Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bedford Fowler Chap 4
Caricato da
Asheesh KumarCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bedford Fowler Chap 4
Caricato da
Asheesh KumarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.
Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
SystemofForcesandMoments
Introduction
Themomentvectorofaforcevector, ,withrespecttoapointhasamagnitudeequalto
theproductoftheforcemagnitude,F,andtheperpendiculardistancefromthepointtothe
lineofactionoftheforce,D:M=DF.Thedirectionofthemomentisthroughthepointand
perpendiculartotheplanecontainingthepointandthelineofactionoftheforce.Itssignis
definedbytherighthandrule.
Figure1Force,F,withleverarm,D Figure2Forcecomponentswithleverarms
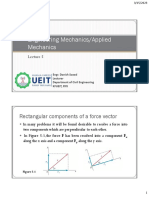
Analternativeequivalenttofindingtheperpendiculardistancebetweenthepointandthe
forceistocomputetheindividualcomponentsofthemomentvector, .Considerforce
componentsintheYZplane, and .TheycauseamomentabouttheXaxis.The
componentsofthepositionvectorinthatplaneare and .Notethatdistance isthe
perpendicularleverarmofcomponent ,andlikewisefor and .However,their
turningeffects,withrespecttotheorigin,havedifferentsigns(counterclockwiseis
positive).Therefore,youcanwritethemomentcomponentabouttheXaxisas
. (1a)
Notethexyzsequenceofthefirstthreesubscripts.Theothertwocomponentsofthe
momentvectorfollowapermutationofthatpattern(xyz,yzx,zxy).Namely,
.(1b)
Thefirsttwotermsineachofthethreemomentcomponentsfollowthexyzpermutation,
andthelastproductinanysinglecomponentreversesthesubscriptsofthepriorproduct.
Theabovealternativecorrespondstothevectorcrossproductofpositionvector and
forcevector :
.(2)
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page1of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
Theabovecomponentsequencepermutationappliestoanycrossproductoftwovectors:
(3)
ThisformofthemomentcomponentcalculationsiseasilyenteredintoTKSolver.This
componentformisusedinthepresentedexamplesbelow.
Inadditiontofindingthemomentofaforceatapoint,youfrequentlyneedtofindthe
portionofthatmomentthatactsonalinethroughthepoint.Thatportioniscalledthe
momentofaforceaboutaline.Themagnitudeofthemomentaboutthelineisthe
perpendicularprojectionofthetotalmomentmagnitudeontotheline.Thatactionis
showninFigure3.Inotherwords,itisthedotproductofthemomentvectorandtheunit
vectorthatdefinesthedirectioncosinesoftheline:
,(4)
andthefullvectormomentabouttheline(includingitscomponentssigns)is
.(5)
Figure3Projectingamomentvectorontoaline
Ingeneral,Newtonsstaticequilibriumrelationsinvolvebothforcesandmoments.
Specifically,theresultantforcemustvanish,asmusttheresultantmomentaboutany
arbitrarypoint,sayP:
0, 0.
Almostallofthefutureapplicationswillinvolvetheuseofmomentequilibrium.
Frequently,thechoiceofthelocationofthemomentpoint,P,istakenatapointontheline
ofactionoftheforcewiththemostunknowncomponents.Sincetheleverarmtosuch
forcesiszero,thoseforcevectorcomponentsdonotappearintheequationsforthe
momentvectorcomponents.
Youcanwritevalidmomentequationsatdifferentpoints.WithTKSolver,itisactually
usefultohaveadditionalvalidequationsintheruleset.Inthepast,studentswererequired
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page2of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
tosolvemanydifferentapplicationstolearnbyexperiencehowtopickpointsthat
introducetheminimumnumberofunknownsintothemomentequilibrium.UsingTK
Solver,youjustneedtocountthenumberofunknownsandwriteatleastthatmanyvalid
equilibriumrulesbyusingvariousFBDsand/orbyselectingvariouspointsforcalculating
theresultantmoments.
