Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Dr. Tandiono Hermanda, SP - KK
Caricato da
Achmad Fahri BaharsyahTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dr. Tandiono Hermanda, SP - KK
Caricato da
Achmad Fahri BaharsyahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
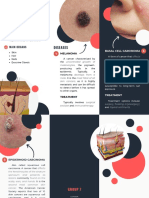
Definition Differential Diagnosis Clinical Patterns of
Facial Melasma
Derived from the Greek word melas to mean
black, Melasma is one of the most common Most authors would generally state
causes of acquired symmetrical centrofacial (63%) predominating over the
hypermelanosis of the face characterized by malar (21%) and the mandibular (16%).
brown to gray brown macules and patches.
In Asia, however, the malar pattern is more
Predilection common than the centrofacial and the
mandibular.
It has predilection for sun exposed areas like
the cheeks, forehead, nose, cutaneous part of In the Philippines, in a study being conducted
upper lip, chin and forearms. at the Research Institute for Tropical Medicine,
centrofacial (59.5%) predominates followed
by malar (32%) and mandibular (8,5%)
Prevalence
As for prevalence, melasma is highest in
1. Drug-induced hyperpigmentation
patients
2. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation due
to: cutaneous LE, skin infections,
Are of Hispanic & East Asian origin
photosensitivity rxns., atopic dermatitis or
Are of Fitzpatrick Skin Types IV-VI
contact dermatitis
Live in areas with intense UV Radiation
3. Exogenous ochronosis
4. Actinic lichen planus
Female: Male Ratio
5. Erythema dischronicum perstans
6. Poikiloderma of Civatte
In the Western hemisphere, Guevarra et al
7. Follicularis faciei et colli
puts a female to male ratio at 9:1.
8. Cutaneous mercury deposits
This is in contrast to the Asian Region as Prof
Types of melasma
Goh puts a higher predominance of women
vs. men having melasma at 21:1.
1. Epidermal Type
Patient Characteristics
suprabasal / and basal layers
of the epidermis
797 patients: 782 women (98.1%)
Most common and most
treatable form
Age
Mean: 44.2 years
2. Dermal Type
Range: 2176 years
milder epidermal
40 years: 287 (36%) hyperpigmentation
> 40 years: 510 (64%) dermal macrophages
Torok H et al. Long term safety and
efficacy of Tri-Luma in patients with less responsive to
melasma of the face. Submitted to J Drugs conventional therapy
Dermatol 2005
Torok H et al. A safe and efficacious 12
months treatment for melasma. Cutis 2005; 3. Mixed Type
75; 57-62 combination of 1 & 2
* Examine under Woods lamp
Etiology cells within the dermis, and the production of
endothelin-1 by keratinocytes
Etiology still remains unclear.
Melasma as a Photocontact Dermatitis
Pathogenesis
Photoallergens are present in
The following factors in the pathogenesis of products used daily in much lower
melasma are concentrations than those used in
1. UV Exposure photo testing
2. Genetic Influence
3. Hormonal changes including Over time, cumulative exposure may
4. Cosmetics reach irradiance test doses.
Some authors do include drugs such as Development of photosensitivity
hydantoin. Ruling out everything, UV (asymptomatic suberythematous
exposure is still the number one factor to dermatitis), by about 30 to 40,
consider. followed by a post-inflammatory facial
hypermelanosis, called MELASMA
Pigmentation Formation Mechanism
B. IRRITATION OR DISEASES
1. UV Exposure
2. Irritation or Diseases The pathogenesis of this skin disorder
3. Hormonal includes at least two major processes. An
increase in melanocyte activity with increased
A. UV EXPOSURE melanogenesis and transfer of melanin
granules to surrounding keratinocytes may
UV Irradiation on Melanocytes occur. In addition, accumulation of
melanophages in the upper dermis as a result
Single exposure to UV of destruction of the basal cell layer in the
Increases size of melanocytes inflamed skin leads to hyperpigmentation
Increases Tyrosinase activity (Tomita, Maeda, & Tagami, 1989). This
Repeated exposure to UV distinction between epidermal versus dermal
Increases the number of Stage involvement is important when considering
IV Melanosome transfer to therapeutic options.
