Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Funciones Del Gerundio Y El Infinitivo
Caricato da
urmanjmCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Funciones Del Gerundio Y El Infinitivo
Caricato da
urmanjmCopyright:
Formati disponibili
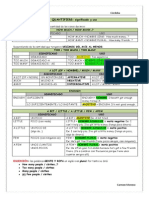
El Gerundio
El gerundio o gerund en ingls es la versin sustantiva del verbo
que acaba con -ing en ingls y con -endo o -ando en espaol, por ejemplo
eating (comiendo), speaking (hablando).
Formacin del Gerundio
La regla general para construir el gerundio es aadir el sufijo -ing al verbo.
Pero esta regla tiene 3 excepciones:
Doblado de Consonante en el Gerundio
Algunos verbos doblan su consonante final en la formacin el gerundio.
Esto sucede cuando se cumplen las siguientes condiciones:
El verbo es monoslabo o recae el acento en la ltima slaba o
bien que termina en "L".
El verbo termina en una sola consonante (sin ser r, w, x y).
Que la ltima consonante sea precedida de una nica vocal.
Verbo Gerundio Significado
to swim swimming nadar
to run running correr
to win winning ganar
Verbos terminados en "-ie"
Para estos verbos, la "i latina" pasa a ser "y griega". Se ve ms fcil
con unos ejemplos
Verbo Gerundio Significado
die dying morir
lie lying mentir
tie tying atar
Verbos terminados en "-e"
Los verbos terminados en "-e", pierden esta letra al formar el gerundio.
Solo el verbo to be, la conserva.
Verbo Gerundio Significado
to make making hacer
to cause causing causar
to be being ser
Los Diferentes Usos del Gerundio en Ingls
Despus de las preposiciones:
Las preposiciones son las (normalmente) pequeas palabras que
conectan sustantivos y pronombres a otras palabras en una oracin. Existen
ms preposiciones en ingls que en espaol, habitualmente hay dos o tres
para cada una en espaol. Ejemplos de las preposiciones en ingls son:
in, on, at, to, of, from, since, with, without, for, by, through, about,
until, before, after, etc.
Cuando una preposicin en espaol va seguida de infinitivo, en ingls su
equivalente va seguida de gerundio. Por ejemplo:
Im interested in improving my English. (Estoy interesado en mejorar mi
ingls)
John went to bed without having dinner. (John se acost sin cenar)
Hes good at listening. (Escucha bien.)
I always read before going to bed. (Siempre leo antes de acostarme.)
You cant leave without saying goodbye. (No puedes salir sin despedirte.)
Despus de ciertos verbos:
Con algunos verbos, cuando usamos el gerundio o el infinitivo, el
significado cambia. En espaol algunos verbos como disfrutar, seguir y
continuar van seguidos de gerundio as que no es un concepto radicalmente
extrao para los hablantes de espaol. Sin embargo, hay muchos ms
verbos en ingls que van seguidos por el gerundio que en espaol y sin una
regla que puedes seguir para saber cules son, hay que aprenderlos poco a
poco uno por uno.
Algunos verbos como continue y start pueden ir seguidos de infinitivo o
gerundio sin que cambie el significado. Por ejemplo:
Gerundio: David stopped smoking. (David par/dej de fumar)
Infinitivo: David stopped to smoke. (David par para fumar)
Gerundio: I forgot writing that email. (Me olvid escribiendo ese correo
electrnico.)
Infinitivo: I forgot to write that email. (Me olvid de escribir el correo
electrnico.)
Gerundio: Stop watching the news. (Deja de ver las noticias)
Infinitivo: Stop to watch the news. (Para, para ver las noticias.)
Como sujeto, objeto o complemento de una frase:
Podemos usar el gerundio como objeto, sujeto o complemento de una
frase. Cuando el infinitivo en espaol funciona como sujeto de una oracin,
en ingls se usa el gerundio.
Ejemplos:
Como Sujeto:
Swimming is good exercise. (Nadar es un buen ejercicio)
Drinking and driving is dangerous. (Beber y conducir es peligroso.)
