Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Vertebrates Nervous System Muscles Cardiac Muscle
Caricato da
Christopher MasseyTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Vertebrates Nervous System Muscles Cardiac Muscle
Caricato da
Christopher MasseyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tessa McCann
5-9-11
Biology G
Week 30
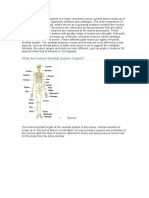
A. Name the functions of the skeletal system and of the muscular system.
The muscular system is the anatomical system of a species that allows it to move. The muscular
system in vertebrates is controlled through the nervous system, although some muscles (such as
the cardiac muscle) can be completely autonomous.
B. Define the following terms: ossification: is when the cartilage is replaced by hard deposits of calcium
phosphate and stretchy collagen, the two main components of bone. It takes about 20 years for this process
to be completed.
growth plate: plates consist of columns of multiplying cartilage cells that grow in length, and then change
into hard, mineralized bone.
osteocyte: which carry nutrients and waste products to and from blood vessels in the bone.
osteoblast: which make new bone and help repair damage.
osteoclast: which break down bone and help to sculpt and shape it.
bone marrow: inside many of our bones is where most of the blood cells flowing through our bodies are
made.
periosteum: the bone's membrane covering, to its inner parts.
cartilage: a flexible, rubbery substance in our joints, supports bones and protects them where they rub
against each other.
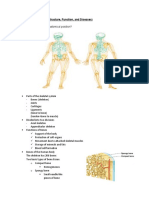
C. Name and describe the 2 types of muscle be sure to include their functions.
Skeletal muscle is attached to bone, mostly in the legs, arms, abdomen, chest, neck, and face.
Skeletal muscles are called striated because they are made up of fibers that have horizontal stripes
when viewed under a microscope. These muscles hold the skeleton together, give the body shape,
and help it with everyday movements.
Cardiac muscle is found in the heart. The walls of the heart's chambers are composed almost
entirely of muscle fibers. Cardiac muscle is also an involuntary type of muscle. Its rhythmic,
powerful contractions force blood out of the heart as it beats.
D. Compare and contrast tendons and ligaments.
Tough, cord-like tissues called tendons, which allow the muscles to pull on bones. Bones are
fastened to other bones by long, fibrous straps called ligaments.
E. What is a joint? Name and describe the 3 types.
Joints allow our bodies to move in many ways. Some joints open and close like a hinge (such as
knees and elbows), whereas others allow for more complicated movement a shoulder or hip
joint, for example, allows for backward, forward, sideways, and rotating movement.
Hinge joints allow movement in one direction, as seen in the knees and elbows.
Pivot joints allow a rotating or twisting motion, like that of the head moving from side to side. Ball-
and-socket joints allow the greatest freedom of movement. The hips and shoulders have this type
of joint, in which the round end of a long bone fits into the hollow of another bone.
F. Name and describe the 3 types of freely movable joints.
Hinge joints allow movement in one direction, as seen in the knees and elbows.
Pivot joints allow a rotating or twisting motion, like that of the head moving from side to side. Ball-
and-socket joints allow the greatest freedom of movement. The hips and shoulders have this type
of joint, in which the round end of a long bone fits into the hollow of another bone.
G. Make a chart listing the symptoms, treatment, and causes of: fracture, osteoporosis, and scoliosis.
Fracture Osteoporosis Scoliosis
Symptoms Bones break easily, and which causes the spine
the spine sometimes to curve too much.
begins to crumble and
collapse
Treatment After a bone fracture, Exercising regularly and three to five people out
new bone cells fill the getting plenty of calcium of 1,000 have the
gap and repair the when you're a kid and condition.. The condition
break. Applying a strong teen can prevent or can be hereditary, so a
plaster cast, which delay you from getting person who has scoliosis
keeps the bone in the osteoporosis later in life. often has family
correct position until it members who have it.
heals, is the usual
treatment.
Causes when a bone breaks; it bone tissue becomes a certain amount of
may crack, snap, or brittle, thin, and spongy curvature is necessary
shatter. for people to move and
walk properly.