keratinocytes
Increases the number of active C. HORMONAL
melanocytes
Density of melanocytes 2x Hyperpigmentation induced by UVB at
greater in sun exposed sites. the application site of Estradiol
What causes increased melanin production? First report suggesting a direct
relationship between estrogen and
This results from activation of protein kinase melanogenesis in humans
A or C as well as exposure to growth factors
such as basic fibroblast growth factor or Pathogenesis of Melasma :
ultraviolet irradiation. Hypothesis
UV irradiation can lead to an increase in the 1. *GM-CSF ( Granulocyte
number and activity of Melanocortin 1- Macrophage Colony Stimulating
Receptor on melanocytes, the expression of Factor) is a growth factor for human
Propiomelanocortin and its derivative melanocytes involved in UVA- induced
peptides like MSH by keratinocytes and other hypermelanosis
Tyrosinase catalyzes three different reactions reside in the basal layer of the epidermis,
in the biosynthetic pathway of melanin: its dendrites coming in contact with
keratinocytes as far away as the mid stratum
spinosum, to which it transfer melanosomes.
Strategies
Melanin Biosynthetic Pathway
Dr. Thada Piamphongsant in his book
Practical Dermatology gave us simple
2. Increased expression of alpha strategies to treat melasma: To protect the
melanocyte-stimulating hormone in skin from sunlight, to reduce melanocyte
the lesional skin of melasma activity, to remove melanin, inhibit melanin
synthesis and to disrupt melanin granules.
3. Involvement of -MSH in Melasma
IDEAL DEPIGMENTING AGENT
Prognosis
1. Has a potent, rapid and selective bleaching
Idiopathic Melasma usually persists for effect on hyperactivated
several years. melanocytes
2. Carries no short or long-term side-effects
Pregnancy related Melasma persists for 3. Leads to a permanent removal of
several months after delivery undesired pigment.
Melasma related to hormonal changes can
persist for long periods after discontinuation INHIBITION OF MELANIN SYNTHESIS
of the oral contraceptive pills.
I. Before melanin synthesis
Recurrences
Common place after sun exposure. A. Tyrosinase transcription inhibitor
C2-ceramide Tretinoin
Diagnosis
B. Tyrosinase glycosylation inhibitor
Melasma is usually a clinical diagnosis. PaSSO3Ca
Tyrosinase
Tyrosinase, which is a metallo enzyme,
II. During melanin synthesis
requiring copper ions for its activity, is the
starting material and key regulatory enzyme A. Tyrosinase inhibition
that controls the initial chemical reaction Hydroquinone Kojic acid
4-hydroxy- Methyl Gentisate
1. the hydroxylation of tyrosine to 3,4- Anisole
dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) 4-S-CAP & Ellagic Acid
2. the oxidation of DOPA to dopaquinone derivatives
3. the oxidation of 5,6- dihydroxyindole
Arbutin Resveratrol
(DHI) to indole quinin
Aloesin Oxyresveratrol
To understand the strategies of Azelaic acid Licorice
depigmentation it is of outmost importance to Lactic Acid
know the basic knowledge that melanocytes B. Peroxidase inhibition
Methimazole Phenols/Catechols Hydroquinone shown to decrease
Green Tea Topical Indomethacin tyrosinase activity by
90%.
C. Product reduction and ROS scavengers
4 hydroxy-anisole exhibits strong
Ascorbic -Toc melanocytotoxicity
acid 4-S-CAP & capable of reacting with
Ascorbic D, L- TF derivative crucial SH groups and
Acid forming thiol adducts, for
Palmitate example with GSH and
DNA polymerase
D. Inhibitors of Inflammation Induced
Melanogenic Response Arbutin reversible inhibition of
Chamomile melanosomal tyrosinase
Corticosteroids activity rather than
Glabridin suppression of the
Tranexamic Acid expression & synthesis of
tyrosinase
Aloesin a competitive inhibitor on
III. After melanin synthesis DOPA oxidation and as
A. Tyrosinase degradation an non-competitive on
Linoleic acid -Linolenic acid tyrosine hydroxylase
activity.
