Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pandas Python For Data Science
Caricato da
chowdamhemalathaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pandas Python For Data Science
Caricato da
chowdamhemalathaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
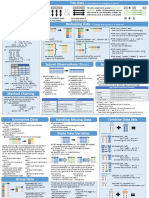
Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet Asking For Help Dropping
>>> help(pd.Series.loc)
>>> s.drop(['a', 'c']) Drop values from rows (axis=0)
Pandas Basics Selection Also see NumPy Arrays >>> df.drop('Country', axis=1) Drop values from columns(axis=1)
Learn Python for Data Science Interactively at www.DataCamp.com
Getting
>>> s['b'] Get one element Sort & Rank
-5
Pandas >>> df.sort_index() Sort by labels along an axis
>>> df.sort_values(by='Country') Sort by the values along an axis
>>> df[1:] Get subset of a DataFrame
The Pandas library is built on NumPy and provides easy-to-use Country Capital Population >>> df.rank() Assign ranks to entries
data structures and data analysis tools for the Python 1 India New Delhi 1303171035
2 Brazil Braslia 207847528
programming language. Retrieving Series/DataFrame Information
Selecting, Boolean Indexing & Setting Basic Information
Use the following import convention: By Position >>> df.shape (rows,columns)
>>> import pandas as pd >>> df.iloc([0],[0]) Select single value by row & >>> df.index Describe index
'Belgium' column >>> df.columns Describe DataFrame columns
Pandas Data Structures >>> df.iat([0],[0])
>>>
>>>
df.info()
df.count()
Info on DataFrame
Number of non-NA values
Series 'Belgium'
Summary
A one-dimensional labeled array a 3 By Label
>>> df.loc([0], ['Country']) Select single value by row & >>> df.sum() Sum of values
capable of holding any data type b -5
'Belgium' column labels >>> df.cumsum() Cummulative sum of values
>>> df.min()/df.max() Minimum/maximum values
c 7 >>> df.at([0], ['Country']) >>> df.idxmin()/df.idxmax()
Index Minimum/Maximum index value
d 4 'Belgium' >>> df.describe() Summary statistics
>>> df.mean() Mean of values
>>> s = pd.Series([3, -5, 7, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
By Label/Position >>> df.median() Median of values
>>> df.ix[2] Select single row of
DataFrame Country
Capital
Brazil
Braslia
subset of rows Applying Functions
Population 207847528 >>> f = lambda x: x*2
Columns
Country Capital Population A two-dimensional labeled >>> df.ix[:,'Capital'] Select a single column of >>> df.apply(f) Apply function
>>> df.applymap(f) Apply function element-wise
data structure with columns 0 Brussels subset of columns
0 Belgium Brussels 11190846 1 New Delhi
of potentially different types 2 Braslia Data Alignment
1 India New Delhi 1303171035
Index >>> df.ix[1,'Capital'] Select rows and columns
2 Brazil Braslia 207847528 Internal Data Alignment
'New Delhi'
NA values are introduced in the indices that dont overlap:
Boolean Indexing
>>> data = {'Country': ['Belgium', 'India', 'Brazil'], >>> s3 = pd.Series([7, -2, 3], index=['a', 'c', 'd'])
>>> s[~(s > 1)] Series s where value is not >1
'Capital': ['Brussels', 'New Delhi', 'Braslia'], >>> s[(s < -1) | (s > 2)] s where value is <-1 or >2 >>> s + s3
'Population': [11190846, 1303171035, 207847528]} >>> df[df['Population']>1200000000] Use filter to adjust DataFrame a 10.0
b NaN
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data, Setting
c 5.0
columns=['Country', 'Capital', 'Population']) >>> s['a'] = 6 Set index a of Series s to 6
d 7.0
I/O Arithmetic Operations with Fill Methods
You can also do the internal data alignment yourself with
Read and Write to CSV Read and Write to SQL Query or Database Table
the help of the fill methods:
>>> pd.read_csv('file.csv', header=None, nrows=5) >>> from sqlalchemy import create_engine >>> s.add(s3, fill_value=0)
>>> pd.to_csv('myDataFrame.csv') >>> engine = create_engine('sqlite:///:memory:') a 10.0
>>> pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM my_table;", engine) b -5.0
Read and Write to Excel c 5.0
>>> pd.read_sql_table('my_table', engine) d 7.0
>>> pd.read_excel('file.xlsx') >>> pd.read_sql_query("SELECT * FROM my_table;", engine) >>> s.sub(s3, fill_value=2)
>>> pd.to_excel('dir/myDataFrame.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1') >>> s.div(s3, fill_value=4)
read_sql()is a convenience wrapper around read_sql_table() and
Read multiple sheets from the same file >>> s.mul(s3, fill_value=3)
read_sql_query()
>>> xlsx = pd.ExcelFile('file.xls')
>>> df = pd.read_excel(xlsx, 'Sheet1') >>> pd.to_sql('myDf', engine) DataCamp
Learn Python for Data Science Interactively
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Numpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDocumento7 pagineNumpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDeepak Gupta100% (13)
- Python Matplotlib Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaPython Matplotlib Cheat SheetsreedharNessuna valutazione finora
- Python NumPy cheat sheet for data scienceDocumento14 paginePython NumPy cheat sheet for data scienceraghavandra ethish manickam100% (1)
- Numpy Python Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaNumpy Python Cheat Sheetyellow_birdNessuna valutazione finora
- Seaborn Cheat Sheet for Python Data VisualizationDocumento1 paginaSeaborn Cheat Sheet for Python Data VisualizationFrâncio Rodrigues100% (1)
- Pandas Cheat SheetDocumento2 paginePandas Cheat SheetRoberto83% (12)
- NumPy, SciPy, Pandas, Quandl Cheat SheetDocumento4 pagineNumPy, SciPy, Pandas, Quandl Cheat Sheetseanrwcrawford100% (3)
- Python 3 Cheat SheetDocumento2 paginePython 3 Cheat SheetLaurent Pointal94% (48)
- Python Cheat SheetsDocumento11 paginePython Cheat SheetsAndrew Khalatov96% (26)
- Matplotlib Cheat SheetDocumento8 pagineMatplotlib Cheat SheetTuan Ton100% (5)
- Numpy Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaNumpy Cheat SheetIan Flores100% (1)
- Python 3.2 Reference CardDocumento2 paginePython 3.2 Reference CardLaurent Pointal100% (12)
- Data Analysis With PANDAS: Cheat SheetDocumento4 pagineData Analysis With PANDAS: Cheat Sheetnesayu67% (3)
- Python For Data Science - Cheat SheetsDocumento10 paginePython For Data Science - Cheat SheetsMustafa Ibrahim100% (4)
- Python Pandas TutorialDocumento178 paginePython Pandas TutorialDavid Charles100% (18)
- Coffee Break NumPy PDFDocumento211 pagineCoffee Break NumPy PDFKiran Kumar100% (3)
- Programming Languages and Kernels in Jupyter NotebookDocumento1 paginaProgramming Languages and Kernels in Jupyter NotebookAnurag AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- All Python CSDocumento10 pagineAll Python CSAnkit Shukla100% (2)
- Python Cheat SheetDocumento2 paginePython Cheat Sheetebookkarthi100% (2)
- Core Python Cheat SheetDocumento9 pagineCore Python Cheat Sheetsalim100% (4)
- Beginners Python Cheat Sheet PCC AllDocumento26 pagineBeginners Python Cheat Sheet PCC Alljohn smith96% (24)
- Python Quick Reference CardDocumento17 paginePython Quick Reference CardSérgio Luiz Araújo Silva94% (16)
- Python Cheat SheetDocumento16 paginePython Cheat SheetjhdmssNessuna valutazione finora
- 65 Free Data Science Resources For Beginners PDFDocumento19 pagine65 Free Data Science Resources For Beginners PDFgirishkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Numpy ReferenceDocumento1.183 pagineNumpy ReferenceLucian GhituNessuna valutazione finora
- Ai Cheat Sheet Machine Learning With Python Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineAi Cheat Sheet Machine Learning With Python Cheat SheetA.K. Mars100% (3)
