Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Gains From Trade PDF
Caricato da
IncubusTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Gains From Trade PDF
Caricato da
IncubusCopyright:
Formati disponibili
GAINS
FROM
TRADE
Country
A
Country
B
World
Produc0on
Food
Clothing
Food
Clothing
Food
Clothing
1.
Autarky
(No
Trade)
Produc'on
2
units
2
units
3
units
1
unit
5
units
3
units
Consump'on
2
units
2
units
3
units
1
unit
5
units
3
units
2.
Specializa0on
and
Trade
Produc'on
0
units
4
units
6
units
0
units
6
units
4
units
Consump'on
3
units
2
units
3
units
2
units
6
units
4
units
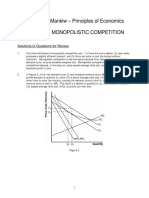
Assume
that
we
have
two
countries
Country
A
and
Country
B.
Each
country
has
a
xed
amount
of
resources,
which
it
allocate
to
the
produc'on
of
food
and
clothing,
and
a
xed
technology.
Consider
the
autarky
case,
wherein
each
country
is
self-sucient
and
does
not
engage
in
trade.
In
this
scenario,
each
country
is
able
to
consume
only
what
it
produces.
Country
A
has
a
compara've
advantage
in
producing
clothing.
It
needs
to
give
up
only
1
unit
of
food
to
produce
1
unit
of
clothing,
whereas
Country
B
must
give
up
3
units
of
food
to
produce
1
unit
of
clothing.
Country
B
has
a
compara've
advantage
in
producing
food.
It
needs
to
give
up
only
1
unit
of
clothing
to
produce
3
units
of
food,
whereas
Country
A
has
to
give
up
1
unit
of
clothing
to
produce
1
unit
of
food.
Both
countries
can
benet
if
each
country
specializes
in
the
product
at
which
it
has
a
compara've
advantage
and
opens
itself
up
to
trade.
Country
A
can
specialize
in
the
produc'on
of
clothing,
while
Country
B
can
specialize
in
the
produc'on
of
food.
With
specializa'on,
Country
A
can
produce
4
units
of
clothing,
whereas
Country
B
can
produce
6
Laza'n & Medrano, 2015
units of food.
If the countries trade, Country A can export 2 units of clothing to Country B in exchange for
3 units of food, while Country B can export 3 units of food to Country A in exchange for 2
units of clothing. Thus, Country A needs only to give up 1 unit of clothing to gain 1.5 units of
food, and Country B can now gain 2 units of clothing from giving up 3 units of food.
Hence, specializa'on and trade enable the two countries to consume beyond their PPFs.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Batman Animated (1998) (Scan) (Stacalkas)Documento169 pagineBatman Animated (1998) (Scan) (Stacalkas)João Gabriel Zó100% (11)
- Propht William Marrion Branham Vist IndiaDocumento68 paginePropht William Marrion Branham Vist IndiaJoshuva Daniel86% (7)
- Construction Agreement SimpleDocumento3 pagineConstruction Agreement Simpleben_23100% (4)
- ESS Revision Session 2 - Topics 5-8 & P1 - 2Documento54 pagineESS Revision Session 2 - Topics 5-8 & P1 - 2jinLNessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Engineering Interview QuestionsDocumento19 pagineCivil Engineering Interview QuestionsSrivardhanSrbNessuna valutazione finora
- History of KoreaDocumento9 pagineHistory of KoreaIncubusNessuna valutazione finora
- The Basics of Foreign Trade and Exchange - Economic Education..Documento30 pagineThe Basics of Foreign Trade and Exchange - Economic Education..William FanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual For Economics 11th Edition David ColanderDocumento9 pagineSolution Manual For Economics 11th Edition David ColanderSuzanneSantosscoq100% (37)
- Complete Cocker Spaniel Guide 009 PDFDocumento119 pagineComplete Cocker Spaniel Guide 009 PDFElmo RNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 Science - 2Documento5 pagineGrade 10 Science - 2Nenia Claire Mondarte CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Posthumanism Cyborgs and Interconnected Bodies by Jon BaileyDocumento59 paginePosthumanism Cyborgs and Interconnected Bodies by Jon BaileyDavid García MonteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Task Performance Valeros Roeul GDocumento6 pagineTask Performance Valeros Roeul GAnthony Gili100% (3)
- 1 Intro To Society, Community and EducationDocumento29 pagine1 Intro To Society, Community and EducationMaria Michelle A. Helar100% (1)