B. Melanosome transfer Inhibition Azelaic Acid due to its antiproliferative
Serine Niacinamide and cytotoxic effects. As
protease effective as topical
inhibitors hydroquinone
Soybean/milk extracts Kojic Acid more stable than
C. Skin turnover acceleration hydroquinone
Ellagic Acid induced a reversible
Lactic acid Retinoic acid inhibition of melanin
Glycolic acid Linoleic acid synthesis only in only in
UV-activated
melanocytes
Resveratrol anti-inflammatory effects
and inhibits
cyclooxygenase and
hydroperoxidase
functions
Oxyresveratrol A stronger inhibitor than
resveratrol
Licorice Extract Lowered the activities of
T1 & T3 tyrosinase
isoenzymes
Lactic Acid Inhibition of tyrosinase &
tyrosinase activity equal
to Kojic acid
TYROSINASE INHIBITORS
PEROXIDASE INHIBITORS
Methimazole induces mild to moderate Chamomile Inhibits UVB-induced
inhibition of melanization pigmentation, by avoiding
ET-1-induced DNA
Green Tea Epigallocatechin-3-gallate synthesis
(EGCG)- responsible for the Corticosteroids Suppression of cytokines
biochemical or through the inhibition of NF-
pharmacological effects kB activation, which may
explain their short-lived
Topical Acts like a steroid by non- effect with a transient loss
Indomethacin selectively suppressing of color
melanogenesis. Glabridin inhibit cyclooxygenase
activity and superoxide
PRODUCT REDUCTION & ROS anion production
SCAVENGERS
Tranexamic Acid Inhibits prostaglandins by
suppressing epidermal
Inhibits melanin production by pasmin activity
Ascorbic Acid
reducing o- quinones
Prevents UV-induced photo- TYROSINASE DEGRADATION
-Lipoic Acid
oxidative damage
Linoleic Acid Tyrosinase is selectively
targeted by linoleic acid, that
-tocopheryl ferulate inhibits act on the degradation of the
-Tocopherol tyrosinase hydroxylase activity enzyme
in an indirect manner.
A- Linolenic Unsaturated fatty acid
Glutathione cysteinyl reactive thiol group is acid suppress pigmentation;
responsible for many of the correlated with the degree of
antioxidant functions of GSH unsaturation
metabolism
Pycnogenol Several times more powerful
than vitamin E and vitamin C
INHIBITORS OF INFLAMMATION- Melanosome Transfer Inhibition
INDUCED MELANOGENIC Serine Protease inhibit PAR 2 cleavage
Inhibitors and reduce keratinocyte
RESPONSE phagocytosis
Soybean/ Milk soymilk and soymilk-
Extracts derived proteins are able
to inhibit PAR-2
activation and thus
induce skin
depigmentation
Lecithins & the transfer of
Neoglycoproteins melanosomes from
melanocytes to
keratinocytes include
plasma membrane
lectins and their
glycoconjugates.
Niacinamide Reduces cutaneous
pigmentation by
suppressing
melanosome transfer
from melanocytes to
keratinocytes
Depigmenting Agent Safety and
eficacy
Dermatology Update
Makassar 16 april 2017
Dr. Tandiono Hermanda SpKK
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- AJGP 12 2021 Focus Doolan Melasma WEBDocumento6 pagineAJGP 12 2021 Focus Doolan Melasma WEBضحى الغزيNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperpigmentation and Melasma: D Rigopoulos, MD, PHD, S Gregoriou, MD, & A Katsambas, MD, PHDDocumento8 pagineHyperpigmentation and Melasma: D Rigopoulos, MD, PHD, S Gregoriou, MD, & A Katsambas, MD, PHDGÜLSÜM GÜNEŞNessuna valutazione finora
- Focus Doolan MelasmaDocumento7 pagineFocus Doolan MelasmaEnderson MedeirosNessuna valutazione finora
- O Que Deve Ser Considerado No Tratamento Do MelasmaDocumento6 pagineO Que Deve Ser Considerado No Tratamento Do MelasmaTatianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Melasma Insights and PerspectivesDocumento6 pagineMelasma Insights and PerspectivesTatianaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 The Pathogenesis of Melasma and Implications For TreatmentDocumento14 pagine2021 The Pathogenesis of Melasma and Implications For Treatmentyezafig4001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Current Concepts in MelasmaDocumento5 pagineCurrent Concepts in MelasmaNikhil ShrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Melasma: Evangeline B. Handog and Maria Juliet E. MacarayoDocumento17 pagineMelasma: Evangeline B. Handog and Maria Juliet E. Macarayochash75Nessuna valutazione finora
- Current State of Melanoma Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento14 pagineCurrent State of Melanoma Diagnosis and TreatmentAdniana NareswariNessuna valutazione finora