Inthischapter,youlearnhowtocalculateresultantmomentsandforcesneededfor
equilibrium.Inthenextchapter,youwillusetheminsolvingequilibriumrelationsfor
objectsofmorecomplicatedshapes.
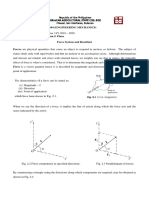
Example4.3
ThesystemandtheFBDsareshowninFigure4.Assumethatforce isincompression
andactsuptotheright.Here,therearethreeunknowns,forcesC_x,C_y,andthecable
tensionmagnitude,T(sincethepinsupportforceatBmustbeequaltothestraightcable
forcethere).Asatwodimensionalproblem,forceequilibriumgivestwoequations,and
momentequilibriumgivesoneequation(abouttheaxisperpendiculartotheplane)per
FBD.Here,youcoulddrawthreeFBDs:thesystem,theinclinedbar,theinclinedcable.
Withexperience,youwouldnotethattakingmomentsaboutpointCwouldgiveyouthe
tensionmagnitudedirectlyasthesingleunknown.But,thatisnotanecessarychoiceas
shownbelow.
Figure4Aconcurrentbarcablesystemwithdimensions
First,notethegeometrydata.ItisclearthatpointsBandCaredirectlyaboveeachother.
Thecableforce(andtheexternalforceatsupportB)hasaknowndirection.Fromthe
givencoordinates(formingtherare3:4:5triangle)youcouldwritethedirectioncosinesof
thecablebyinspection.Instead,youcanalwaysconstructthe(straight)cablesunitvector
fromthosedata( ).Alsonotethatthehorizontalleverarmsoftheweight,withrespect
topointsA,B,C,aresoobviousthattheycanbeuseddirectly,withoutbuildingaunit
vector.Thegivenhorizontalandverticaldistanceswillbedenotedbyhandv,respectively
here.Invokemomentequilibrium.TakemomentsaboutthezaxisatpointA(with
counterclockwisetakenasthepositivesense),inFBD1:
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page3of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
0.
ForceequilibriuminFBD1gives
0,
0.
ThissystemofthreeequationsandthreeunknownscanbesolvedbyTK.Youcanalso
writearedundantequationbytakingmomentsaboutpointB(and/oraboutC):
0.
Notethattheverticalforcecomponent didnotenterthelastequationbecauseitslineof
actionpassedthroughpointB( 0).Nowyouhavefourequilibriumequationsand
threeunknowns.ThoserulesaregiveninFigure5.Especiallynotethatthelengthswere
giventheirabsolutevalues.Thus,thesignsoftheunitvectorweredeterminedby
inspection.Thatisalsotrueforthemomentcalculations.Formorecomplicated
geometriestobecoveredlateryouwoulduseEq1directly,andsupplythealgebraicvalues
fortheknowndistanceorforcecomponents.Asnotedabove,youcouldhaveoriginally
writtenaredundantfourth(orfifth)equationofequilibrium(showninFigure6).
Figure5Equilibriumandgeometryrelationsforthebarcablesystem
Figure6Redundantmomentequilibriumrelation
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page4of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
Here,thoseadditionaltwolineswereappendedtothebottomofthefile.They,ofcourse,
didnotchangetheoutputsfortheforcecomponents.Thecorrespondingoriginaloutputis
giveninFigure7,anditagreeswiththetextresult.
Figure7Forceandgeometryresultsforthebarcablesystem
Example4.8
Thisproblemisastraightforwardcalculationoffindingthemomentatapointonalineand
thenprojectingthatmomentontotheline.Thegeometryandgivenvectorsareshownin
Figure8.Therearemoregeometrycalculationsthatforthemoments.Therulesforboth
Figure8Forcecausingamomentaboutaline
areshowninFigure9.Again,notethenonproceduralnatureofTKSolverinthatposition
vector isutilizedinthefirstrow,butisnotdefineduntillater.Inthiscase,thealgebraic
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page5of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
signofeachcomponentisinputandthegeneralmomentequationsofEqs1,4and5are
employed.TheoutputsaregiveninFigure10.