Studying is so boring (Estudiar es tan Aburrido)
Learning English is fun and easy (Aprender ingls es divertido y fcil)
Como Objeto:
I like cooking. (Me gusta cocinar)
She continued working. (Continu trabajando.)
Como Complemento:
The best thing to do when you are sick is to drink a lot of water. (Lo
mejor que puedes hacer cuando ests enfermo es beber mucha agua.)
My favorite exercise is swimming. (Mi ejercicio favorito es la natacin.)
Gerundio como Adjetivo
El gerundio puede servir para completar la informacin de un
sustantivo. En este caso, el gerundio se colocar antes que el sustantivo
como cualquier otro adjetivo. Ejemplos:
Waiting room (sala de espera)
Programming language (lenguaje de programacin)
The crying boy is my brother (El chico lloron es mi hermano)
The swimming pool is over there
Formacin del Infinitivo
El infinitivo es la forma bsica de un verbo. En ingls, cuando hablamos
del infinitivo normalmente nos referimos al "present infinitive", que es el ms
utilizado. Sin embargo, existen otras cuatro formas verbales compuestas con
infinitivos en ingls: el "perfect infinitive", el "perfect continuous infinitive",
el "continuous infinitive" y el "passive infinitive".
El infinitivo tiene dos formas:
infinitivo con to = to + raz del verbo
infinitivo sin to o "zero infinitive" = raz
Infinitivo con "to" Infinitivo sin "to"
to sit sit
to eat eat
to have have
to remember remember
La forma negativa del infinitivo se construye aadiendo la partcula "not"
delante del infinitivo, con o sin "to". Ejemplos:
I decided not to go to London.
He asked me not to be late.
I'd like you not to sing so loudly.
I'd rather not eat meat.
I might not come.
Funciones del infinitivo con "to"
El infinitivo con "to" o "to-infinitive" se emplea en numerosas
construcciones sintcticas. A menudo, expresa un propsito u opinin. Hay
un nmero considerable de verbos que van seguidos por esta forma del
infinitivo. Consulta esta pgina sobre verbos seguidos de infinitivo.
Infinitivo con "to" para indicar propsito o intencin de
una accin:
En este caso, "to" significa lo mismo que las expresiones "in order to" o
"so as to". Ejemplos:
She came to collect her pay cheque.
The three bears went to find firewood.
I am calling to ask you about dad.
You sister has gone to finish her homework.
Infinitivo con "to" como sujeto de la oracin
Este uso es propio del registro formal y es mucho ms habitual en el
ingls escrito que en la lengua hablada. Ejemplos:
To be or not to be, that is the question.
To know her is to love her.
To visit the Grand Canyon is my life-long dream.
To understand statistics, that is our aim.
Infinitivo con "to" para indicar el uso posible o previsto de
algo
En esta construccin, el infinitivo con "to" sigue a un nombre o a un
pronombre. Ejemplos:
The children need a garden to play in.
I would like a sandwich to eat.
I don't have anything to wear.
Would you like something to drink?
El infinitivo con "to" tras adjetivos
Existe un patrn habitual para el uso del infinitivo con "to" con un
adjetivo. La estructura de estas construcciones es: sujeto + "to be" +
adjetivo + ("for","of" + alguien) + infinitivo con "to" + (resto de la
oracin)
Sujeto + to be + adjetivo (+ "for", "of" alguien) + infinitivo con
"to" (+ resto de la oracin)
It is good to talk.
It is good of you to talk
to me.
It is important to be patient.
It is important for Jake to be patient with
his little brother.
I am happy to be
here.
The dog is naughty to destroy
our couch.
Infinitivo con "to" para hacer un juicio o comentario
Para emplear el infinitivo con "to" a la hora de hacer un comentario o
emitir un juicio sobre un nombre, la estructura es: Sujeto + "to be" +
frase nominal + infinitivo con "to". Ejemplos:
It was a stupid placeto park.
That is a dangerous way to behave.
What you said was a rude thing to say.
This is the right thing to do.
Those were the wrong kind of eggs to buy.
Jim is the best person to hire.