- Todj 3 103Documento8 pagineTodj 3 103Nafiatul MuasyarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatological Reviews - 2022 - Honigman - Differential Diagnosis of Melasma and Hyperpigmentation - RemovedDocumento4 pagineDermatological Reviews - 2022 - Honigman - Differential Diagnosis of Melasma and Hyperpigmentation - Removedmeisya 102018090Nessuna valutazione finora
- D. AtopikDocumento4 pagineD. AtopikDias SeptariiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dic 2021 11 2Documento14 pagineDic 2021 11 2Kopo Sentral MedikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin Pigmentation Disorders: Aetiology, Assessment and Aesthetic Treatment OptionsDocumento6 pagineSkin Pigmentation Disorders: Aetiology, Assessment and Aesthetic Treatment OptionsGÜLSÜM GÜNEŞNessuna valutazione finora
- MelanomaDocumento1 paginaMelanomaapi-518183280Nessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of PigmentationDocumento4 pagineDisorders of Pigmentationعبدالعزيز احمد علي عتشNessuna valutazione finora
- Update PatogenesisDocumento22 pagineUpdate PatogenesisUI KipediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin Toxicity During Breast Irradiation: Pathophysiology and ManagementDocumento5 pagineSkin Toxicity During Breast Irradiation: Pathophysiology and Managementalejandromfunes1749Nessuna valutazione finora
- 19-Article Text-66-1-10-20210506Documento4 pagine19-Article Text-66-1-10-20210506George DragosNessuna valutazione finora
- Artigo Melasma Happy HourDocumento14 pagineArtigo Melasma Happy HourAline Brito Ferreira de CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Melasma: Continuing Education ActivityDocumento9 pagineMelasma: Continuing Education ActivityEldie RahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Tranexamic Acid For MelasmaDocumento7 pagineTranexamic Acid For MelasmaRobertoNessuna valutazione finora
- PCMR 12404Documento14 paginePCMR 12404Riefka Ananda ZulfaNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Access Textbook of General Surgery: Melanoma Jej KrigeDocumento6 pagineOpen Access Textbook of General Surgery: Melanoma Jej KrigeZakkiyah PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Melasma: An Up-to-Date Comprehensive Review: Oluwatobi A. Ogbechie-Godec Nada ElbulukDocumento14 pagineMelasma: An Up-to-Date Comprehensive Review: Oluwatobi A. Ogbechie-Godec Nada ElbulukDra Natalia Maria ZuluagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tratment Melasma PDFDocumento18 pagineTratment Melasma PDFGheavita Chandra DewiNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Options For Management of MelasmaDocumento17 pagineNatural Options For Management of Melasmapuji lestari100% (1)
- Hyperpigmented DisorderDocumento49 pagineHyperpigmented Disorderضبيان فرحانNessuna valutazione finora
- (Krobotova, 2012) PDFDocumento3 pagine(Krobotova, 2012) PDFrosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Disorders of Pigmentation: Elizabeth Arnold Spenceri, MDDocumento9 pagineDisorders of Pigmentation: Elizabeth Arnold Spenceri, MDGÜLSÜM GÜNEŞNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermnet NZ: MelasmaDocumento5 pagineDermnet NZ: MelasmaWin TheinNessuna valutazione finora
- Deka Upl Melasma Ipl Zoccali Et Al 2010Documento9 pagineDeka Upl Melasma Ipl Zoccali Et Al 2010isma drNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 Article 827Documento39 pagine2021 Article 827Ahmad TaufikNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatologica Sinica: Ai-Young LeeDocumento7 pagineDermatologica Sinica: Ai-Young LeeNatta ApucaranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pigmentasi GingivaDocumento11 paginePigmentasi GingivapelangiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hereditary Tumor Syndromes With Skin InvolvementDocumento7 pagineHereditary Tumor Syndromes With Skin Involvementghinan jamilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Keperluan PentingDocumento4 pagineJurnal Keperluan PentingmhdtaufikkNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Skin Disorders in The Elderly WordDocumento7 pagineCommon Skin Disorders in The Elderly WordGhinaSofianaLestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Kulit PDFDocumento4 pagineJurnal Kulit PDFAidarnaWanSariNessuna valutazione finora
- Pigmentary Disorders: DR - Sri Yusfinah Masfah Hanum, SP - KKDocumento35 paginePigmentary Disorders: DR - Sri Yusfinah Masfah Hanum, SP - KKHBrNessuna valutazione finora