- Harlem Renaissance LiteratureDocumento2 pagineHarlem Renaissance LiteratureSylvia Danis100% (1)
- Cooking Oils and Smoke Points - What To Know and How To Choose The Right Cooking Oil - 2020 - MasterClassDocumento7 pagineCooking Oils and Smoke Points - What To Know and How To Choose The Right Cooking Oil - 2020 - MasterClasschumbefredNessuna valutazione finora
- 5) Activity 4.4 Comparative Advantage - Print OutDocumento2 pagine5) Activity 4.4 Comparative Advantage - Print Outbjm2jcNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics 10th Edition Colander Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento30 pagineMacroeconomics 10th Edition Colander Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcarlarodriquezajbns100% (10)
- 2.7 Tackle The Test: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocumento4 pagine2.7 Tackle The Test: Multiple-Choice QuestionsAntonia Tascon Z.Nessuna valutazione finora
- King's College Secondary 7A (2008-2009) Economics AssignmentDocumento2 pagineKing's College Secondary 7A (2008-2009) Economics Assignmentapi-3728615Nessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To The Questions in Quiz 3Documento1 paginaAnswers To The Questions in Quiz 3Ahmad ZarwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set #2 - The Gains From Trade: This Document Contains 7 PagesDocumento4 pagineProblem Set #2 - The Gains From Trade: This Document Contains 7 PagesJBNessuna valutazione finora
- The Benefits of Trade: GlossaryDocumento9 pagineThe Benefits of Trade: GlossarySara PattersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Trade Concepts and Theories: Rosalia Tan Benoza Faculty, CBMADocumento27 pagineTrade Concepts and Theories: Rosalia Tan Benoza Faculty, CBMAAngelica ArcenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ 12.1 PDFDocumento6 pagineEcon 12.1 PDFpeter wongNessuna valutazione finora
- File - 20210823 - 100510 - Chapter 03Documento6 pagineFile - 20210823 - 100510 - Chapter 03Trãi NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercises Week1 2011Documento5 pagineExercises Week1 2011Ardit MucaNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 4.4: Comparative Advantage: © 2015, BFW/ Worth Publishers Section 1 Teacher's Resource MaterialsDocumento3 pagineWorksheet 4.4: Comparative Advantage: © 2015, BFW/ Worth Publishers Section 1 Teacher's Resource MaterialsJoaquin Sebastian Albuja CalderonNessuna valutazione finora
- International Trade HandoutDocumento2 pagineInternational Trade HandoutIsabella Cuyco GalangNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers - Sheet 1 International Eco PDFDocumento5 pagineAnswers - Sheet 1 International Eco PDFMaryam MagdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise Chapter 7 - S62755Documento3 pagineExercise Chapter 7 - S62755Aqila Syakirah IVNessuna valutazione finora
- Model A: Damietta University Faculty of Commerce Department of Economics 2 Semester Final Exam 2020/ 2021Documento6 pagineModel A: Damietta University Faculty of Commerce Department of Economics 2 Semester Final Exam 2020/ 2021Testo PartNessuna valutazione finora
- ch05sg PDFDocumento8 paginech05sg PDFSpinosaursusNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento2 pagineLecture 1Md Rayhan UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics 9th Edition Colander Solutions ManualDocumento8 pagineMacroeconomics 9th Edition Colander Solutions Manualgrainnematthew7cr3xy100% (31)
- Macroeconomics 9th Edition Colander Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento29 pagineMacroeconomics 9th Edition Colander Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcaibache0x60h100% (13)
- Interdependence and The Gains From TradeDocumento41 pagineInterdependence and The Gains From TradeJohn ChristaphNessuna valutazione finora
- IT ch.1 B.2023Documento2 pagineIT ch.1 B.2023Amgad ElshamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 4.4 Comparative AdvantageDocumento3 pagineWorksheet 4.4 Comparative AdvantageAnderson WuNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 EFM Class 3 Macro IDocumento28 pagine4 EFM Class 3 Macro ISiu EricNessuna valutazione finora
