Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Insulin Transition Guidelines Final 2-10-15
Caricato da
rizwan234Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Insulin Transition Guidelines Final 2-10-15
Caricato da
rizwan234Copyright:
Formati disponibili
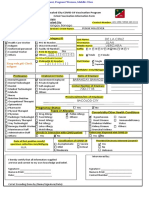
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER
MULTIDISCIPLINARY SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE
SURGICAL INTENSIVE CARE UNIT INSULIN TRANSITION PROTOCOL
Purpose: To improve glycemic control when transitioning from a continuous insulin infusion (CII) to
subcutaneous insulin and provide guidance on appropriate insulin dosing regimens.
Patient Categories:
-Category 1: Patients with a history of DM OR those requiring insulin infusion of 3 units/h
-Category 2: Patients without a history of diabetes requiring CII < 3 units/h infusion transition to SSI
Transition From IV to SQ Insulin
For Category 1 patients:
1. Determine average hourly rate of CII and multiply by 24 to obtain the average insulin
requirement for the past 24 hours.
Clinical judgment may supersede exact calculation of 24 hour insulin requirements if
patients clinical status has rapidly changed or if the patients BG/CII rate has not been
stable
2. Calculate 70% of the 24h insulin requirement. This will be the total daily dose (TDD) of
subcutaneous insulin divided into long and short acting insulin.
a. Give 50% of TDD as basal insulin (insulin glargine)
i. Basal insulin should be administered 2 hours prior to discontinuation of CII
ii. Give regardless of oral intake
b. Give 50% of TDD as scheduled short acting insulin in divided doses
i. For patients on continuous tube feeds or those not with stable diet (preferred):
1. Divide TDD into 4 doses of regular insulin given every 6 hours.
2. If tube feeds are stopped, hold scheduled regular insulin
a. Consider starting a 10% dextrose infusion to maintain euglycemia
ii. For patients stable on a regular diet (three meals per day):
1. Divide TDD into 3 doses of rapid acting insulin and give before meals
2. Hold if patient is NPO
3. Order SQ insulin sliding scale per the SICU protocol to be given with scheduled short acting
insulin (same type of insulin and same frequency)
For Category 2 patients:
Order sliding scale lispro insulin per the SICU protocol in Wiz/HEO
SSI dose based on a formula calculated as:
[blood glucose (mg/dL)] 90
15
SSI adjusted by changing denominator in calculation: range 8-15
o 8 as most restrictive scale and 15 as least restrictive scale
Clinical failure on SQ insulin defined as two consecutive BG readings >250 mcg/dL
Results in transition back to CII
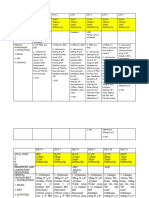
Suggested starting doses for SQ insulin based
Average hourly rate Dose of bolus insulin
Dose of basal insulin
of IV insulin (CII) (short/rapid acting)
4 units every 6 hours or
2 units/hour = 16 units one daily + +
5 units before each meal (TID)
6 units every 6 hours or
3 units/hour = 24 units one daily + +
8 units before each meal (TID)
8 units every 6 hours or
4 units/hour = 32 units one daily + +
10 units before each meal (TID)
Sliding
10 units every 6 hours or
5 units/hour = 42 units one daily + + Scale
14 units before each meal (TID)
Insulin
12 units every 6 hours or
6 units/hour = 50 units one daily + +
16 units before each meal (TID)
14 units every 6 hours or
7 units/hour = 58 units one daily + +
20 units before each meal (TID)
16 units every 6 hours or
8 units/hour = 66 units one daily + +
22 units before each meal (TID)
TID= three times per day
Example calculation for SSI administration
Units of lispro to administer based on denominator of SSI calculation
Patients blood glucose
8 12 15
120 mg/dL 3.75 units 2.5 units 2 units
170 mg/dL 10 units 6.6 units 5.3 units
250 md/dL 20 units 13.3 units 10.6 units
Authors:
Michael Kenes, PharmD, BCPS
Kelli Rumbaugh PharmD, BCPS
Date last updated: 2/10/2015
References:
1. Bode BW, Braithwaite SS, Steed RD, Davidson PC. Intravenous insulin infusion therapy:
indications, methods, and transition to subcutaneous insulin therapy. Endocr
Pract 2004;10(2):71-80.
1. Hsia E, Seggelke S, Gibbs J, et al. Subcutaneous administration of glargine to diabetic patients
receiving insulin infusion prevents rebound hyperglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab
2012;97(9):3132-7.
2. Weant KA, Ladha A. Conversion from continuous insulin infusion to subcutaneous insulin in
critically ill patients. Ann Pharmacother 2009;43:629-34.
