Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Clasificación de Productos para El Cuidado de La Piel
Caricato da
PapaindoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Clasificación de Productos para El Cuidado de La Piel
Caricato da
PapaindoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SKIN PREPARATION PRODUCTS 27
TABLE 1.9. Classification of Skin-Care Products
Product Purpose
Baby preparations
Oils and lotions Cleansing, soothing
Diaper-rash Products Prevention, cure drying
Powders Drying
Foot preparations
Antifungals Antiinfective
Emollients Soothing, crack-prevention
Powders Drying
Facial preparations
Lotions and creams Smoothing, protecting, rejuvenating
Body preparations
Lotions and creams Smoothing, protecting
Oils Smoothing, protecting
Powders Drying
Hand preparations
Lotions and creams Smoothing, protecting
Gels Antichapping
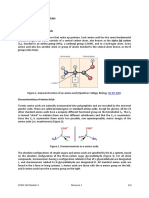
The flexibility of isolated stratum corneum is dependent on the presence of water: dry
stratum corneum is brittle and difficult to stretch or bend. Thus, any increase in the water
content of skin is believed to improve the skin quality.
The ability to moisturize the stratum corneum has also been claimed for the presence
of certain hydrophilic polymers, for example, guar hydroxypropyl trimonium chloride
[65497-29-2], on the skin. By far the most popular way to moisturize skin is with humec-
tants, some of which are listed in Table 1.10. It is claimed that humectants attract water
from the environment and thereby provide moisture to the skin.
Studies of the interactions between water and the lipid constituents of the stratum cor-
neum suggest that the supply of water per se is not responsible for skin quality and condi-
tion. Water vapor from lower layers provides a constant supply of moisture to the
epidermis. Instead, the ability of the skin to retain the moisture is critical, and this ability
depends on the lipid lamellar bilayers that occupy the spaces between the cells of the
stratum corneum (36, 37).
In the United States, products claimed to reverse or alleviate the stigmata of facial skin
aging are considered drugs. Claims for improvement of fine wrinkling, mottled hyperpig-
mentation, and roughness associated with photodamage, on the part of products contain-
ing all trans-retinoic acid [302-79-4], have received some favorable comments from
regulatory advisory panels. Other approaches for antiaging products are based on desqua-
mation by a-hydroxyacids, for example, lactic acid [50-21-5]. Finally, a number of sub-
stances, such as hyaluronic acid [9004-61-9] and collagen [9007-34-5], have been
claimed to improve the appearance of wrinkled skin.
The amounts and types of lipids used in skin-care products control their application
properties. Methods for assessing these characteristics using expert panelists have been
described (38).
The ability of skin-care products to supply moisture to the skin remains in question. In
the United States, however, the OTC panel has sanctioned the use of skin-protectant
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Homemade Shampoo: a Step by Step Guide for Making Homemade Shampoo and Beauty Products Using Special Organic Recipes: Homemade Body Care & Beauty, #2Da EverandHomemade Shampoo: a Step by Step Guide for Making Homemade Shampoo and Beauty Products Using Special Organic Recipes: Homemade Body Care & Beauty, #2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmetic Preparations Cosmetic PreparationsDocumento24 pagineCosmetic Preparations Cosmetic PreparationsKevin Garala0% (1)
- 1.0 Chapter OneDocumento48 pagine1.0 Chapter OneAnonymous KokV9JBCNessuna valutazione finora
- Moisturizing Agents: Murooj Abudabaat MPH PCR Faculty of Pharmacy Hebron UniversityDocumento23 pagineMoisturizing Agents: Murooj Abudabaat MPH PCR Faculty of Pharmacy Hebron UniversityMurooj Abu Dabaat0% (1)
- The Science Behind Skincare MoisurizersDocumento7 pagineThe Science Behind Skincare MoisurizersNguyễn Thanh Bình100% (1)