H. Distinguish between a sprain and a strain be sure to discuss treatment of each injury.
Strains occur when a muscle or tendon is overstretched. Sprains are an overstretching or a partial
tear of the ligaments. Strains usually happen when a person takes part in a strenuous activity
when the muscles haven't properly warmed up or the muscle is not used to the activity (such as a
new sport or playing a familiar sport after a long break). Sprains, on the other hand, are usually the
result of an injury, such as twisting an ankle or knee. Both strains and sprains are common in teens
because they're active and still growing.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Anatomy of The BoneDocumento12 pagineAnatomy of The BoneOpen Sea Ever CapturedNessuna valutazione finora
- Bone FractureDocumento13 pagineBone FractureShiehan Mae ForroNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer The Following QuestionsDocumento8 pagineAnswer The Following QuestionsHussain HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer The Following QuestionsDocumento8 pagineAnswer The Following QuestionsHussain HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Fracture Open or Closed. If The Skin Over The Break Is DisruptedDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Fracture Open or Closed. If The Skin Over The Break Is DisruptedfayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of FractureDocumento6 pagineTypes of FractureChristine Marie Barce MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- BoneDocumento25 pagineBoneDark EnoughNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Bone Fractures and Clinical ManifestationsDocumento10 pagineTypes of Bone Fractures and Clinical ManifestationsFryam BellsNessuna valutazione finora
- Fractures BasicDocumento10 pagineFractures BasicAnish BishwakarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Human Skeletal System Organs?: 1. BonesDocumento5 pagineWhat Are Human Skeletal System Organs?: 1. BonesKiara Denise TamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Skeletal System (Structure, Function, and Diseases)Documento8 pagineA. Skeletal System (Structure, Function, and Diseases)Kim LiatNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair: Break A LegDocumento8 pagineLesson 3: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair: Break A LegEduardo SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninDocumento36 pagineIntroduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninArlene Ferrer100% (1)
- The Fascinating World of The Skeletal SystemDocumento13 pagineThe Fascinating World of The Skeletal SystemREBECCA MITRANessuna valutazione finora
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento11 pagineThe Musculoskeletal SystemJenielynFerreraArriolaNessuna valutazione finora
- All About FractureDocumento59 pagineAll About FractureJohn John Torres100% (1)
- CHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemDocumento4 pagineCHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemArlen Joy V. AMPARONessuna valutazione finora
- Fracture Fixation and ArthroplastyDocumento39 pagineFracture Fixation and Arthroplastyzony khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathological FracturesDocumento48 paginePathological FracturesHafidah RakhmatinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Movement (Human Skeleton)Documento65 pagineMovement (Human Skeleton)Keyondre McBeanNessuna valutazione finora
- See 78267 Chapter 06Documento40 pagineSee 78267 Chapter 06SmileCaturasNessuna valutazione finora
- (ANA) - Online ActivityDocumento4 pagine(ANA) - Online ActivityJomari ManalansanNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Musculo-Skeletal System Grade 6Documento23 pagineHuman Musculo-Skeletal System Grade 6Natividad LozaritoNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal - Break A LegDocumento9 pagineSkeletal - Break A LegShannon SandersNessuna valutazione finora
- Orthopedic NursingDocumento19 pagineOrthopedic NursingDa BondadNessuna valutazione finora
- The Skeletal System HDocumento23 pagineThe Skeletal System HRajorshi MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Documento13 pagineLecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Muhammad FaizNessuna valutazione finora
- A Bone Fracture... ZarateDocumento8 pagineA Bone Fracture... ZarateRose SalviejoNessuna valutazione finora
- تروما محاضرة 1Documento58 pagineتروما محاضرة 1202003339Nessuna valutazione finora
- FRACTUREDocumento8 pagineFRACTUREJee Ho SohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Four Lesson 1.1A Your Skeletal SystemDocumento5 pagineScience Four Lesson 1.1A Your Skeletal SystemSara GNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal SystemDocumento20 pagineSkeletal SystemAshish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bone Fracture PaperDocumento12 pagineBone Fracture Paperdiah100% (1)
