Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Zoology Reviewer 1
Caricato da
Jojit Espiritu100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
433 visualizzazioni3 paginebranches of zoology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentobranches of zoology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
433 visualizzazioni3 pagineZoology Reviewer 1
Caricato da
Jojit Espiritubranches of zoology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
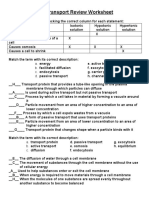
MICROFILAMENT - Lipid soluble substances
- Intermediate filaments OSMOSIS net movement of water through the semi
- Microtubules permeable membrane from regions of high concentration
-cilia and flagella to lower
-cell movement
- Water moves to higher concentration of
CILIA solute
- Short hair like projections FACILITATED DIFFUSION diffusion across the help
- Found In the lining of the trachea of a channel or carrier molecule
- Propel substances on cell surface
- Glucose
FLAGELLA (FLAGELLUM) - Amino acid
- Long tail like projection OSMOTIC PRESSURE required to prevent the
- Provides motility to sperm movement of water into a solution containing solutes
when the solution are separated by a selective permeable
INCLUSIONS membrane
- Metabolically inert accumulations of cell products FILTRATION smaller molecules forced through porous
- Dispensable contingents of the cell membrane
NUCLEUS (control center of the cell) - Hydrostatic pressure important in the
body
- Double membrane enclosed organelle - E.g. molecules leaving the blood
- Spherical/oval capillary
- Control center of the cell
- Contains chromatin, dna, proteins and some rna ACTIVE TRANSPORT carrier molecules transport
- With nuclear pores substances across a membrane from a region of lower to
higher concentration
CELL NUCLUES
e.g. sugars, amino acid, sodium ions, potassium ions
- Nuclear envelope
- Semi permeable membrane SODIUM POTASSIUM PUMP
- Separates nucteoplasm from cytoplasm
- Pumps three sodium out and two
NUCLEOLUS potassium into the cell
- Maintain low intracellular concentration
- Dense collection of rna and proteins of sodium ions
- Site of ribosome production
ENDOCYTOSIS cell engulfs a substance by forming a
CHROMATIN vesicle around the substances:
- Fibers - PINOCYTOSIS taking up fluid by
Hereditary material containing dna endocytosis; cell drinking
Nucleoprotein material of a chromosome - PHAGOCYTOSIS the engulfment of
a particle by a phagocyte or protozoan
TRANSLOCATION OF MATERIALS (movement
into and out of the cell) INVAGINATION an infolding of a layer of tissue to
form a sac-like structure; depression
PASSIVE PROCESSES (PHYSICAL)
EVAGINATION an outpocketing from a hollow
- Require no cellular energy include:
structure
- simple diffusion
- Facilitated diffusion Receptor mediated
- Osmosis
- Filtration - Protein
SIMPLE DIFFUSION movement of substances from Only those who will fit the cell active site is allowed to
regions of higher concentration to lower concentration enter the cell
- Oxygen Receptor ligand
- Carbon dioxide
EXOCYTOSIS reverse of endocytosis
- Substances in a vesicle fuse with a cell
membrane
- Contents release outside the cell
- Reverse of neurotransmitter from nerve
cell
TRANSCYTOSIS
- Endocytosis is followed by exocytosis
- Transports a substance rapidly through
a cell
Ex. HIV crossing a cell
CELL CYCLE series of change on the time it forms to
the time it divides
- Pre apoptotic cell
CYTOPLASMIC DIVISION also known as - Early apoptotic cell
cytokinesis - Late apoptotic cell
CONTROL OF CELL DIVISION Changes include:
- Cell division capacities vary greatly - Blebbing
among cell types - Cell shrinkage
- Skin and blood divide often continually - Nuclear fragmentation
- Chromatin condensation
CHROMOSOME TIPS - Chromosomal DNA fragmentation
- Shorter with each mitosis provide a mitotic clock
- Cell provides a more favorable surface area to
volume relationship
Growth factors and hormones stimulates cell division
- Hormones stimulates mitosis of smooth muscle
in the uterus
CELL DEATH
APOPTOSIS programmed cell death; acts as protective
mechanism
