Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Summary of All The Grammar
Caricato da
Rocío Pinedo Rodríguez0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
39 visualizzazioni5 paginesummary of preset and past simples, continuous and perfect
Titolo originale
Summary of All the Grammar
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentosummary of preset and past simples, continuous and perfect
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
39 visualizzazioni5 pagineSummary of All The Grammar
Caricato da
Rocío Pinedo Rodríguezsummary of preset and past simples, continuous and perfect
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 5
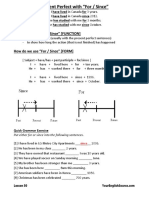
PRESENT SIMPLE
Structure
+ subject verb (-s) complement(s)
- subject dont/doesnt verb complement(s)
? do/does subject verb complement(s)?
Usage
Daily routines
Timetables and schedules
Things that are always true
Things that happen regulary
Verbs which describe states or feelings even if they mean now
Examples
I like football
I dont like football
Do you like football?
PAST SIMPLE
Structure
+ subject verb (in past) complement(s)
- subject didnt verb complement(s)
? did subject verb complement(s)?
Usage
Finished past actions
Examples
I ate soup
I didnt eat soup
Did you eat soup?
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Structure
+ subject to be verb (-ing) complement(s)
- subject to be + not verb (-ing) complement(s)
? to be subject verb (-ing) complement(s)?
Usage
Actions in progress at the time of speaking
Future arrangements (= be going to)
Examples
I am going to the party
I am not going to the party
Are you going to the party?
PAST CONTINUOUS
Structure
+ subject was/were verb (-ing) complement(s)
- subject was/were + not verb (-ing) complement(s)
? was/were subject verb (-ing) complement(s)?
Usage
Action in progress at a specific time in the past
Action in progress which was interrupted by another action (expressed in the
past simple)
With while for two actions happening at the same time
Describe the beginning of a story or anecdote
Examples
I was cooking dinner
I wasnt cooking dinner
Were you cooking dinner?
PRESENT PERFECT
Structure
+ subject to have verb (past complement(s)
participle)
- subject to have + not verb (past complement(s)
participle)
? to have subject verb (past complement(s)?
participle)
Usage
Past experiences not saying exactly when they happened
Recent past actions (often with just)
With yet and already
Examples
I have done something
I havent done anything
Have you done anything?
PAST PERFECT
Structure
+ subject had verb (past complement(s)
participle)
- subject had + not verb (past complement(s)
participle)
? had subject verb (past complement(s)?
participle)
Usage
We are talking about the past and we want to talk about an earlier past
action. Compare:
o When John arrived, they went out (= first John arrived, then they
went out)
o When John arrived, they had gone out (= they went out before John
arrived)
Examples
She had already cooked the dinner when you called
She hadnt already cooked the dinner when you called
Had she already cooked the dinner when I called?
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS
Structure
+ subject to have been verb (-ing) complement(s)
- subject to have + not been verb (-ing) complement(s)
? to have subject been verb (-ing) complement(s)?
Usage
Examples
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS
Structure
+ subject had been verb (-ing) complement(s)
- subject had + not been verb (-ing) complement(s)
? had subject been verb (-ing) complement(s)?
Usage
Examples
FUTURE SIMPLE
Structure
+ subject will verb complement(s)
- subject wont verb complement(s)
? will subject verb complement(s)?
Usage
Examples
WHEN DO I HAVE TO USE?
Present continuous, be going to or will?
Present continuous: future arrangements (= be going to)
Be going to: future arrangements (= be going to), something is already
decided and make evident predictions
Will: instant decisions, promises, offers, suggestions and predictions or talk
about future facts
o Shall instead of will in suggestions and offers when they are questions
Present perfect or past simple?
