Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Differentiationsummary PDF
Caricato da
J LevinsTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Differentiationsummary PDF
Caricato da
J LevinsCopyright:
Formati disponibili
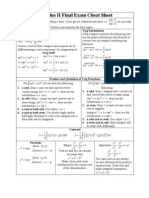
SUMMARY OF DIFFERENTIATION
du dv
v dx u dx
d dv du d u
Product Rule: dx (uv) = u dx + v dx Quotient Rule: dx v = v2
dy dy du d
Chain Rule: If y = f(u) and u = g(x), then dx = du dx e.g. dx sin3 x2 = 3 sin2 x2 (cos x2) 2x
d d
Trigonometric Functions: dx sin x = cos x dx cos x = sin x
d 2 d 2
dx tan x = sec x dx cot x = cosec x
d d
dx sec x = sec x tan x dx cosec x = cosec x cot x
d x d
Exponential Functions: dx e = e
x
y = ax ln y = x ln a dx ax = ax ln a
d 1 d d ln x 1
Logarithmic Functions: dx ln x = x dx loga x = dx ln a = x ln a
Inverse Trigonometric Functions (given in Formula List):
d 1 1 d 1 1 d 1 1
dx sin x = 2 dx cos x = 2 dx tan x = 1 + x2
1x 1x
dy dy
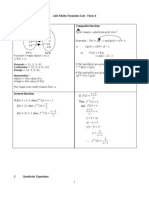
Implicit Differentiation e.g. Differentiating x2 + y3 = xy gives 2x + 3y2 dx = y + x dx
dy dy dt 2 dy dy/dt cos t
Parametric Differentiation: dx = dt dx e.g. if y = sin t, x = t , then dx = dx/ = 2t
dt
y y0 dy
Equation of tangent at the point (x0 , y0) is x x = m where m = value of dx at x = x0
0
y y0 1
Equation of normal at the point (x0 , y0) is x x = m
0
E.g. If y = x2, then the equation of the tangent at (2, 4) is y 4 = 4(x 2) i.e. y = 4x 4
1 1 9
and the equation of the normal is y 4 = 4 (x 2) i.e. y = 4 x + 2
Rate of Change:
4 dr dV dV dr
E.g. Given V = 3 r3, dt = 10 m s1. When r = 1 m, dt = dr dt = 4r210 = 40 m3 s1.
Maximum and Minimum: Find the maximum area of a rectangle inscribed in a circle of radius r.
Area A = xy = x2 r2 2 = x 4r2 x2
x 2
A2 = x2(4r2 x2) = 4r2x2 x4
dA r
2A dx = 8r2x 4x3 = 4x(2r2 x2) = 0 x = r 2 y/2
x/2
d2A dA2 d2A
2A dx2 + 2 dx = 8r 12x = 16r < 0 when x = r 2 dx2 < 0
2 2 2
maximum A = r 2 4r2 2r2 = 2r2
dy
Gradient: If dx > 0, then the curve is increasing.
dy
If dx < 0, then the curve is decreasing.
d2y dy
Concavity: If dx2 > 0, then dx is increasing and the curve is concave upwards.
d2y dy
If dx2 < 0, then dx is decreasing and the curve is concave downwards.
12
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsDa EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Integrals PDFDocumento19 pagine9 Integrals PDFthinkiitNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential EquationDocumento28 pagineDifferential Equationronhuman14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesDa EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fe Tutorials Sem2Documento8 pagineFe Tutorials Sem2narendasreNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsDa EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 2.3 and 2.4 Differentiation FormulasDocumento12 pagine2.3 and 2.4 Differentiation FormulasMaylalaine AguinaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Integral CalculusDocumento25 pagineIntegral CalculusCarl Kristopher PeloniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Da EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Bab-I & Bab IiDocumento28 pagineTugas Bab-I & Bab IiblackzmillianNessuna valutazione finora
- Math ReveiwDocumento3 pagineMath ReveiwApache_mooNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus: Differentiation RulesDocumento17 pagineCalculus: Differentiation RulesAoSd' TikmanNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocumento2 pagineAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Da EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Nessuna valutazione finora
- VJ Integrali PDFDocumento52 pagineVJ Integrali PDFAgrif.bg-fovkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDa EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Integral Calculus HandoutsDocumento8 pagineIntegral Calculus Handoutsishtemash_hazeljaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineMicrosoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetHunterKing199375% (4)
- Add Maths Formulae ListDocumento8 pagineAdd Maths Formulae ListWong Hui SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tables of Weber Functions: Mathematical Tables, Vol. 1Da EverandTables of Weber Functions: Mathematical Tables, Vol. 1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mathematics Formula SheetDocumento2 pagineEngineering Mathematics Formula Sheetsimpsonequal100% (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageDa EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFDocumento16 pagineSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4 PDFNicholas Rogers80% (5)