- Understanding Moisturizers and Their Clinical BenefitsDocumento4 pagineUnderstanding Moisturizers and Their Clinical BenefitsTaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Acting On Skin and Mucous Membrane, Lecture Notes-Dr - Jibachha SahDocumento38 pagineDrug Acting On Skin and Mucous Membrane, Lecture Notes-Dr - Jibachha Sahjibachha sahNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Humectants Moisturizing Agents in CosmeticsDocumento1 pagina13 Humectants Moisturizing Agents in CosmeticsAat Prayoga MuhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Urea - The Gold Standard Ingredient For Emollients?Documento7 pagineUrea - The Gold Standard Ingredient For Emollients?Dany DidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cold CreamDocumento9 pagineCold CreamArumm88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Engineering Department College of Technology University of San Agustin Iloilo CityDocumento23 pagineChemical Engineering Department College of Technology University of San Agustin Iloilo CityReynee Shaira Lamprea MatulacNessuna valutazione finora
- SkinDocumento7 pagineSkinStefan LucianNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of Moisturizers in Addressing Various Kinds of Dermatitis - A ReviewDocumento16 pagineThe Role of Moisturizers in Addressing Various Kinds of Dermatitis - A ReviewlolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmetic PresentationDocumento8 pagineCosmetic PresentationBonheur GladysNessuna valutazione finora
- Hariom - Rajput - Pragya - Sharma - A1312010116Documento16 pagineHariom - Rajput - Pragya - Sharma - A1312010116Hariom RajputNessuna valutazione finora
- Moisturizers Practical Approach To Product SelectionDocumento12 pagineMoisturizers Practical Approach To Product SelectionkurutalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin Care ProductsDocumento26 pagineSkin Care ProductsRhea Jugnalia100% (1)
- A Review On:-Formulation and Development of Face WashDocumento8 pagineA Review On:-Formulation and Development of Face WashSuci PurwaningsihNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review On:-Formulation and Development of Face WashDocumento8 pagineA Review On:-Formulation and Development of Face WashSuci PurwaningsihNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmeceuticals For The Skin An OverviewDocumento6 pagineCosmeceuticals For The Skin An Overviewmigaloooo334Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hand & Body: Lotion BarDocumento12 pagineHand & Body: Lotion BarmjacobmarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento57 pagineChapter 5Adugnaw Biks100% (1)
- Definition of CosmeticsDocumento10 pagineDefinition of CosmeticsJai MurugeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian J DermatolDocumento10 pagineIndian J DermatolSalamahNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 AshLand Product ListDocumento34 pagine6 AshLand Product Listkhoachi100% (1)
- Cold Cream USPDocumento4 pagineCold Cream USPRon OlegarioNessuna valutazione finora
- CREAMDocumento7 pagineCREAMrajan mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Sciences: Skin Cream As Topical Drug Delivery System: A ReviewDocumento6 pagineJournal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Sciences: Skin Cream As Topical Drug Delivery System: A ReviewDr-Md Abul BarkatNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmeceuticals 131120231920 Phpapp01Documento39 pagineCosmeceuticals 131120231920 Phpapp01Ania AniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Moisture Wor XDocumento1 paginaMoisture Wor Xdoc_abdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Emollients Jun 23Documento6 pagineEmollients Jun 23Thu HươngNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmeceuticals: What's Real, What's NotDocumento9 pagineCosmeceuticals: What's Real, What's NotVita BūdvytėNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulation and Invitroevaluation of Poly Herbal Anti Aging Face CreamDocumento17 pagineFormulation and Invitroevaluation of Poly Herbal Anti Aging Face CreamVaishali PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- New Treatments For Restoring Impaired Epidermal Barrier Permeability: Skin Barrier Repair CreamsDocumento4 pagineNew Treatments For Restoring Impaired Epidermal Barrier Permeability: Skin Barrier Repair CreamsElaine MedeirosNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Article MDocumento8 pagineNotes Article MNarmathaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmetics Before CitationDocumento6 pagineCosmetics Before CitationzobryNessuna valutazione finora
- Moisturizers - The Slippery RoadDocumento11 pagineMoisturizers - The Slippery RoadSam NickNessuna valutazione finora
- The Science Behind Skin Care: Cleansers: Zoe Diana Draelos MDDocumento7 pagineThe Science Behind Skin Care: Cleansers: Zoe Diana Draelos MDkinayungNessuna valutazione finora
