Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tissue Engineering Day 5
Caricato da
CaitlinKyaw0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
4 visualizzazioni2 pagineTE5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoTE5
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
4 visualizzazioni2 pagineTissue Engineering Day 5
Caricato da
CaitlinKyawTE5
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
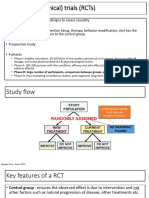
Clinical Trials are the scientific basis for therapeutics
What are the types of trials?
HYPOTHESIS-GENERATING are trials that cannot rigorously test a hypothesis,
give you testable hypotheses for interventions and their outcomes, include:
case studies - trying a novel treatment method on a few patients/one),
case control study - trying a novel treatment method on a small group of
patients with a control group that is age matched, gender matched, and
ethnicity matched
cohort study - follow two groups of people in the same demographic, one
of whom has a certain condition, then look at outcomes (not as valid bc of
confounding factors)
confounding factors - separate factors that can systematically
affect results
prospective vs retrospective
HYPOTHESIS-TESTING TRIALS/ GOLD STANDARD - randomized,
controlled, double-blinded clinical trials
randomized - participants randomly assigned control/active participation
controlled - receives current standard of care, not necessarily just
placebos (on a case-by-case basis)
double-blinded - neither participants or caregivers/study evaluators know
who is in which group (surgeries CANNOT be double-blinded)
What are the sources of bias?
Four types of bias:
Selection bias - bias in the selection of patients for the intervention;
combat through randomization and blinding
Performance bias - bias in terms of the overall treatment a patient
receives whether they be in the control group or not, combat through
blinding and randomization
Detection bias - bias in the detection of an effect, bias in the
measurement of a clinical endpoint by the caregiver; combat through
blinding and randomization
Attrition bias - bias with regard to trial dropouts/non compliance; combat
through intention-to-treat
What is the gold standard?
How might this present issues for tissue engineering?
HYPOTHESIS: If I perform an intervention then I will see difference in outcome/clinical
endpoint.
If I implant cardiac stem cells in patients with heart failure, then I will see fewer heart
attacks in this group versus the control group receiving the standard of care
Clinical endpoints:
blood pressure
blood glucose levels
enzyme levels
cholesterol levels
advantage: short term results are visible, BUT are not the most clinically
meaningful
number of major coronary events
exercise tolerance
visits to hospital
overall survival (YOU WILL NEVER BE WRONG WITH THIS ANSWER)
most clinically meaningful BUT results take longer
Define intervention
Define target patient population
inclusion criteria
exclusion criteria
meant to preserve safety
Define clinical endpoints
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Critical appraisal of journal articles: A guide to evaluating research evidenceDocumento29 pagineCritical appraisal of journal articles: A guide to evaluating research evidencemonique marwick100% (2)
- Ebp - Best Practice For Sedation Protocol in Icu PatientsDocumento32 pagineEbp - Best Practice For Sedation Protocol in Icu Patientsapi-435628975Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14 - The Russian CoreDocumento4 pagineChapter 14 - The Russian CoreCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Trials Types Bias Gold Standard Tissue EngineeringDocumento2 pagineClinical Trials Types Bias Gold Standard Tissue EngineeringCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- What Study Design Should I Choose Caroline SabinDocumento70 pagineWhat Study Design Should I Choose Caroline SabinaurielleNessuna valutazione finora
- Epid Unit 3Documento13 pagineEpid Unit 3api-633127517Nessuna valutazione finora
- RCTs MD PHD - 290514 - 284 - 30426 - v1Documento94 pagineRCTs MD PHD - 290514 - 284 - 30426 - v1Tuhin DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical TrialsDocumento30 pagineClinical TrialsMartina ZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- EBM Prognosis (DR - Osman)Documento33 pagineEBM Prognosis (DR - Osman)Afra HanifiNessuna valutazione finora
- Desain Uji KlinikDocumento49 pagineDesain Uji KlinikAndika AfriansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- JULY 22 2021 - RWE - Michele Jonnson Funk - FINALDocumento21 pagineJULY 22 2021 - RWE - Michele Jonnson Funk - FINALNational Press FoundationNessuna valutazione finora
