 0=unspecified
Combined systolic (congestive) and iastolic 1=acute
I50.4 2=chronic
(congestive) heart failure
3=acute on chronic
I50.9 Heart failure, unspecified
I11.0 Hypertensive heart disease w/heart failure Use additional code to identify type of heart failure (I50.-)
I11.9 Hypertensive heart disease w/o heart failure
Hypertensive heart and CKD Use additional code to identify type of heart failure (I50.-)
I13.0 w/heart failure and stage 1-stage 4 CKD,
or unspecified CKD Use additional code to identify stage of CKD (N18.1-N18.4, N18.9)
Hypertensive heart and CKD
I13.10 w/o heart failure, w/stage 1 stage 4 CKD, Use additional code to identify stage of CKD (N18.1-N18.4, N18.9)
or unspecified CKD
Hypertensive heart and CKD
I13.11 w/o heart failure, w/stage 5 CKD, or Use additional code to identify stage of CKD (N18.5, N18.6)
end stage renal disease
Hypertensive heart and CKD Use additional code to identify type of heart failure (I50.-)
I13.2 w/heart failure, w/stage 5 CKD, or
Use additional code to identify stage of CKD (N18.5, N18.6)
end stage renal disease
*Hunt, SA, Abraham, WT, Chin, MH, et.al; 2009 Focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2005 guidelines for the diagnosis and management of heart failure in adults: a report of the American College
of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. JACC. 2009; 53(15): e1-e90.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Normal Hemodynamic Parameters and Laboratory Values PDFDocumento3 pagineNormal Hemodynamic Parameters and Laboratory Values PDFKenNiyaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Fun Facts About ICD-10 HandoutDocumento7 pagineFun Facts About ICD-10 HandoutDhsc01Nessuna valutazione finora
- TEE in Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento249 pagineTEE in Congenital Heart DiseaseAdriana VasilicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardio - ECGDocumento13 pagineCardio - ECGSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNessuna valutazione finora
- Sician Advisor's Guide To Clinical Documentation Improvem: Phy EntDocumento28 pagineSician Advisor's Guide To Clinical Documentation Improvem: Phy EntBudi YunantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy 2nd-U-1 CVSDocumento121 pagineAnatomy 2nd-U-1 CVSsinte beyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal AssessmentDocumento44 pagineAbdominal Assessmentdbryant010191% (11)
- Acute Stroke ProtocolDocumento3 pagineAcute Stroke ProtocolKarissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Risk of Complications at Femoral Vascular Access Sites in Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocumento16 pagineManaging Risk of Complications at Femoral Vascular Access Sites in Percutaneous Coronary InterventionydtrgnNessuna valutazione finora
- Redbook - ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA PDFDocumento323 pagineRedbook - ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA PDFrizka100% (1)
- Sinus ArrhythmiaDocumento6 pagineSinus ArrhythmiaVincent Maralit MaterialNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional Nursing ResumeDocumento5 pagineProfessional Nursing Resumeapi-556406464Nessuna valutazione finora
- ACC/AHA STEMI GuidelinesDocumento94 pagineACC/AHA STEMI GuidelinesDika DekokNessuna valutazione finora
- STEMI Guidline 23.11.2022Documento60 pagineSTEMI Guidline 23.11.2022NATARAJAN RAJENDRANNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting Without Persistent ST-segment ElevationDocumento32 pagineManagement of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting Without Persistent ST-segment ElevationLiviuNessuna valutazione finora
- Wound Care Guidelines SummaryDocumento44 pagineWound Care Guidelines SummaryrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Practice ProtocolsDocumento46 pagineBest Practice ProtocolsRaigheil LayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter38 Assessment and Management of Patients With Rheumatic DisordersDocumento38 pagineChapter38 Assessment and Management of Patients With Rheumatic Disordersjericho dinglasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Penetrating Abdominal TraumaDocumento67 paginePenetrating Abdominal TraumarizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Biomarkers PDFDocumento5 pagineCardiac Biomarkers PDFSaraswati Wulandari HartonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 HTDocumento56 pagineChapter 5 HTtesfamichael mengistu100% (1)