- Moisturizers For Skin Diseases New Insights - Peter LioDocumento4 pagineMoisturizers For Skin Diseases New Insights - Peter Liomakam sNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Products Ils TemplateDocumento6 pagineConsumer Products Ils TemplatepangantihonjohnearlNessuna valutazione finora
- Cream and CosmeticsDocumento2 pagineCream and CosmeticsTerdy ViloriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Beauty & Skincare DocketDocumento125 pagineBeauty & Skincare DocketShrutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cleansers and Their Role in Various Dermatological DisordersDocumento7 pagineCleansers and Their Role in Various Dermatological DisordersHarish KakraniNessuna valutazione finora
- L2 Classification CosmeticsDocumento23 pagineL2 Classification CosmeticsshiennamariedarishNessuna valutazione finora
- English For Cosmetologists: What Is Aloe ?Documento16 pagineEnglish For Cosmetologists: What Is Aloe ?Anonymous erkddV1fyDNessuna valutazione finora
- Components of Olay Ultra Moisture Outlast Beauty BarDocumento7 pagineComponents of Olay Ultra Moisture Outlast Beauty Barlara candilosasNessuna valutazione finora
- 2320-Article Text-8384-1-10-20231011Documento12 pagine2320-Article Text-8384-1-10-20231011anggawiryabonnieNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin WhiteningDocumento6 pagineSkin WhiteningAneyo OyekolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaceutical Preparation and Evaluation of Cold CreamDocumento7 paginePharmaceutical Preparation and Evaluation of Cold CreamInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Related LiteratureDocumento7 pagineRelated Literaturecappuccino muffinNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviw Paper of RenukaDocumento12 pagineReviw Paper of RenukaRenuka DeviNessuna valutazione finora
- Review On Polyherbal Facial ScrubDocumento21 pagineReview On Polyherbal Facial ScrubPratiksha khadkeNessuna valutazione finora
- TFDocumento2 pagineTFBryleNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Topical Dermatologic Therapy - Dermatologic Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocumento6 paginePrinciples of Topical Dermatologic Therapy - Dermatologic Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionFantahunNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi KrimDocumento20 pagineMateri Krimsiti salma haniyyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiacne Herbal CreamDocumento11 pagineAntiacne Herbal CreamIJRASETPublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Astri GentsDocumento15 pagineAstri GentsJerilee SoCute WattsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmeceutic ALS: Cosmetics and PharmaceuticalsDocumento19 pagineCosmeceutic ALS: Cosmetics and PharmaceuticalssowjanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Creams and Ointments, What's The Difference, Which Is BestDocumento3 pagineCreams and Ointments, What's The Difference, Which Is Bestchrizela20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formulation and Evaluation of Herbo-Mineral FacialDocumento3 pagineFormulation and Evaluation of Herbo-Mineral FacialMuhammad FazilNessuna valutazione finora
- MRL Benzylpenicillin - Procaine BenzylpenicillinDocumento1 paginaMRL Benzylpenicillin - Procaine BenzylpenicillinPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual de Residuos 2017Documento1 paginaManual de Residuos 2017PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- MRL ClosantelDocumento1 paginaMRL ClosantelPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- MRL TestosteroneDocumento1 paginaMRL TestosteronePapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- MRL - AmoxicillinDocumento1 paginaMRL - AmoxicillinPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS JCX31Documento9 pagineMSDS JCX31PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- MRL NeomycinDocumento1 paginaMRL NeomycinPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- MRL ColistinDocumento1 paginaMRL ColistinPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- ALBENDAZOLE (Anthelmintic Agent) LMRDocumento1 paginaALBENDAZOLE (Anthelmintic Agent) LMRPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- LT1170X1 - REV E - FD1500 Series - English PDFDocumento62 pagineLT1170X1 - REV E - FD1500 Series - English PDFPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- LT1170X1 - REV E - FD1500 Series - English PDFDocumento62 pagineLT1170X1 - REV E - FD1500 Series - English PDFPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- MANUAL MUFLA FD1500 EnglishDocumento56 pagineMANUAL MUFLA FD1500 EnglishPapaindo67% (3)
