Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Et 6
Caricato da
MuhammadZaydArattKhan0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
38 visualizzazioni3 pagineSingle Phase Transformer exp
Titolo originale
et6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoSingle Phase Transformer exp
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
38 visualizzazioni3 pagineEt 6
Caricato da
MuhammadZaydArattKhanSingle Phase Transformer exp
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
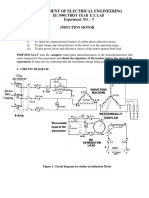
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
EE 19001 FIRST YEAR E.T. LAB
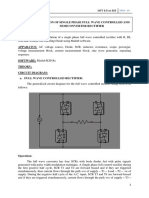
Experiment No. 5
SINGLE PHASE TRANSFORMER
OBJECT:
To determine the efficiency and regulation of a single phase transformer by conducting:
(a) Open Circuit test;
(b) Short Circuit test;
(a) OPEN CIRCUIT TEST:
Fig. 1 Circuit diagram for Open Circuit test of a transformer
INDIVIDUALLY note the complete name-plate data/information of the motor/transformer
that is/are required for the experiment and obtain the signature of the teacher before the
start of the experiment. It must also be confirmed that the fuse/meter ratings being used are
suitable.
PROCEDURE:
i) Note the transformer ratings;
ii) Connect the circuit as shown in Fig- 1 choosing suitable instruments;
iii) Note: supply is connected to the Low-Voltage side of the transformer-under-test;
iv) Set the autotransformer output to zero. Switch on the supply. Increase the voltage,
in steps, up to rated voltage of the LV side and tabulate in Table no. 1 the no load
current, (Primary Current, I1), input power, P1 and the primary & secondary
voltages, V1 and V2, corresponding to each value of the applied voltage.
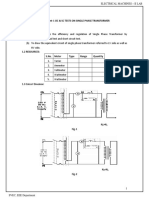
Table no. 1 Open Circuit test
Sl. Primary Voltage V1 Primary Input Power P1 Secondary Voltage V2
No. L. V. side Current I1 (W) H. V. side
(V) (I) (V)
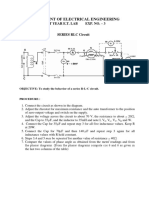
(b) SHORT CIRCUIT TEST:
Fig. 2 Circuit diagram for Short Circuit test of a transformer
PROCEDURE:
i) Connect the circuit as shown in Fig- 2, choosing instruments of ranges suitable to
go up to the rated current.
ii) Set the autotransformer output to zero. Switch on the supply. Increase the voltage,
in steps, slowly, and observe the primary and secondary currents. (Note: The
current flowing through the any of the windings must not exceed their rated
levels.)
iii) Adjust the output voltage of the autotransformer to get secondary short circuit
current of 25%, 50%, 75% and 100% of the rated current of the LV side. Note down
in Table no. 2 the value of the input voltage, V1, primary current (HV side) I1, input
power, P1 and the secondary current, I2 (LV side).
Table no. 2 Short Circuit test
Primary Voltage V1 Primary
Sl. Input Power P1 Secondary Current I2
H. V. side Current I1
No. (w) L. V. side
(v) (I)
RESULTS:
From the observations of the open circuit test:
i) Plot no load current (refer to L.V side) and power input Vs applied voltage on a graph
paper.
ii) Calculate the parallel branch parameters of the equivalent circuit of the
transformer referred to L.V side.
From the observations of the short circuit test:
iii) Calculate the equivalent circuit series parameters of the transformer with respect to
H.V. side.
Finally determine the following:
i) Complete equivalent circuits of the transformer referred to both H.V. & L.V. side.
ii) Efficiency of the Transformer at 25%, 50%, 75%, & 100% of the full load current
at unity p.f.
iii) Full load regulation at power factor of (a) 1.0 (b) 0.8 lagging and (c) 0.8 leading.
iv) A graph showing efficiency at unity p.f. against load current at rated voltage.
v) The maximum efficiency at the load (at unity p.f.) at which the maximum efficiency has
occurred from the graph.
