Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Mi 2 Mark 2015
Caricato da
balaji1986Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mi 2 Mark 2015
Caricato da
balaji1986Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Manakula Vinayagar Institute of Technology
(Affiliated to Pondicherry University)
Kalitheerthalkuppam, Mannadipet Commune, Pondicherry 605107.
EET55- MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION
TWO MARKS
UNIT I: INTRODUCTION TO MEASUREMENT
Elements of Generalized measurement system- Methods of measurement- Classification of
instrumentsStatic & Dynamic characteristics of instruments-Mean, Standard deviation-
Probability of errors-Types of error Accuracy, Precision, Sensitivity, Linearity, Resolution,
Hysteresis, Threshold, Input impedance, loading effects.
1. Write the main static characteristics?
The main static characteristics are:
Accuracy
Sensitivity
Reproducibility
Drift
Static error
Dead zone
Resolution
Precision
Repeatability
Stability
2. List the functional elements of the measurement systems.
The three main functional elements of the measurement systems are:
Primary sensing element
Variable conversion element
Data presentation element
3. Write the different types of systematic errors.
These types of errors are divided into three categories:
Instrument Errors
Environmental Errors
Observational Errors
4. What is standard? What are the different types of standards?
A standard is a physical representation of a unit of measurement. The term standard is applied to
a piece of equipment having a known measure of physical quantity.
Types of Standards
International Standards (defined based on international agreement )
Primary Standards (maintained by national standards laboratories)
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
Secondary Standards ( used by industrial measurement laboratories)
Working Standards ( used in general laboratory)
5. Why must instruments be calibrated?
Calibration of all instruments is important since it affords the opportunity to check the
instruments against a known standard and subsequently to find errors and accuracy.
Calibration Procedure involve a comparison of the particular instrument with either
a primary standard
a secondary standard with a higher accuracy than the instrument to be calibrated
a instrument of known accuracy
6. What is mean by accuracy of an instrument?
It is the closeness with an instrument reading approaches the true value of the quantity
being measured.
7. Define: Calibration
Calibration is defined as the process by which comparing the instrument with a standard to
correct the accuracy.
8. Define static error and Reproducibility?
Static error:
Static error is defined as the difference between the true value and the measured value of the
quantity.
Static error = At Am
Where
Am =measured value of quantity
At =true value of quantity.
Reproducibility:
It is specified in terms of scale readings over a given period of time
9. What is primary sensing element?
The primary sensing element is that which first receives energy from the measured medium and
produces an output depending in some way on the measured quantity (measured).
10. What are primary standards? Where are they used?
These are highly accurate absolute standards, which can be used as ultimate reference
standards.
These primary standards representing fundamental units as well as some electrical and
mechanical derived units are calibrated independently by absolute measurements at each
of the national laboratories. These are not available for use, outside the national
laboratories.
The main function of the primary standards is the calibration and verification of
secondary standards.
11. What is the importance of dynamic characteristic of systems?
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
When the quantity under measurement changes rapidly with time, it is necessary to find the
dynamic relations existing between input and output. These types of characteristics are called as
Dynamic Characteristics.
12. Why calibration of instrument is important?
The calibration of all instruments is important since it affords the opportunity to check
the instrument against a known standard and subsequently to errors in accuracy.
13. Define dynamic error
Dynamic error is defined as the difference between the true value of the quantity changing with
time and the value indicated by the measurement system if no static error is assumed. It is also
called measurement error. It is one the dynamic characteristics.
14. Define threshold
Threshold is defined as the minimum value of the input at which the output starts changing /
increasing from zero.
15. Mention the functions performed by the measurement system.
The functions performed by the measurement system are
Indicating function
Recording function
Controlling function
16. State the function of measurement system.
The measurement system consists of a transducing element which converts the quantity
to be measured in an analogous form the analogous signal is then processed by some
intermediate means and is then fed to the end device which presents the results of the
measurement.
UNIT II: ELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENT
Basic effects of electromechanical instrumentsAmmeter and voltmeterMoving coil
Moving IronElectrodynamo meter and induction typeExtension of range. Wattmeter
Dynamometerand induction type energy meterinduction typeInstrument transformers.
Power factor meterSynchroscope Frequency meter-Digital voltmeter.
1. Why the PMMC instruments are not used for a.c measurement?
When the PMMC instruments are connected to a.c, the torque reverse as the current reveres and
the pointer cannot follow the rapid reversals. Hence the deflection corresponding to mean torque
is zero thus making the PMMC instrument not suitable for a.c measurements.
2. What is the basic principle PMMC instrument?
A current carrying coil is placed in the magnetic field experiences a force proportional to the
current it carries.
3. For which type of measurements PMMC devices are suitable.
These are suitable only for D.C. In A.C torque produced on coil is reversing which cannot give
accurate reading.
4. What are the sources of error in DC voltage measurement?
Friction in the moving system
Heat generated changes the resistance of the working coil.
The ageing if the magnet and control spring.
5. List the possible causes of errors in moving iron instruments.
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
Hysteresis error
Temperature error
Stray magnetic field error
Frequency error
Eddy current error
6. Define instrumental error.
These errors are arises due to inherent short comings in the instrument, misuse of the instruments
and loading effects.
