Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
s1 s2 Lesson Plan
Caricato da
mani0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
56 visualizzazioni4 pagine1) The lesson plan outlines a course on basics of electrical engineering over 42 hours across 6 modules, covering topics such as Kirchhoff's laws, AC and DC circuits, magnetic circuits, transformers, motors and generators.
2) Teaching methods include lectures, assignments, simulations, tutorials and activities using a combination of teaching styles.
3) The plan schedules coverage of topics such as phasor representation, three-phase systems, power generation and distribution across the semester.
Descrizione originale:
lesson plan for basic electrical engineering
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documento1) The lesson plan outlines a course on basics of electrical engineering over 42 hours across 6 modules, covering topics such as Kirchhoff's laws, AC and DC circuits, magnetic circuits, transformers, motors and generators.
2) Teaching methods include lectures, assignments, simulations, tutorials and activities using a combination of teaching styles.
3) The plan schedules coverage of topics such as phasor representation, three-phase systems, power generation and distribution across the semester.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
56 visualizzazioni4 pagines1 s2 Lesson Plan
Caricato da
mani1) The lesson plan outlines a course on basics of electrical engineering over 42 hours across 6 modules, covering topics such as Kirchhoff's laws, AC and DC circuits, magnetic circuits, transformers, motors and generators.
2) Teaching methods include lectures, assignments, simulations, tutorials and activities using a combination of teaching styles.
3) The plan schedules coverage of topics such as phasor representation, three-phase systems, power generation and distribution across the semester.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 4
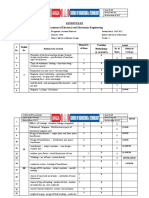
LESSON PLAN
Name of the Faculty: Designation: Assistant Professor Department : Electrical & Electronics
Academic Year: 2016-17 Semester : First Branch : Electrical & Electronics
Subject Code: EE 100 Subject : Basics Of Electrical Engineering Credit :3
Planned Teaching Actual
Module
S. No. Portions to be Covered No. of Methodology Date(s) of
No. No. of Hours
Hours (L/A/S/SS/T) Coverage
Elementary concepts of electric circuits: Kirchhoff's laws, 2 L
1
constant voltage and current sources-Problems
Formation of network equations by mesh current and node 3 L/T
2 I 15% voltage methods-matrix representation-solution of
network equations by matrix methods-problems
star-delta conversion(resistive networks only-derivation is 1 L
3 not needed)-problems
Magnetic Circuits: MMF, field strength, flux density, L
reluctance(definition only)-comparison between electric and 2
4
magnetic circuits
II Energy stored in magnetic circuits, magnetic circuits with air 2 L/T
5
gap-Numerical problems on series magnetic circuits
Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday's laws, lenz's laws- 2 L
6 statically induced and dynamically induced emfs-self
inductance and mutual inductance, coefficient of coupling
(derivation not needed)
Alternating Current fundamentals: Generation of alternating 2 L/T
voltages-waveforms, frequency, period, average , RMS
8
values and form factor of periodic waveform(pure
sinusoidal)- Numerical Problems
AC Circuits: Phasor representation of alternating quantities- 1 L
9
15% rectangular and polar representation
Analysis of simple AC circuits: concept of impedance, power 2 L/T
10 and power factor in ac circuits-active, reactive and apparent
III power
solution of RL,RC and RLC series circuits-Numerical 2 L
11
problems
Three phase systems: Generation of three phase voltages 3 L/T
advantages of three phase systems, star and delta connection
12
(balanced only), relation between line and phase voltages,
line and phase currents
three phase power measurement by two wattmeter method 1 L
13
(derivation is not required) - Numerical problems
IV Generation of power: Block schematic representation of 1 L
17
generating stations- hydroelectric power plants
Block schematic representation of Thermal and nuclear 2 L/T
18
power plants
19 Renewable energy sources: solar, wind, tidal and geothermal A
(Block diagram and working only- No Problems)
Power transmission: Typical electrical power transmission 1 L
20 scheme-need for high voltage transmission-(Derivation is not
needed, No Problems)
Power Distribution: substation equipments, primary and 1 L
21 secondary transmission and distribution systems- feeder,
service mains
Electric Machines: DC Generator and Motor- 2 L/T
27
Constructionworking principle- Back EMF
Types of motor-shunt, series, compound (short and long)- 3 L
28 principle of operation of dc motor, applications-numerical
problems ( voltage -current relations only)
V
Transformer: Construction of single phase and three phase 1 L/T
29 Transformers (core type only)-EMF equation and related
numerical problems