Stages of Apoptosis:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ZoologyDocumento32 pagineZoologyChrisshalyn Sy PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Zoology ReviewerDocumento5 pagineZoology ReviewerYearmeh CandiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ringworms and Skin Fungal Infections Ringworm BushDocumento9 pagineRingworms and Skin Fungal Infections Ringworm Bushjonette carataoNessuna valutazione finora
- The CellDocumento94 pagineThe CellKorean DramaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 What IS SYSTEMATICS Definition Scope and AimsDocumento28 pagine1 What IS SYSTEMATICS Definition Scope and AimsKhara TeanoTan100% (2)
- Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsDocumento11 pagineProkaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsRosemarie OngNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.4 Kingdom FungiDocumento14 pagine11.4 Kingdom Fungiinfinity_justice24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Reviewer Notes PDFDocumento26 pagineBiology Reviewer Notes PDFAntonea50% (2)
- MEDT02 Lesson 1Documento4 pagineMEDT02 Lesson 1SHELDY AGONCILLONessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem Prelims Set A.Documento6 pagineBiochem Prelims Set A.Lymberth BenallaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology ReviewerDocumento4 pagineGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 16 Reproductive SystemDocumento172 pagineCHAPTER 16 Reproductive SystemCindy BelmesNessuna valutazione finora
- SYSTEMATICTAXONOMYmainDocumento26 pagineSYSTEMATICTAXONOMYmainRachel BiagNessuna valutazione finora
- Uts Chapter 4: Psychological Perspective of The SelfDocumento8 pagineUts Chapter 4: Psychological Perspective of The SelfAngeline VegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive System ReviewerDocumento2 pagineDigestive System ReviewerDivino BauzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocumento32 pagineIntroduction To BiochemistryHazel LouNessuna valutazione finora
- REVISED Skeletal System of The Frog 2 (PAOLO)Documento42 pagineREVISED Skeletal System of The Frog 2 (PAOLO)Paolo Naguit100% (2)
- Cell ModificationDocumento2 pagineCell ModificationLovelle Jade RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Bio 2 Reviewer ExamDocumento14 pagineGen Bio 2 Reviewer ExamJamaica RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Botany Reviewer For First Quarter PDFDocumento6 pagineBotany Reviewer For First Quarter PDFDale Maristela Peñalosa100% (3)
- Plant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyDocumento4 paginePlant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Different Division of ZoologyDocumento2 pagineDifferent Division of ZoologyEiann Jasper Longcayana100% (1)
- Biology Module 3Documento21 pagineBiology Module 3Joemmel MagnayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellsummativereview AnswersDocumento5 pagineCellsummativereview Answersapi-422802678Nessuna valutazione finora
- MLS - HISTOLOGY Lec - M1-UNIT1 (Introduction To Histology)Documento16 pagineMLS - HISTOLOGY Lec - M1-UNIT1 (Introduction To Histology)ataraNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Experiment On OsmosisDocumento5 pagineBiochemistry Experiment On OsmosisEna FarillasNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem Module 1 and 2Documento16 pagineBiochem Module 1 and 2almira garciaNessuna valutazione finora
- AnaPhy ReviewerDocumento4 pagineAnaPhy ReviewerIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pee (Module 4) - Aquatic EcosystemDocumento28 paginePee (Module 4) - Aquatic EcosystemToni Rose Hernandez LualhatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocumento13 pagineKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsErjie GerasmioNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Reviewer 1Documento4 paginePhysics Reviewer 1Liel Yap100% (2)
- Phylogeny and SystematicsDocumento11 paginePhylogeny and Systematicszorbax100% (1)
- Zoology LectureDocumento6 pagineZoology LectureMARIA ELIZA LOMUNTADNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Reviewer Final Na TalagaDocumento40 pagineMidterm Reviewer Final Na Talagakhensie khey kirit100% (1)
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocumento28 pagineBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Introduction To Genetics Unit 3Documento19 pagineIntroduction To Genetics Unit 3Vanee Gzz100% (1)