7. Define limiting errors.
Instruments having analog meters are usually guaranteed to be accurate within certain percentage
limits called limiting errors or guarantee errors.
Limiting error= accuracy* full scale value
8. State the essential torques required for successful operation of an instruments.
Deflecting torque
Controlling torque
Damping torque.
9. Which torque is absent in energy meter? Why?
The controlling torque is not present in energy meter. As the disc of energy meter has to rotor
continuously and there is no need to reset its position any time, the controlling torque is not
required.
10. Give the importance of iron loss measurement.
Many apparatus like transformer, generator, and motor etc. use magnetic materials for their
construction. The design of transform core, armature for motor and generator is very important.
To have high efficiency, the losses must be as minimum as possible. Hence from ideal designing
point of view, the iron loss measurement is important.
11. Name the methods used in wattmeter calibration.
The methods used in wattmeter calibration are:
Comparing with standard wattmeter.
Using voltmeter ammeter method.
Using Potentiometer.
12. Name the errors caused in Dynamometer type wattmeter.
Error due to pressure coil inductance
Error due to pressure coil capacitance
Error due to methods of connection
Error due to stray magnetic fields
Error due to eddy current.
13. State the disadvantages of Dynamometer type wattmeter.
Readings may be affected by stray magnetic fields.
At low power factor it causes error.
14. State the advantages of Moving iron type instruments
Less expensive
Can be used for both dc and ac
Reasonably accurate.
15. State the advantages of instrument transformers.
Used for extension of range
Power loss is minimum
High voltage and currents can be measured.
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
16. State the disadvantages of PMMC instruments
Cannot be used for ac measurements
Some errors are caused by temperature variations.
17. What are the adjustments in energy meter?
Main speed adjustment
Power factor adjustment
Friction adjustment
Creep adjustment
18. Write about DC tests in magnetic measurements.
These are used to determine B-H curve and hysteresis loop of Ferromagnetic materials. The
direct current is used to have variable m.m.f. and flux meter is used to measure the flux density.
A ballistic galvanometer can be used to measure flux density. Such tests are also called ballistic
tests.
19. Give two differences between analog and digital type phase meters.
20. What is creeping?
Without any current through current coil, disc rotates due to the supply voltage exciting its
pressure coil. This is called creeping.
21. Write some advantages of instrument transformer.
The normal range ammeters and voltmeters can be used along with these transformers to
measure high currents and voltage.
The rating of low range meter can be fixed irrespective of the value of high voltage or
current to be measured.
These transformers isolate the measurement from high voltage and current circuits. This
ensures safety of the operator and makes the handling of the equipments very easy and
safe.
These can be used for operating many types of protecting devices such as relays or pilot
lights.
22. What are the requirements of a shunt?
The temperature coefficient of shunt and the meter should be low and should be as equal
as possible.
The shunt resistance should be stable and constant with time.
The shunt resistance should not carry currents which will cause excessive temperature
rise.
The soldering joints should not cause a voltage drop.
The values of resistance should not change due to soldering.
The resistance should have low thermal electromotive force with copper.
23. Mention any two precautions to be taken while using a voltmeter.
It should be always connected across the circuit or component whose voltage is to be
measured.
The polarities must be observed correctly.
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
First use the highest range and then decrease the voltage range until the sufficient
deflection is obtained.
Take care of loading effect.
24. Mention the two main differences between an ammeter and a voltmeter.
25. Write about AC tests in magnetic measurements.
When a ferro-magnetic material is subjected to cycle of magnetization and demagnetization then
the eddy current and hystereis losses occur. Hence alternating current is used to determine iron
losses, having provision of a variable frequency and form factor. Such tests are carried out at
power, audio or radio frequencies.
26. How can we prevent creeping in energy meter?
Two holes are drilled in the aluminum disc 180o opposite to each other. When this holes comes
under the shunt magnet pole, it gets acted upon by a torque opposite to the rotation.
27. Mention the purpose of Schmitt trigger in frequency meter.
To convert the amplified signal from sine wave to square wave with fast rise and fall times.
28. Define torque to weight ratio in electrodynamometer instrument.
To have reasonable deflecting torque, mmf of the MC must be enough. Thus mmf=NI, hence
current through MC should be high or no. Of turns should be large. The current cannot be made
high because it may cause excessive heating of spring. Large no. of N hence is the only option
but it increases weight of the coil.
29. Mention any two precautions to be taken while using an Ammeter.
It should never be connected across any source.
The polarity must be observed correctly.
First use the highest range and then decrease the voltage range until the sufficient
deflection is obtained.
30. List the Instruments for measurement of frequency.
Vibrating Reed type
Electrical resonance type
Weston frequency meter
Digital type
Wiens bridge
UNIT III: AC MEASUREMENT & MAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS
Measurement of resistance-Low Medium and High- AC bridges-Maxwells, Hays Andersons
for L, Desautys bridge and Schering bridge for C and Wiens bridge for measurement of
frequency. BH curve and hysteresis loop using ballistic galvanometer, and Loss measurement
using wattmeter method.