Losses and efficiency of transformer for full load numerical 2 L
30
problems (no equivalent circuit)
AC Motors: Three phase induction motor-squirrel cage and 1 L
33
slip ring induction motor
Working principle-synchronous speed, slip and related 1 L/T
34
numerical problems. (no equivalent circuit)
VI AC Motors: Construction, principles of operation of single 1 L
35
phase induction motor (no equivalent circuit)
Starting methods in single phase induction motors -split 2 L
36 phase and capacitor start
42
Total No. of Hours
Prepared by Approved by
Signature of Faculty: Signature:
Name & Designation: Name & Designation:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- SEM1Documento26 pagineSEM1Soham JoitaNessuna valutazione finora
- SyllabusDocumento78 pagineSyllabushariswamy1984Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Circuit Analysis-I Syllabus: Resource 2013-14Documento15 pagineElectrical Circuit Analysis-I Syllabus: Resource 2013-14Dileep VarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Year Syllabus 2018 19Documento89 pagine1st Year Syllabus 2018 19Abhishek GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocumento3 pagineBasic Electrical EngineeringAyush PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- CSE 1st-SEMDocumento24 pagineCSE 1st-SEMPrasiddh KotianNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus For ElectDocumento30 pagineSyllabus For Elects MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ma202 Numerical Methods: L T P CDocumento8 pagineMa202 Numerical Methods: L T P CVIGNESH L RNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus KEE101TDocumento1 paginaSyllabus KEE101TDr. Abhishek MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee100 Basics of Electrical EngineeringDocumento3 pagineEe100 Basics of Electrical EngineeringSh PNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee I Basic Electricals Engg. 15ele15 NotesDocumento135 pagineEee I Basic Electricals Engg. 15ele15 NotesOmeshwarNessuna valutazione finora
- BET - CoursePlan 2011Documento4 pagineBET - CoursePlan 2011Vignesh NatarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- T2F50C1 Type of Course: Core: Teaching Scheme (L-T-P: 3-0-2) Credits 04 Marks: 150 Theory: 100 Practical: 50Documento6 pagineT2F50C1 Type of Course: Core: Teaching Scheme (L-T-P: 3-0-2) Credits 04 Marks: 150 Theory: 100 Practical: 50sunilNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee001 Power Generation Systems: L T P CDocumento32 pagineEe001 Power Generation Systems: L T P CPARTH DAVENessuna valutazione finora
- BSC Electronics Syllabus Kerala UniversityDocumento64 pagineBSC Electronics Syllabus Kerala UniversityVarunRaj67% (3)
- Electricity and ElectronicsDocumento5 pagineElectricity and Electronicsvaikunth18vallavi02Nessuna valutazione finora
- BEEE Mech SyllabusDocumento2 pagineBEEE Mech SyllabusSATHISH MOTHENessuna valutazione finora
- NewSyllabus 1643201471840258Documento3 pagineNewSyllabus 1643201471840258Abhinav KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Beeg 1001: Basic Electrical Engineering: Credits: 04 L-T-P-J:3-1-0-0Documento1 paginaBeeg 1001: Basic Electrical Engineering: Credits: 04 L-T-P-J:3-1-0-0ChetanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- EE SyllabusDocumento95 pagineEE Syllabusvikram patilNessuna valutazione finora
- Anna UniversityDocumento14 pagineAnna UniversityRohit VetrivelNessuna valutazione finora
- ENDTC Second Year 3 SemDocumento6 pagineENDTC Second Year 3 Sempravin23105921Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eeu 201 Electric Circuit TheoryDocumento2 pagineEeu 201 Electric Circuit TheorykalscribNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Electrical Engineering-BESCK104B 2022-23: Mr. Chiranth L, Asst. ProfessorDocumento34 pagineIntroduction To Electrical Engineering-BESCK104B 2022-23: Mr. Chiranth L, Asst. ProfessorDevikaNessuna valutazione finora
- III Sem SyllbusDocumento11 pagineIII Sem SyllbusS B RajNessuna valutazione finora
- VR22 - EEE - ANT SyllabusDocumento2 pagineVR22 - EEE - ANT Syllabusp_maheswararaoNessuna valutazione finora
- EE110Documento2 pagineEE110Varsha VasthaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Power ElectronicsDocumento2 paginePower ElectronicspakalagopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai: Total Period 08Documento19 pagineChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai: Total Period 08Piyush KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocumento4 pagineBasic Electrical EngineeringSwaraj SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics 4 PDFDocumento1 paginaAnalog Electronics 4 PDFsunil singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Govt. College of Engineering & TechnologyDocumento1 paginaGovt. College of Engineering & Technologysunil singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocumento4 pagineFundamentals of Electrical & Electronics Engineeringandruz1896Nessuna valutazione finora