- FDA - Approved Drugs For Oral - Non - Lactanting CattleDocumento1 paginaFDA - Approved Drugs For Oral - Non - Lactanting CattlePapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tiempos de RetiroDocumento41 pagineTiempos de RetiroHéctor Martínez VelázquezNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple and Rapid Determination of ATP, ADP and AMPDocumento4 pagineA Simple and Rapid Determination of ATP, ADP and AMPPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Usp 2008 P 2 Supplement 3Documento166 pagineUsp 2008 P 2 Supplement 3EstiPramestiningtyas100% (1)
- CARBADOXDocumento20 pagineCARBADOXPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A53 PDFDocumento22 pagineAstm A53 PDFhiugarNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A53 PDFDocumento22 pagineAstm A53 PDFhiugarNessuna valutazione finora
- SulfonamidesDocumento9 pagineSulfonamidesPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trimethoprim 7Documento1 paginaTrimethoprim 7PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- SulfonamidesDocumento18 pagineSulfonamidesPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- SPECTINOMYCINDocumento5 pagineSPECTINOMYCINPapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trimethoprim 6Documento1 paginaTrimethoprim 6PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trimethoprim 3Documento1 paginaTrimethoprim 3PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trimethoprim 8Documento1 paginaTrimethoprim 8PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trimethoprim 4Documento1 paginaTrimethoprim 4PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trimethoprim 5Documento1 paginaTrimethoprim 5PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trimethoprim 2Documento1 paginaTrimethoprim 2PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trimethoprim 1Documento1 paginaTrimethoprim 1PapaindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Phoenicia University Department of Engineering Faculty of Petroleum Engineering Petroleum Fluid Properties Laboratory PENG212L Dean Stark Plug SizeDocumento14 paginePhoenicia University Department of Engineering Faculty of Petroleum Engineering Petroleum Fluid Properties Laboratory PENG212L Dean Stark Plug SizeEmanuelta NaibahoNessuna valutazione finora
- Q A CoatingDocumento29 pagineQ A CoatingHau Le100% (1)
- 120131-Perforated Sheet Metal - IPRF - CD PDFDocumento239 pagine120131-Perforated Sheet Metal - IPRF - CD PDFMisagh100% (1)
- Swagelok Ball ValveDocumento4 pagineSwagelok Ball ValvePhornlert WanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Note 2. Familiarization With ApparatusesDocumento28 pagineLecture Note 2. Familiarization With ApparatuseskkkNessuna valutazione finora
- REACHDocumento16 pagineREACHTranVinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Tea Pest and Pesticide Use in NepalDocumento13 pagineCommon Tea Pest and Pesticide Use in Nepalkhadka80% (5)
- Advanced Construction MaterialsDocumento37 pagineAdvanced Construction MaterialsZara AliNessuna valutazione finora
- HSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 19Documento5 pagineHSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 19Ali HaidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Copper Sulphate Penta HydrateDocumento2 pagineCopper Sulphate Penta HydrateBLi'H'Abiee100% (1)
- DEC Kapton FN DatasheetDocumento3 pagineDEC Kapton FN DatasheetfabrikaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 160 Module 3 Resource 1Documento9 pagineCHEM 160 Module 3 Resource 1meyaNessuna valutazione finora
- PaintDocumento28 paginePaintAnna KateurinaNessuna valutazione finora
- SDS ARC Ethylene Oxide 2013-04-01Documento17 pagineSDS ARC Ethylene Oxide 2013-04-01Van SotNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Santo Tomas: Williamson Ether Synthesis: Preparation of PhenacetinDocumento4 pagineUniversity of Santo Tomas: Williamson Ether Synthesis: Preparation of PhenacetinMarilou MagdalagaNessuna valutazione finora
- PO - Lapox P 62Documento2 paginePO - Lapox P 62alpesh.samruddhigroupNessuna valutazione finora
- DrillingDocumento21 pagineDrillingNabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Procedure For Proper Chemical StorageDocumento5 pagineProcedure For Proper Chemical StorageDavish GurriahNessuna valutazione finora
- 17.salt Aluminium Sulphate 3Documento3 pagine17.salt Aluminium Sulphate 3Sarthika GaulkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Quadrajet Service Manual 1981Documento46 pagineQuadrajet Service Manual 1981Garrett Ross100% (4)