1. Write the two conditions to be satisfied to make an A.C. bridge balance?
The two conditions are,
1. Z1Z4=Z2Z3 .magnitude condition
2. 1 + 4 = 2 + 3 ..angle or phase condition
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
2. Write four applications of A.C. Bridge? (MAY/JUNE 2007)
1. To measure unknown inductance.
2. To measure unknown capacitance.
3. To measure dissipation factor.
4. To measure quality factor.
5. To measure frequency.
3. When Kelvin bridge is used and why?
In the Wheatstone bridge, the bridge contact and lead resistance causes significant errors, while
measuring low resistances below 1. To consider the effect of contact and lead resistance and to
reduce the corresponding errors, the Kelvin Bridge is preferred over Wheatstone bridge to
measure low resistances.
4. What is important condition for Kelvin Bridge to achieve perfect balance condition?
To eliminate the effect of lead and contact resistances, it is necessary that in a Kelvins double
bridge the ratio of the resistances of ratio arms (R1 / R2) must be same as the ratio of the
resistances f the second ratio arms (a/b).
5. State the difficulties in measuring high resistances?
Due to high resistance, very small current flows through measuring circuit which is
difficult to sense.
Presence of leakage currents.
The stray charges appearing due to electrostatic effects.
The delay time is required in the measurement so that charging and absorbing currents
get stabilize. This time may be very long in some cases.
The very high voltage is required to raise the magnitude of current. This may damage the
galvanometer if proper case is not taken.
6. What is the basic principle used in potentiometer.
In potentiometer the unknown emf is measured by comparing it with a standard known emf.
7. Name the potentiometer material used.
German silver
Manganin wire
8. Define standardization.
It is the process by which adjusting the current flows through the potentiometer coil to make
the voltage across the standardization cell is equal.
9. State the applications of potentiometer.
Used for m/s of unknown emf
Used for ammeter calibration
Used for Voltmeter calibration
Used for wattmeter calibration
10. State the advantages of crompton potentiometer.
More accurate
Easy to adjust
11. What are the practical difficulties in ac potentiometers?
More complicated
Accuracy is seriously affected
Difficulty is experienced in standardization.
12. Classify ac potentiometers.
Polar potentiometer
Coordinate potentiometer.
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
13. How the phase angle is measured in polar type potentiometers.
It is measured from the position of phase shifter.
14. Name some ac potentiometers.
Drysdale Tinsley potentiometer
Gall Tinsley potentiometer
15. State the advantages of ac potentiometers.
Can be used for m/s of both magnitude and phase angle
Can be used for m/s of inductance of the coil.
It is used in m/s of errors in CTS
14. State the applications of ac potentiometers.
M/s of self inductance.
Ammeter calibration
Voltmeter calibration
Wattmeter calibration.
15. What are the constructional parts of current transformer?
Primary winding
Secondary winding
Magnetic core.
16. Name the errors caused in current transformer.
Ratio error
Phase angle error
17. Give the purpose of bridge circuits. What are the different types?
The bridge circuits are used in instrumentation systems for the measurement of resistance,
inductance and capacitance.
Types:
DC type and
AC type
18. What are the 2 types of Wheatstone bridge?
Null type bridge
Deflection type bridge
19. What are detectors normally used for AC bridges?
(i) Head phones (250 Hz to 4kHz)
(ii) Vibration galvanometers- most commonly used below 200Hz.
since below 200Hz, there are more sensitive then head phones.
(iii) Tunable amplifier detectors ( 10 Hz to 100 Hz)
UNIT IV: DISPLAY AND RECORDING DEVICES
LED & LCD Display Dot Matrix Display, 7 Segment Display Strip Chart Recorders Single point
and multipoint RecordersX-Y Recorders-Magnetic Tape Recorders-Data Loggers
Electromagnetic and Electrostatic interference.
1. List the components of a magnetic tape recorder.
The components of a magnetic tape recorder are:
Recording head
Magnetic head
Reproducing head
Tape transport mechanism
Conditioning devices.
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
2. What are the advantages of magnetic tape recorders?
The advantages of magnetic tape recorders are:
They have a wide frequency range from D.C. to several MHz.
They have low distortion,
They have a wide dynamic range which exceeds 50dB. This permits the linear recording
from full scale signal level to approximately 0.3% of full scale.
The magnitude of the electrical input signal is stored in magnetic memory and this signal
can be reproduced whenever desired. The reproduced signal can be analyzed by
automatic data reduction methods.
3. Mention the different methods of magnetic tape recording.
The different methods of magnetic tape recording are:
i. Direct recording
ii. Frequency modulation (FM) recording and
iii. Pulse duration modulation (PM) recording
4. Mention is the purpose of erase head.
The purpose of erase head is to erase the content of magnetic tape. It consists of a signal of high
frequency and level sweeps the magnetic tape thereby completely wiping out the information
contained there. This renders the magnetic tape to be used fresh for another signal.
5. List the advantages of direct recording.
The advantages of direct recording are:
This recording process has a wide frequency response ranging from 50 Hz to about 2
MHz for a tape speed of 3.05 m/s. It provides the greatest bandwidth obtainable from a
given recorder.
It requires only simple, modulately priced electronic circuitry.
It is used to record signals where information is contained in the relation between
frequency and amplitude, such as spectrum analysis of noise.