Infinitivo con "to" acompaado de adverbios
El infinitivo con "to" se emplea frecuentemente con los adverbios "too"
y "enough" para expresar el razonamiento que subyace a nuestra
satisfaccin o insatisfaccin. En esta construccin, "too" y "enough" se
colocan antes o despus del adjetivo, adverbio o nombre al que modifican,
en la misma posicin que ocuparan de no haber un infinitivo con "to". A
continuacin, situamos el infinitivo con "to" para explicar el motivo por el
cual la cantidad que expresan resulta excesiva, suficiente o insuficiente.
Normalmente, el infinitivo con "to" y todo lo que le sigue puede eliminarse
sin que la oracin deje de ser gramaticalmente funcional. Ejemplos
There's too much sugar to put in this bowl.
I had too many books to carry.
This soup is too hot to eat.
She was too tired to work.
He arrived too late to see the actors.
I've had enough food to eat.
She's old enough to make up her own mind.
There isn't enough snow to ski on.
You're not old enough to have grand-children!
Infinitivo con "to" despus de partculas interrogativas
Los verbos "ask", "decide", "explain", "forget", "know", "show", "tell" y
"understand" pueden ir seguidos por un trmino interrogativo como "where",
"how", "what", "who" y "when" + infinitivo con "to". Ejemplos
She asked me how to use the washing machine.
Do you understand what to do?
Tell me when to press the button.
I've forgotten where to put this little screw.
I'm not sure I know who to call.
Infinitivo sin "to" detrs de verbos auxiliares
Ejemplos
She can't speak to you.
He should give her some money.
Shall I talk to him?
Would you like a cup of coffee?
I might stay another night in the hotel.
They must leave before 10.00 a.m.
Infinitivo sin "to" tras verbos de percepcin
Con verbos de sensacin y percepcin, la estructura seguida es verbo +
objeto + infinitivo sin "to". Ejemplos
He saw her fall from the cliff.
We heard them close the door.
They saw us walk toward the lake.
She felt the spider crawl up her leg.
Infinitivo sin "to" tras los verbos "make" y "let"
Ejemplos
Her parents let her stay out late.
Let's go to the cinema tonight.
You made me come with you.
Don't make me study that boring grammar book!
Infinitivo sin "to" tras la expresin "had better"
Ejemplos
We had better take some warm clothing.
She had better ask him not to come.
We had better reserve a room in the hotel.
You'd better give me your address.
They had better work harder on their homework.
Infinitivo sin "to" con "why"
La partcula interrogativa "why" va seguida de infinitivo sin "to" para
hacer una sugerencia. Ejemplos
Why wait until tomorrow?
Why not ask him now?
Why leave before the end of the game?
Why walk when we can go in the car?
Why not buy a new bed?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 1º ESO. Naturales. Tema 12. La Atmósfera Terrestre (SM)Documento3 pagine1º ESO. Naturales. Tema 12. La Atmósfera Terrestre (SM)Angela Torregrosa NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- La oración simple: estructura y análisisDocumento3 pagineLa oración simple: estructura y análisisCristian Rubio PamiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Apuntes de Morfosintaxis IDocumento10 pagineApuntes de Morfosintaxis IaulariovirtualNessuna valutazione finora
- Aprende A Conjugar El Verbo Haber PDFDocumento3 pagineAprende A Conjugar El Verbo Haber PDFLuis MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 EsoDocumento1 pagina1 EsonuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Primaria - Santillana - Lengua Refuerzo Voces - 1Documento4 pagine6-Primaria - Santillana - Lengua Refuerzo Voces - 1Nagore100% (1)
- Lengua 4 PrimariaDocumento2 pagineLengua 4 PrimariaSonia GamezNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocales abiertas y cerradas: diptongos e hiatosDocumento4 pagineVocales abiertas y cerradas: diptongos e hiatosAnonymous p9dumECNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 SM Ampliacion MATESDocumento15 pagine3 SM Ampliacion MATESconyNessuna valutazione finora