- Melasma A Prospective Study of Clinico Etiological and Dermoscopic Pattern in MenDocumento4 pagineMelasma A Prospective Study of Clinico Etiological and Dermoscopic Pattern in MenInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure & Funtion NailsDocumento5 pagineStructure & Funtion NailsrikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neagu 2021Documento40 pagineNeagu 2021meenakshi.r.agrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- 9-05 Skin Tum IDocumento36 pagine9-05 Skin Tum Idiego.guerra.smithNessuna valutazione finora
- Is Dermal Melasma A Phototoxic Reaction? A Case: AbbrevationsDocumento2 pagineIs Dermal Melasma A Phototoxic Reaction? A Case: AbbrevationsTika Renwarin Tua ElNessuna valutazione finora
- Recent Advances in Melasma: Manas Chatterjee, Biju VasudevanDocumento11 pagineRecent Advances in Melasma: Manas Chatterjee, Biju VasudevanFitta PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Meds CapeDocumento14 pagineMeds CapeMeta SakinaNessuna valutazione finora
- ReviewDocumento6 pagineReviewGalery NapolitanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Exogenous Ochronosis Following Hydroquinone For Melasma: V P Zawar & S T MhaskarDocumento3 pagineExogenous Ochronosis Following Hydroquinone For Melasma: V P Zawar & S T MhaskarStella SunurNessuna valutazione finora
- MelasmDocumento22 pagineMelasmLeonardo Alves F AlmeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- PRELIMS - Indd 17 1/18/2018 11:06:42 AMDocumento7 paginePRELIMS - Indd 17 1/18/2018 11:06:42 AMhoang ho LeNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview On Melasma 2376 0427 1000216Documento18 pagineAn Overview On Melasma 2376 0427 1000216dhilaidrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chatterjee2014 Recent Advences in MelasmaDocumento11 pagineChatterjee2014 Recent Advences in MelasmaErnawati HidayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Integumentary System: FunctionDocumento2 pagineIntegumentary System: FunctionAngelynNessuna valutazione finora
- A Novel Cream Formulation Containing Nicotinamide 4% Arbutin 3% Bisabolol 1% and Retinaldehyde 0.05% For Treatment of Epidermal MelasmaDocumento6 pagineA Novel Cream Formulation Containing Nicotinamide 4% Arbutin 3% Bisabolol 1% and Retinaldehyde 0.05% For Treatment of Epidermal MelasmaSebastian RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rosacea 2022Documento10 pagineRosacea 2022ucarecufinochiettoNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study BanilaDocumento5 pagineCase Study BanilaJane A. BanilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Melasma: Treatment StrategyDocumento15 pagineMelasma: Treatment StrategyRiefka Ananda ZulfaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyper-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment, And Related ConditionsDa EverandHyper-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment, And Related ConditionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- The Truth About Melasma: What You Need to Know About the Root Causes of Melasma and How to Treat It HolisticallyDa EverandThe Truth About Melasma: What You Need to Know About the Root Causes of Melasma and How to Treat It HolisticallyNessuna valutazione finora
- DR - Marhaen HardjoDocumento1 paginaDR - Marhaen HardjoAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal DBD 3 2010Documento10 pagineJurnal DBD 3 2010Sukma ArdiNessuna valutazione finora
- 5Documento5 pagine5Achmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Mti PaluDocumento36 pagineMti PaluAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation of Skin: AppearanceDocumento2 paginePost-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation of Skin: AppearanceAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 PDFDocumento5 pagine5 PDFAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Congenital Hypertropic Pyloric Stenosis: ReferatDocumento2 pagineCongenital Hypertropic Pyloric Stenosis: ReferatAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Leaflet 1000 HPKDocumento1 paginaLeaflet 1000 HPKAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- TRICHOMONIASISDocumento25 pagineTRICHOMONIASISAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex Education at SchoolDocumento2 pagineSex Education at SchoolAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Referensi 9Documento6 pagineReferensi 9Achmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex Education at SchoolDocumento2 pagineSex Education at SchoolAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Sat 20 EchoMVD HanzevackiDocumento33 pagineSat 20 EchoMVD HanzevackiPitoAdhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Uk Crigler PDFDocumento4 pagineUk Crigler PDFAchmad Fahri BaharsyahNessuna valutazione finora