It can be used for recording voice and in multiplexing a number of channels of
information into one channel of tape recording.
6. Mention the disadvantages of direct recording.
The disadvantages of direct recording are:
Direct recording is used only when maximum bandwidth is required and when variations
in amplitude are acceptable.
Direct recording can be used for instrumentation purposes but it is mainly used for
recording of speech and music.
7. What is drop out?
In direct recording, some portions of the tape may not be perfectly recorded owing to dirt or poor
manufacture and this is called drop out.
8. Mention the two factors in frequency modulation recording.
The two factors in frequency modulation recording are:
i. Percentage deviation and
ii. Deviation ratio.
9. Define: percentage deviation
Percentage deviation is defined as the carrier deviation to centre frequency.
i.e. Percentage deviation or modulation index, m =(f/fc) x 100,
where f = carrier deviation from centre frequency
fc = centre or carrier frequency
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
10. Define: Deviation ratio
Deviation ratio is defined as the ratio of carrier deviation from centre frequency to signal or
modulating frequency.
Deviation ratio, = (f/fm)
Where, fm = data signal
11. List few disadvantages of frequency modulation recording.
The disadvantages of frequency modulation recording are:
i. The circuitry of an FM recording system is more complicated than that of a direct recording
system. This complexity of circuitry is an account of separate modulation systems.
ii. It has a limited high frequency of about 80 kHz.
iii. It requires a high tape speed.
iv. It requires a high quality of tape transport and speed control and therefore expensive than the
direct recording system.
12. Give few advantages of frequency modulation recording.
The advantages of frequency modulation recording are:
i. It is useful when the D.C. component of the input signal is to be preserved or when the
amplitude variations of the direct recording process cannot be tolerated.
ii. This system has wide frequency range can record from D.C. voltages to several kHz.
iii. It is free from dropout effect.
iv. It is independent of amplitude variations and accurately reproduces the waveform of the input
signal.
v. It is used extensively for recording the voltages from the force, pressure and acceleration
transducers.
13. List the classification of printer.
Printers are classified into three broad categories. They are
i. Impact and non-impact printers.
ii. Fully formed character and dot matrix character printer
iii. Character at a time and a line at time.
14. Give short notes on dot-matrix printers.
In dot-matrix printers, the characters are formed by printing a group of dots to form a letter,
number or other symbol. It can print any combination of dots with all available print position in
the matrix.
15. Enumerate the merits and demerits of pulse width modulation recording.
The merits of pulse width modulation recording are:
It has the ability to simultaneously record information from a large number of channels.
It has a high accuracy due to the fact that it can be self-calibrated.
It has a high 3/N ratio.
The demerits of pulse width modulation recording are:
It has the limited frequency response
It has a highly complex electronic circuitry and therefore, the reliability of such systems
is low.
It is used only for special applications such as flight recorders, where a large number of
slowly changing variables are involved.
16. List the characteristics of LCD.
The characteristics of LCD are:
i. They are light scattering.
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
ii. They can operate in a reflective or transmissive configuration.
iii. They do not actively generate light and depend for their operation on ambient or back
lighting.
17. What is LED?
The LED is basically a semiconductor PN junction diode capable of emitting electromagnetic
radiation under forward conductions.
18. List the characteristics of LCD.
Light scattering
Can operate in reflective or Transmissive configuration.
Do not actively generate light and depend for their operation on ambient or back light.
19. On what does the operation of LCD depend?
The utilization of a class of organic materials which remain a regular crystal like structure even
when they have melted.
20. Name the 2 commonly available types of LCDs.
Dynamic scattering and
Field effect type.
21. What is the purpose of dot matrix displays?
Excellent alphanumeric characters can be displayed by using dot matrix LEDs with an LED at
each dot location.
22. What are the commonly used dot matrices for the display of characters?
The commonly used dot matrices for the display of prominent characters are 5 x 7, 5 x 8 & 7 x 9
23. What are the 2 writing patterns of dot matrix displays?
Common anode or common cathode connection (uneconomical)
X-Y array connection (economical and can be extended vertically or horizontally using a
minimum number of wires)
24. What is electromagnetic interference?
The energy associated with the current or charge variation in a conductor gets radiated away
from it, at high frequencies such radiations are the form of waves called electromagnetic
waves
e.g. Signal from radio or radar transmitters or by some other sources. These waves have
influence in the performance of measuring instruments, which is termed as
electromagnetic interference.
25. What is electrostatic interference?
Two conductors which are near each other form a capacitive effect and get electrically coupled
to each other. Voltage change in one conductor causes corresponding interference in the other.
This is called electrically coupled interference. This is also known as electrostatic interference or
capacitive interference.
UNIT V: TRANSDUCERS
Temperature transducers-RTD, Thermistor, Thermocouple-Displacement transducer-Inductive,
capacitive, LVDT, Pressure transducerBourdon tube, BellowsFlow transducer
Electromagnetic
flow
1. meter 2Strain
Mention gauges Piezoelectric
disadvantages of capacitiveand Hall effect transducer.
transducer?
Output impedance of capacitive transducer is very high. So its measuring circuit becomes
Very complicated.
The capacitance of capacitive transducer change with change in temperature or account
of presence of small external matter.