- HFandVADRoleDocumento34 pagineHFandVADRoleJohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard 2.1: The Governing Body Leads The Organisation in Its Commitment To Improving Performance and Ensures The Effective Management of Corporate and Clinical RisksDocumento17 pagineStandard 2.1: The Governing Body Leads The Organisation in Its Commitment To Improving Performance and Ensures The Effective Management of Corporate and Clinical RisksIntan PermataNessuna valutazione finora
- CPHQ Detailed Content OutlineDocumento8 pagineCPHQ Detailed Content Outlineempire707Nessuna valutazione finora
- Common HCC Codes and Diabetes Manifestations SheetDocumento2 pagineCommon HCC Codes and Diabetes Manifestations SheetmeikaizenNessuna valutazione finora
- AHIMA Conference Agenda 2018Documento8 pagineAHIMA Conference Agenda 2018drrskhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Case StudyDocumento44 pagineCardiac Case StudyNatalia Bernard100% (1)
- Stroke: AHA/ASA Guidelines For The Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke (2019)Documento14 pagineStroke: AHA/ASA Guidelines For The Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke (2019)Natalia OrtizNessuna valutazione finora
- Heartbeat Irregularities ExplainedDocumento5 pagineHeartbeat Irregularities ExplainedKayelyn-Rose Combate100% (1)
- CCU GuidelinesDocumento31 pagineCCU Guidelinesameena ramzanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNDocumento34 pagineBasic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNMavic Martinez BuntalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitral Valve Regurgitation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandMitral Valve Regurgitation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Congenital Heart Disease 1Documento14 pagineCongenital Heart Disease 1OzzeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento45 pagineCongenital Heart DiseaseBrandedlovers OnlineshopNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Guidelines Acute Rehab Management 2010 InteractiveDocumento172 pagineClinical Guidelines Acute Rehab Management 2010 InteractivenathanaelandryNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation Acute Coronary Syndrome (Learner)Documento2 pagineSimulation Acute Coronary Syndrome (Learner)Wanda Nowell0% (1)
- K - 28 Gizi Pada Lansia (Gizi)Documento26 pagineK - 28 Gizi Pada Lansia (Gizi)Vinanda Maria AlexandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Prehospital STEMI CareDocumento39 paginePrehospital STEMI Careapi-21568727Nessuna valutazione finora
- KeyboardDocumento24 pagineKeyboardAndrea BalasabasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiology Billing ServicesDocumento3 pagineCardiology Billing Servicesnixxe mbsNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.2 Peritoneal Cavity and The Esophagus (Banez)Documento4 pagine3.2 Peritoneal Cavity and The Esophagus (Banez)Norjetalexis CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sudil Paudyal: 11/01/12 Abdomen Presentation by Sudil 1Documento58 pagineSudil Paudyal: 11/01/12 Abdomen Presentation by Sudil 1Haba CristianNessuna valutazione finora
- Bedside Pediatric Early Warning SystemDocumento38 pagineBedside Pediatric Early Warning SystemMike SihombingNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanism of Urine FormationsDocumento20 pagineMechanism of Urine FormationsGAURAVNessuna valutazione finora
- Calcium and Phosphate HomeosatsisDocumento35 pagineCalcium and Phosphate HomeosatsisnirilibNessuna valutazione finora
- NIOSH Skin Notation ProfilesDocumento24 pagineNIOSH Skin Notation ProfilesJesús Rafael Méndez NateraNessuna valutazione finora
- SBAR Communication Form: and Progress NoteDocumento3 pagineSBAR Communication Form: and Progress NoteTisa Meriel100% (1)
- Peripheral IVs For BeginnersDocumento19 paginePeripheral IVs For BeginnersMark Hammerschmidt86% (7)
- Clinical practice guidelines critical appraisal guideDocumento2 pagineClinical practice guidelines critical appraisal guideWijitha VarenniNessuna valutazione finora
- Degeneration and Regenration of Nerve Fibers by Dr. RoomiDocumento11 pagineDegeneration and Regenration of Nerve Fibers by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg PDFDocumento2 pagineEcg PDFNaveen SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
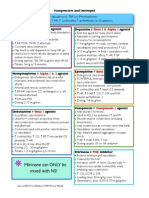
- Milrinone Can ONLY Be Mixed With NS!: Alpha 1 Beta 1 & Alpha 1Documento1 paginaMilrinone Can ONLY Be Mixed With NS!: Alpha 1 Beta 1 & Alpha 1njones33Nessuna valutazione finora