- Une Mediante Flechas Los Órganos y Aparatos Con Las Tareas Que Realizan y Con La Función en La Que ParticipanDocumento9 pagineUne Mediante Flechas Los Órganos y Aparatos Con Las Tareas Que Realizan y Con La Función en La Que Participanmiraquebonito miraquebonitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 2: Ciencias Naturales 4º PrimaraDocumento2 pagineTema 2: Ciencias Naturales 4º Primaraisarc74Nessuna valutazione finora
- 82 - Teoria 3. Sujeto y PredicadoDocumento5 pagine82 - Teoria 3. Sujeto y PredicadoCésar Javier Quispe MontalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Conjugación Verbo Tener en Español - Conjugador ReversoDocumento2 pagineConjugación Verbo Tener en Español - Conjugador ReversoDe Matos Cerza0% (1)
- Relieve de EspañaDocumento4 pagineRelieve de EspañaRocio Jover CortesNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas de Física y Química 2o ESODocumento26 pagineProblemas de Física y Química 2o ESOuguygug100% (2)
- Sustantivos y Adjetivos PDFDocumento1 paginaSustantivos y Adjetivos PDFM. Carmen QuilesNessuna valutazione finora
- Primariaejercicios InglesDocumento21 paginePrimariaejercicios InglesyulyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fracciones Problemas 3Documento3 pagineFracciones Problemas 3Daneryslove StardollNessuna valutazione finora
- Clasificación de los seres vivos en 5 reinosDocumento4 pagineClasificación de los seres vivos en 5 reinosGuillermoNessuna valutazione finora
- Esquemas Ciencias de La Naturaleza 5 PrimariaDocumento47 pagineEsquemas Ciencias de La Naturaleza 5 PrimariaAlberto TortosaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Plan de Clase - Ciencias Naturales 6to PrimariaDocumento30 pagine8 Plan de Clase - Ciencias Naturales 6to Primariaedson coca gomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Los Seres Vivos Mas SencillosDocumento28 pagineLos Seres Vivos Mas SencillosBioBeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios Diptongos e HiatosDocumento2 pagineEjercicios Diptongos e HiatosLiz DuvaluwurNessuna valutazione finora
- Plan de Mejora Naturales 3º Ep Tema 1 La NutriciónDocumento3 paginePlan de Mejora Naturales 3º Ep Tema 1 La NutriciónRaquel Benítez RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Secuencia Didactica 4to. Starter UnitDocumento21 pagineSecuencia Didactica 4to. Starter UnitMariana Fernanda LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Santillana Quinto Atencion Diversidad Matematicas SaviaDocumento23 pagineSantillana Quinto Atencion Diversidad Matematicas SaviaLuisaAlvarezLorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pendientes 1 ESODocumento40 paginePendientes 1 ESOAlvaro Lavandera SastreNessuna valutazione finora
- 5º Primaria - Conocimiento Del MedioDocumento6 pagine5º Primaria - Conocimiento Del MedioIP GuessNessuna valutazione finora
- Resumen Tema 3 y 4 Lengua EsoDocumento4 pagineResumen Tema 3 y 4 Lengua EsoLorenaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.7.cuadro Resumen Coordinadas y SubordinadasDocumento2 pagine10.7.cuadro Resumen Coordinadas y Subordinadasesther20170% (1)
- Adverbios 1º EsoDocumento5 pagineAdverbios 1º EsopepeNessuna valutazione finora
- Esquema Reino AnimalDocumento2 pagineEsquema Reino AnimalBeatriz LoboNessuna valutazione finora
- Examen DiagnosticoDocumento8 pagineExamen DiagnosticoAnaitz BeHappyNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Evaluacion Prueba Evaluacion ADocumento6 pagine04 Evaluacion Prueba Evaluacion ARaquelNessuna valutazione finora
- Morfologia Esquema PDFDocumento1 paginaMorfologia Esquema PDFd4hu31Nessuna valutazione finora
- Matem 4 Guia T 01 15 2015 03Documento20 pagineMatem 4 Guia T 01 15 2015 03ErikaDominguezGaliñanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 4Documento6 pagineTema 4DAVIDNessuna valutazione finora