Present perfect: we dont specify the time
Past simple: the time is mentioned or understood
REPORTED SPEECH
Present simple Past simple
Present continuous Past continuous
Past simple
Present perfect Past perfect
Past perfect
Past continuous
Present perfect continuous Past perfect continuous
Past perfect continuous
Modals
will would
can could
may might
must/have to had to
would/could/might/should/ought to would/could/might/should/ought to
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pres Simpl, Cont, Past Simpl, Cont, Pres PerfDocumento4 paginePres Simpl, Cont, Past Simpl, Cont, Pres PerfRocío Pinedo RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Verbos Irregulares Por Tipo de IrregularidadDocumento1 paginaVerbos Irregulares Por Tipo de IrregularidadRocío Pinedo RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- For and Since. Explanation and ExercisesDocumento7 pagineFor and Since. Explanation and ExercisesRocío Pinedo RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pizza QuestDocumento16 paginePizza QuestRocío Pinedo RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Journal of Visual Culture 2009 Nardelli 243 64Documento23 pagineJournal of Visual Culture 2009 Nardelli 243 64Yce FlorinNessuna valutazione finora
- Purposive Communication - Post TestDocumento3 paginePurposive Communication - Post TestMarydhel Hope EvardoneNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 ReferencesDocumento2 pagine09 ReferencesLizweNessuna valutazione finora
- TV Is Bad For ChildrenDocumento1 paginaTV Is Bad For ChildrenUmisadidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marshall Mcluhan Myth and Mass MediaDocumento11 pagineMarshall Mcluhan Myth and Mass MediaKaren CtNessuna valutazione finora
- Celebrity Endorsement For Sporting Events Using Classical Conditioning PDFDocumento12 pagineCelebrity Endorsement For Sporting Events Using Classical Conditioning PDFAndrea Mahecha100% (1)
- City Branding JournalDocumento11 pagineCity Branding JournalWillyNessuna valutazione finora
- Total English Intermediate Photocopiable Worksheets PDFDocumento118 pagineTotal English Intermediate Photocopiable Worksheets PDFramiona2333% (3)
- Richard L. Crocker - Discant, Counterpoint, and HarmonyDocumento22 pagineRichard L. Crocker - Discant, Counterpoint, and Harmonyqvrlenarasegt100% (2)
- Little Women by Sandra DocringDocumento7 pagineLittle Women by Sandra DocringrienxternelNessuna valutazione finora
- SPT Presentation FinalDocumento14 pagineSPT Presentation Finalzaheer malikNessuna valutazione finora
- The Roots of Cognitive Neuroscience - Behavioral Neurology and NeuropsychologyDocumento431 pagineThe Roots of Cognitive Neuroscience - Behavioral Neurology and NeuropsychologycharbelhannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Body LanguageDocumento94 pagineBody Languagej9855552515Nessuna valutazione finora
- History of Wushu - IWUFDocumento5 pagineHistory of Wushu - IWUFStanislav Ozzy PetrovNessuna valutazione finora
- Hellenistic CosmologyDocumento2 pagineHellenistic CosmologyDelores WeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Vlastos, Equality and Justice in Early Greek CosmologiesDocumento24 pagineVlastos, Equality and Justice in Early Greek CosmologiesJocelinPonceNessuna valutazione finora
- OMTDocumento19 pagineOMTjamos200Nessuna valutazione finora
- Policy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Documento21 paginePolicy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Jamena abbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chaosmosis: An Ethico-Aesthetic ParadigmDocumento50 pagineChaosmosis: An Ethico-Aesthetic ParadigmCaetano VillaçaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stravinsky - The Rite of Spring (Full Score) PDFDocumento161 pagineStravinsky - The Rite of Spring (Full Score) PDFgotchimusicNessuna valutazione finora
- MICROWAVE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM DESIGN by Kathleen Sales, Pia Libutan, Gem Cabanos & Pau PantonDocumento10 pagineMICROWAVE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM DESIGN by Kathleen Sales, Pia Libutan, Gem Cabanos & Pau PantonKathleen SalesNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.05.15 Proposed Removal - Kellie Greene-RedactedDocumento10 pagine10.05.15 Proposed Removal - Kellie Greene-RedactedNina RenNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Vision Nanodegree Syllabus: Before You StartDocumento5 pagineComputer Vision Nanodegree Syllabus: Before You StartCristi PopaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fabbri 1982Documento14 pagineFabbri 1982Alexandre FerreiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tide ReportDocumento11 pagineTide ReportAhmad AbdelsattarNessuna valutazione finora
- Treinamento Sap Apo Planejamento de FornecimentoDocumento103 pagineTreinamento Sap Apo Planejamento de FornecimentoAntoniniNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz With Ans CHap 7 8 10 11Documento9 pagineQuiz With Ans CHap 7 8 10 11Junaid Khan Afridi100% (1)
- Research ProjectDocumento70 pagineResearch ProjectSuraj DubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Empathy: Rumbling With VulnerabilityDocumento4 pagineEmpathy: Rumbling With VulnerabilityClaire TsaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 - Manpower & Competency ProfilingDocumento11 pagineUnit 2 - Manpower & Competency ProfilingArjun SinghNessuna valutazione finora