- LMC ICD-10 PowerPointDocumento77 pagineLMC ICD-10 PowerPointNicholas HenryNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Flow Q: The Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) GradientDocumento1 paginaBlood Flow Q: The Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) GradientNicholas HelmstetterNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Surgical Nursing Critical Thinking in Patient Care Single Volume 4th Edition Lemone Test BankDocumento4 pagineMedical Surgical Nursing Critical Thinking in Patient Care Single Volume 4th Edition Lemone Test BankRebeccaGilliamNessuna valutazione finora
- Icd 10Documento4 pagineIcd 10Radhika ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- The Medico-Legal Back An Illustrated Guide, 2004 PDFDocumento210 pagineThe Medico-Legal Back An Illustrated Guide, 2004 PDFvitaarfianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Nursing Assessment For Care Plan: AllergiesDocumento14 pagineComprehensive Nursing Assessment For Care Plan: AllergiesBrittany ShrewsburyNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Cardiac Muscle and Conducting SystemsDocumento38 pagineProperties of Cardiac Muscle and Conducting Systemsnirilib100% (4)
- DTW BOOK - (p1-58)Documento58 pagineDTW BOOK - (p1-58)Humayoun Ahmad Farooqi100% (1)
- Interdisciplinary Plan of Care and Patient EducationDocumento26 pagineInterdisciplinary Plan of Care and Patient Educationhuggr84629Nessuna valutazione finora
- Patient Care SkillsDocumento15 paginePatient Care SkillsIts John100% (1)
- Pocket Guide To 2015 Beers Criteria PDFDocumento7 paginePocket Guide To 2015 Beers Criteria PDFYuliEdySeringnyungsepNessuna valutazione finora
- PQRSTDocumento64 paginePQRSTiduhilagNessuna valutazione finora
- AlopeciaDocumento1 paginaAlopeciachoobiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2melnyk Ebp The Seven StepsDocumento3 pagine2melnyk Ebp The Seven Stepsapi-272725467100% (1)
- Kdoqi Vasc Access Review2019 v2Documento163 pagineKdoqi Vasc Access Review2019 v2Humairah AnandaNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Renal NeoplasiaDocumento5 pagineHistory of Renal NeoplasiarizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensus Pasien Bedah Urologi: NO. Nama Umur Diagnosis RuangDocumento1 paginaSensus Pasien Bedah Urologi: NO. Nama Umur Diagnosis RuangrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jadwal MayorDocumento1 paginaJadwal MayorrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- ACME Sales NumbersDocumento7 pagineACME Sales NumbersCENTARBEOTCHNessuna valutazione finora
- ID Case Detection Rate TB Paru Bta MelaluiDocumento7 pagineID Case Detection Rate TB Paru Bta MelaluirizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Pustaka LAPSUSDocumento6 pagineDaftar Pustaka LAPSUSrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical records template for patient monitoringDocumento2 pagineMedical records template for patient monitoringrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- DapusDocumento1 paginaDapusrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Orientasi: Lapsus & Status: Dr. Lilis Handayani, SP - OG Referat: Dr. Iwan Darma Putra, Sp. OG (K)Documento1 paginaOrientasi: Lapsus & Status: Dr. Lilis Handayani, SP - OG Referat: Dr. Iwan Darma Putra, Sp. OG (K)rizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensus Pasien Stase Ilmu Kesehatan AnakDocumento6 pagineSensus Pasien Stase Ilmu Kesehatan AnakDede MarizalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensus 2 Gastro - DoneDocumento3 pagineSensus 2 Gastro - DonerizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Pustaka REFERATDocumento3 pagineDaftar Pustaka REFERATrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Bites and Rabies RiskDocumento28 pagineAnimal Bites and Rabies RiskrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart Failure CHFDocumento3 pagineCongestive Heart Failure CHFrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Abdominal SurgeryDocumento4 pagineJournal Abdominal SurgeryrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- S1 2013 280476 BibliographyDocumento4 pagineS1 2013 280476 BibliographyrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemorrhagic ShockDocumento46 pagineHemorrhagic ShockrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Acute & Surgical Wounds in 40 CharactersDocumento28 pagineManagement of Acute & Surgical Wounds in 