Thesignofthemagnitudeofthemoment ispositive(whichdiffersfromthetext).
Thatmeansithasthesamedirectionasunitvector .Ifusingtherighthandrule,point
yourthumbtowardpointCfrompointB.Yourfingersthenshowthedirectionofthe
turningeffectoftheforceFaboutlineBC.
Figure9Rulessheetformomentofaforceaboutaline.
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page6of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
Figure10Outputsformomentaboutalinebyaforce
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page7of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
Example3.5Revisited
YoufoundthethreeunknowncableforcesinExample3.5byusingonlyforceequilibrium.
Thatwasprobablythesimplestwaytosolvethatproblem.Youcouldhaveusedonlythe
threemomentequilibriumequationaboutthex,yandzaxes.Thefiguresforthat
problemarerepeatedhereinFigure11.
Withexperience,youmightobservethatcableforcesT_ABandT_ACwouldpassthrough
lineBCandthereforewouldhavenomomentsaboutthatline.OnlytheweightWandcable
forceT_ADdonotintersectthatline.Therefore,arulethatsaysthattheresultantmoment
aboutlineBCiszerowouldgiveyouoneequationandoneunknown.Youreallydonot
needobservationslikethat,unlessyouaretryingtominimizehandcalculations(orsave
timeonatest).Nevertheless,theTKrulesforthatcalculationareshowninFigure12to
illustratemomentequilibriumaboutalinecausedbymultipleforces.
Figure11Momentoftwoforcesaboutaline
KnowingthatyouaregoingtotakemomentsaboutlineBC,therearetworeasonsthat
justifyomittingthemomentofcabletension .Thefirstisthephysicalobservationthat
thelineofactionofforceACintersectslineBC.Therefore,ithasnoleverarmwithrespect
tothatline.Thesecondreasonisapurelymathematicalone.Thevectoralgebradefinition
ofthemagnitudeofthemomentoftension aboutthelineisidenticallyzero:
_ 0.
Thatisbecauseforanytwovectors, and , 0since( )is
perpendiculartoboth and .Thus,itsdotproductwith iszero.
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page8of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
Figure12Equilibriumviamomentsaboutaline
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page9of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
Figure13FindingtensionT_ADwithoneequation
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page10of11
Bedford,Fowler:Statics.Chapter4:SystemofForcesandMoments,ExamplesviaTKSolver
Admittedly,thenumberofanalyticgeometrycalculationsislarge,buttheyrepresentterms
youwouldhavetocalculatebyhand.Youcouldprobablydothosecalculationsbyhand
fasterthanyoucouldtypetheTKrules.Themainpointhereistoemphasizethemechanics
giveninthelastsevenrules.Notethatitwouldhavetakenfewerrulestoincludethe
equilibriumaboutlineBCiftheyhadjustbeenaddedtotherulesinthepriorsolutionof
Example3.5.Before,positionvector wasemployedandyoucouldhavejustusedits
negativevalueastheleverarmforboththeweightandtensioninsteadofcomputing .
Thesameistruefortheunitvectorsintroducedinthisrevision.
Forthebeginner,stepslikerequiringequilibriumaboutalineareusuallynotneeded.
Instead,youcanusuallyjustrequirethattheresultantforceandmomentvanishineach
FBD.Then,theimportanteffortistoconstructmultiplecorrectFBDs.