- SkeletAl SystemDocumento18 pagineSkeletAl SystemYen BailadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninJoem DagusanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninJoem DagusanNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal Pathology NotesDocumento20 pagineMusculoskeletal Pathology Notesdinia fitrianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal Pathology Notes PDFDocumento20 pagineMusculoskeletal Pathology Notes PDFvevestephaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of FracturesDocumento10 pagineTypes of Fracturesazeencancer2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal System (2) - 2Documento71 pagineSkeletal System (2) - 2alazarademe797Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal SystemDocumento4 pagineSkeletal Systemapi-26052253Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Skeletal SystemDocumento52 pagineThe Skeletal SystemrizzamaearancesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Body in Sport - LearnerDocumento31 pagineThe Body in Sport - Learnerplumbs23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bone FracturesDocumento22 pagineBone FracturesSamantha EllaineNessuna valutazione finora
- The Skeletal SystemDocumento5 pagineThe Skeletal SystemMika SaldañaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Skeletal System LessonDocumento20 pagineThe Skeletal System Lessony72qx9vcj7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal and Articular SystemDocumento14 pagineSkeletal and Articular SystemG4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENessuna valutazione finora
- Bones AnatomyDocumento17 pagineBones AnatomyMonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principals of Anatomy Energy Systems IncDocumento224 paginePrincipals of Anatomy Energy Systems Inckevinramirezzz365Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal System Functions and Bone ClassificationDocumento7 pagineSkeletal System Functions and Bone ClassificationKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2: Anatomy - The Skeleton: in This Module You Will LearnDocumento10 pagineModule 2: Anatomy - The Skeleton: in This Module You Will LearnMarkus KaltenhauserNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal System: CartilageDocumento20 pagineSkeletal System: CartilageGrace PascualNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal SystemDocumento13 pagineSkeletal Systemariolajose5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer Zoo LecDocumento27 pagineReviewer Zoo LecayeyedumpNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal System E-Unit Reading - Use As Additional Resource - Same Objectives As PPT PDFDocumento5 pagineSkeletal System E-Unit Reading - Use As Additional Resource - Same Objectives As PPT PDFMacks Oy IINessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal DisorderDocumento7 pagineSkeletal Disorderhxqf25mbvvNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Skeletal SystemDocumento32 pagine02 Skeletal SystemHarshika KDGNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento12 pagineChapter 3Deolita BadiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Skeletal SystemDocumento48 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The Skeletal SystemAster fayisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Article 3Documento2 pagineArticle 3Christopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- English 102 Portfolio Submitted by Tessa Mccann Presented To L. Hemmings Spring Quarter 2015 New England Institute of TechnologyDocumento8 pagineEnglish 102 Portfolio Submitted by Tessa Mccann Presented To L. Hemmings Spring Quarter 2015 New England Institute of TechnologyChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocab ListDocumento4 pagineVocab ListChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 9 10 Religion HomeworkDocumento1 pagina9 9 10 Religion HomeworkChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Exercise 3.3 Not FinishedDocumento1 paginaJournal Exercise 3.3 Not FinishedChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- SociologyDocumento2 pagineSociologyChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Religion Week 6Documento1 paginaReligion Week 6Christopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- 11-29-10 ReligionDocumento1 pagina11-29-10 ReligionChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology HMWK Week 10Documento3 pagineBiology HMWK Week 10Christopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- CWI 7 B WebQuest WorksheetDocumento2 pagineCWI 7 B WebQuest WorksheetChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of TechnologyDocumento1 paginaImpact of TechnologyChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Exercise 2.6.odtDocumento1 paginaJournal Exercise 2.6.odtChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Self Assessment 2Documento5 pagineSelf Assessment 2Christopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Please WorkDocumento1 paginaPlease WorkChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Impressionist Post ImpressionistDocumento1 paginaImpressionist Post ImpressionistChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Alice in WonderlandDocumento1 paginaAlice in WonderlandChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Listening EvaluationDocumento2 pagineListening EvaluationChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lion and ShepherdDocumento1 paginaLion and ShepherdChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Exercise 1.2Documento1 paginaJournal Exercise 1.2Christopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- DorothyDocumento1 paginaDorothyChristopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled 1Documento1 paginaUntitled 1Christopher MasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- CDI-500 Specialized Crime Investigation and Legal MedicineDocumento20 pagineCDI-500 Specialized Crime Investigation and Legal MedicineCherry Len FaroniloNessuna valutazione finora
- Demo DLLDocumento2 pagineDemo DLLArlene Diokno100% (1)
- JMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Education Department City of Koronadal, South CotabatoDocumento13 pagineJMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Education Department City of Koronadal, South CotabatoNestor Gerotape DiosanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Pathophysiology of Hypoxemia and HypoxiaDocumento15 pagineOverview of Pathophysiology of Hypoxemia and HypoxiaMARY ANN CAGATANNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating and Installation Guide For The Digital Instrument: Motoscope Tiny / Speedster / VintageDocumento12 pagineOperating and Installation Guide For The Digital Instrument: Motoscope Tiny / Speedster / Vintagepeter timmermansNessuna valutazione finora
- SXMDocumento7 pagineSXMLi NearNessuna valutazione finora
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris - Narrative TextDocumento21 pagineMakalah Bahasa Inggris - Narrative TextFenny KartikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pick The Gender of Your Baby - Free EditionDocumento26 paginePick The Gender of Your Baby - Free EditionAlicia Adrianti0% (1)
- Australian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1Documento32 pagineAustralian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1binoyrajcrNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Guide For PpeDocumento45 pagineSolution Guide For PpeTrek Apostol57% (7)
- DG350 ManualDocumento17 pagineDG350 ManualCareergamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Manual: EQ1030T47D-820 Light Commercial TruckDocumento175 pagineService Manual: EQ1030T47D-820 Light Commercial TruckYonny ColqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminal BlockDocumento12 pagineTerminal BlockAlmaforNessuna valutazione finora
- Turbine Stress EvaluatorDocumento14 pagineTurbine Stress EvaluatorsumitNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 SM PDFDocumento14 pagine1 SM PDFSiti HamsyiahNessuna valutazione finora
- @MedicalBooksStore 2016 AntibioticDocumento349 pagine@MedicalBooksStore 2016 Antibioticant bee100% (1)
- Design of Steel BeamsDocumento4 pagineDesign of Steel BeamsSankalp LamaNessuna valutazione finora
- The LM393Documento2 pagineThe LM393mayron vasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer preference towards branded milk: A comparative analysis of Verka milk and Amul milkDocumento12 pagineConsumer preference towards branded milk: A comparative analysis of Verka milk and Amul milkBhawna RehanNessuna valutazione finora
- Shop Math PDFDocumento29 pagineShop Math PDFKen LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- I Wanna Be Yours Arctic Monkeys Love SongDocumento3 pagineI Wanna Be Yours Arctic Monkeys Love SongAndréia E NiltonNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Check Valves SlamDocumento2 pagineWhy Check Valves SlamBramJanssen76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blues, Rock and Americana MixDocumento4 pagineBlues, Rock and Americana MixLuis CrownNessuna valutazione finora
- FHM Espana 2010 12 PDFDocumento2 pagineFHM Espana 2010 12 PDFBrandenNessuna valutazione finora
- January 2010 QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocumento23 pagineJanuary 2010 QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-Levelpraveen alwisNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 F.Y.B.Sc - Chemistry PDFDocumento22 pagine11 F.Y.B.Sc - Chemistry PDFmalini PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics: Minimum Level Learning MaterialDocumento60 pagineMathematics: Minimum Level Learning MaterialTusar SardarNessuna valutazione finora
- Finite Element Simplified Fatigue AnalysisDocumento4 pagineFinite Element Simplified Fatigue AnalysisJin Hwan KimNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S2214860417301148 Main PDFDocumento16 pagine1 s2.0 S2214860417301148 Main PDFQuy Hoang KimNessuna valutazione finora
- LirikDocumento537 pagineLirikMuhamad Iqbal FahmiNessuna valutazione finora