- BMC Dermatology: Erythroderma: A Clinical Study of 97 CasesDocumento5 pagineBMC Dermatology: Erythroderma: A Clinical Study of 97 CasesteguhNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemzo M. Marketing Luxury Services. Concepts, Strategy and Practice 2023Documento219 pagineHemzo M. Marketing Luxury Services. Concepts, Strategy and Practice 2023ichigosonix66Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Letter To GodDocumento9 pagineA Letter To GodUjjwal ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Isl Isl StyleguideDocumento50 pagineIsl Isl StyleguideCole FranklinNessuna valutazione finora
- Incremental and TwiceDocumento12 pagineIncremental and TwiceAgung KaryawinaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Condition Monitoring 021711 v3Documento40 pagineCondition Monitoring 021711 v3Kevin_INessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology KROK-1 PDFDocumento121 pagineMicrobiology KROK-1 PDFHimanshu RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cohort 2 Assignment Essay FinalDocumento4 pagineCohort 2 Assignment Essay Finalapi-652640066Nessuna valutazione finora
- Las Grade 7Documento16 pagineLas Grade 7Badeth Ablao67% (3)
- MRL WP1 D ANS 013 06 D1 1 Railway Network Key Elements and Main Sub Systems SpecificationDocumento145 pagineMRL WP1 D ANS 013 06 D1 1 Railway Network Key Elements and Main Sub Systems SpecificationMarc MPNessuna valutazione finora
- Torts and Damages Midterm ReviewerDocumento25 pagineTorts and Damages Midterm ReviewerErika-Anne ThereseNessuna valutazione finora
- Mambisas. Rebel Women in Nineteenth-Century Cuba (Libro Digital)Documento201 pagineMambisas. Rebel Women in Nineteenth-Century Cuba (Libro Digital)SusanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan (Kinder1)Documento3 pagineLesson Plan (Kinder1)MadelNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1 ReteachDocumento2 pagine5.1 ReteachCarlos Pastrana0% (1)
- Eniserver Quickstart EDocumento14 pagineEniserver Quickstart EYESSER CHANNANessuna valutazione finora
- Radiology Developing Technique ChartsDocumento4 pagineRadiology Developing Technique ChartsVarghese NellimoottilNessuna valutazione finora
- The Oldest Man - Made Structures On EarthDocumento5 pagineThe Oldest Man - Made Structures On EarthDoug Hoseck100% (1)
- Krok1 EngDocumento27 pagineKrok1 Engdeekshit dcNessuna valutazione finora
- A REPORT ON MIMO IN WIRELESS APPLICATIONS - FinalDocumento11 pagineA REPORT ON MIMO IN WIRELESS APPLICATIONS - FinalBha RathNessuna valutazione finora
- Changing Views of Tattoos in JapanDocumento14 pagineChanging Views of Tattoos in JapanpanpapogNessuna valutazione finora
- Knee Jerk Libertarianism by Frank Van DunnDocumento9 pagineKnee Jerk Libertarianism by Frank Van DunnLuis Eduardo Mella GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- TNR Evaluation RD 2Documento7 pagineTNR Evaluation RD 2api-302840901Nessuna valutazione finora
- STaD 01 C 4Documento4 pagineSTaD 01 C 4rogeraccuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Food and Medicine Label 1-50Documento11 pagineFood and Medicine Label 1-50Muthia KumalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Delhi Public School, Agra: The HolocaustDocumento3 pagineDelhi Public School, Agra: The Holocaustkrish kanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: Demand, Supply & Market EquilibriumDocumento15 pagineChapter 2: Demand, Supply & Market EquilibriumRaja AfiqahNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Sheet (English) - 8036 Industrial ControlsDocumento44 pagineData Sheet (English) - 8036 Industrial ControlsNabil ShaukatNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Behavior of Closed-Loop Control Systems: 10.1 Block Diagram RepresentationDocumento26 pagineDynamic Behavior of Closed-Loop Control Systems: 10.1 Block Diagram Representationratan_nitNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic Categorization Based On User Behaviour in Random Social Networks Using Firefly AlgorithmDocumento5 pagineTopic Categorization Based On User Behaviour in Random Social Networks Using Firefly AlgorithmBONFRINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Certified Quality Director - CQD SYLLABUSDocumento3 pagineCertified Quality Director - CQD SYLLABUSAnthony Charles ANessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Neural NetworkDocumento16 pagineArtificial Neural NetworkSahil ChopraNessuna valutazione finora