Discussion:
1). Why is OC test carried out by energising LV side?
2). Why is SC test carried by energising side?
3). When is the efficiency maximum for a transformer?
4). Why does no-load losses arise in a transformer?
References:
HUGHES: Electrical Technology.
NAGARTH & KOTHARI: Electrical Machines.
M.G.Say: AC Machine.
A.S.Langsdorf: Theory of Alternating Current Machinery.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Code of Practice for Industrial LightingDocumento33 pagineCode of Practice for Industrial Lightingt_syamprasadNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Aritech CS350 Installation InstructionsDocumento32 pagineAritech CS350 Installation Instructionslesliegilmore100% (1)
- Engineering Laboratory (En19003) Experiment No. 4 (Ee2) : Open Circuit and Short Circuit Test of Single Phase TransformerDocumento4 pagineEngineering Laboratory (En19003) Experiment No. 4 (Ee2) : Open Circuit and Short Circuit Test of Single Phase TransformerEvan JoshyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tests On Single Phase Transformer (Procedure) - Analog Signals, Network and Measurement Laboratory - Electrical Engineering - IIT KHARAGPUR Virtual LabDocumento4 pagineTests On Single Phase Transformer (Procedure) - Analog Signals, Network and Measurement Laboratory - Electrical Engineering - IIT KHARAGPUR Virtual Labvjvijay88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Addis Ababa University Single-Phase Transformer TestDocumento6 pagineAddis Ababa University Single-Phase Transformer TestHanan ShayiboNessuna valutazione finora
- Two-winding transformer testsDocumento7 pagineTwo-winding transformer testsKrishnaa SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Circuit and Short Circuit Test On Single Phase TransformerDocumento5 pagineOpen Circuit and Short Circuit Test On Single Phase TransformerPratap SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Phase TransformerDocumento6 pagineSingle Phase TransformersivaiahjettiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Machines LaboratoryDocumento44 pagineElectric Machines Laboratory11mustafa.mNessuna valutazione finora
- MTE 320 Lab Session #2 Transformer TestsDocumento8 pagineMTE 320 Lab Session #2 Transformer TestsMarc AlfredNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy150 Lab 3 DC Circuit (Sabah)Documento28 paginePhy150 Lab 3 DC Circuit (Sabah)Izz002Nessuna valutazione finora
- UuDocumento48 pagineUuSHYAM SUNDAR OJHA SHYAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment: Title: DC Power Supply Unit: Transformer ObjectiveDocumento14 pagineExperiment: Title: DC Power Supply Unit: Transformer ObjectiveLian Ai Chen100% (1)
- 10eel58 Transformers and Induction Machines LaboratoryDocumento32 pagine10eel58 Transformers and Induction Machines Laboratorysvinod s100% (2)
- BeeeDocumento66 pagineBeeejaydeep gudetiNessuna valutazione finora
- 637 - 2024 Lab-2 TransformersDocumento15 pagine637 - 2024 Lab-2 Transformerseren.alliNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt No 2Documento3 pagineExpt No 2puja maneNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Lab Manuals Final Modified On 12-2-2019Documento67 pagineMachine Lab Manuals Final Modified On 12-2-2019Danyal NasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocumento18 pagineGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & Drivesshashi kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocumento18 pagineGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesVK DNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation of Single Phase Full Wave RectifiersDocumento11 pagineSimulation of Single Phase Full Wave RectifiersHahahNessuna valutazione finora
- BXE Experiment No.4Documento6 pagineBXE Experiment No.4DsgawaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Test TransformerDocumento10 pagineLoad Test TransformerUpinder Pal Singh0% (1)
- E1.08 (2016) Single Phase TransformerDocumento5 pagineE1.08 (2016) Single Phase TransformerDalilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Pw5 Transformer v1Documento5 paginePw5 Transformer v1Hairul Anuar MasrolNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Asia Pacific: Department-EEE Course Code - EEE-204 Course Name - Machine - IDocumento20 pagineUniversity of Asia Pacific: Department-EEE Course Code - EEE-204 Course Name - Machine - InayonNessuna valutazione finora