- Unidad 1 3º Eso AlgaidaDocumento40 pagineUnidad 1 3º Eso AlgaidaAna Del MontecarmeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Matematicas 4o Primaria Santillana Saber HacerDocumento6 pagineMatematicas 4o Primaria Santillana Saber HacerJUANNessuna valutazione finora
- Examen Aparato LocomotorDocumento2 pagineExamen Aparato LocomotorAlejandro Albahaca PeralilloNessuna valutazione finora
- El complemento predicativo CPredDocumento12 pagineEl complemento predicativo CPredJesús PérezNessuna valutazione finora
- Gerundio e InfinitivoDocumento6 pagineGerundio e InfinitivoCésar Muñoz NicolásNessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher Guide - 5º Lengua Anaya - Unidad 1Documento51 pagineTeacher Guide - 5º Lengua Anaya - Unidad 1SoniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Correo electrónico y lenguajeDocumento74 pagineCorreo electrónico y lenguajeEvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 8 Animales VertebradosDocumento4 pagineTema 8 Animales VertebradosAgustín Roldán VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ficha 1-Lengua 1 ESoDocumento8 pagineFicha 1-Lengua 1 ESoaragorn13100% (1)
- Gasto energético y dieta balanceadaDocumento6 pagineGasto energético y dieta balanceadaHasly valenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- EXAMEN Lengua Tema 2 4ºDocumento7 pagineEXAMEN Lengua Tema 2 4ºCarla Gante RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- 10-Sist Met Dec PDFDocumento11 pagine10-Sist Met Dec PDFJuanito ZavalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reinos Monera, Protoctistas y HongosDocumento18 pagineReinos Monera, Protoctistas y HongosVANEA LAZURNessuna valutazione finora
- Expresiones de CantidadDocumento1 paginaExpresiones de CantidadmoncaciNessuna valutazione finora
- Las PlantasDocumento6 pagineLas Plantascarlos rus rusNessuna valutazione finora
- Siglas, Acronimos, Abreviaturas 1º ESODocumento2 pagineSiglas, Acronimos, Abreviaturas 1º ESOChente Miguel GalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Curso de OrtografíaDocumento32 pagineCurso de OrtografíaBecky ZarateNessuna valutazione finora
- Verticalidad OrtografíaDocumento3 pagineVerticalidad OrtografíaEvaPérezSánchezNessuna valutazione finora
- ECOSISTEMASDocumento20 pagineECOSISTEMASÂngél Gåbrîël PčNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 2 El Clima y Vegetación de España y EuropaDocumento2 pagineTema 2 El Clima y Vegetación de España y EuropaSusana Soria LapeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo de Idiomas 2Documento8 pagineTrabajo de Idiomas 2Victoria Vegas SandovalNessuna valutazione finora
- El Gerundio Es Llamado en InglésDocumento36 pagineEl Gerundio Es Llamado en InglésCoriangela Mercedes Cumarin SolorzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Infinitivo y GerundioDocumento12 pagineInfinitivo y Gerundiomaria vanesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principios para El Análisis Conservación y RestauraciónDocumento4 paginePrincipios para El Análisis Conservación y RestauraciónJaime Delgado rubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaceta Oficial No 4103 Inst Sanit P Urbanisticos PDFDocumento38 pagineGaceta Oficial No 4103 Inst Sanit P Urbanisticos PDFurmanjmNessuna valutazione finora
- Principios para El Análisis Conservación y RestauraciónDocumento4 paginePrincipios para El Análisis Conservación y RestauraciónJaime Delgado rubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Triptico Agua - ener.ITLPDocumento2 pagineTriptico Agua - ener.ITLPDIANA100% (2)
- Drenaje Pluvial PDFDocumento23 pagineDrenaje Pluvial PDFDianna VillavicencioNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaceta Oficial No 4103 Inst Sanit P Urbanisticos PDFDocumento38 pagineGaceta Oficial No 4103 Inst Sanit P Urbanisticos PDFurmanjmNessuna valutazione finora