Example: dust particles, moisture.
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
2. Give the 2 types of principles for the operation of optical transducers
INTRINSIC SENSOR: In this the fiber optic cables itself is the sensor.
EXTRINSIC SENSOR: In this fiber optic cable is only used to guide light to or from a
conventional sensor.
3. Write the function of transducer
Transducers are defined as a device which when actuated, transforms energy from one form to
another. Generally, any physical parameter is converted into electrical form.
4. Define inverse transducer with example
An inverse transducer is defined as device which converts an electrical quantity into a
non electrical quantity.
It is a precision actuator which has an electrical input and a low power non electrical
output.
5. Define the primary and secondary transducers?
Primary Transducer:
When the input signal is directly sensed by the transducer and physical phenomenon is
converted into electrical form directly then such a transducer is called the primary transducer.
Secondary Transducer:
When the input signal is sensed first by some detector or sensor and then its output being
of some from other than input signals is given as input to a transducer for conversion into
electrical form, then such a transducer falls in the category of secondary transducers.
6. How do you classify transducers?
On the basis of transduction form used.
As primary and secondary transducers.
As active and passive transducers.
As analog and digital transducers.
As transducers and inverse transducers.
7. What is piezo-electric effect?
A piezoelectric material is one in which an electric potential appears across certain surfaces of
the crystal if the dimensions of the crystals are changed by the application of a mechanical force
this potential is produced by the displacement of charges .
This effect is reversible.
This phenomenon is known as piezoelectric effect.
8. Explain the working principle of capacitive transducers?
The principle of capacitive transducer is based on the familiar equation of capacitance of parallel
plate capacitor.
C= A /d
9. What are the selection criteria for the transducer?
Sensitivity.
Electrical output characteristics.
Environmental conditions
Errors.
Accuracy.
10. What is meant by strain gauge? What for it is used?
It is an example of a passive transducer that uses the variation in electrical resistance in wires to
sense the strain produced by a force on the wires.
11. What is POT? It is active or passive transducer?
POT is a resistive potentiometer used for the purpose of voltage division.
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
It consists for a resistive element provided with a sliding contact called as wiper.
The POT is a passive transducer since it requires an external power source for its
operation.
12. Which are the materials used in piezo-electric transducer?
Rochelle salt.
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP).
Quartz.
Ceramic made with barium titanate, dipottasium tartrate, potassium dihydrogen
phosphate and lithium sulphate.
13. Name the transducer that uses sensing acceleration?
Piezo-electric transducer.
14. Mention the use of capacitive transducer?
Capacitive transducers can be used for measurement of both linear and angular
displacements.
It can be used for measurement of force and pressure.
Can be used for measuring humidity.
It is used in conjunction with mechanical modifiers for measurement of volume, density
etc.
15. Write any four basic requirements of transducer?
RUGGEDNESS: It should be capable for withstanding overload.
LINEARITY: The input-output characteristics should be linear.
NO HYSTERISIS: It should not give any hysteresis during measurement while input
signal is varied from low to high value and vice versa.
RESIDUAL DEFORMATION: There should be no deformations on removal of load
after long period of time.
16. Mention the factors considered while selecting a transducer.
Operating range
Sensitivity
Frequency response & resonant frequency
Environmental compatibility
Minimum sensitivity
Accuracy
Usage and ruggedness
Electrical parameters
17. Explain the working principle of a strain gauge.
Strain gauge works on the principal that the resistance of a conductor or a semiconductor
changes when strained. This property can be used for measurement of displacement, force and
pressure.
18. Name the different types of strain gauges.
Un-bonded metal strain gauge
Bonded metal wire strain gauge
Bonded metal foil strain gauge
Vacuum deposited thin metal film strain gauge
Sputter deposited thin metal strain gauge
Bonded semiconductor strain gauge
Diffused metal strain gauge
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
19. What is meant by rosette?
It is a combination of strain gauges to a single element strain gauge.
20. Write notes on LVDT
It is the linear variable differential transformer which is used to translate the linear motion into
electrical signals. It consists of a single primary winding and 2 secondary winding.
21. List the advantages of LVDT
High range of displacement measurement
Friction & electrical isolation
Immunity from external effects
High I/p and high sensitivity
Ruggedness
Low hysteresis & low power consumption
22. List the various electrical transducers.
1. Resistive 2. Inductive 3. Capacitive 4. Electromagnetic 5. Piezo-electric 6. Photo-emissive
7. Photo-resistive 8. Potentiometric 9. Thermo-electric 10. Frequency generating
23. What is resistance transducer?
Resistive transducers are those in which the resistance changes due to a change in some physical
phenomenon.
Eg. The change in value of resistance with a change in length of the conductor can be
used to measure displacement.
24. What is the principle of working of strain gauge? What are the types?
Strain gauge is a passive transducer that uses the variation in resistance in wires to sense the
stress produced by the force on the wire.
Types of Strain Gauges:
1. Wire Strain Gauges
2. Foil Strain Gauges
3. Semiconductor Strain Gauges
25. What is the commonly used material as sensor in resistance thermometer?
Platinum, Nickel and copper among which platinum
26. Give the 3 working principles of variable inductance transducers
Change of self inductance
Change of mutual inductance
Production of eddy currents.