- Appraising Evidence for Therapy Articles Using PICO, Validity, Applicability & NNTDocumento5 pagineAppraising Evidence for Therapy Articles Using PICO, Validity, Applicability & NNTMike CabotageNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic Research DesignDocumento51 pagineTopic Research Designsultana rajeaNessuna valutazione finora
- (PREVMED) 3.4 Assessing Articles On Therapy - Dr. Sta. MariaDocumento10 pagine(PREVMED) 3.4 Assessing Articles On Therapy - Dr. Sta. MariaCamille Grace CalisaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Expermintal EpidDocumento9 pagineExpermintal EpidHannan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Reliability and ValidityDocumento3 pagineReliability and ValidityAldana TammamNessuna valutazione finora
- Randomized TrialsDocumento45 pagineRandomized TrialsSyed Sanan shahNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Trials 2Documento16 pagineClinical Trials 2Franz SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Evidence Based Dentistry: M. Shalaby BDS, Mendo RcsedDocumento72 pagineEvidence Based Dentistry: M. Shalaby BDS, Mendo Rcsedmshalaby1707Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental epidemiology123Documento16 pagineExperimental epidemiology123ljilffbNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebm TherapyDocumento3 pagineEbm TherapyVivienne MiguelNessuna valutazione finora
- BiostatDocumento17 pagineBiostatNayabNessuna valutazione finora
- DI Lab-6Documento48 pagineDI Lab-6Hossam Mohamed Ahmed ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Desien - by Tahani AlghamdiDocumento41 pagineStudy Desien - by Tahani AlghamdiMian. Shoaib.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 10 CTDocumento29 pagineLecture 10 CTArokiasamy JairishNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Trial Endpoints ExplainedDocumento19 pagineClinical Trial Endpoints ExplainedSAURABH SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Clinical TrialsDocumento19 pagineDesign of Clinical TrialsSonu SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOSTAT MIDTERM: EVALUATING CLINICAL TRIALSDocumento14 pagineBIOSTAT MIDTERM: EVALUATING CLINICAL TRIALSRoh BilalNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Epidemiology[1] 1Documento27 pagineExperimental Epidemiology[1] 1ljilffbNessuna valutazione finora
- Observational Overview and Case Control Studies 2022 Student Handout 3 SlidesDocumento24 pagineObservational Overview and Case Control Studies 2022 Student Handout 3 SlidesEdward HNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Designs in Clinical ResearchDocumento43 pagineStudy Designs in Clinical ResearchCrețu GabrielaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Design MethodologyDocumento26 pagineResearch Design MethodologyTadele DandenaNessuna valutazione finora
- How to Review Therapy Article ResultsDocumento2 pagineHow to Review Therapy Article ResultsWida MarianeNessuna valutazione finora
- Study DesignsDocumento44 pagineStudy DesignsAmir OmairNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental EpidemiologyDocumento23 pagineExperimental EpidemiologyMuqadas BatoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 10 - Experimental Study DesignDocumento33 pagineSession 10 - Experimental Study Designsaurabh chaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- HLTC27Documento28 pagineHLTC27naz harunNessuna valutazione finora
- RCT GuideDocumento29 pagineRCT Guidemvs hardhikNessuna valutazione finora
- Studies, Trials and Scientific Evidence Hierarchy - Lecture 1 - BTDocumento48 pagineStudies, Trials and Scientific Evidence Hierarchy - Lecture 1 - BTblack.hadi194Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study DesignsDocumento43 pagineStudy DesignsPalavalasa toyajakshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Research Studies Aug 1507Documento42 pagineTypes of Research Studies Aug 1507vicky23242526Nessuna valutazione finora
- HTA Methods (Part 3)Documento5 pagineHTA Methods (Part 3)ROJANE LAMENTACNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidemiologic Study DesignsDocumento186 pagineEpidemiologic Study DesignsAmanuel MaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Trials (Mauro Schechter)Documento33 pagineClinical Trials (Mauro Schechter)National Press FoundationNessuna valutazione finora
- Ph-Info Reviwer (Topic 3)Documento9 paginePh-Info Reviwer (Topic 3)Joanne De JoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- RCTdeck_204a170b45eefcfb7613e05208e44e36Documento22 pagineRCTdeck_204a170b45eefcfb7613e05208e44e36saurabh chaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Research Design - 2 - 2021Documento32 pagineClinical Research Design - 2 - 2021Verena NatasiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio StatisticsDocumento21 pagineBio StatisticsanaeshklNessuna valutazione finora