3. Furnary AP, Braithwaite SS. Effects of outcome on in-hospital transition from intravenous
insulin infusion to subcutaneous therapy. Am J Cardiol 2006;98(4):557-64.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Surgery History and PhysicalDocumento23 pagineSurgery History and PhysicalBilal RowaihiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rab Flow CHT 3 PeopleDocumento2 pagineRab Flow CHT 3 PeopleWDIV/ClickOnDetroitNessuna valutazione finora
- Charcot Marie Tooth DiseaseDocumento4 pagineCharcot Marie Tooth DiseaseAbdul QuyyumNessuna valutazione finora
- DISCHARGE PLANNING - AnemiaDocumento2 pagineDISCHARGE PLANNING - AnemiaJOEY MEAD ARUGAY0% (1)
- Problem Statement 5Documento17 pagineProblem Statement 5priyankaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer Program SeminarDocumento98 pagineCancer Program SeminarhemihemaNessuna valutazione finora
- J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 97 16 38Documento23 pagineJ Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 97 16 38rizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge SummaryDocumento1 paginaDischarge SummaryeresdNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Trigeminal Nerve & Trigeminal Neuralgia: Presented By: DR - Vansh Vardhan Madahar PG1 YearDocumento47 pagineAnatomy of Trigeminal Nerve & Trigeminal Neuralgia: Presented By: DR - Vansh Vardhan Madahar PG1 YearVansh Vardhan MadaharNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Waste GuideDocumento2 pagineBiological Waste Guiderizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- FCPS Online Application Training Manual NEWDocumento18 pagineFCPS Online Application Training Manual NEWrizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 2017 RevDocumento1 paginaExam 2017 Revrizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Post-Operative Instructions: Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDocumento2 paginePost-Operative Instructions: Laparoscopic Cholecystectomyrizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 2017 RevDocumento1 paginaExam 2017 Revrizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lap CholeDocumento1 paginaLap Cholerizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stroke and Transient Ischaemic Attack in Over 16s Diagnosis and Initial Management 975574676437Documento29 pagineStroke and Transient Ischaemic Attack in Over 16s Diagnosis and Initial Management 975574676437rizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lap CholeDocumento1 paginaLap Cholerizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cyc Poster Clinics UruDocumento1 paginaCyc Poster Clinics Ururizwan234Nessuna valutazione finora
- CDC Cough No LogoDocumento1 paginaCDC Cough No LogoSuresh PalaniveluNessuna valutazione finora
- Knot Tying ManualDocumento50 pagineKnot Tying ManualAdriana Vick100% (1)
- RXPG Series-Preventive and Social Medicine BUSTER (2004) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Documento156 pagineRXPG Series-Preventive and Social Medicine BUSTER (2004) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Premangshu Ghoshal75% (4)
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocumento13 pagineAmniotic Fluid EmbolismMARIANN JEAN ANDREA CULANAG MATALINESNessuna valutazione finora
- 7325-300 C-Peptide & Insulin AccuBind VAST ELISA Rev 6Documento2 pagine7325-300 C-Peptide & Insulin AccuBind VAST ELISA Rev 6Luisa MaríaNessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of Mental HealthDocumento2 pagineImportance of Mental HealthCp CsNessuna valutazione finora
- RSP Sys Pathology Dec2011Documento6 pagineRSP Sys Pathology Dec2011Kelly YeowNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study NCP - Forcep BirthDocumento4 pagineCase Study NCP - Forcep BirthKent CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- K1 Hubungan Biomedik Dasar Dengan Ilmu KedokteranDocumento21 pagineK1 Hubungan Biomedik Dasar Dengan Ilmu Kedokteranhartinissa vaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Confidential: Rugby Club Municipal Universitatea de Vest TimișoaraDocumento5 pagineConfidential: Rugby Club Municipal Universitatea de Vest TimișoaraKirk WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ministry Health Medicines Formulary 1 2015Documento371 pagineMinistry Health Medicines Formulary 1 2015David Lim Su ShenNessuna valutazione finora
- Limfoproliferari Cronice MaligneDocumento18 pagineLimfoproliferari Cronice MaligneAlice MuscaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Chapter 3 Goals of Prevention Methods of PreventionDocumento4 pagine7 Chapter 3 Goals of Prevention Methods of Preventionaryam aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepsheet Study Guide Med AdminDocumento7 paginePrepsheet Study Guide Med AdminHannaNessuna valutazione finora
- 737-Article Text-3361-2-10-20220827Documento4 pagine737-Article Text-3361-2-10-20220827Melinda NurfadhilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutri QuizDocumento5 pagineNutri QuizAngel Kaye FabianNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccination Form (Sample)Documento1 paginaVaccination Form (Sample)Godfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Paper On The IntegumentaryDocumento2 pagineReaction Paper On The IntegumentaryCamile Elaine Borromeo NocheNessuna valutazione finora
- Food AllergyDocumento2 pagineFood Allergydyfc25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus AssignmentDocumento6 pagineSystemic Lupus Erythematosus AssignmentnehaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data For EMRDocumento13 pagineData For EMRggggangNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject - Obstetrics and Gynecology Batch - BBA (HA) IV Sem. Submit To - Dr. Jyoti Joshi Ma'am Submit by - Shivam Rajput & Umesh ChoyalDocumento19 pagineSubject - Obstetrics and Gynecology Batch - BBA (HA) IV Sem. Submit To - Dr. Jyoti Joshi Ma'am Submit by - Shivam Rajput & Umesh ChoyaldevNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis MachineDocumento1 paginaDialysis MachineMarifer NazNessuna valutazione finora
- Biolase TimelineDocumento19 pagineBiolase Timelinemohamed radwanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Use of Vancomycin With Its Therapeutic and Adverse Effects: A ReviewDocumento11 pagineThe Use of Vancomycin With Its Therapeutic and Adverse Effects: A Reviewdea yuniarNessuna valutazione finora