27. Define Gauge Factor of Strain Gauge?
Gauge Factor is the ratio of Change in resistance of the resistive transducer to the Change in
Strain applied on it.
Prepared by D.BALAJI AP/EEE
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- SafetyDocumento17 pagineSafetybalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisDa EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Cantilever Flex ExperimentDocumento8 pagineCantilever Flex ExperimentJhonattan PardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement and Instrumentation Lecture NotesDocumento73 pagineMeasurement and Instrumentation Lecture NotesRakesh Thapliyal83% (6)
- Multiple Choice Questions On Three Phase Induction MotorDocumento33 pagineMultiple Choice Questions On Three Phase Induction Motorbalaji198664% (28)
- Analytical ChemistryDocumento12 pagineAnalytical Chemistrybalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageDa EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageNessuna valutazione finora
- Omega Dyne NH - SGDocumento89 pagineOmega Dyne NH - SGChallengerPowerNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering For Mechatronics by Felix Huning PDFDocumento274 pagineThe Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering For Mechatronics by Felix Huning PDFarup100% (1)
- Rua Al Madinah Geotech SpecsDocumento121 pagineRua Al Madinah Geotech Specsalqadad ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- C8: Sensor and Sensor TechnologyDocumento72 pagineC8: Sensor and Sensor TechnologyOladokun Sulaiman Olanrewaju100% (4)
- Handbook of Microwave Component Measurements: with Advanced VNA TechniquesDa EverandHandbook of Microwave Component Measurements: with Advanced VNA TechniquesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Ee8403 2 Mark PDFDocumento16 pagineEe8403 2 Mark PDFAnonymous b7jVZ9cbs100% (1)
- Notes For EMIDocumento25 pagineNotes For EMIHoney Rose100% (1)
- M& I 2mark Q& ADocumento21 pagineM& I 2mark Q& Asathyasony100% (1)
- EC1255-Measurements and Instrumentation: Two Mark Question AnswerDocumento8 pagineEC1255-Measurements and Instrumentation: Two Mark Question AnswervjospinNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring Instruments SyllabusDocumento0 pagineMeasuring Instruments SyllabusvjnrkzNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee6404 Measurements and InstrumentationDocumento69 pagineEe6404 Measurements and InstrumentationAbiodun IloriNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-1 Performance CharacteristicsDocumento19 pagineUnit-1 Performance CharacteristicswisorowNessuna valutazione finora
- Dept. of EEE Rajalakshmi Engineering College Two Mark Question AnswerDocumento8 pagineDept. of EEE Rajalakshmi Engineering College Two Mark Question AnswerRadha NandhiniNessuna valutazione finora
- I 1251-Electrical Measurements and InstrumentationDocumento11 pagineI 1251-Electrical Measurements and Instrumentationsatishcoimbatore2Nessuna valutazione finora
- EMDocumento18 pagineEMSuprava GhoshPaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Mark Question & Answer Unit I - Introduction: Saraswathi Velu College of Engineering - SholinghurDocumento20 pagineTwo Mark Question & Answer Unit I - Introduction: Saraswathi Velu College of Engineering - SholinghurarchumeenabaluNessuna valutazione finora
- EE8403 2marks IqDocumento18 pagineEE8403 2marks IqG Krishna swamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Mark Question Answer: Unit I Measurement of Voltage and CurrentDocumento8 pagineTwo Mark Question Answer: Unit I Measurement of Voltage and CurrentPraveen Chandran C RNessuna valutazione finora
- Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122Documento23 pagineSelvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122Anonymous jrJm4BZM6Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3.two Marks QuestionsDocumento20 pagine3.two Marks QuestionsPullareddy AvulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Emi Unit 11Documento23 pagineEmi Unit 11ADEPOJU AyobamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumentation Intro 1Documento25 pagineInstrumentation Intro 1trunks rosarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement and InstrumentationDocumento4 pagineMeasurement and InstrumentationAbirami RajendranNessuna valutazione finora
- MT8591 S&I IA1 Q&A IIIyearDocumento60 pagineMT8591 S&I IA1 Q&A IIIyearILYASNessuna valutazione finora
- Module3Documento11 pagineModule3divyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Marks EE 2201Documento20 pagine2 Marks EE 2201Karthik KolliparaNessuna valutazione finora
- EMI Assignment 1: Measurement Terms, Standards, MethodsDocumento1 paginaEMI Assignment 1: Measurement Terms, Standards, MethodsRavi VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- EI1361 Measurements and Instrumentation NotesDocumento20 pagineEI1361 Measurements and Instrumentation NotesKaree MullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Measurement 2nd Elect.2022-2023 Lecture1 PDFDocumento39 pagineElectrical Measurement 2nd Elect.2022-2023 Lecture1 PDFHero ModeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Measurements and Instrumentation FundamentalsDocumento23 pagineElectrical Measurements and Instrumentation FundamentalsDereje DeribNessuna valutazione finora
- InstrumentationDocumento81 pagineInstrumentationkingsford obeng kwakyeNessuna valutazione finora
- EE2201 Measurement and Instrumentation Lecture NotesDocumento73 pagineEE2201 Measurement and Instrumentation Lecture NotesDeepa Dhilip100% (1)