- Evidence Based Practice: DR - Muhammad Rizwan Shs Umt LahoreDocumento30 pagineEvidence Based Practice: DR - Muhammad Rizwan Shs Umt LahoreZulqarnain AbidNessuna valutazione finora
- Pregnancy and Birth: Week 4Documento22 paginePregnancy and Birth: Week 4gonzalezpedro774Nessuna valutazione finora
- HOW TO EVALUATE A RESEARCH PAPERDocumento33 pagineHOW TO EVALUATE A RESEARCH PAPERTarun GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Randomized Controlled TrialDocumento38 pagineRandomized Controlled TrialkundagolNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical TrialDocumento26 pagineClinical TrialCandela NewtonNessuna valutazione finora
- Randomized Controlled TrialsDocumento22 pagineRandomized Controlled TrialsJerome G ThampiNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change and Health 2Documento66 pagineClimate Change and Health 2AngellaNessuna valutazione finora
- (EPI) 5.05 Overview of Analytic Experimental Studies - Dr. JavierDocumento7 pagine(EPI) 5.05 Overview of Analytic Experimental Studies - Dr. JavierJoshua CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 Definitions & Terminologies in Experimental DesignDocumento11 pagineLecture 1 Definitions & Terminologies in Experimental DesignMalvika PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidemiologic Case-Control Study DesignDocumento38 pagineEpidemiologic Case-Control Study DesignZvanakireni Maggie ChikashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Regimental TherapyDocumento39 pagineRegimental Therapyafira khanamNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Types Cohort and Case-Control Studies: Charlotte Glümer Bendix CarstensenDocumento20 pagineStudy Types Cohort and Case-Control Studies: Charlotte Glümer Bendix Carstensenarun_rana_11Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Slim Book of Health Pearls: The Prevention of Medical ErrorsDa EverandThe Slim Book of Health Pearls: The Prevention of Medical ErrorsNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering Day 7Documento3 pagineTissue Engineering Day 7CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering Day 9Documento2 pagineTissue Engineering Day 9CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering Day 8Documento3 pagineTissue Engineering Day 8CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering Day 2Documento3 pagineTissue Engineering Day 2CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering Day 6Documento2 pagineTissue Engineering Day 6CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering - Day 1Documento2 pagineTissue Engineering - Day 1CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering Day 3Documento5 pagineTissue Engineering Day 3CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering Day 7Documento3 pagineTissue Engineering Day 7CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- TE FinalDocumento1 paginaTE FinalCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Southeast Asia QuestionsDocumento4 pagineSoutheast Asia QuestionsCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 Northwestern EuropeDocumento5 pagineChapter 11 Northwestern EuropeCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- TE FinalDocumento1 paginaTE FinalCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering Day 2Documento3 pagineTissue Engineering Day 2CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Engineering - Day 1Documento2 pagineTissue Engineering - Day 1CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- East AsiaDocumento10 pagineEast AsiaCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Strontium 90Documento2 pagineStrontium 90CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Northern EuropeDocumento3 pagineChapter 10 Northern EuropeCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Africa NotesDocumento8 pagineAfrica NotesCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 - Southern EuropeDocumento3 pagineChapter 12 - Southern EuropeCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- HI 2353 Syllabus D 2017 Final-2Documento7 pagineHI 2353 Syllabus D 2017 Final-2CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Eastern MedDocumento6 pagineEastern MedCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- South Asia QuestionsDocumento6 pagineSouth Asia QuestionsCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- CH1010 Exam 1 CoversheetDocumento2 pagineCH1010 Exam 1 CoversheetCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- CH1010-C17-C02 