CopyrightJ.E.Akin.Allrightsreserved.Page11of11
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- L3: Equivalent Systems of Forces Moment of A Force: Statics of Rigid BodiesDocumento8 pagineL3: Equivalent Systems of Forces Moment of A Force: Statics of Rigid BodiesJohn Laurence Gonzaga AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Forces and EquilibriumDocumento53 pagineChapter 2 Forces and EquilibriumvinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 7 Quiz Exception HandlingDocumento6 pagineSection 7 Quiz Exception Handlingsyahndra100% (1)
- Rigid body statics and dynamics equationsDocumento20 pagineRigid body statics and dynamics equationsJulia ChiesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Node Nodal Degrees of Freedom: 1. The Definition of The Finite Element Method (FEM)Documento32 pagineNode Nodal Degrees of Freedom: 1. The Definition of The Finite Element Method (FEM)KomarudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bar Elements in 2D SpaceDocumento49 pagineBar Elements in 2D SpaceMohd NasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Chapter 4-5Documento29 pagineReview Chapter 4-5fannyparamitaNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 STARTER Connection To Target Device en - IDESA - BRASKEMDocumento41 pagine04 STARTER Connection To Target Device en - IDESA - BRASKEMADRIANA ESCOBAR HERNANDEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Ladder Diagram: Rung 1 Rung 2 Rung 3Documento26 pagineLadder Diagram: Rung 1 Rung 2 Rung 3abdullah 3mar abou reashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ms Word ProjectDocumento1 paginaMs Word Projectapi-27149177Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bilgmon488 Instruction Manual VT PDFDocumento33 pagineBilgmon488 Instruction Manual VT PDFharikrishnanpd3327Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes in Strength of Materials - 1Documento93 pagineLecture Notes in Strength of Materials - 1Rhea MambaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 em - CDT9 - Week3 - 2022-23Documento3 pagine9 em - CDT9 - Week3 - 2022-23suchith reddy arukalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mechanics Couple MomentDocumento10 pagineEngineering Mechanics Couple MomentRaafa AliankaNessuna valutazione finora
- LN 10, 11 & 12 - ME 1227 Engineering MechanicsDocumento33 pagineLN 10, 11 & 12 - ME 1227 Engineering MechanicsSakibNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2. Force VectorDocumento18 pagineTopic 2. Force VectorArnold Apostol Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 Chapter 2 - Force Systems 2DDocumento61 pagineLecture 3 Chapter 2 - Force Systems 2Drobel metikuNessuna valutazione finora
- Force System Resultants: Moment of A ForceDocumento33 pagineForce System Resultants: Moment of A ForceErikNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5b Force Resultant SystemDocumento38 pagineChapter 5b Force Resultant SystemRyan Philip CatapangNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture (1) : Vectors and ScalarsDocumento20 pagineLecture (1) : Vectors and ScalarsAhmad DaqaladNessuna valutazione finora
- Force System and ResultantDocumento20 pagineForce System and ResultantMyra GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec4Statics Moment of A Forcepptx 1Documento54 pagineLec4Statics Moment of A Forcepptx 1Jared RoseNessuna valutazione finora
- 1973_Journal of Structural Mechanics_1_497-518_WITTRICKW-An Algorithm for Computing Critical Buckling Loads of Elastic StructuresDocumento23 pagine1973_Journal of Structural Mechanics_1_497-518_WITTRICKW-An Algorithm for Computing Critical Buckling Loads of Elastic StructuresZhangJiayongNessuna valutazione finora
- Statics of Rigid Bodies Force SystemsDocumento22 pagineStatics of Rigid Bodies Force SystemsJam LarsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5Documento17 pagineLecture 5Mr. Danish SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Scalars and Vectors: ScalarDocumento22 pagineScalars and Vectors: Scalarsuwilanji kawambaleNessuna valutazione finora
- A (Bold Faced) : by HandDocumento79 pagineA (Bold Faced) : by Handএ. এইচ ফিরোজNessuna valutazione finora