- chapter 6 - CopyDocumento12 paginechapter 6 - CopyIshwar KNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Measurement Instruments and Systems ExplainedDocumento68 pagineElectrical Measurement Instruments and Systems ExplainedPradeep Kumar VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- EI6401-Transducer Engineering PDFDocumento16 pagineEI6401-Transducer Engineering PDFVinoth KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- EI6401-Transducer Engineering PDFDocumento16 pagineEI6401-Transducer Engineering PDFJeyamalar RajarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Power Quality MonitoringDocumento21 pagine4 Power Quality Monitoringhabte gebreial shrashrNessuna valutazione finora
- Dept: Ii Eee Sub/ Code: Measurements and Instrumentation/Ee33 2marks: Unit-IDocumento16 pagineDept: Ii Eee Sub/ Code: Measurements and Instrumentation/Ee33 2marks: Unit-IAyyasamy SabariNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 33-Measurements and Instrumentation: Unit-I-IntroductionDocumento73 pagineEE 33-Measurements and Instrumentation: Unit-I-IntroductionSOWKATHKUTHBUDEEN_J14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment With AnswersDocumento19 pagineAssignment With AnswersMythily VedhagiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 1 PPT Instr. & Meas PCE 4203 From GUDocumento43 pagineChap 1 PPT Instr. & Meas PCE 4203 From GUTemesgen workiye100% (1)
- UNIT 1 - Introduction To Measurement SystemDocumento55 pagineUNIT 1 - Introduction To Measurement SystemPoornima ANessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement and Instrumentation Lab ManualDocumento3 pagineMeasurement and Instrumentation Lab ManualSudhakar RamanNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 315 L3cture Note 2023Documento22 pagineEEE 315 L3cture Note 2023Kadiri DonaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring Basics: Types of Sensors and Transducer CharacteristicsDocumento3 pagineMeasuring Basics: Types of Sensors and Transducer Characteristicssenthilkumar100% (1)
- Oic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and Problem With AnswersDocumento32 pagineOic751-Transducer Engineering 2 Marks, 13 Marks and Problem With AnswersPoovarasan S100% (1)
- Introduction To Instrumentation and MeasurementsDocumento29 pagineIntroduction To Instrumentation and MeasurementsSYAFIQAH ISMAILNessuna valutazione finora
- EI6401 TransducerEngineeringDocumento16 pagineEI6401 TransducerEngineeringPatel DipenNessuna valutazione finora
- DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MEASUREMENTS TWO MARKS Q&ADocumento17 pagineDHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MEASUREMENTS TWO MARKS Q&AVinay KedhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Measurement: Measurement Is The Process by Which One Can Convert Physical ParametersDocumento16 pagineElectrical Measurement: Measurement Is The Process by Which One Can Convert Physical ParametersDereje DeribNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 1 - Intro J5800Documento54 pagineCH 1 - Intro J5800mohd_mizanNessuna valutazione finora
- EMM 2 & 16 MarksDocumento23 pagineEMM 2 & 16 MarksbijuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento43 pagineChapter 1MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- ch1 ch2Documento6 paginech1 ch2MohammadKazaalNessuna valutazione finora
- BMMI Unit 2 - Session 1Documento31 pagineBMMI Unit 2 - Session 1Yashi SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT I Introduction ACTDocumento56 pagineUNIT I Introduction ACTSelva LakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical and Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation LecDocumento25 pagineElectrical and Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation LecAbdulhamid DaudaNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 311: Measurement & Instrumentation Course OverviewDocumento25 pagineECE 311: Measurement & Instrumentation Course OverviewSamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurment InstrumentationDocumento74 pagineMeasurment InstrumentationVikas KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurements and Instrument CharacteristicsDocumento26 pagineMeasurements and Instrument CharacteristicsWalid KhaledNessuna valutazione finora
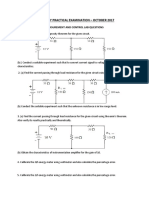
- MEASUREMENT AND CONTROL LAB EXAM QUESTIONSDocumento2 pagineMEASUREMENT AND CONTROL LAB EXAM QUESTIONSbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement & Instrumentation Test at MVITDocumento1 paginaMeasurement & Instrumentation Test at MVITbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Mark Test MiDocumento3 pagine2 Mark Test Mibalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Model EeDocumento2 pagineModel Eebalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Control System Objective Type QuestionsDocumento25 pagineControl System Objective Type Questionsbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- EXPT - NO:8 Display Using SubroutinesDocumento5 pagineEXPT - NO:8 Display Using Subroutinesbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Address Label Mnemonics Opcode CommentsDocumento6 pagineAddress Label Mnemonics Opcode Commentsbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement and Instrumentation Question BankDocumento5 pagineMeasurement and Instrumentation Question Bankbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento21 pagineUnit 5balaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions On Synchronous MotorDocumento29 pagineMultiple Choice Questions On Synchronous Motorbalaji1986100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions On Synchronous AlternatorDocumento31 pagineMultiple Choice Questions On Synchronous Alternatorbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions On Single Phase Induction MotorDocumento26 pagineMultiple Choice Questions On Single Phase Induction Motorbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lcs QuestionsDocumento6 pagineLcs Questionsbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- University Prac QuestionsDocumento2 pagineUniversity Prac Questionsbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ee Question Bank PDFDocumento7 pagineEe Question Bank PDFbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- GK 2015Documento43 pagineGK 2015balaji1986100% (1)