- Stas Finals ReviewerDocumento13 pagineStas Finals ReviewerAkira Anne KreyceNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 3 Structure of A Plant CellDocumento3 pagineActivity 3 Structure of A Plant CellGIRLPLAY G100% (1)
- History of The Philippine Medical Technology Profession and PAMET AjajjajaDocumento3 pagineHistory of The Philippine Medical Technology Profession and PAMET AjajjajaAngela ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 - Intro To SystematicsDocumento20 pagineLecture 2 - Intro To SystematicsBren DonatosNessuna valutazione finora
- Zoology Lecture (Reviewer)Documento4 pagineZoology Lecture (Reviewer)Maria GrasyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Med Lab Science 1: Laboratory SafetyDocumento10 paginePrinciples of Med Lab Science 1: Laboratory SafetyNino Joseph B EnriquezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Perspective of 1st Year BS Pharmacy Students in UPHSDDocumento12 pagineThe Perspective of 1st Year BS Pharmacy Students in UPHSDAn LoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer in General ZoologyDocumento12 pagineReviewer in General ZoologyJasmine Fritz CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Principles of Selecting Animals For Slaughter - Branding Sites in HogsDocumento4 pagineBasic Principles of Selecting Animals For Slaughter - Branding Sites in HogsAlliah MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Physical and Sexual SelfDocumento49 pagineThe Physical and Sexual SelfFuransuhito100% (1)
- Principles of Medical Laboratory Science Practice 1Documento30 paginePrinciples of Medical Laboratory Science Practice 1JACOB AQUINTEYNessuna valutazione finora
- Bot1 General Botany SyllabusDocumento9 pagineBot1 General Botany Syllabusstephen carlosNessuna valutazione finora
- PMLS .Docx 1Documento9 paginePMLS .Docx 1ain't your saintessNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of ZoologyDocumento2 pagineFundamentals of ZoologyJeanine Bianca Lastino100% (3)
- General Biology 1: Prepared By: Pamela May L. Raposa RN, LPTDocumento21 pagineGeneral Biology 1: Prepared By: Pamela May L. Raposa RN, LPTJean Raziel MantesNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories On The Origin of The UniverseDocumento9 pagineTheories On The Origin of The UniverseRek Napmas100% (1)
- 619e4d83b653b Biology Genetics Laboratory Exercise The Central Dogma of GeneticsDocumento10 pagine619e4d83b653b Biology Genetics Laboratory Exercise The Central Dogma of GeneticsKimNessuna valutazione finora
- Evidences of EvolutionDocumento14 pagineEvidences of Evolutionmoonshyne100% (1)
- Group 2 Field Eco Lab Rep 5Documento10 pagineGroup 2 Field Eco Lab Rep 5Theodore FormosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 6 External Stem StructureDocumento3 pagineExercise 6 External Stem StructureKristin Denis CorveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Genbio 1 1ST Grading ReviewerDocumento11 pagineGenbio 1 1ST Grading ReviewerTodo Roki100% (1)
- Pmls Notes (Lesson 5)Documento5 paginePmls Notes (Lesson 5)Eloisa LourdesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 7 Cell MembraneDocumento3 pagineLesson 7 Cell MembraneThea MillanesNessuna valutazione finora
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 NotesDocumento4 pagineGENERAL BIOLOGY 1 NotesAlfie Lyn PedregosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Conditioning: Espiritu, Shannen DorothyDocumento30 pagineConditioning: Espiritu, Shannen DorothyJojit EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- l5 - Different Media and ProcessesDocumento1 paginal5 - Different Media and ProcessesJojit EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Tasks For AquaponicsDocumento1 paginaDaily Tasks For AquaponicsLuis Gerardo Lara AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Build A ComputerDocumento52 pagineHow To Build A ComputersankopubNessuna valutazione finora
- LIST of SET-UP FabricatorsDocumento8 pagineLIST of SET-UP FabricatorsJojit EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Reasons Not To Skimp On SleepDocumento2 pagine10 Reasons Not To Skimp On SleepJojit EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- A Physical Absorption Process For The Capture of Co From Co - Rich Natural Gas StreamsDocumento6 pagineA Physical Absorption Process For The Capture of Co From Co - Rich Natural Gas StreamssinhleprovietNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor SizesDocumento10 pagineMotor SizesBruno KosNessuna valutazione finora
- Fick's Laws of DiffusionDocumento6 pagineFick's Laws of DiffusionEn CsakNessuna valutazione finora
- DCC Technicals For All MachinesDocumento38 pagineDCC Technicals For All MachinesKareem TrainmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure QuizDocumento7 pagineAtomic Structure QuizJohanna Martin LipioNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Intervention Material in Earth Science (Atmosphere)Documento13 pagineStrategic Intervention Material in Earth Science (Atmosphere)ira era71% (7)
- Analysis Done in LPILE Plus v5.0Documento9 pagineAnalysis Done in LPILE Plus v5.0Afzal WaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- 047-Itp For Oxygen Lines Fabrication and Installation PDFDocumento28 pagine047-Itp For Oxygen Lines Fabrication and Installation PDFKöksal PatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Flavor ChemistryDocumento1 paginaFlavor ChemistryMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Sumitomo PDFDocumento20 pagineSumitomo PDF何家銘Nessuna valutazione finora
- Food Chemistry: Da-Wei Li, Ming Zhu, Yun-Dong Shao, Zhe Shen, Chen-Chen Weng, Wei-Dong YanDocumento9 pagineFood Chemistry: Da-Wei Li, Ming Zhu, Yun-Dong Shao, Zhe Shen, Chen-Chen Weng, Wei-Dong YanTrần Hồ Hữu LuânNessuna valutazione finora
- Che 381 N 2011915200Documento3 pagineChe 381 N 2011915200trienphatphanNessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate of Analysis of Goat MilkDocumento1 paginaCertificate of Analysis of Goat MilkBoonyi Unai100% (2)
- Notice: Final Decision On A No Migration Petition Reissuance: Underground Injection Control Program Et Al., Veolia ES Technical Solutions, L.L.C., Port Arthur, TXDocumento1 paginaNotice: Final Decision On A No Migration Petition Reissuance: Underground Injection Control Program Et Al., Veolia ES Technical Solutions, L.L.C., Port Arthur, TXJustia.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical DosingDocumento3 pagineChemical DosingMasoodyNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulation and Evaluation of Gel Containing Econazole NitrateDocumento9 pagineFormulation and Evaluation of Gel Containing Econazole NitrateSaiesh PhaldesaiNessuna valutazione finora
- HAZOP For Blasting ChamberDocumento5 pagineHAZOP For Blasting Chambersepri manerson sinaga0% (1)
- Astm 578Documento5 pagineAstm 578ASWANTH T S100% (1)
- Group Two'S Seminar Work: Topic: Enzyme Regulation Allosteric Regulation and Models OutlineDocumento13 pagineGroup Two'S Seminar Work: Topic: Enzyme Regulation Allosteric Regulation and Models OutlineOluwasegun ModupeNessuna valutazione finora
- 28 Amazing Benefits and Uses For Hydrogen Peroxide Wake Up WorldDocumento6 pagine28 Amazing Benefits and Uses For Hydrogen Peroxide Wake Up WorldStephen AdamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Au in C - HutchingsDocumento8 pagineAu in C - HutchingsLuis TolentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- QuietR Rotary Duct Liner Product Data SheetDocumento2 pagineQuietR Rotary Duct Liner Product Data SheetJorge SandovalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Process Calculations: Autumn 2021Documento23 pagineChemical Process Calculations: Autumn 2021Ujjwal AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Van't HoffDocumento6 pagineVan't HoffKrisna PamungkasNessuna valutazione finora
- Texture 160203172810Documento28 pagineTexture 160203172810NainaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bitumat TopsealDocumento5 pagineBitumat TopsealsathiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Salinity EOR 2012Documento41 pagineLow Salinity EOR 2012Pondok Huda100% (2)
- Pengaruh Suhu Terhadap Laju ReaksiDocumento22 paginePengaruh Suhu Terhadap Laju Reaksiayrajiu alexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Saudi Aramco Steam Turbine Training CourseDocumento45 pagineSaudi Aramco Steam Turbine Training CourseDhananjay B K100% (2)
- JUM RF Technical DocumentDocumento2 pagineJUM RF Technical DocumentMaxime HullmanNessuna valutazione finora