- Pandas Cheat SheetDocumento2 paginePandas Cheat Sheetngyncloud100% (4)
- Learning The Pandas Library Python Tools For Data Munging Analysis and Visual PDFDocumento208 pagineLearning The Pandas Library Python Tools For Data Munging Analysis and Visual PDFAlicia Brett100% (11)
- Cheat Sheet: The Pandas Dataframe Object: Preliminaries Get Your Data Into A DataframeDocumento12 pagineCheat Sheet: The Pandas Dataframe Object: Preliminaries Get Your Data Into A Dataframetoddae100% (1)
- Python Machine Learning - Sample ChapterDocumento57 paginePython Machine Learning - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing86% (7)
- Python Cheatsheet: Data Science Basics in 40Documento1 paginaPython Cheatsheet: Data Science Basics in 40acutotu67% (3)
- Python Cheat Sheet For Data Scientists by Tomi Mester 2019 PDFDocumento23 paginePython Cheat Sheet For Data Scientists by Tomi Mester 2019 PDFDanBarbera100% (3)
- 100 Skills To Better PythonDocumento80 pagine100 Skills To Better Pythonaerofit100% (2)
- Python Data Science Cheat SheetDocumento15 paginePython Data Science Cheat SheetMuhammad Wahyu Dwimulyo100% (3)
- Python Reference CardDocumento2 paginePython Reference Cardmarczucker100% (4)
- Python Programming BlueprintsDocumento449 paginePython Programming Blueprintsmadhu905595% (20)
- Beginners Python Cheat SheetDocumento28 pagineBeginners Python Cheat Sheetpavithra67% (3)
- Pandas PythonDocumento115 paginePandas Pythoncss_said100% (2)
- Python Cheat Sheet: Ata TructuresDocumento2 paginePython Cheat Sheet: Ata Tructuresfreyespadaa100% (6)
- NumPy: Beginner's Guide - Third Edition - Sample ChapterDocumento54 pagineNumPy: Beginner's Guide - Third Edition - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing75% (4)
- Python Data Science Essentials - Sample ChapterDocumento36 paginePython Data Science Essentials - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing50% (4)
- Python 3 Orientado A ObjetoDocumento405 paginePython 3 Orientado A ObjetoJack Lummer100% (18)
- Pandas 1.x Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes for scientific computing, time series analysis, and exploratory data analysis using Python, 2nd EditionDa EverandPandas 1.x Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes for scientific computing, time series analysis, and exploratory data analysis using Python, 2nd EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Hands-On Data Analysis with Pandas: Efficiently perform data collection, wrangling, analysis, and visualization using PythonDa EverandHands-On Data Analysis with Pandas: Efficiently perform data collection, wrangling, analysis, and visualization using PythonNessuna valutazione finora
- Text Analytics with Python: A Brief Introduction to Text Analytics with PythonDa EverandText Analytics with Python: A Brief Introduction to Text Analytics with PythonNessuna valutazione finora
- Python Data Science Essentials - Second EditionDa EverandPython Data Science Essentials - Second EditionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Python For Beginners.Learn Data Science in 5 Days the Smart Way and Remember it Longer. With Easy Step by Step Guidance & Hands on Examples. (Python Crash Course-Programming for Beginners): Python for BeginnersDa EverandPython For Beginners.Learn Data Science in 5 Days the Smart Way and Remember it Longer. With Easy Step by Step Guidance & Hands on Examples. (Python Crash Course-Programming for Beginners): Python for BeginnersNessuna valutazione finora
- Isim Database Schema Reference Guide PDFDocumento288 pagineIsim Database Schema Reference Guide PDFAlbertoNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica TeradataDocumento21 pagineInformatica TeradataSanthuMithinti100% (1)
- Agg AwareDocumento26 pagineAgg AwareyaswanthrdyNessuna valutazione finora