- Latihan SLM SPLTV Billing 240116 053053Documento2 pagineLatihan SLM SPLTV Billing 240116 053053dearmissporterNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 9: International Trade: Case & Fair (Ch. 33)Documento18 pagineTopic 9: International Trade: Case & Fair (Ch. 33)chan xianNessuna valutazione finora
- International TradeDocumento10 pagineInternational Traderijanadeem2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative AdvantageDocumento2 pagineComparative AdvantageSergio BorromeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Aplicatii Avantaje Absolute Si ComparativeDocumento5 pagineAplicatii Avantaje Absolute Si ComparativeTeodora NicuNessuna valutazione finora
- ECONS02Documento9 pagineECONS02ART.ASNNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Border Issues: Nguyễn Hồng Thắng, UEHDocumento67 pagineCross Border Issues: Nguyễn Hồng Thắng, UEHDUNG NGUYỄN THỊ TRUNGNessuna valutazione finora
- EconDocumento7 pagineEconKhaera Aaliyah OntarNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions To Study Guide QuestionsDocumento43 pagineSolutions To Study Guide Questionsmohammad ali tayaraniNessuna valutazione finora
- EC351 International Trade Class 1 Comparative Advantage and The Ricardian ModelDocumento2 pagineEC351 International Trade Class 1 Comparative Advantage and The Ricardian ModelHhhNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Economics: Principles of Economics: Interdependence and The Gains From TradeDocumento34 pagineBusiness Economics: Principles of Economics: Interdependence and The Gains From TradeMiquel PuertasNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Kit E2 Answers EngDocumento6 pagineExam Kit E2 Answers EngWasangLiNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 1Documento7 pagineQuiz 1Ngọc DiệpNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Final Ch.1.2023Documento16 pagineIT Final Ch.1.2023Amgad ElshamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Global Trade and Investment: Part - 1Documento28 pagineUnit 1 Global Trade and Investment: Part - 1Chintan RamnaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ 102 Spring 2004 Practice Questions 1 I. ConceptsDocumento4 pagineEcon 102 Spring 2004 Practice Questions 1 I. ConceptsjuniorNessuna valutazione finora
- TradeDocumento12 pagineTradejuliekonpesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 International Trade TheoryDocumento5 pagineChapter 2 International Trade TheoryTrần Hải AnhNessuna valutazione finora
- Trisha Paola Lagura - Activity No. 4 How Globalized Is Your HomeDocumento2 pagineTrisha Paola Lagura - Activity No. 4 How Globalized Is Your HomeTrisha Paola LaguraNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3 Part 2Documento20 pagineCH 3 Part 2Heyam NaimNessuna valutazione finora
- Table 2.5 SolutionDocumento3 pagineTable 2.5 SolutionMarghoob AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- First Partial Sep 2020 2Documento4 pagineFirst Partial Sep 2020 2Rafael MaldonadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Princ Ch03 StudenthandoutDocumento10 paginePrinc Ch03 StudenthandoutPham Viet HungNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 - Intl Trade Theory - FinalDocumento119 pagineModule 4 - Intl Trade Theory - FinalArham Kumar JainBD21064Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento41 pagineChapter 3sbjafri0Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Why Nations TradeDocumento17 pagine2 Why Nations TradeJuliana Tovar saavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- TB 14ComparativeAdvantageTradeDocumento8 pagineTB 14ComparativeAdvantageTradeLe Vu nguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- ASSIGNMENTDocumento4 pagineASSIGNMENTzainabkhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Trends in World TradeDocumento40 pagineTrends in World TradeSourabh BhattacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Absolute Comparative AdvantageDocumento4 pagineAbsolute Comparative AdvantageAtakilti TadesseNessuna valutazione finora
- International TradeDocumento48 pagineInternational TradeBonny writerNessuna valutazione finora