40 CharactersrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laparotomy PDFDocumento3 pagineLaparotomy PDFrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blunt Abdominal Trauma PDFDocumento6 pagineBlunt Abdominal Trauma PDFrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laparotomy PDFDocumento3 pagineLaparotomy PDFrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Acute & Surgical Wounds in 40 CharactersDocumento28 pagineManagement of Acute & Surgical Wounds in 40 CharactersrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- NHSSB Wound Management ManualDocumento102 pagineNHSSB Wound Management ManualxcalibursysNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal Trauma EmergenciesDocumento3 pagineAbdominal Trauma EmergenciesrizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring Vital SignsDocumento4 pagineMeasuring Vital SignsZYRAH LUKE E. VILBARNessuna valutazione finora
- Managemnet Arterial UlcersDocumento24 pagineManagemnet Arterial UlcersMohamad Zulfikar100% (1)
- European J of Heart Fail - 2021 - Moura - Integration of Imaging and Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Failure A ConsensusDocumento20 pagineEuropean J of Heart Fail - 2021 - Moura - Integration of Imaging and Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Failure A Consensustotya91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rekapitulasi Kunjungan Pasien BPJS: NO Tanggal No Kartu Nama PesertaDocumento30 pagineRekapitulasi Kunjungan Pasien BPJS: NO Tanggal No Kartu Nama PesertaEdo Anugrah HutamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment On CPR Knowledge AnDocumento7 pagineAssessment On CPR Knowledge AnGolden HopeNessuna valutazione finora
- Vital Signs 10 Am 2pm Clinical Interpretation: 37.0 Degrees Celsius 37.5 Degrees CelsiusDocumento4 pagineVital Signs 10 Am 2pm Clinical Interpretation: 37.0 Degrees Celsius 37.5 Degrees CelsiusYamete KudasaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Hande's Cardiology OPD SheetDocumento1 paginaDr. Hande's Cardiology OPD SheetSunil RahangdaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Systemic Venous Anomalies - DR RanjithDocumento96 pagineSystemic Venous Anomalies - DR RanjithKhaled S. HarbNessuna valutazione finora
- PN-1150653405 OCHOL Sellsheet DISTDocumento4 paginePN-1150653405 OCHOL Sellsheet DISTMarin MarianNessuna valutazione finora
- Icpc Heart ScreeningDocumento2 pagineIcpc Heart ScreeningMahmoud TitilayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Failure: Causes, Effects on Organs, and TypesDocumento18 pagineHeart Failure: Causes, Effects on Organs, and TypesCarlos Fernando Banegas FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient anticoagulation trackingDocumento2 paginePatient anticoagulation trackingbrendacoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter25Documento29 pagineChapter25Evelyn MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Form Vehicle Licensing CharnwoodDocumento12 pagineMedical Form Vehicle Licensing CharnwoodKalkin43Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unstable AnginaDocumento20 pagineUnstable AnginaMoon AudioNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract IctromiDocumento2 pagineAbstract Ictromiyayasan harapan ummatNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardio QuizDocumento100 pagineCardio QuizEvidence ChaibvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsDocumento10 pagineAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsIssac LauNessuna valutazione finora
- HBP 2.0-For Website V2 PDFDocumento26 pagineHBP 2.0-For Website V2 PDFapurva shahNessuna valutazione finora
- ArtículoDocumento8 pagineArtículoManuel Arzaba LaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vascular DisordersDocumento13 pagineVascular DisordersMichelle Dona MirallesNessuna valutazione finora
- Dexmedetomidine ICU Sedation and UsesDocumento2 pagineDexmedetomidine ICU Sedation and UsesWinter HyuckNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab5388d Sell Sheet PviDocumento2 pagineLab5388d Sell Sheet Pviravi010582Nessuna valutazione finora
- ECG & Heart Sounds Lab ExperimentDocumento5 pagineECG & Heart Sounds Lab ExperimentWalaa AlzoubiNessuna valutazione finora
- ImpellaDocumento6 pagineImpellaCesar Limón SierraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. S. Parimala & I. Arockia MaryDocumento6 pagineDr. S. Parimala & I. Arockia MaryTJPRC PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora