Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Silicon Slides Topic 4
Caricato da
AhmadSalimAlwohoush0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
10 visualizzazioni7 pagineSolar system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoSolar system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
10 visualizzazioni7 pagineSilicon Slides Topic 4
Caricato da
AhmadSalimAlwohoushSolar system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 7
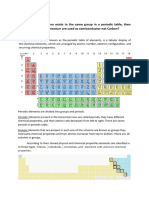
Properties
Silicon has atomic number
14
Each atom has 14 electrons:
10 are tightly bound to the
nucleus
4 are valence electrons (crucial
for PV story).
Pure Silicon is intrinsic
semiconductor
Neither an insulator nor a
conductor
Electrons and Holes
Electron 1 is free
It leaves a broken bond (dotted line)
and left with a positive charge (hole).
Electron 2 is free from somewhere
else.
It may jump into the vacant spot left
by 1, so that the positive charge (hole)
moves.
Motion of Electrons and holes is
random.
A pure Silicon, even in strong sunlight,
cannot generate electricity and become a
Solar Cell.
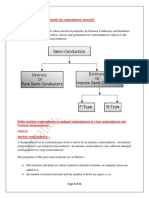
p-Type Silicon
Boron is added
Boron has 3 valence
electrons.
The extra electron can
entice away.
Silicon doped with boron
provides plenty of free holes
(majority carriers) and few
electrons (minority carriers).
Good conductor known as
p-type.
n-Type Silicon
Phosphorus is added
Phosphorus has 5 valence
electrons.
The extra electron can
entice away.
Silicon doped with
phosphorus provides plenty of
free electrons (majority
carriers) and few holes
(minority carriers).
Good conductor known as
n-type.
p-n Junction
Free electrons in the n-type
material starting diffusing into
p-type side, leaving behind a
layer that is positively
charged.
Holes in the p-type material
diffuse into the n-side, leaving
behind a layer that is
negatively charged.
p-n Junction
Near the interface, diffusion
of the two types of majority
carriers in opposite directions
across the interface, setting up a
strong electric field and
creating a potential barrier to
further flow.
Equilibrium occurs when
diffusing is offset by the
potential barrier forming
depletion region.
Diode
Depletion region makes the p-n junction into a diode.
The external voltage V makes the p-type positive with
respect to n-type (forward bias).
If V is reversed, the potential barrier increases and a
very small dark saturation current flows (reverse bias).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Presentation On Condition MonitoringDocumento71 paginePresentation On Condition MonitoringShahin Manjurul AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Semiconductor DevicesDocumento27 pagineIntroduction To Semiconductor DevicesMuhammad Sufyan100% (2)
- SEMICONDUCTORSDocumento7 pagineSEMICONDUCTORSPaul KagunyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Water and Sediment in Crude Oil by The Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure)Documento13 pagineWater and Sediment in Crude Oil by The Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure)Jeferson RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep Beams and Continuous Deep BeamsDocumento63 pagineDeep Beams and Continuous Deep BeamsBency Mendoza100% (1)
- PV SemiconductorsDocumento61 paginePV SemiconductorsGaurav Sapkota0% (1)
- A Simulation of Roll Wear in Hot Rolling ProcessesDocumento336 pagineA Simulation of Roll Wear in Hot Rolling ProcessesVinay Rajput100% (1)
- Brief Analysis of Waste Paper Pulp ProcessingDocumento12 pagineBrief Analysis of Waste Paper Pulp ProcessingtisaNessuna valutazione finora
- EC 104 Unit-1 1st JuneDocumento189 pagineEC 104 Unit-1 1st JuneHarsh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 201806014043+HASAN MD TANVIR + Homework of Chapter 2Documento10 pagine201806014043+HASAN MD TANVIR + Homework of Chapter 2nahar elaNessuna valutazione finora
- EC 104 Unit 1 Part-1Documento64 pagineEC 104 Unit 1 Part-1Harsh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Analogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Documento50 pagineAnalogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Arvish RamseebaluckNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 9 SemiconductorDocumento10 pagineUnit 9 SemiconductorSahil ChawlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics DevicesDocumento44 pagineElectronics DevicesRhemjohn Dave PitongNessuna valutazione finora
- PN Junction DiodeDocumento44 paginePN Junction DiodePrasanth. SNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT3ECEDDocumento26 pagineUNIT3ECEDpadmavathy2kNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT - IV - Semiconductor DevicesDocumento23 pagineUNIT - IV - Semiconductor DevicesGirish Shankar MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Bipolar Transistors: The Designer's Guide CommunityDocumento19 pagineIntroduction To Bipolar Transistors: The Designer's Guide CommunityQasim AliNessuna valutazione finora
- PN Junction Lecture NotesDocumento10 paginePN Junction Lecture Notessuperbangadak100% (1)
- HW1 SolutionDocumento1 paginaHW1 Solution1 11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductors CH14 Part 2Documento17 pagineSemiconductors CH14 Part 2Rishab SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- EDC Unit-1 (Semiconductor Diode) PDFDocumento17 pagineEDC Unit-1 (Semiconductor Diode) PDFSaiKrishna81% (16)
- Semiconductors Module 2Documento10 pagineSemiconductors Module 2zaidkadiri9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elex 1Documento25 pagineElex 1cedricdimaligalig51Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento28 pagineLecture 1abram samNessuna valutazione finora
- P-N Junction Diode: (Silicon - Trivalent Impurity)Documento5 pagineP-N Junction Diode: (Silicon - Trivalent Impurity)NishantNessuna valutazione finora
- PN Junction Lecture 3Documento44 paginePN Junction Lecture 3Vimal KunwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Barrier Potential Across Semiconductor P-N Junction and Resting Membrane PotentialDocumento3 pagineBarrier Potential Across Semiconductor P-N Junction and Resting Membrane PotentialkpilNessuna valutazione finora
- SemiconductorDocumento3 pagineSemiconductorzubairwahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics For EngineersDocumento74 paginePhysics For EngineersJohn ZhouNessuna valutazione finora
- P-N Junction DiodeDocumento22 pagineP-N Junction DiodeRama SukumarNessuna valutazione finora
- SEMICONDUCTORDocumento40 pagineSEMICONDUCTORfarhan jalaludinNessuna valutazione finora
- U4Documento173 pagineU4Virthish DKNessuna valutazione finora
- ED and CA Unit 1Documento25 pagineED and CA Unit 1rsnagakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode FundamentalsDocumento24 pagineDiode Fundamentalsmuvin236Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ProjectDocumento11 paginePhysics ProjectJayesh PandyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ProjectDocumento11 paginePhysics ProjectDimpySurya44% (25)
- What Is Photovoltaic Effect?Documento2 pagineWhat Is Photovoltaic Effect?Anonymous xGKmBSrNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode:: Unbiased Diode and Depletion LayerDocumento10 pagineDiode:: Unbiased Diode and Depletion LayerAnonymous ovAm3yJXNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Note 1Documento15 pagineLecture Note 1nehal hasnain refathNessuna valutazione finora
- How A PN Junction Is FormedDocumento3 pagineHow A PN Junction Is FormedHuidrom SharatNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec8252 Electronicdevices 997787639 Ec8252 NotesDocumento96 pagineEc8252 Electronicdevices 997787639 Ec8252 NoteschandanpgowdachandanpNessuna valutazione finora
- N TypeDocumento3 pagineN TypeTayyaba ButtNessuna valutazione finora
- The PN Junction:: Formation of The Depletion RegionDocumento3 pagineThe PN Junction:: Formation of The Depletion RegionemgNessuna valutazione finora
- Elecctronics Unit 1Documento17 pagineElecctronics Unit 1Tangent ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Coulomb's Law: Application in Diodes: 3.electrical ChargeDocumento3 pagineCoulomb's Law: Application in Diodes: 3.electrical ChargeRegidor PetilunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrons in The Outer Shell Than The Semiconductor. Each Atom of DopantDocumento38 pagineElectrons in The Outer Shell Than The Semiconductor. Each Atom of Dopantfisho abukeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 01 2Documento17 pagineLecture 01 2সায়েম মুহাম্মাদNessuna valutazione finora
- Outreach 11Documento24 pagineOutreach 11amanuelfitsum589Nessuna valutazione finora
- ELS 2202 Week 2 (1) .PPT - PpsDocumento61 pagineELS 2202 Week 2 (1) .PPT - PpsYohana Crisma LimbongNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2Documento4 pagineLesson 2Pavan G MNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrons and ''Holes'' - S.Documento5 pagineElectrons and ''Holes'' - S.Manikandan SundararajNessuna valutazione finora
- Semi Conductor: Prepared By: Mohammed QashlanDocumento19 pagineSemi Conductor: Prepared By: Mohammed QashlanMohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Correlation Course in ElectronicsDocumento5 pagineCorrelation Course in ElectronicsCarmie BasilloteNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor Diodes and Special Purpose DiodesDocumento33 pagineSemiconductor Diodes and Special Purpose DiodesSaidur Rahman SidNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch1 EECE169 CSE16 Semiconductor DiodesDocumento45 pagineCh1 EECE169 CSE16 Semiconductor Diodessabbir hossainNessuna valutazione finora
- Photovoltaic SystemsDocumento1 paginaPhotovoltaic SystemsNina AuslanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding The P-N JunctionDocumento21 pagineUnderstanding The P-N JunctionwarrenronaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 10 (Introduction To Semiconductor)Documento31 pagineLecture 10 (Introduction To Semiconductor)samiullaharain636Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Semiconductor DevicesDocumento31 pagineChapter 3 - Semiconductor DevicesLij Abebe SonozNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor DiodeDocumento48 pagineSemiconductor DiodeSubhash MurkuteNessuna valutazione finora
- 14-How Do Solar Panels WorkDocumento4 pagine14-How Do Solar Panels WorkwalisyhNessuna valutazione finora
- Charge Carriers Crossing The JunctionDocumento5 pagineCharge Carriers Crossing The Junctionhoangloc NgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fresh Air CalculationDocumento2 pagineFresh Air CalculationAhmadSalimAlwohoushNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrolic and Pnumatic Systems Project No. 3Documento6 pagineHydrolic and Pnumatic Systems Project No. 3AhmadSalimAlwohoushNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Circuits Lab Experiment 1 Introduction To Basic Test and Management Equipment Part2 Oscilloscope Prepared By: Ahmad AlwohoushDocumento5 pagineElectrical Circuits Lab Experiment 1 Introduction To Basic Test and Management Equipment Part2 Oscilloscope Prepared By: Ahmad AlwohoushAhmadSalimAlwohoushNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Circuits Lab Experiment 4 DC Circuit Measurements-Part A Prepared By: Ahmad AlwohoushDocumento4 pagineElectrical Circuits Lab Experiment 4 DC Circuit Measurements-Part A Prepared By: Ahmad AlwohoushAhmadSalimAlwohoushNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcgraw-Hill Series in Chemical Engineering: The Chemical Process IndustriesDocumento67 pagineMcgraw-Hill Series in Chemical Engineering: The Chemical Process IndustriesSHASHWA USOPNessuna valutazione finora
- Greenboro Polychem PVT LTDDocumento57 pagineGreenboro Polychem PVT LTDMehdi MadaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemical CellsDocumento4 pagineElectrochemical CellsAlph BrickNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM D1856 092015 Aug 2019Documento4 pagineASTM D1856 092015 Aug 2019karenmerino94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ambipolar and Non-Ambipolar Diffusion in An RF Plasma Source Containing A Magnetic FilterDocumento10 pagineAmbipolar and Non-Ambipolar Diffusion in An RF Plasma Source Containing A Magnetic FilterTOP 10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shear Strengthening of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Steel Plates Bonded On Beam Web: Experiments and AnalysisDocumento8 pagineShear Strengthening of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Steel Plates Bonded On Beam Web: Experiments and Analysisjuan carlosNessuna valutazione finora
- MuscoviteDocumento15 pagineMuscoviteLyrine SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Stewmac: Two-Tone Fender Sunburst in The Pre-1956 StyleDocumento4 pagineStewmac: Two-Tone Fender Sunburst in The Pre-1956 StyleAlexandre KlüppelNessuna valutazione finora
- AE 6604 Aircraft Materials and Processes-Question Bank Unit I Part - BDocumento3 pagineAE 6604 Aircraft Materials and Processes-Question Bank Unit I Part - BRahul100% (1)
- Šmejkal Et Al. - 2022 - Beyond Conventional Ferromagnetism and AntiferromaDocumento16 pagineŠmejkal Et Al. - 2022 - Beyond Conventional Ferromagnetism and AntiferromaVil LabNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 120611e Kolliphor SLS Kolliphor SLS FineDocumento6 pagine03 120611e Kolliphor SLS Kolliphor SLS FineMahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- PK Valve Page-13-17Documento5 paginePK Valve Page-13-17ICASA IngenieríaNessuna valutazione finora
- 66404Documento23 pagine66404amdevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep 4 ProcessDocumento1 paginaDeep 4 ProcessGeorge ChedraouiNessuna valutazione finora
- WOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon CompoundDocumento32 pagineWOW Notes! DLP Chemistry, Carbon Compoundnur asyiqinNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Reflow Tin Plating & What Are Its Benefits?Documento9 pagineWhat Is Reflow Tin Plating & What Are Its Benefits?cooperplatingcompanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 (Lesson 1 and 2)Documento10 pagineModule 3 (Lesson 1 and 2)rocky.mercado2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Detalle de Caja Da RegistroDocumento2 pagineDetalle de Caja Da RegistroCarlos VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2014 Question Paper 62 PDFDocumento20 pagineJune 2014 Question Paper 62 PDFLast MadanhireNessuna valutazione finora
- Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using CFRP JacketingDocumento4 pagineRetrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using CFRP JacketingTaanzNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm B786Documento6 pagineAstm B786cantigiNessuna valutazione finora
- COOL - 006 Advances in Liquid Coolant Technologies For Electronics Cooling 2005Documento7 pagineCOOL - 006 Advances in Liquid Coolant Technologies For Electronics Cooling 2005Leslie Diaz JalaffNessuna valutazione finora
- Bai 4 - Thin FilmDocumento17 pagineBai 4 - Thin FilmBé Kem Xưởng MayNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 1 (Isolation of Caffeine)Documento2 pagineExercise 1 (Isolation of Caffeine)Albert CorderoNessuna valutazione finora