- Fire Pump AccessoriesDocumento23 pagineFire Pump AccessoriesMuhammad ArslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assay of Aspirin PDFDocumento9 pagineAssay of Aspirin PDFyeleidispNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study of Vessel As Per BS 4994Documento4 pagineCase Study of Vessel As Per BS 4994nagarathinam82100% (1)
- E&DPlan 0506Documento44 pagineE&DPlan 0506Farhan ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation of Tin TetraiodideDocumento2 paginePreparation of Tin Tetraiodidestudent_4_evaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculo Consumo Teorico WaukeshaDocumento8 pagineCalculo Consumo Teorico Waukeshahugohelo100% (1)
- Sistema de Lubricacion Emd 645Documento21 pagineSistema de Lubricacion Emd 645Adriana Rojas VerasteguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepartion of 4 Bromo 2 ChloroacetanildeDocumento11 paginePrepartion of 4 Bromo 2 ChloroacetanildeAmil Patel0% (1)
- Failure of 9FA Gas Turbine Compressor - A Unique Experience. D.Nandi (AGM-OS/GT) K.R.C.Murty (AGM-OS/GT)Documento10 pagineFailure of 9FA Gas Turbine Compressor - A Unique Experience. D.Nandi (AGM-OS/GT) K.R.C.Murty (AGM-OS/GT)Thanapaet RittirutNessuna valutazione finora
- Sikacrete Fire Protection Mortar 201102Documento12 pagineSikacrete Fire Protection Mortar 201102maximgh100% (1)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarDa EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (351)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellDa EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNessuna valutazione finora
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyDa EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Eat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessDa EverandEat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessNessuna valutazione finora
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonDa EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (33)
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietDa EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookDa EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Grit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeDa EverandGrit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- The Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyDa EverandThe Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthDa EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeDa EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Da EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (378)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeDa EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- The Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodDa EverandThe Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomDa EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsDa EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (49)
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainDa EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (38)
- Molecules of Emotion: Why You Feel the Way You FeelDa EverandMolecules of Emotion: Why You Feel the Way You FeelValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (128)
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingDa EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouDa EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouNessuna valutazione finora
- The Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthDa EverandThe Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthNessuna valutazione finora
- The Volumetrics Eating Plan: Techniques and Recipes for Feeling Full on Fewer CaloriesDa EverandThe Volumetrics Eating Plan: Techniques and Recipes for Feeling Full on Fewer CaloriesNessuna valutazione finora
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellDa EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (81)
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleDa EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- How to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeDa EverandHow to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- How Not to Die by Michael Greger MD, Gene Stone - Book Summary: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseDa EverandHow Not to Die by Michael Greger MD, Gene Stone - Book Summary: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (84)
- Glucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingDa EverandGlucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (61)