- Lineamientos Mínimos para Elaborar Una Tesis de ArquitecturaDocumento43 pagineLineamientos Mínimos para Elaborar Una Tesis de ArquitecturaOscar ArsonistNessuna valutazione finora
- Normas de Equipamiento Urbano AnalisisDocumento5 pagineNormas de Equipamiento Urbano AnalisisurmanjmNessuna valutazione finora
- Normas Fede CompletasDocumento198 pagineNormas Fede CompletasCarlos Arellano79% (34)
- Ley Organica de Ordenacion Urbanistica - 33.868Documento30 pagineLey Organica de Ordenacion Urbanistica - 33.868Jelmarys RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Desague PluvialDocumento28 pagineDesague PluvialAntonio JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Prerrequisitos de TopografíaDocumento31 paginePrerrequisitos de TopografíaJuan Martin RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ley Organica de Ordenación UrbanisticaDocumento34 pagineLey Organica de Ordenación UrbanisticaCoraima MarreroNessuna valutazione finora
- Sala PolivalenteDocumento7 pagineSala PolivalenteurmanjmNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Desagues CloacalesDocumento75 pagine2 Desagues CloacalescarhugoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lectura de PlanosDocumento87 pagineLectura de PlanosLeidys Paola Daza Molina100% (11)
- Manual Servicio Comunitario Actualizado PDFDocumento65 pagineManual Servicio Comunitario Actualizado PDFisraeleonsNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Portada Indice Manual para La Elaboración Del Trabajo de GradoDocumento8 pagine1 Portada Indice Manual para La Elaboración Del Trabajo de GradoRocío Romero GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Artes Plásticas - Pintura PDFDocumento2 pagineArtes Plásticas - Pintura PDFGeneLouNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Manual para La Elaboracion de Trabajo de GradoDocumento121 pagine2 Manual para La Elaboracion de Trabajo de GradohiustynsNessuna valutazione finora
- Reglamento y Ordenación UrbanísticaDocumento24 pagineReglamento y Ordenación UrbanísticaDaniela CordovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaceta Norma para Equipamiento UrbanoDocumento11 pagineGaceta Norma para Equipamiento Urbanoamms249100% (2)
- Teatro - Actuación PDFDocumento2 pagineTeatro - Actuación PDFurmanjmNessuna valutazione finora
- Lineamientos Mínimos para Elaborar Una Tesis de ArquitecturaDocumento43 pagineLineamientos Mínimos para Elaborar Una Tesis de ArquitecturaOscar ArsonistNessuna valutazione finora
- Dotaciones de agua para edificacionesDocumento6 pagineDotaciones de agua para edificacionesOswaldo RivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistemas de suministro y distribución de agua potableDocumento25 pagineSistemas de suministro y distribución de agua potable'Santiago Razzak MelianNessuna valutazione finora
- Teatro - Actuación PDFDocumento2 pagineTeatro - Actuación PDFurmanjmNessuna valutazione finora
- Cimientos 1Documento12 pagineCimientos 1urmanjmNessuna valutazione finora
- Artes Plásticas - Pintura PDFDocumento2 pagineArtes Plásticas - Pintura PDFGeneLouNessuna valutazione finora
- Consideraciones para La Sostenibilidad de Los Sistemas Constructivos.Documento6 pagineConsideraciones para La Sostenibilidad de Los Sistemas Constructivos.urmanjmNessuna valutazione finora
- Griego I Introducción Al Verbo GriegoDocumento32 pagineGriego I Introducción Al Verbo GriegoLeopoldoOrellanaAravenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Decir Si de Griselda GambaroDocumento13 pagineDecir Si de Griselda Gambaroannialux100% (1)
- Organigrama: definición, partes y tiposDocumento41 pagineOrganigrama: definición, partes y tiposNelson Yauri GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Análisis de la sintaxis en educación secundariaDocumento52 pagineAnálisis de la sintaxis en educación secundariaDaniel Tello SoteloNessuna valutazione finora