- ETP Economics HW1 Solution Fall 2014Documento7 pagineETP Economics HW1 Solution Fall 2014Musa RemonNessuna valutazione finora
- An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of NationsDa EverandAn Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of NationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic MarketingDocumento8 pagineStrategic MarketingIncubus100% (1)
- Ans. Practice Set 1Documento2 pagineAns. Practice Set 1IncubusNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - What Is MarketingDocumento33 pagineModule 1 - What Is MarketingIncubusNessuna valutazione finora
- Inventory Models ExercisesDocumento3 pagineInventory Models ExercisesIncubus100% (1)
- Practice Set 2 Econ 100.1 60 Points Due Tuesday in ClassDocumento2 paginePractice Set 2 Econ 100.1 60 Points Due Tuesday in ClassIncubusNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Analysis: Download Free Books atDocumento36 pagineCost Analysis: Download Free Books atIncubusNessuna valutazione finora
- Man Kiw Chapter 17 Solutions ReviewDocumento2 pagineMan Kiw Chapter 17 Solutions ReviewIncubusNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Theories of Social Stratification: OutlineDocumento40 pagineModern Theories of Social Stratification: OutlineAnonymous I5fRKHrnWNessuna valutazione finora
- Buttons and Ceramic Pieces Made in Different Places Not Just in The Philippines ButDocumento2 pagineButtons and Ceramic Pieces Made in Different Places Not Just in The Philippines ButIncubusNessuna valutazione finora
- Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddin IIIDocumento14 pagineSultan Omar Ali Saifuddin IIISekolah Menengah Rimba100% (3)
- Bike Chasis DesignDocumento7 pagineBike Chasis Designparth sarthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Acuity: Opthalmology CEX StepsDocumento5 pagineVisual Acuity: Opthalmology CEX StepsVanessa HermioneNessuna valutazione finora
- Bon JourDocumento15 pagineBon JourNikolinaJamicic0% (1)
- Lunch Hour Meetings: Kiwanis Mission:: - Officers & Directors, 2018-2019Documento2 pagineLunch Hour Meetings: Kiwanis Mission:: - Officers & Directors, 2018-2019Kiwanis Club of WaycrossNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Notified Bodies Under Directive - 93-42 EEC Medical DevicesDocumento332 pagineList of Notified Bodies Under Directive - 93-42 EEC Medical DevicesJamal MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Anglicisms in TranslationDocumento63 pagineAnglicisms in TranslationZhuka GumbaridzeNessuna valutazione finora
- Bimetallic ZN and HF On Silica Catalysts For The Conversion of Ethanol To 1,3-ButadieneDocumento10 pagineBimetallic ZN and HF On Silica Catalysts For The Conversion of Ethanol To 1,3-ButadieneTalitha AdhyaksantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Question 1 (1 Point) : SavedDocumento31 pagineQuestion 1 (1 Point) : SavedCates TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Lab Report GerminationDocumento10 pagineBio Lab Report GerminationOli Damaskova100% (4)
- LECTURE 1.COMMUNICATION PROCESSES, PRINCIPLES, AND ETHICS - Ver 2Documento24 pagineLECTURE 1.COMMUNICATION PROCESSES, PRINCIPLES, AND ETHICS - Ver 2Trixia Nicole De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- EFL Listeners' Strategy Development and Listening Problems: A Process-Based StudyDocumento22 pagineEFL Listeners' Strategy Development and Listening Problems: A Process-Based StudyCom DigfulNessuna valutazione finora
- Surge Protectionfor ACMachineryDocumento8 pagineSurge Protectionfor ACMachineryvyroreiNessuna valutazione finora
- Intimate TemporalitiesDocumento12 pagineIntimate TemporalitiesmittentenNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Networking ProjectDocumento11 pagineSocial Networking Projectapi-463256826Nessuna valutazione finora
- Air Microbiology 2018 - IswDocumento26 pagineAir Microbiology 2018 - IswOktalia Suci AnggraeniNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.4 Marketing Arithmetic For Business AnalysisDocumento12 pagine5.4 Marketing Arithmetic For Business AnalysisashNessuna valutazione finora
- Bakery Management SynopsisDocumento13 pagineBakery Management SynopsisSHiVaM KRNessuna valutazione finora