- Half & Full Controlled Rectifier Output WaveformsDocumento4 pagineHalf & Full Controlled Rectifier Output Waveformsbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- What is Meant by Protective Relay and its FunctionsDocumento1 paginaWhat is Meant by Protective Relay and its Functionsbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manakula Vinayagar Institute of TechnologyDocumento1 paginaManakula Vinayagar Institute of Technologybalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- PSG QBDocumento4 paginePSG QBbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calculate Alternator Regulation using EMF MethodDocumento2 pagineCalculate Alternator Regulation using EMF Methodbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ee t42 Electrical MachinesDocumento2 pagineEe t42 Electrical Machinesbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Answer All The Questions:: Manakula Vinayagar Institute of TechnologyDocumento2 pagineAnswer All The Questions:: Manakula Vinayagar Institute of Technologybalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Two Marks Protection and Switch GearDocumento7 pagineTwo Marks Protection and Switch Gearbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 1Documento20 pagineUnit - 1balaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- SSD NotesDocumento11 pagineSSD Notesbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Temperature Compensationon Strain Gages05414Documento4 pagineTemperature Compensationon Strain Gages05414Nestor Carmelo Ranieri JuniorNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - 20 Ma Signal Conditioner P/N 2078-Series: Part Number 2078-08 Revision BDocumento24 pagine4 - 20 Ma Signal Conditioner P/N 2078-Series: Part Number 2078-08 Revision BLuis Eduardo Albarracin RugelesNessuna valutazione finora
- MQC LabDocumento70 pagineMQC LabAjit BandgarNessuna valutazione finora
- 135 An 112018Documento2 pagine135 An 112018Ruler NanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Aero 6sem ESADocumento103 pagineAero 6sem ESAram rakNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Structures II LabDocumento15 pagineAircraft Structures II Labproxymo10% (1)
- An Experimental Study of Ball-On-flat Wear On A Newly Developed Rotational TribometerDocumento10 pagineAn Experimental Study of Ball-On-flat Wear On A Newly Developed Rotational TribometerDavid Rafael RamírezNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics and Instrumentation Syla PDFDocumento134 pagineElectronics and Instrumentation Syla PDFchetanNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - ISSN - 1392-1215 - Analysis of Balancing Methods of Measurement of Small Resistance ChangesDocumento4 pagine01 - ISSN - 1392-1215 - Analysis of Balancing Methods of Measurement of Small Resistance Changescuco777Nessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE 1451d4 Templates Tutorial 061804Documento19 pagineIEEE 1451d4 Templates Tutorial 061804Rui F. S. NetoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensors and ActuatorsDocumento2 pagineSensors and Actuatorssrinivasan govindarajan100% (1)
- CIVE #302 Lab #2: Wheatstone Bridge For Strain Measurement: 1. PurposeDocumento3 pagineCIVE #302 Lab #2: Wheatstone Bridge For Strain Measurement: 1. PurposeAhmadAliAKbarPhambraNessuna valutazione finora
- An Improved Specimen Geometry For ASTM C633-79 To Estimate Bond Strengths of Thermal Spray Coatings 1993Documento6 pagineAn Improved Specimen Geometry For ASTM C633-79 To Estimate Bond Strengths of Thermal Spray Coatings 1993Ngo BinhNessuna valutazione finora
- HSM17 04Documento2 pagineHSM17 04sadiqaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sherborne Product BrochureDocumento12 pagineSherborne Product BrochureS Arun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Cell Troubleshooting GuideDocumento14 pagineLoad Cell Troubleshooting GuideMobin CheriyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Force Sensors in Robotics Research PDFDocumento35 pagineForce Sensors in Robotics Research PDFYahia Mustafa AlfazaziNessuna valutazione finora
- s1266 PDFDocumento48 pagines1266 PDFM JefriantoNessuna valutazione finora
- BIT Paper QuestionDocumento4 pagineBIT Paper QuestionVuyyuri GaneshNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Stress Analysis Two Marks With AnswersDocumento24 pagineExperimental Stress Analysis Two Marks With Answersmatrixrajiv34100% (2)
- Strain Gauge: 1. Thin-Film Strain GaugesDocumento2 pagineStrain Gauge: 1. Thin-Film Strain GaugesanshulNessuna valutazione finora
- Facial Performance Sensing Head-Mounted DisplayDocumento9 pagineFacial Performance Sensing Head-Mounted DisplayAndreea ProdanNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Measurements 2Documento3 pagineEngineering Measurements 2KCCNessuna valutazione finora
- Masukawa Junji 201206 PHD ThesisDocumento353 pagineMasukawa Junji 201206 PHD Thesisjorge mathaeusNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics EBook - Strain Gages and Strain RosetteDocumento2 pagineMechanics EBook - Strain Gages and Strain Rosettesahnis aslamNessuna valutazione finora