- SpecSimVR MEGDocumento6 pagineSpecSimVR MEGMatthew GarnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Md. Musfiqur Rahman Milton: Lecturer, CSE BaiustDocumento15 pagineMd. Musfiqur Rahman Milton: Lecturer, CSE Baiustadiba adibNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Force SystemsDocumento46 pagineUnit 2 Force Systemsputex247Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter+2Documento24 pagineChapter+2Mary Jane SañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4.1 - Direct Stiffness Method - StructuralDocumento49 pagineChapter 4.1 - Direct Stiffness Method - Structuralsanyam KanungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotational Spectrum Generation Using ExcelDocumento8 pagineRotational Spectrum Generation Using ExcelJuan MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct Stiffness Method: Finite Elements for Springs, Bars, Trusses and BeamsDocumento69 pagineDirect Stiffness Method: Finite Elements for Springs, Bars, Trusses and BeamsRamendra KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Statics Fundamentals ExplainedDocumento12 pagineStatics Fundamentals ExplainedBruce RiversNessuna valutazione finora
- IMs Eng Mechanics ENSC 20143 1ST SEM 21 22 1 3Documento37 pagineIMs Eng Mechanics ENSC 20143 1ST SEM 21 22 1 3JON MANNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet (3) Moment of F Abount Point 2D-3DDocumento13 pagineSheet (3) Moment of F Abount Point 2D-3DSamir ZaghloolNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 1Documento37 pagineUnit - 1Hanan ShayiboNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Rigid BodyDocumento21 pagineChapter 3 Rigid BodyimfendiNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Analysis for Architects: An IntroductionDocumento82 pagineStructural Analysis for Architects: An IntroductionALAWI SSEKUBUNGANessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: Force SystemsDocumento28 pagineChapter 2: Force SystemsFawad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic1 2to1 4Documento35 pagineTopic1 2to1 4Sesha Sai KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Vibration analysis of a Duffing oscillatorDocumento18 pagineVibration analysis of a Duffing oscillatorDaniyal AsifNessuna valutazione finora
- LN 5 & 6 - ME 1227 Engineering MechanicsDocumento32 pagineLN 5 & 6 - ME 1227 Engineering MechanicsSakibNessuna valutazione finora
- 03b Direct Stiffness Method TrussDocumento18 pagine03b Direct Stiffness Method TrussAnamolNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 in Abe 215 Statics1 l1 5Documento22 pagineModule 2 in Abe 215 Statics1 l1 5Cynel DelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 Chapter 2 - Part IDocumento60 pagineLecture 2 Chapter 2 - Part IFeye MumichaNessuna valutazione finora
- CE201 Statics Chap2Documento49 pagineCE201 Statics Chap2taniaNessuna valutazione finora
- LECTURE for Mechanical Engineer 2Documento30 pagineLECTURE for Mechanical Engineer 2smuapnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Statics of Rigid Bodies: Chapter 3: Equilibrium of A ParticleDocumento23 pagineStatics of Rigid Bodies: Chapter 3: Equilibrium of A ParticleRyan Philip CatapangNessuna valutazione finora
- JJ205 Engineering Mechanic Chapter 3 Jj205Documento5 pagineJJ205 Engineering Mechanic Chapter 3 Jj205Ah TiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 PDFDocumento8 pagineLecture 2 PDFYunus qanoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Chapter 2 PDFDocumento17 pagineMechanics Chapter 2 PDFsoma SarkawtNessuna valutazione finora
- force_table_labDocumento5 pagineforce_table_labqwesghwqedfgNessuna valutazione finora
- Forces and EquilibriumDocumento57 pagineForces and EquilibriumUnknown_unknown_unknownNessuna valutazione finora
- Engg - Mech Lab Manual 2017 18Documento28 pagineEngg - Mech Lab Manual 2017 18Girish ShindeNessuna valutazione finora