- Turn Ratio of 1 Phase XFDocumento3 pagineTurn Ratio of 1 Phase XFtusarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase TransformerDocumento6 pagine1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase Transformerchandrakanth100% (3)
- Single Phase Fully Controlled ConverterDocumento10 pagineSingle Phase Fully Controlled ConverterDeepu Chinna75% (4)
- EC Lab Manual (08.407)Documento101 pagineEC Lab Manual (08.407)Assini HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Verification of Circuit TheoremsDocumento35 pagineExperimental Verification of Circuit TheoremsPraveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- NT Lab MannualDocumento31 pagineNT Lab MannualsagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No:01 Name of The Experiment: Observation of No Load and Full Load Characteristics of A Three-PhaseDocumento16 pagineExperiment No:01 Name of The Experiment: Observation of No Load and Full Load Characteristics of A Three-PhaseRupalNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE260 Exp3Documento2 pagineEEE260 Exp3shoiliebuet09Nessuna valutazione finora
- EML Manual (2019 2023)Documento43 pagineEML Manual (2019 2023)Areeba NasirNessuna valutazione finora
- User Manual Machine Lab FullDocumento40 pagineUser Manual Machine Lab FullMd. Sojib KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 3 Buck ConverterDocumento8 pagineExperiment 3 Buck Converterprop_kcpNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab PE1Documento7 pagineLab PE1Yuci IcuyNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE20L - 2 - Expt4Documento10 pagineECE20L - 2 - Expt4Niko de LemosNessuna valutazione finora
- Operational Amplifier CircuitsDocumento44 pagineOperational Amplifier CircuitsIshaku BalamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt2 - Single Phase Uncontrolled (Diode) RectifierDocumento4 pagineExpt2 - Single Phase Uncontrolled (Diode) RectifierORK BUNSOKRAKMUNYNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No 6 Single-Phase CT at Overcurrent: ObjectivesDocumento2 pagineExperiment No 6 Single-Phase CT at Overcurrent: ObjectivesMr Hassan Raza50% (2)
- Operational Amplifiers GuideDocumento4 pagineOperational Amplifiers Guideampalacios1991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer Performance TestDocumento6 pagineTransformer Performance TestVIJAY KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- DOC-20240331-WA0008.Documento8 pagineDOC-20240331-WA0008.syeddanishali43210% (1)
- Simulate DC Circuits & Analyze Voltmeter LoadingDocumento6 pagineSimulate DC Circuits & Analyze Voltmeter Loadingjaswinder singhNessuna valutazione finora
- EE251 Experiment 02Documento5 pagineEE251 Experiment 02Ziad HaliloNessuna valutazione finora
- Choppers and Cyclo ConvertersDocumento12 pagineChoppers and Cyclo ConvertersPaul MatshonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromechanics Lab Manual ExperimentsDocumento25 pagineElectromechanics Lab Manual ExperimentsAnurag ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 4 - ZCD, Comparator With Hysteresis (Schmitt Trigger)Documento5 pagineExp 4 - ZCD, Comparator With Hysteresis (Schmitt Trigger)Sharib JalisNessuna valutazione finora
- ACFrOgCqMBIt9H4SGXoNbXT-GN-A9BhEOWL3VO9AanTPs6DGeV10cYwyieLlBwEA3k36t FjyG68rM9GJHU9s-V3hVT2PJDvCl9ggaCLeBc zAJaHKcNH9hdIuVnO6t0DjQJ3KBhluInkic 29MjDocumento18 pagineACFrOgCqMBIt9H4SGXoNbXT-GN-A9BhEOWL3VO9AanTPs6DGeV10cYwyieLlBwEA3k36t FjyG68rM9GJHU9s-V3hVT2PJDvCl9ggaCLeBc zAJaHKcNH9hdIuVnO6t0DjQJ3KBhluInkic 29MjEzekiel IyamuNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverters Explained: DC to AC Conversion CircuitsDocumento11 pagineInverters Explained: DC to AC Conversion CircuitsSukhpal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual EE851 PDFDocumento20 pagineLab Manual EE851 PDFswarnasrikNessuna valutazione finora
- Eep 203 Electromechanics LaboratoryDocumento65 pagineEep 203 Electromechanics Laboratorysourabh_rohillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Circuits Lab ManualDocumento17 pagineElectrical Circuits Lab ManualShahid AdnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment ManualDocumento17 pagineExperiment ManualKavita BishtNessuna valutazione finora