- Los Objetivos... (Texto) Dr. AnduxDocumento70 pagineLos Objetivos... (Texto) Dr. Anduxnestor aguilar gonzálezNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminacion EARDocumento22 pagineTerminacion EARIsrael ZepahuaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01verbos IrregularesDocumento3 pagine01verbos IrregularesbiskwitkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Past PerfectDocumento2 paginePast PerfectmaxiNessuna valutazione finora
- Secuencia Didáctica de LenguaDocumento14 pagineSecuencia Didáctica de LenguaAnabel GranadosNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller de InglesDocumento15 pagineTaller de InglesMario Luis Luquez100% (1)
- RV-2BIM-1ro SecDocumento23 pagineRV-2BIM-1ro SecEddie Rafaele ValenzuelaNessuna valutazione finora
- El español arcaico, la influencia extranjera y los cambios fonéticos en la Edad MediaDocumento19 pagineEl español arcaico, la influencia extranjera y los cambios fonéticos en la Edad MediaFlavia Anhai SisnerosNessuna valutazione finora
- Sintagmas nominales, adjetivales, verbales, adverbiales y preposicionales: funciones sintácticasDocumento2 pagineSintagmas nominales, adjetivales, verbales, adverbiales y preposicionales: funciones sintácticasTOMAS GARIBALDINessuna valutazione finora
- El Comentario de Texto PauDocumento6 pagineEl Comentario de Texto Paularara51100% (1)
- Did - Ctica de La Lengua en La Educaci - N Infantil PDFDocumento373 pagineDid - Ctica de La Lengua en La Educaci - N Infantil PDFIrma Jiménez Del ValleNessuna valutazione finora
- Un soneto popular: la inspiración universal detrás del soneto No me mueve mi Dios para quererteDocumento21 pagineUn soneto popular: la inspiración universal detrás del soneto No me mueve mi Dios para quererteamnajar_one355Nessuna valutazione finora
- Los Verbos en InglesDocumento62 pagineLos Verbos en InglesLuis Felipe MazariegosNessuna valutazione finora
- 2balc SV Es Ud06 La SoDocumento8 pagine2balc SV Es Ud06 La SoAdriana Delgado RománNessuna valutazione finora
- Analisis Del Error en El Marco de La Linguistica ContrastivaDocumento10 pagineAnalisis Del Error en El Marco de La Linguistica ContrastivaValeria SalemeNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseño Curricular Nivel Secundario Parte 3Documento100 pagineDiseño Curricular Nivel Secundario Parte 3Maurdic ArtNessuna valutazione finora
- Apuntes Sintaxis ComplementosDocumento3 pagineApuntes Sintaxis ComplementosAgustín García Romero-Nieva100% (1)
- MALLA CURRICULAR INGLES 2017 .PDF POR COMPETENCIADocumento27 pagineMALLA CURRICULAR INGLES 2017 .PDF POR COMPETENCIAHengelbert SotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rubrica 10 GradeDocumento2 pagineRubrica 10 GradeWaly's English Course - Curso de InglésNessuna valutazione finora
- Bosque Guti Rrez Rexach 2009 Ascenso y ControlDocumento6 pagineBosque Guti Rrez Rexach 2009 Ascenso y ControlGuillerminaNessuna valutazione finora
- TOMO 1 Ocr PDFDocumento267 pagineTOMO 1 Ocr PDFPinTaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicina y Visiones Canto de Un Curandero Shipibo Conibo Texto y Contexto Jacques TOURNONDocumento31 pagineMedicina y Visiones Canto de Un Curandero Shipibo Conibo Texto y Contexto Jacques TOURNONAgustín PaganiNessuna valutazione finora
- 02) Cáceres, N. E. (2000)Documento79 pagine02) Cáceres, N. E. (2000)Ivonne Castañeda HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Bonifacio Sotos Ochando - Gramática de La Lengua Universal (1863)Documento203 pagineBonifacio Sotos Ochando - Gramática de La Lengua Universal (1863)CarlosJesusNessuna valutazione finora
- Componedor de cuentosDocumento4 pagineComponedor de cuentosJUAN CARLOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Aymara Libro VerDocumento29 pagineAymara Libro VerAlbita MarinaNessuna valutazione finora