- Network Analysis &transmission Lines PDFDocumento183 pagineNetwork Analysis &transmission Lines PDFmlsawhney2996Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 TransformersDocumento23 pagineModule 4 TransformersvijayNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Sem 4 Electrical Engineering Syllabus For WB PolytechnicDocumento35 pagine3rd Sem 4 Electrical Engineering Syllabus For WB PolytechnicParthasarothi SikderNessuna valutazione finora
- ES103Documento3 pagineES103Sualé SualéNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical SyllabusDocumento2 pagineElectrical Syllabusharsh dubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- EeeDocumento391 pagineEeeGhulam AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- EeeDocumento268 pagineEeeNajiruddin ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Analysis SyllabusDocumento4 pagineNetwork Analysis SyllabusAyushnaitik PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and Protection PDFDocumento4 pagine1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and Protection PDFHaripriya k aNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and ProtectionDocumento4 pagine1 EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and ProtectionAnuja VargheseNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Electrical and Electronics Engineering SEM - IDocumento4 pagineBasics of Electrical and Electronics Engineering SEM - IohhNessuna valutazione finora
- Ma205 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations: L T P CDocumento8 pagineMa205 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations: L T P CBharathwaj SreedharNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 SemesterDocumento4 pagineElectrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 Semestersameerpatel15770Nessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Syllabi BTECH - EEE - R2016Documento40 pagineDetailed Syllabi BTECH - EEE - R2016KALLURI MANI SIMHA REDDYNessuna valutazione finora
- BMR PE Syllabus R17 NewDocumento3 pagineBMR PE Syllabus R17 NewRajesh Reddy KakarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- EPS - II - 6ht Sem Micro LP - TBDocumento3 pagineEPS - II - 6ht Sem Micro LP - TBNIKUL PATELNessuna valutazione finora
- Course 2. Basic Electrical Technology (Video Course) Faculty Coordinator(s) : 1Documento32 pagineCourse 2. Basic Electrical Technology (Video Course) Faculty Coordinator(s) : 1Ursap BuddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical Engineering (14ele15-14ele25)Documento3 pagineBasic Electrical Engineering (14ele15-14ele25)Swati MuttuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pee Hand Book For Ece-II-IIDocumento16 paginePee Hand Book For Ece-II-IISurya Ch VenkataNessuna valutazione finora
- B.sc. I ElectronicsDocumento6 pagineB.sc. I ElectronicsitsquitenNessuna valutazione finora
- Topics To Be Covered SECTION A: D.C. Networks Laws and TheoremsDocumento3 pagineTopics To Be Covered SECTION A: D.C. Networks Laws and Theoremsrajkumar rNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum S T R U C T U R E of S.Y.-B.Tech (Electrical Engineering) (Regularstudents)Documento56 pagineCurriculum S T R U C T U R E of S.Y.-B.Tech (Electrical Engineering) (Regularstudents)Bhushan RaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Materials OF Basic Electrical Engineering KEE 101/201 Session 2019-20Documento115 pagineCourse Materials OF Basic Electrical Engineering KEE 101/201 Session 2019-20ManishNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsDa EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksDa EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlDa EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Mean Gbest and Gravitational Search AlgorithmDocumento22 pagineMean Gbest and Gravitational Search AlgorithmmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Reg - No. Sixth Semester B.Tech Degree Examination, JUNE 2009Documento2 pagineName: Reg - No. Sixth Semester B.Tech Degree Examination, JUNE 2009maniNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 2018 April EE208-C PDFDocumento2 pagine9 2018 April EE208-C PDFmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear MachineDocumento7 pagineLinear MachinemaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Time Table Odd 2020Documento1 paginaTime Table Odd 2020maniNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 A Lesson Plan EMD KtuDocumento4 pagine7 A Lesson Plan EMD KtumaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 B Time Table Odd 2020Documento1 pagina1 B Time Table Odd 2020maniNessuna valutazione finora