- NUS EEE DC-DC Converter Lab ReportDocumento19 pagineNUS EEE DC-DC Converter Lab ReportlionNessuna valutazione finora
- Edc Manual RoseDocumento48 pagineEdc Manual RoseRagabindu GuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Valutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coal Used in Thermal Power PlantsDocumento3 pagineCoal Used in Thermal Power PlantsMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- AliahDocumento4 pagineAliahMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Job Offer Letter: (Company Information or On Letterhead)Documento1 paginaSample Job Offer Letter: (Company Information or On Letterhead)Ridwan KingdomNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Design Guidelines For Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Inverters With Damped Resonant Harmonic CompensatorsDocumento10 pagineControl Design Guidelines For Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Inverters With Damped Resonant Harmonic CompensatorsMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- HIT ChecklistDocumento1 paginaHIT ChecklistMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- IBM Chatbot TutorialDocumento29 pagineIBM Chatbot TutorialMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimal P-Q Control of Grid-Connected InvertersDocumento19 pagineOptimal P-Q Control of Grid-Connected InvertersMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Arabic Study GuideDocumento7 pagineArabic Study GuideMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lighting Design Students Guide - CIBSE PDFDocumento133 pagineLighting Design Students Guide - CIBSE PDFsameerray12100% (1)
- Apply HIT Tech Job FormDocumento3 pagineApply HIT Tech Job FormMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Design Guidelines For Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Inverters With Damped Resonant Harmonic CompensatorsDocumento10 pagineControl Design Guidelines For Single-Phase Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Inverters With Damped Resonant Harmonic CompensatorsMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Letters of Maulana Saeed Ahmad Khan Saheb PDFDocumento44 pagineThe Letters of Maulana Saeed Ahmad Khan Saheb PDFMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Economics of Halal IndustryDocumento16 pagineThe Economics of Halal IndustryMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Al Adab Al Mufrad Al BukhariDocumento148 pagineAl Adab Al Mufrad Al BukhariNazar Jo50% (2)
- Commentary on Surah Yusuf Provides Insights into Prophet Yusuf's LifeDocumento54 pagineCommentary on Surah Yusuf Provides Insights into Prophet Yusuf's LifeLuisa de CesareNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electricity PDFDocumento16 pagineBasic Electricity PDFMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- CNC MaterialDocumento1 paginaCNC MaterialMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Temperature Controller PDFDocumento3 pagineTemperature Controller PDFMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt 1Documento4 pagineExpt 1MuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- A.C. FundamentalsDocumento11 pagineA.C. FundamentalsMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Auckland ProspectusDocumento52 pagineUniversity of Auckland ProspectusMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Et 8Documento3 pagineEt 8MuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical MachinesDocumento403 pagineElectrical Machinessasikumar100% (9)
- Facebook Paid Marketing SecretsDocumento22 pagineFacebook Paid Marketing SecretsMuhammadZaydArattKhan100% (1)
- Et 3Documento2 pagineEt 3MuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Shredded Club Workout Log PDFDocumento5 pagineShredded Club Workout Log PDFMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Muslim Entrepreneurship in IrelandDocumento99 pagineMuslim Entrepreneurship in IrelandMuhammadZaydArattKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimal TCSC Placement for Power System StabilityDocumento13 pagineOptimal TCSC Placement for Power System StabilityBelayneh TadesseNessuna valutazione finora