Weekly 5Documento3 pagineCH1010-C17-C02 Weekly 5CaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissection PaperDocumento2 pagineDissection PaperCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Covalent Molecules Preparation QuestionsDocumento1 paginaCovalent Molecules Preparation QuestionsCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Useful Conversions FormulasDocumento1 paginaUseful Conversions FormulasCaitlinKyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set On Food SafetyDocumento4 pagineProblem Set On Food Safetyceresni8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Development of "Mang Kepweng's Lab": A Mobile Android Information On Herbal PlantsDocumento160 pagineDevelopment of "Mang Kepweng's Lab": A Mobile Android Information On Herbal PlantsMac John Teves Poblete100% (3)
- CONCHEM q4 m4 Anticancerdrugs-V3Documento24 pagineCONCHEM q4 m4 Anticancerdrugs-V3NovaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 The Doctor-Patient Relationship - ClinicalKeyDocumento19 pagine1 The Doctor-Patient Relationship - ClinicalKeyLuiz SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Neurological Disorder ReviewDocumento11 pagineFunctional Neurological Disorder Reviewjoao marcelo lealNessuna valutazione finora
- IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVES OPHTHALMOLOGYDocumento24 pagineIMMUNOSUPPRESSIVES OPHTHALMOLOGYAnumeha JindalNessuna valutazione finora
- Feminist Therapy HandoutDocumento10 pagineFeminist Therapy HandoutJamie CanauayNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification and Causes of Anemia ExplainedDocumento30 pagineClassification and Causes of Anemia ExplainedhercolaniumNessuna valutazione finora
- Emma Holliday Surgery Notes - Cornell StyleDocumento299 pagineEmma Holliday Surgery Notes - Cornell StyleBanana MuffinNessuna valutazione finora
- Induction: Guidelines and ChecklistsDocumento18 pagineInduction: Guidelines and ChecklistsNaba majeadNessuna valutazione finora
- Dosage CalculationsDocumento40 pagineDosage CalculationsKate FaustNessuna valutazione finora
- Erotictransference: Alberto StefanaDocumento9 pagineErotictransference: Alberto StefanaRozita RoziniNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Reverse Roleplay Training To Improve The Counselor's Mind SkillsDocumento8 pagineThe Effect of Reverse Roleplay Training To Improve The Counselor's Mind SkillsJournal of Education and LearningNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of Grief and AttachmentDocumento4 pagineTheories of Grief and AttachmentbriraNessuna valutazione finora
- OECD 202 Daphnia Immobilisation TestDocumento12 pagineOECD 202 Daphnia Immobilisation TestŠenan HadžidedićNessuna valutazione finora
- Pruritus in Elderly - Diagnostic and Treatment Approach PDFDocumento25 paginePruritus in Elderly - Diagnostic and Treatment Approach PDFikhlaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical VentilationDocumento108 pagineMechanical Ventilationrizal aljufri100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocumento5 pagineDaftar Pustakaanggun pratissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Why people start and continue smoking cigarettesDocumento7 pagineWhy people start and continue smoking cigarettesJaypee CabinganNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario Unit 7 PDFDocumento3 pagineSolucionario Unit 7 PDFLaura Ortiz MoraisNessuna valutazione finora
- Ward RoutineDocumento103 pagineWard Routinedarling ariwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Studies:: The Purpose of The ResearchDocumento3 pagineClinical Studies:: The Purpose of The ResearchSpac CatalinaNessuna valutazione finora
- We Get Results!: BarreDocumento36 pagineWe Get Results!: BarreCoolerAdsNessuna valutazione finora
- InfertilityDocumento10 pagineInfertilityHarish Labana100% (1)
- Little AlbertDocumento9 pagineLittle Albert20528055 SHAISTA RAHMANNessuna valutazione finora
- Thiamazole PretreatmentDocumento7 pagineThiamazole PretreatmentWendy WijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroscience of Substance Abuse and DependenceDocumento62 pagineNeuroscience of Substance Abuse and Dependencedrkadiyala2100% (1)
- Rrrresidual Ridge ResorbtionDocumento54 pagineRrrresidual Ridge Resorbtionsrinivaskalluri100% (1)
- Neurosurgery Research PaperDocumento7 pagineNeurosurgery Research PaperAhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- ScabiesDocumento6 pagineScabiesJayson ShieldsNessuna valutazione finora




























![Experimental Epidemiology[1] 1](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/719742795/149x198/c335b883fc/1712168237?v=1)