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDa EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Additional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Documento19 pagineAdditional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Syazleen Nabilah AkmalNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Analysis and Probability: Solutions to ProblemsDa EverandReal Analysis and Probability: Solutions to ProblemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 37 - Chapter 2Documento28 pagineMath 37 - Chapter 2mrnrmrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions: If F (X) 2x - 2x + 1, Find F ( - 1) - (B) If F (T) 3t - 1, Find F (A)Documento14 pagineFunctions: If F (X) 2x - 2x + 1, Find F ( - 1) - (B) If F (T) 3t - 1, Find F (A)Dinesh RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Mth134 - Calculus II - Final Exam Formula Sheet: e e X e e XDocumento3 pagineMth134 - Calculus II - Final Exam Formula Sheet: e e X e e Xafaflotfi_155696459Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Revision Sheet For Class 11 and Class 12 PhysicsDocumento0 pagineMathematics Revision Sheet For Class 11 and Class 12 PhysicsSunil PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Circles (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDa EverandCircles (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNessuna valutazione finora
- INTEGRAL CALCULUS HandoutsDocumento7 pagineINTEGRAL CALCULUS Handoutsurfriend_jjn05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankDa EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry & CalculusDocumento69 pagineAnalytic Geometry & CalculusanonreteeNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometric functions in computer aided geometric designDa EverandGeometric functions in computer aided geometric designNessuna valutazione finora
- Rule For DifferentionDocumento16 pagineRule For DifferentionTemesgen BihonegnNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentDa EverandMathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDocumento25 pagineBab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDeazzy AndriyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYDa EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocumento3 pagineCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNessuna valutazione finora
- Kalkulus 03-DerivatDocumento86 pagineKalkulus 03-DerivatFajar Nur HidayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27Da EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Definite and Indefinite IntegrationDocumento18 pagineDefinite and Indefinite Integrationskj6272Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ecuac. Diferenc - Calc.40Documento47 pagineEcuac. Diferenc - Calc.40Mariale LeuzingerNessuna valutazione finora
- CalA - 6 - 2 PDFDocumento8 pagineCalA - 6 - 2 PDFGeorge Leon RibeiroNessuna valutazione finora
- HSC 3U Maths FormulaeDocumento7 pagineHSC 3U Maths FormulaeHotz InatorNessuna valutazione finora
- F (T) Is Changing With Respect To The Independent Variable T, It Is Natural That Equations InvolvingDocumento5 pagineF (T) Is Changing With Respect To The Independent Variable T, It Is Natural That Equations InvolvingMelvin EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector CalculusDocumento108 pagineVector CalculusHani Barjok100% (1)
- Text Book: Barrante, 3rd, 2004.: Applied Mathematics For Physical ChemistryDocumento38 pagineText Book: Barrante, 3rd, 2004.: Applied Mathematics For Physical ChemistryTzung-Ying YangNessuna valutazione finora
- Color For MenDocumento232 pagineColor For MenSteve101101100% (17)
- Sat Subject Tests Student Guide PDFDocumento72 pagineSat Subject Tests Student Guide PDFNishchay BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- Breakfast Recipes FINALDocumento20 pagineBreakfast Recipes FINALFazil Duraman75% (4)
- GCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2Documento35 pagineGCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2purityplus89% (9)
- Edexcel AS PhysicsDocumento172 pagineEdexcel AS PhysicsNishchay Bhatt93% (14)
- GCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2Documento35 pagineGCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2purityplus89% (9)
- Sudoku (Medium Difficulty)Documento54 pagineSudoku (Medium Difficulty)Nishchay BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- Run Ons+Fragments+Dangling ModifiersDocumento5 pagineRun Ons+Fragments+Dangling ModifiersNishchay BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.2 QuestionsDocumento4 pagine5.2 QuestionsNaeemKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Properties of Period 3 Elements WorkSheetDocumento1 paginaChemical Properties of Period 3 Elements WorkSheetNishchay BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- CORMS BiologyDocumento13 pagineCORMS BiologyNishchay BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- EDEXCEL 4CH0 1C Chemistry JAN 2012 Question PaperDocumento28 pagineEDEXCEL 4CH0 1C Chemistry JAN 2012 Question PaperMoen RahmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeDa EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (8)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeDa EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsDa EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingDa EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (21)











































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)
