- DataBase AdministrationDocumento50 pagineDataBase AdministrationHelp me get to 10k subscribersNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started Guide for ActiveData Analytics SoftwareDocumento31 pagineGetting Started Guide for ActiveData Analytics Softwaret_luc2210Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ee PDF V2019-May-17 by Theobald 40q VceDocumento12 pagineEe PDF V2019-May-17 by Theobald 40q VceRysiek ZdzisiekNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Practicle File For RDBMS-IIDocumento41 pagineReference Practicle File For RDBMS-IIkingsofleon18200% (1)
- 5 PL/SQL Collections and Records GuideDocumento59 pagine5 PL/SQL Collections and Records Guidevarjunreddy87Nessuna valutazione finora
- SQL Interview QuestionsDocumento24 pagineSQL Interview Questionshari100% (1)
- Essentials of Database Management 1st Edition Hoffer Test Bank DownloadDocumento24 pagineEssentials of Database Management 1st Edition Hoffer Test Bank DownloadShirley Scott100% (25)
- Oracle Retail Integration Bus: Data Model Release 16.0Documento26 pagineOracle Retail Integration Bus: Data Model Release 16.0Mohammad Adnan AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Na2009 Enus Devi 02Documento60 pagineNa2009 Enus Devi 02harikiranNessuna valutazione finora
- New Features in FileMaker Pro 16Documento5 pagineNew Features in FileMaker Pro 16Ricardo RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Foxpro: DBMS Stand For Data Base Management System. in This System You Can Create Files, Reports, Labels EtcDocumento22 pagineFoxpro: DBMS Stand For Data Base Management System. in This System You Can Create Files, Reports, Labels EtcSurjeet kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- File Structures PDFDocumento616 pagineFile Structures PDFRoberta Costa100% (5)
- Informix14 Migrating and Upgrading LesterKnutsenDocumento72 pagineInformix14 Migrating and Upgrading LesterKnutsengenNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Writing FinalDocumento74 pagineThesis Writing FinalBaitul AmanNessuna valutazione finora
- HP Oracle DW - BI Sizing QuestionnaireDocumento15 pagineHP Oracle DW - BI Sizing Questionnairebehera.eceNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL Les12Documento28 pagineSQL Les12ram5584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Postgresql InterviewQuestionDocumento5 paginePostgresql InterviewQuestionmontosh100% (1)
- Billing DataDocumento210 pagineBilling Datakrishnacfp2320% (1)
- DB2 AdministrationGuide PDFDocumento1.352 pagineDB2 AdministrationGuide PDFYerman Mauricio100% (1)
- Relational Database: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento6 pagineRelational Database: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAnwar PasaribuNessuna valutazione finora
- C++ Fem Object OrientedDocumento17 pagineC++ Fem Object OrientedTuýp Phờ NờNessuna valutazione finora
- Nav2013 Enus Csintro 02Documento50 pagineNav2013 Enus Csintro 02Cesar Alexander Gutierez RuedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Searching Faster and Better in PeopleSoft ApplicationDocumento6 pagineSearching Faster and Better in PeopleSoft ApplicationKathiravanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tunning Oracle Reports 6iDocumento24 pagineTunning Oracle Reports 6iMelvin GrijalbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geoprocessing Data TypesDocumento6 pagineGeoprocessing Data TypesPhilip VerpotenNessuna valutazione finora
- Adventure Works 2014Documento146 pagineAdventure Works 2014manojNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Management Assignment E-R Diagram and IndexesDocumento10 pagineDatabase Management Assignment E-R Diagram and IndexesMa JessaNessuna valutazione finora