- MECH 211 - Couples, Moment of ForceDocumento28 pagineMECH 211 - Couples, Moment of ForceJohn David AbarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Part1 EmotionDocumento46 paginePart1 EmotionhohoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 - Scalars and VectorsDocumento9 pagine1.4 - Scalars and Vectorsmutahar khanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Material Obeys Hooke's Law. 3. Forces Are Applied Only at The Ends of The Bar. 4. The Bar Supports Axial Loading Only Bending, Torsion, and Shear Are NotDocumento16 pagineThe Material Obeys Hooke's Law. 3. Forces Are Applied Only at The Ends of The Bar. 4. The Bar Supports Axial Loading Only Bending, Torsion, and Shear Are NotMuket AgmasNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental Principles of Mechanics: ME231: Solid Mechanics-IDocumento14 pagineFundamental Principles of Mechanics: ME231: Solid Mechanics-IRohan sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 1 - Static Force Analysis PDFDocumento29 pagineChapter - 1 - Static Force Analysis PDFSourabh JangraNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4: Deflection of Structures Lecture 6: Maxwell-Betti Law of Reciprocal DeflectionsDocumento7 pagineModule 4: Deflection of Structures Lecture 6: Maxwell-Betti Law of Reciprocal DeflectionsTHE BOSS DRAWINGBAAZNessuna valutazione finora
- Nit Calicut TicketDocumento2 pagineNit Calicut TicketAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Rr410307 Non Conv - Sourse of EnergyDocumento2 pagineRr410307 Non Conv - Sourse of EnergySRINIVASA RAO GANTANessuna valutazione finora
- Python Data Science Exam Mar 4Documento4 paginePython Data Science Exam Mar 4Asheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Workshop Practice Createspace 22-06-2013 AcademiaDocumento33 pagineWorkshop Practice Createspace 22-06-2013 Academiamanojkhadka23100% (1)
- O 8 OppopDocumento4 pagineO 8 OppopAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- National Institute of Technology, Manipur Langol, Imphal, Manipur - 795 001Documento11 pagineNational Institute of Technology, Manipur Langol, Imphal, Manipur - 795 001Asheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- New Draft UGCRegulation-2018!9!2Documento84 pagineNew Draft UGCRegulation-2018!9!2Meeit GuleriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 12BDocumento3 pagineForm 12BAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Gwec Iweo 2016 LR PDFDocumento20 pagineGwec Iweo 2016 LR PDFbaz chackoNessuna valutazione finora
- IIA Outreach Scientist RecruitmentDocumento4 pagineIIA Outreach Scientist RecruitmentSwathy NikhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Registration Page by Team LeaderDocumento3 pagineRegistration Page by Team LeaderAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 07a1ec04 - Computer ProgrammingDocumento4 pagine07a1ec04 - Computer ProgrammingSRINIVASA RAO GANTANessuna valutazione finora
- 10 - Chapter 5Documento61 pagine10 - Chapter 5Asheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Consent Letter For EWSDocumento1 paginaConsent Letter For EWSAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- rr10101 EnglishDocumento8 paginerr10101 EnglishSrinivasa Rao GNessuna valutazione finora
- r05010204 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocumento11 paginer05010204 Electronic Devices and CircuitsSrinivasa Rao GNessuna valutazione finora
- Nontraditional MachiningDocumento22 pagineNontraditional MachiningSagar WakankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Rr420204 Embedded SystemsDocumento1 paginaRr420204 Embedded SystemsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANessuna valutazione finora
- Unconventional Machining Process - Unit 1: Prepared by S. Senthil Kumar Ap / Mech SvcetDocumento57 pagineUnconventional Machining Process - Unit 1: Prepared by S. Senthil Kumar Ap / Mech Svcetmiraculas GNessuna valutazione finora
- Merged PDFDocumento121 pagineMerged PDFAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB MANUAL COVERS TURNING, MILLING, DRILLING PROCESSESDocumento24 pagineLAB MANUAL COVERS TURNING, MILLING, DRILLING PROCESSESAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 07a1bs08 Physical ChemistryDocumento4 pagine07a1bs08 Physical ChemistrySRINIVASA RAO GANTANessuna valutazione finora
- Non TradDocumento70 pagineNon TradHelliel OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Me2026 Ump PDFDocumento68 pagineMe2026 Ump PDFDr R LOGANATHANNessuna valutazione finora
- B.tech Mechanical Consolidated Time Tables Sem-II 2017Documento21 pagineB.tech Mechanical Consolidated Time Tables Sem-II 2017Asheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 40 Non Conventional MachiningDocumento20 pagine40 Non Conventional MachiningPRASAD326100% (6)