- Int1 EE303 LCSDocumento4 pagineInt1 EE303 LCSmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part - A: Marks CO PO PSO BLDocumento1 paginaPart - A: Marks CO PO PSO BLmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Int 2 Ee409 Emd ManickavasagamDocumento2 pagineInt 2 Ee409 Emd ManickavasagammaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PhDnotification2018 9evenDocumento5 paginePhDnotification2018 9evenmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Int2 Eet203 MI MANICKAVASAGAMDocumento2 pagineInt2 Eet203 MI MANICKAVASAGAMmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Int 2 EE303 LCS MANICKAVASAGAMDocumento2 pagineInt 2 EE303 LCS MANICKAVASAGAMmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Programme Agenda - Green 9 ENSAV ClubDocumento1 paginaProgramme Agenda - Green 9 ENSAV ClubmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part - A: Electrical Machine DesignDocumento2 paginePart - A: Electrical Machine DesignmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Invitation Iste - Corrected Version FinalDocumento2 pagineInvitation Iste - Corrected Version FinalmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Invitation Iste - Corrected VersionDocumento2 pagineInvitation Iste - Corrected VersionmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- IoT BrochureDocumento2 pagineIoT BrochuremaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Generation Transmission and Protection Series 2Documento3 paginePower System Generation Transmission and Protection Series 2maniNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Books s8 ElectiveDocumento2 pagineList of Books s8 ElectivemaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Register Number: Name: Register Number:: Answer Any Two Full Question Each Carries 10 MarksDocumento1 paginaName: Register Number: Name: Register Number:: Answer Any Two Full Question Each Carries 10 MarksmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Membership Fees IsteDocumento2 pagineStudent Membership Fees IstemaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1 Overview of VibrationsDocumento56 pagine5.1 Overview of VibrationsAbhishek PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Aircraft Final Seminar Report PDFDocumento39 pagineSolar Aircraft Final Seminar Report PDFRohit HarpudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lux MeterDocumento0 pagineLux Meterapostolidis83Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jacket Launching AnalysisDocumento7 pagineJacket Launching Analysisiw2fualNessuna valutazione finora
- GeoTech ProblemsDocumento25 pagineGeoTech Problemsev xvNessuna valutazione finora
- Laser & Fiber OpticDocumento28 pagineLaser & Fiber OpticDwi Tiara TanjungNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics Notes and Past PapersDocumento38 pagineKinematics Notes and Past PapersSuhaan HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- DQE Tip - YJangDocumento16 pagineDQE Tip - YJangAqua BlueNessuna valutazione finora
- Mineral Insulation Material For MI CableDocumento3 pagineMineral Insulation Material For MI CablekmiqdNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 1Documento15 pagineLec 1umarNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 4 FMDocumento17 pagineExp 4 FMKhadijah Ulol AzmiNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 The Hand Warmer Design ChallengeDocumento2 pagine12 The Hand Warmer Design ChallengeMohommad YawariNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 13-Under Voltage and Over Voltage Monitoring Numerical RelayDocumento5 pagineLab 13-Under Voltage and Over Voltage Monitoring Numerical RelayAliza Sharif100% (1)
- Coursera SA682WVEP78QDocumento1 paginaCoursera SA682WVEP78Qshilpmehta007Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1-1 Master Thesis MEng3 GCDocumento11 pagine1-1 Master Thesis MEng3 GCCabrel FankamNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind Farm FaultDocumento68 pagineWind Farm Faultmary1368Nessuna valutazione finora
- VT Level III Study NoteDocumento5 pagineVT Level III Study NoteAllen Situ100% (3)
- M Us 22054 LC-WM Handbook Reva PDFDocumento120 pagineM Us 22054 LC-WM Handbook Reva PDFneo43Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Science of Bioenergetic Bioelectric TechnologiesDocumento199 pagineThe Science of Bioenergetic Bioelectric TechnologiesKamen KaloqnkovNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Genral PhysicsDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To Genral PhysicsمريمNessuna valutazione finora
- chapter 4 (updated materials for final exam) -محولDocumento17 paginechapter 4 (updated materials for final exam) -محولمروان الشباليNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid DynamicsDocumento44 pagineFluid DynamicsMoosa Salim Al KharusiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tanks, Terminals and Storage-Kim (Covestro Bechtel)Documento12 pagineTanks, Terminals and Storage-Kim (Covestro Bechtel)cristianNessuna valutazione finora
- Conservation of Linear Momentum Online PHETDocumento7 pagineConservation of Linear Momentum Online PHETArlene PenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mole Concept IDocumento8 pagineMole Concept ISohil Paudel100% (2)
- Urea Hydrolysis To Ammonia in CSTRDocumento12 pagineUrea Hydrolysis To Ammonia in CSTRCeci100% (1)
- Chapter 6 GravitationDocumento16 pagineChapter 6 GravitationXiujun GohNessuna valutazione finora
- FMM Anna University Unit IV QuestionsDocumento4 pagineFMM Anna University Unit IV QuestionsUma MaheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Andrade EqDocumento10 pagineAndrade EqHima Bindu KolliNessuna valutazione finora