- GJSET - Paper 00078 PDFDocumento7 pagineGJSET - Paper 00078 PDFdennypolariszNessuna valutazione finora
- Pro Slate 12 DisassemblyDocumento7 paginePro Slate 12 DisassemblyDan GriffithsNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor Protection Calculation Tool For SPAM 150 C: User S Manual and Technical DescriptionDocumento28 pagineMotor Protection Calculation Tool For SPAM 150 C: User S Manual and Technical Descriptionhizbi7Nessuna valutazione finora
- 422e 428e Elektro2 PDFDocumento4 pagine422e 428e Elektro2 PDFdenisNessuna valutazione finora
- EE202L Half and Full-wave RectifiersDocumento12 pagineEE202L Half and Full-wave RectifiersM usman UsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating and Automating the HP 8410 Network AnalyzerDocumento10 pagineOperating and Automating the HP 8410 Network AnalyzerkdebesNessuna valutazione finora
- Refraction AssignmentDocumento2 pagineRefraction AssignmentSai Viswanath BommakantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Electric Machines A Primer With MatlabDocumento411 pagineFundamentals of Electric Machines A Primer With MatlabKONANNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Protection (Vol 3 - Application) 2nd Ed (IEEE, 1995) WWDocumento479 paginePower System Protection (Vol 3 - Application) 2nd Ed (IEEE, 1995) WWJamile_P_N100% (8)
- Ba Msf220vu e PDFDocumento8 pagineBa Msf220vu e PDFSyariefNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.boq Ges P-1Documento6 pagine6.boq Ges P-1RoshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Siemens LFE1 Data SheetDocumento14 pagineSiemens LFE1 Data SheetJosé Fabio Lou0% (1)
- Wiring Manual: MeagleDocumento97 pagineWiring Manual: MeagleUdham100% (3)
- Experiment No. 5 Sizing and Selection of Neutral LinkDocumento8 pagineExperiment No. 5 Sizing and Selection of Neutral LinkJude JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Software Engineering: Lab1: Familiarization of Basic Gates and Digital IcsDocumento14 pagineDepartment of Software Engineering: Lab1: Familiarization of Basic Gates and Digital IcsMuhammad RehanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2GCS201088A0030 CLMD ManualDocumento20 pagine2GCS201088A0030 CLMD ManualFlávio MendesNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Fault Analysis in 40 CharactersDocumento147 paginePower System Fault Analysis in 40 CharactersSyafrizal Syafrizal100% (1)
- Wireless Power Transmission Seminar Report 2019Documento35 pagineWireless Power Transmission Seminar Report 2019MAHENDRA KUMAR100% (7)
- Invented by Binnig and Rohrer at IBM in 1981 (Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986)Documento15 pagineInvented by Binnig and Rohrer at IBM in 1981 (Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986)voladri manohar reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Collins 20170425 SolidStateBatteryDocumento28 pagineCollins 20170425 SolidStateBatteryJames RowsellNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiological Effects of Electricity HazardsDocumento26 paginePhysiological Effects of Electricity HazardsMinh Thuan HuynhNessuna valutazione finora
- Jumbo C Saver CatalogueDocumento19 pagineJumbo C Saver CatalogueMuhammad Iqbal ANessuna valutazione finora
- Proficiency Testing Program Status: E26 E23 E35 E39 E11 E45 E42 E43-1 E43-2 E40-2 E40-1 E40-1 E29Documento3 pagineProficiency Testing Program Status: E26 E23 E35 E39 E11 E45 E42 E43-1 E43-2 E40-2 E40-1 E40-1 E29Muttaki HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Zone Sensor LT460 - Installation ManualDocumento16 pagineZone Sensor LT460 - Installation ManualLuis Alberto Huamán MalcaNessuna valutazione finora
- SMK0825FDocumento8 pagineSMK0825FfernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- 30kVA 3 Breaker Maintenance Bypass PanelsDocumento6 pagine30kVA 3 Breaker Maintenance Bypass Panelsdisanty94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mshengeli Issa H.150 323481421Documento20 pagineMshengeli Issa H.150 323481421roger damianNessuna valutazione finora
- General Service Solenoid Valves: FeaturesDocumento4 pagineGeneral Service Solenoid Valves: FeaturesabrahamNessuna valutazione finora