- 2018 Journal Impact Factor 2018Documento252 pagine2018 Journal Impact Factor 2018knighthood4allNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization techniques and applicationsDocumento1 paginaOptimization techniques and applicationsAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- M.techthermalengineering Isem1 PDFDocumento13 pagineM.techthermalengineering Isem1 PDFAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- M Tech IYearISemOpenElectives PDFDocumento10 pagineM Tech IYearISemOpenElectives PDFAsheesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer AIS Chap 1 and 2Documento10 pagineReviewer AIS Chap 1 and 2Jyasmine Aura V. AgustinNessuna valutazione finora
- DQx8-24V 6ES75221BF000AB0 - Datasheet - enDocumento3 pagineDQx8-24V 6ES75221BF000AB0 - Datasheet - enCarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- HT12D Ht12d-20soplf HT12FDocumento13 pagineHT12D Ht12d-20soplf HT12FAnonymous t9tLb3WgNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Communication Process and Product 8th Edition Guffey Solutions ManualDocumento23 pagineBusiness Communication Process and Product 8th Edition Guffey Solutions ManualDanielLopezfzio100% (51)
- (LTE) - Default Bearer, Dedicated Bearer PDFDocumento7 pagine(LTE) - Default Bearer, Dedicated Bearer PDFABHISHEK AGARWALNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyber Security Analyst ResumeDocumento5 pagineCyber Security Analyst Resumeafiwgbuua100% (2)
- 05 - 05 LISTA de LCD - XLSX - Carlos CellDocumento2 pagine05 - 05 LISTA de LCD - XLSX - Carlos CellThiago QueirozNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study of Building A Data Warehouse With Analysis ServicesDocumento10 pagineCase Study of Building A Data Warehouse With Analysis ServicesbabussnmcaNessuna valutazione finora
- ELE 353L - 01 - Spring - 24Documento3 pagineELE 353L - 01 - Spring - 24b00092571Nessuna valutazione finora
- Create A Report of The Employees Under Various Education Qualification in A List BoxDocumento5 pagineCreate A Report of The Employees Under Various Education Qualification in A List BoxnishantNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Coil WindingDocumento8 pagineHandbook of Coil WindingSREENATH S.SNessuna valutazione finora
- The Brocard - Ramanujan Diophantine Equation N! + 1 M 2Documento2 pagineThe Brocard - Ramanujan Diophantine Equation N! + 1 M 2api-26401608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Philippines Weekly Home Learning Plan for Science 8Documento1 paginaPhilippines Weekly Home Learning Plan for Science 8Jaeda BaltazarNessuna valutazione finora
- آسامی، بنگالی طلسمی راز (کتب خانہ طبیب)Documento377 pagineآسامی، بنگالی طلسمی راز (کتب خانہ طبیب)baba hameedNessuna valutazione finora
- India's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future TrendsDocumento5 pagineIndia's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future Trendspriyaa2688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ict Skills IIDocumento28 pagineIct Skills IIShraddha DubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- IC-FR3000 FR4000 Series BrochureDocumento2 pagineIC-FR3000 FR4000 Series BrochureMikeNessuna valutazione finora
- CitectSCADA 7.20 Service Pack 2 Release NotesDocumento31 pagineCitectSCADA 7.20 Service Pack 2 Release Notesbasecamp cikarangNessuna valutazione finora
- Umfluxus Wdv2-1enDocumento193 pagineUmfluxus Wdv2-1engelealdo souza ferreiraNessuna valutazione finora
- C-Band Block Frequency ConvertersDocumento2 pagineC-Band Block Frequency ConvertersThanhNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparing a Highway ModelDocumento4 paginePreparing a Highway Modelrinlu patilNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Maximum Value When Evaluating ProductsDocumento18 pagineGetting Maximum Value When Evaluating ProductsLilianneNessuna valutazione finora
- Degrees of Freedom Analysis in Process Control: PergamonDocumento7 pagineDegrees of Freedom Analysis in Process Control: PergamonPriyam NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Fyp ProjectDocumento5 pagineFyp ProjectUsman PashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Recommendation of Dishes Based On FlavorDocumento4 pagineRecommendation of Dishes Based On FlavorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora